

DIY Cruising Catamaran: Complete Building Guide
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
A brand-new cruising catamaran can set you back a hefty amount of money. However, a DIY cruising catamaran provides a more affordable way to own your own boat. While building a large boat can be an extremely challenging and time-consuming experience, nothing beats the pleasure of bringing your own boat to life.
To build a DIY cruising catamaran, buy good design plans, determine your budget and find a working space. Next, choose your hull material, buy supplies and start building the mast beam. Build and sheathe the hull, install bulkheads, the interior, and finally, launch the catamaran boat.
In this article, you will find a complete guide to building your own catamaran. You will also find detailed information on why you may want to consider building your catamaran and approximately how much this project would cost. Finally, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of building a catamaran from scratch.
Why You Might Want To Build Your Own Catamaran
Most people might think that purchasing a used boat to repair and fix it up would be cheaper than a DIY cruising catamaran. But while building your own catamaran could be an enormous undertaking, it also comes with many advantages over buying something used.
Other than the unique opportunity to create beautiful memories and experiences while cruising, sailing, and exploring beautiful coastlines, there are a number of benefits that come along with the DIY approach.
Knowing Your Boat
Building your own catamaran provides you with intimate knowledge of your boat. You will know every corner, including where to find every bolt, wire, bulkhead, rib, hose, and support as you installed them yourself. This knowledge will enhance your confidence while at sea since you will have entrusted your life to a boat whose history you are aware of and deeply connected to.
Pride of Ownership
The satisfaction you get from crafting something with your own hands is immense. As a result, the knowledge that you built your boat from scratch will fill you with absolute pride and an immense sense of achievement. Furthermore, as an owner-builder, you get to keep and enjoy the boat for as many years as you wish.
Substantial Cost Savings
Building your catamaran will work out cheaper than buying a new or even gently used boat. Though you will likely require some additional labor since doing some things will require an extra pair of hands, if you are particularly good at DIY, you will save a significant amount of money on labor costs as a whole.
Freedom To Create Your Own Designs
If you decide to buy a catamaran boat, it might not be easy to find one that meets your unique needs. However, instead of choosing from production boats that bear traditional and outdated designs, you can come up with an ultra-modern design or style for your catamaran. You also get to pick your layout, size, and equipment based on your taste and budget.
Great Learning Experience
Building your own boat will help you pick up numerous skills that will come in handy later when sailing your boat. As much as you might still require an expert to help you with specialized skills like carpentry or wiring, your new skills will serve you well. This will also be beneficial when it comes to your boat’s maintenance and fixing things for yourself.
What To Look For in Catamaran Boat Designs
When deciding on the type of catamaran boat to build, you may want to choose a design that’s simple and easy to build. This is because doing so will allow you to spend a shorter time building the boat.
You also need to have a set of requirements to guide you in choosing your design or what you might call an ideal cruising catamaran wish list. This is essential because, ultimately, you want to build a boat that offers outstanding qualities such as:
- Delivers good speed
- Affordable to own and operate
- Agile, strong, and easy to maintain
- Has a high resistance to capsizing
- Great for sailing and cruising
- Delivers a comfortable and easy motion underway
- Good handling ability and high performance under sail
- User-friendly embarking and disembarking
- Provides ample living and accommodation space
- Presents a reasonable resale value
It’s worth noting that, in general, catamaran boats tend to offer a fair resale value mainly because of scarcity and the high price accorded to production models. So, if you build a well-constructed catamaran, you are bound to get a return that’s much higher than the cost of materials upon resale.
It’s also good to consider whether the design you settle on is from an established designer. This is significant because documentation of the building process is just as valuable when it comes to selling the boat.
How Much Would It Cost To Build Your Own Catamaran?
The cost of building your cruising catamaran will depend heavily on the size of the boat you plan to build and the skills you bring to the table. To give you an idea of probable costs, a professionally built 40 foot (12.1 m) long cruising catamaran could go for up to $300,000.
Though building it yourself will undoubtedly be cheaper, most DIY boatbuilders tend to underestimate the expected costs. Your final costs should cover not only the cost of material and equipment but also the labor and time it would take to come up with the final product.
If you were to build a 40-foot (12.1-meter) catamaran, your cost of materials would range between 20-30% of the total cost. Therefore, for $300,000 total, the boat’s materials would range between $60,000 and $90,000. The hull tends to range between 15-35% of the total build. Again, this depends on the finish and furniture.
But before you even start working on the DIY project, you will need to figure out where to do the work. If your home has ample space, then you can opt for a backyard building. But if you live in a small apartment, then you might want to consider renting a small garage at first and then move on to a boatyard later. This is one of the significant costs involved in building your multi-haul.
What You Will Need
To get a clearer picture of how much the entire project would cost, let’s have a look at what else you will need to purchase.
- Good design plans
- Working space
- Ground tackle
- Matting and roving
- Equipment such as the engine, windows, rudders, deck fittings, mast, and rigging
In addition to the above, you also need to install plumbing and electricals. You may also want to consider going electric rather than using diesel. Not only will this drastically reduce your maintenance costs, but you get to use the regenerated power for all of your housing needs while sailing.
Some catamaran boat designs help you save costs by advocating the use of less expensive corpus materials. Most of the material goes directly into making the boat, which means there is hardly any wastage on vacuum bagging . With this method, there are few molds and temporal building forms and fewer fillers to grind off as waste. All these factors reduce the time and cost it takes to build your catamaran boat.
That said, building a boat of any kind is a huge financial undertaking. As such, you still need to have the financial ability to keep building; otherwise, your project will stall or take much longer than anticipated. Instead of enjoying yourself and making memories cruising to faraway lands, you might end up spending all your time building a seemingly never-ending boat.
To reiterate, this project is more of a labor of love, given that it involves a tremendous amount of manual work. Calculating an hourly rate on the time spent building the boat and adding this cost to that of materials may make it seem a very pricey exercise. However, it is vital to understand that your time matters, and every hour you spend working for “free” should be included.
With that in mind, you need to ensure that you are fully devoted to the boat construction project and are sure you want to do it before you begin. Stopping halfway because it seems like too much work would be incredibly costly.
How To Build a Catamaran
When it comes to building a cruising catamaran, you have 3 main options:
- You can buy an old boat and refurbish it.
- Purchase a bare hull plus deck molding for a home-boat building.
- Start from scratch and build everything, including the hull, on your own.
As mentioned above, renovating an existing boat may end up being more costly than starting from scratch. To build a catamaran boat from scratch, follow the below step-by-step guide.
Prepare the Essentials
Before you jump into such a large project, there are several important aspects to consider:
- Buy your plans from an established catamaran designer. You can also get inexpensive, easy-to-build catamaran designs online.
- Get access to a large working space or build a shed . Depending on your climate, you may need to opt for climate control to avoid an excess of moisture in humid areas.
- Decide on your choice of hull material. This could be fiberglass, aluminum, steel, wood, or ferroconcrete.
- Start working on a bill of materials estimate. Include everything that you think you need to get a better idea of the initial costs.
Build the Mast Beam
Using wood and epoxy, cut and glue together the pieces of wood that will form the mast beam. Most of the work at this stage can occur in a garage since it involves building small parts. Still, the work could take up to 4 months, so be prepared to put in long hours.
Build the Boat Hull
Now, it’s time to build the boat’s hull. A catamaran comprises two hulls which are connected with a deck. Below is a short video showing how to build a hull mold:
This work requires a larger facility, so you might need to move out of the garage and into a boatyard. If you don’t have access to a larger workshop, consider building a shed where you can work as you do the construction. Make sure there’s enough room to fit the boat and also allow you to work comfortably. To cover the shed, you can use opaque white tarps.
Sheathe the Hull
Get all the materials you require for this stage in the construction, such as lots of resin, fiberglass, and foam for use in the hull cores. You’ll also require matting and glass roving to sheath the hull .
Sheathing helps to make the hull impervious to water and other marine borers. But first, you need to prepare the hull using a rotary sander. To make it as smooth as possible, use light, sweeping strokes. This is a very dusty task so be prepared to wear a facemask and safety goggles.
Install the Bulkheads
Next is installing the plywood bulkheads . You might need to call in friends to help turn the hulls or use a crane. In this step, you will need to laminate the hull sides on the molded hull panels and bond them above the bulkheads. Ensure the bulkheads are snug and sealed in place.
Construct the Interior Structure
Over the next couple of months, the boat work will involve joining the hulls together with the beams that you had made back in the garage. Then, install the cuddy cabin, decks , and the cockpit . Soon the boat will start to take the shape of a catamaran.
Next, proceed to construct the major structural components such as stairs, hatches, mini-keels, and the interior. Then comes the work of fairing the boat, which is quite labor-intensive.
Finally, it’s time to apply primer on the catamaran boat and start the paintwork. Before painting the boat, you will need to do additional sanding to finish off the two layers of primer as well as fill all the pinholes. Since it’s a large boat, the catamaran has lots of surface area; thus, the sanding could get extremely exhausting—mentally and physically—at this point.
The painting can take a while, too. The hulls are the easiest to paint, but the topsides, non-skid, as well as masking and prepping could seem never-ending.
The final stretch involves working on the center bridge deck cabin and other final touches like installing the engines, electricals, and plumbing. This is also the time to fix the rudders, rigging, mast, windows, and deck fittings.
Launch Your Cruising Catamaran
After many months or years of hard work, your cruising catamaran is finally ready to test the waters. After lowering the boat into the water, check carefully in case there are leaks. If none, you can set up the sails and take your catamaran out for your first cruise.
Below is a short video that takes you through the entire boat-building process:
If you don’t have deep pockets, don’t despair. It’s also possible to build an inexpensive catamaran boat, as shown in this post from the coastal passage .
The Pros of Building a Catamaran
Though it will be a costly endeavor, there are so many things to look forward to should you decide to build your own catamaran:
- It can be lots of fun.
- You get to have a new boat.
- It’s an excellent hobby for DIY enthusiasts.
- The effort is rewarding.
- It offers a great learning experience.
- You get the exact kind of boat you want.
- You can alter building plans and tailor the boat to suit your specific needs.
- It might be cheaper than buying a new boat.
The Cons of Building a Catamaran
Though there are a number of positive aspects to a DIY build, it is just as important to keep in mind that it won’t always be easy:
- Maintenance costs can be quite high.
- It’s both mentally and physically exhausting.
- It might require some technical know-how.
- It can take many months or even years to complete.
- It requires a lot of commitment to finish the DIY project.
- It might be challenging as well as expensive to get insurance.
- You will spend almost all your free time building the boat.
DIY Cruising Catamaran Tips and Tricks
If you are new to boat building, it would be a good idea to build a small boat first. This would give you a good indication as to whether you’d enjoy tackling a more extensive project like building a catamaran. Again, if you are the handy type, fixing your own electronics could also save you a significant amount of money.
Here are more tips and tricks to get the most out of your DIY cruising catamaran:
- Lower your costs. Bring down your costs even further by sourcing for parts and supplies at marine surplus outlets, Craigslist, eBay, or wholesale suppliers.
- Enhance your resale value. Most home-built boats are not easy to sell since they tend to be too customized. To enhance your resale value, it’s advisable to work with a standard design from a well-established naval architect.
- Follow the design instructions. Make sure to follow the designer’s instructions regarding the type of materials and tools to use during the build to avoid making costly mistakes.
- Maintain your original budget. Avoid any additional customizations once you have started building the boat. Using good plans and sticking to them ensures that your budget doesn’t spiral out of control.
Final Thoughts
Building a catamaran is about more than saving money. It’s fun, exciting, fulfilling, and can be a great learning experience. While it might take many months of back-breaking work, comparative shopping and sourcing for materials will help you save a lot of money. Still, at the end of it all, you’ll have a beautiful catamaran boat, all ready for your first cruising adventure.
However, if you have neither the time nor the energy to build your own catamaran from scratch, refurbishing an existing hull might prove faster and easier. It also works out much cheaper than buying a new boat.
Owner of CatamaranFreedom.com. A minimalist that has lived in a caravan in Sweden, 35ft Monohull in the Bahamas, and right now in his self-built Van. He just started the next adventure, to circumnavigate the world on a Catamaran!
One thought on “ DIY Cruising Catamaran: Complete Building Guide ”
Hello, I am a French Quebecer who is original, imaginative, creative and who finds that all boats and catamarans have a huge flaw and a very big lack of logic. I would have a brand new concept…. I am sending this message to any catamaran creator – designer to make those who have the opportunity and the intelligence to want to know about my innovative idea which will finally upset the market much richer. An idea that will totally change the concept of sailing, navigation and save so much worry!! All I would ask for is a small percentage of each sale of the new product. To be able to make me produce one when I have enough!! It is certain that like that, you just want to tell me: come on Mr. Lessard give us your idea but do not take your word to help me in return! But, if you are the kind of man to have only one word and maybe have a proof of your good faith if the realization of the project would make it… I will be very happy!! Giving it to everyone wouldn’t bother me either…. all I would like is to be able to find flax fiber (too expensive carbon) to be able to try to make my catamaran myself. Because not rich! Have a nice day and looking forward to having a message!!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Must-Have Boat Gear for Catamaran Sailors!
Sailing is probably the most gear-intensive activity I've ever done; there are so many decisions to be made about what gear to buy now, for tomorrow, and what to definitely never buy. The gear on...
6 Best Trailerable Trimarans For Bluewater and Coastal Sailing
Having a boat costs a lot of money, even when you are not using it, marina fees, etc. And once it is in the water most sailors never go very far from their "home marina" and sailing will be somewhat...
Did You Know That We Offer Contract to Closing Services? Click Here to Find Out More.
Need Marine Financing? Apply Here With Our Partner, First Approval Source
- Catamaran Interviews
- Catamaran Reviews
- Buying Advice
- Selling Advice
- Woods Design Advice
- Americat 3014
- Aquila 44 Yacht
- Balance 526
- Bali 40 Catspace
- Beneteau Blue II
- Broadblue 346
- Broadblue 38 Prestige
- Broadblue 385
- Broadblue 435
- Broadblue 46
- Catalac 10M
- Catalac 11M
- Catalac 12M
- Catalac 900
- Catana 42 S
- Chris White 48 Voyager
- Chris White 55
- Corsair F28 R
- De Villiers
- Dolphin 460
- Endeavour 30
- Endeavour 35 Victory
- Endeavour 36
- Endeavour 44
- Endeavour 44 TrawlerCat
- Fortuna 36 Island Spirit
- Fortuna 401 Island Spirit
- FP 32 Maldives
- FP 35 Tobago
- FP 37 Antigua
- FP 38 Athena
- FP 39 Fidji
- FP 40 Lavezzi
- FP 40 Lucia
- FP 40 Summerland MY
- FP 41 Lipari
- FP 42 Astrea
- FP 42 Venezia
- FP 43 Belize
- FP 44 Helia
- FP 44 Orana
- FP 46 Bahia
- FP 46 Casamance
- FP 48 Salina
- FP 56 Marquises
- FP 57 Sanya
- FP 60 Eleuthera
- FP Saona 47
- Gemini 3000
- Gemini 3200
- Gemini 3400
- Grainger 420 Mystery Cove
- Hirondelle 7M
- Lagoon 37 TPI
- Lagoon 42 TPI
- Lagoon 43 PC
- Leopard 39 PowerCat
- Leopard 45 Classic
- Leopard 47 PowerCat
- Leopard 51 PowerCat
- Leopard 53 PowerCat
- Maine Cat 30
- Maine Cat 41
- Matrix 450 Vision
- Matrix 760 Silhouette
- Maverick 400
- Maverick 420
- Maverick 440
- Nautitech 40
- Nautitech 442
- Nautitech 46 Open
- Nautitech 47
- Outremer 40
- Outremer 45
- Outremer 50 Standard
- Outremer 55
- Privilege 37
- Privilege 39
- Privilege 42
- Privilege 43
- Privilege 435
- Privilege 45
- Privilege 465
- Privilege 48 Transcat
- Privilege 482
- Privilege Serie 5
- Prout 31 Quest
- Prout 33 Quest
- Prout 34 Event
- Prout 35 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose Elite
- Prout 38 Manta
- Prout 39 Escale
- Royal Cape 45
- Royal Cape 530 Majestic
- Royal Cape Majestic 500
- Sailcraft 30 Iroquois
- Sailcraft 32 Comanche
- Sailcraft 35 Cherokee
- Sailcraft 41 Apache
- Sailcraft 44 Apache
- Wildcat 350
- Seawind 1000
- Seawind 1160
- Seawind 1200
- Seawind 1260
- Seawind 1600
- Solaris 36 Sunrise
- Solaris 36 Sunstar
- St Francis 44
- St Francis 48
- St Francis 50
- Stealth 11.8
- Heavenly Twins 26
- Ocean Twins 38
- Voyage 380 Maxim
- Voyage 400 Norseman
- Voyage 430 Norseman
- Voyage 450 Cabriolet
- Voyage 47 Mayotte
- Wharram 38 Tiki
- AMI 320 Renaissance
- Woods 22 Wizard
- Woods 35 Banshee
- Woods 35 Flica
- Woods 36 Scylla
- Woods 36 Vardo
- Woods 38 Transit
- Woods 40 Meander
- Xquisite X5
- Xquisite X5+
Catamaran Structure – Bridge Decks and Cross Beams
- Post author By BJ Porter
- Post date April 30, 2021
- 6 Comments on Catamaran Structure – Bridge Decks and Cross Beams

Editor’s Note: Many thanks to Ted Clements of Antares Catamarans and Shane Grover of Seawind Catamarans for patiently answering our questions.
There are a lot of reasons why catamarans are more expensive than monohulls. It’s not just the two hulls. There are many more complicated calculations and structures needed to build the complex shapes.
Building a bridge deck and the structures around a pair of hulls is a lot more difficult to design and build than a single hull, and we’ll explore a little about why.
Part 1: Forces on the Hulls
Load and force calculations on a boat hull isn’t a simple calculation, and even monohulls take a lot of designing to build a shape which performs well and has the strength to hold together at sea. Land vehicles have fairly predictable forces and motion on them, but boats can take forces and stresses in any direction.

Waves slam from all directions, boats plunge off waves and get smacked around in chop. Wind forces stress masts and rigging, which applies bending moments and forces to chain plates and the hull. Hulls flex and bend with this motion, and even from tensions applied to the rig.
Elements of drag, hull shape, keel shape and rig design all factor in, whether it’s a heavy, stiff cruising boat or a light, high performance racing machine. Those forces have to be figured, and materials and constructions are made to suit the conditions and situations where the boat will sail.
And that’s just a single hull. When you add a second hull to mix, you add in a whole new set of loads.

Bananas and Pencils
To illustrate these additional loads, we’ll do a thought experiment with a couple of household items. You can try it for real if you want to – but you’ll need two bananas and a few pencils.
Start with the bananas laying parallel to each other, then run a single pencil through the midpoint of each banana (the hulls) to connect them. They’re connected, but when you pick it up, what happens? They don’t stay parallel, of course. We need a second pencil or even a third one, to keep them in place.

The pencils are the crossbeams you’ll hear about in catamaran construction. If you put two of them through the bananas to connect them about 1/3 of the way from the end of each banana, you’ll get a fairly stable platform (for something made from soft fruit and pencils).
Imagine picking up this banamaran with two crossbeams with one hull in each hand. How can we still move the hulls?

First, we can twist one half back and one hand forward, putting lots of force on the crossbeams. To stop this, we could use much stronger beams, and we could put more beams at the ends of the bananas.
If you rotate your hands and the bananas, you demonstrate another type of force on the crossbeams. Pushing the bows or stern together also can move the hulls.
Building the Boat
Now imagine putting weight on the pencils – you’re adding the bridge deck. The mast sits on the bridge deck and creates additional loads and stresses on the crossbeams and hulls.

Finally, we add a sailing rig on top of the weight on the pencils. The rig needs support to stay up. On a monohull, stays run to the bow and stern to support the rig. But a catamaran the mast is centered between the hulls. The tension on the rig will provide upward pull on the hull shapes and usually attach to bow crossbeams. So we’re now pushing down on the middle of the bananas while pulling up on the tips.
The challenge to the catamaran builders and designers is to account for all these forces and build a pair of hulls capable of absorbing these loads without breaking or separating the hulls.
Part 2: Crossbeam Design
Catamarans are not new concepts; double hulled sailing canoes were used in Polynesia and Melanesia long before European explorers arrived. One of the first recreational catamarans was designed and built in 1876 by Nathanael Herreshoff and sailed well enough that the New York Yacht Club banned multihulls from racing.

Most beams are hollow to save weight in increase strength for the amount of material used. A hollow cylinder or rectangular tube gives more resistance to bending per pound of material than a solid rod of the same weight. There are mathematical explanations beyond both the scope of this article (and my ability to explain), but it’s important to know where the loads on beams are supported to understand this.
Greatly simplified – bending a beam creates compressive loads. The further from the center of the beam, the higher the resistance to compression. A rod will have a narrow diameter and resistance is lower. But if you make a cylinder or square tube from the same amount of metal (or fiberglass) you will have the same cross-sectional area, but the compressive force is applied further from the center of the cylinder.
Think of an I-beam from building construction. The compression is on the sides of the I-Beam, but the part in the middle is mostly to keep the sides in place, not bear the load on the beam in high stress applications.
Original Beams
A close look at these boats shows clear and obvious crossbeams connecting the hulls. Duplex , the early Herreshoff boat, had three clear crossbeams and a cockpit on the aft two between the hulls.

Smaller beach and racing cats will have obvious crossbeams, since the decking is usually a stretched piece of canvas or webbing. Other open bridgedeck catamarans, including many home builds, may have actual beams across them holding the hulls in place. And most cats will have some sort of beam across the bows as well.
But when you look at modern bridgedeck catamarans, you notice something strange about the beams. There aren’t any actual “beams” built into the boats.

Modern Cruising Cats – There Are No Beams
It’s more you notice something missing about the beams. Modern bridgedeck catamarans don’t generally have actual crossbeams built into them, as if you were glassing a beam or post into the boat. Instead, the construction of the boat is built around a design the provides the mathematical equivalent of a “beam.”
Bear with me. It took a while for me to get my head around this, too.
Picture a box – even a simple shoebox has rigidity to its sides. Yes, you can crush it, but the hollow sided box offers a lot more stiffness than a piece of cardboard on its own. The structure of the beams is in essence a box built between the hulls, with super strong modern laminate materials providing stiffness to take the loads and stresses.
When modern cats are designed, the “crossbeam” is a combination of internal structures built and connected to the bulkheads that create the load bearing capabilities of a hollow beam section. So the “beam” exists mathematically in the designer’s wireframe drawing of the boat, but when it is built, it is not an external beam added to the structure, but rather a set of structures that act like a beam because of their physical design.

Developments in materials technology over the last few decades allows for shapes and strengths that couldn’t be built with traditional materials like wood or metal.
Part 3: Building a Bridgedeck
Building the bridgedeck is the key piece of fiberglass catamaran strength. To be able to build a boat which can handle all these twisting and torsion forces, creating that “box” to add the strength, catamaran builders take one of several approaches. All can be effective and meet the design requirements, but there may be other reasons a builder chooses a particular approach.
“Tooling” refers to all the molds needed to shape a fiberglass hull. Tooling can be made from a number of different materials and represents a significant investment for any new production catamaran. Costs can run to many millions for tooling durable enough to build a hundred or more boats without changing design and build tolerances.

Molding and tooling to build hulls is a major expense, no matter which approach a builder takes. Building tools and molds can run into millions of dollars in expenses for materials and labor, and molds built for production runs of boats are considerably more expensive than tooling for a one-off or unique design. All of these factors into the decision making behind a build process.
Building a multihull also presents unique challenges compared to building monohulls. Building a single hull can be a fairly linear process – the hull is laid on the mold and built, the inside is fitted out, and decks are attached. While that’s a simplification of the process, it is relatively straight-forward because there is only one hull.

For catamarans, the integral bridgedeck structure doesn’t lend itself to a step-wise assembly. The crossbeams and bridgedeck need to be built integrally before the interior and decks are completely finished. For the builder, this means some parts of the boat have to be finished with reduced access to interior sections of the boat. For the designer, the challenge to is to make the boat so the builder can build it efficiently. For production vessels with build runs in the hundreds, cost effectiveness and production efficiency is crucial.

Not only does the bridgedeck hold two hulls together against all the twisting and torsion forces we’ve discussed, it also has to carry cargo. It holds the living space in the main saloon, as well as passengers and equipment.
Think back on the shoebox – it has compressive strength from the ends, but any individual side is fairly weak. You can deflect the sides easily. While this is fine on a shoebox, it would be disconcerting if the deck flexed and bounced when you walked across it. The bridgedeck also needs strength from the top and bottom to take this load in the central parts of the boat, away from the “box.” You can’t just make the decks and floors massive, that sacrifices headroom and internal volume. Instead, internal structures and stiff construction materials have to take up the load.
Two Piece Molding
Some builders build two hulls individually. One mold can be used if the hulls are identical, and the hulls joined later in the build process. Like any design and build decision, there are pros and cons for the builder which can affect the cost of the final product. If built correctly, there are no compromises in strength from a one piece mold.

For the builder, a one piece mold is much easier to handle. Any hull built on a mold will have to be removed from the mold once the hull is laid, and a single mold is smaller, lighter, and narrower. Breaking a hull out of a mold is a complex process, and may involve cranes and heavy equipment to support the hull as it comes of the mold and to protect the tooling from damage. To remove a hull, you need space to lift the mold and to get heavy equipment around the tooling. And you’ve got to put the molds some place when it’s done.

Connecting two hulls precisely once they’re molded is a more complex task. Unidirectional fibers bond key structures to bulkheads to build the support “box” making up the crossbeams. Although a one piece mold will give an inherently stronger single-material connection between the hulls, more than sufficient strength can be built in with advanced fiber and resin choices (such as carbon fiber and epoxy) when then build the deck connection.
One Piece Molding
Most production catamaran builders have moved to one piece molding. A single tool is built to lay up both hulls and the bottom of the bridgedeck connection in a single large piece. The fundamental strength of the build is higher, allowing for less expensive materials to get the same strength.
“One piece” is a slight misnomer, as the top of the hulls and decking is built in a second mold which is laid over the hulls and bonded along the joint near the top of the hull molds. The loads on a join between the bottom hull and top deck are considerably lower than those on the bridgedeck. There’s no real twisting and torsion on that part of the boat relative to the join between the hulls, so it can be laminated without the same concerns as building between the hulls. ( Editor’s Note: Some builders mold the bridgedeck and inboard half of the hulls together and then mold on the outboard halves of the hulls and deck on top. There is a seam running stem to stern centerline along the bottom of each hull with this technique. )

There are a number of production and build advantages to this approach. Though the tooling is larger, more expensive and awkward, the lay up process incorporates the core hull joins in the initial build. You don’t have to line anything up and glass it in place when your hulls and deck are built connected. There isn’t need for as much material buildup to shore up the “box” since it’s part of the integral build.
Fitting the interior joinery and finish is more challenging, since the crossbeams and related components must be built early in the process. Extra care and planning in the design process can make this more efficient, but access to internal areas of the hull can be difficult during the build.

Alternative Materials – Wood and Metal
Composite construction – fibers and resin – lets builders make nearly any shape. Fiberglass has allowed for the wide range of affordable to high end production catamarans available today. Stronger fibers and better resins have only expanded the possibilities for light, fast, and strong boats.

Wood is rarely used for structural elements in modern production catamarans. It can be heavy, and it doesn’t lend itself to the complex molded shapes designers demand for optimal strength and seaworthiness. Plywood may be used for stiffening in places, and balsa cored decks may still be found. But mostly in older boats, home builds, and kit boats.

Metal construction has its own problems, and very few catamarans are built from metals. Curved shapes are difficult with metals; bending a smooth radius into a flat sheet without bending it, then welding it into place requires time and skill. And weight will be a problem. On the whole, fiberglass is a better solution for a light, strong catamaran.

Conclusion: Tying it Together
This overview only touches on some of the challenges multihull builders face, which monohull builders do not. But what does it mean for you when you’re looking at catamarans to buy? All the fiberglass build techniques will result in a strong boat if built properly. There may be differences in the amount of materials used, and choices for resins and fibers, but the boat should be evaluated as a whole.
It’s good to understand how your boat is built, and to be aware of some of the strengths and limitations of each build technique. But no build technique is inherently better or worse than the other – no matter how your next boat is built, the designer and builder will ensure the build is up to the task.
- Tags Buying Advice

By BJ Porter
Owner of Hallberg Rassy 53; world explorer.
6 replies on “Catamaran Structure – Bridge Decks and Cross Beams”
Proof read much? But the no build technique is inherently better or worse than the other… Good article spoilt by miss spellings and errors.
I corrected the extra “the” you mention in that sentence. I do not see other errors. We do our best and thank you for reading and commenting.
Great article. Very informative for us non-technical types. Great use of graphics and photos to explain the various torsion forces and different build methods. What is the purpose of the wing-like, rear spoiler-looking feature that you sometimes see spanning across the back of the deck/bridge and sometimes connecting the two hulls?
It doesn’t actually connect the hulls, it rests on them. In the good old days this was named a “RADAR Arch” and was used to mount the RADAR antenna and dinghy davits.
Over the last 20 years this stern “ARCH” became a very convenient spot to mount RADAR, solar panels and it is in this role it serves very well while also handling various antennas and of course, the dinghy.
Thanks for the article, great stuff, very informative and useful info. Kudos
I’m actually researching and trying to figure out how to build my own catamaran. But information is very hard to find.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Outremer 45
- Outremer 4X
- Outremer 4.zero
- Outremer 52
- Outremer 55
- Outremer 51
- Outremer 5X
- All the Outremer Fleet
- Personalized support
- Blue Water Sailing Seminars
- Our concept
- The Outremer team
- Our commitments
- Construction principles
- Our catamaran services
- After-sales customer service & Quality control
- Offshore Connected Catamaran Maintenance
- Concierge Services
- Our owners’ stories
- FAQ – Outremer catamarans

- Brokerage: used catamarans for sale
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Grand Large Yatching
Building expertise: our catamaran construction principles
At Outremer every specification has to be precise and consistent with what the naval architect has drawn. During catamaran construction, he or she works in close collaboration with the designers and engineers to reach a harmonious end result.

Safety, reliability, performance, comfort, and pleasure are the key words throughout the design of an Outremer blue water catamaran.
Peace of mind no matter the weather conditions.
An absolute priority for all sailors! We can accept that for racing boats, risks are knowingly taken into account, but for cruising catamarans, a very big safety margin is fundamental. For this reason, the daggerboards are essential to guarantee good upwind sailing, even in difficult situations (storms, rough seas, etc.). We don’t always choose to find ourselves in such situations, but Outremer will bring you back to port, in all conditions.
Resisting the test of time and continuous improvement
Every Outremer will without doubt cover several hundreds of thousands of miles across oceans or around the world during its lifetime and it is crucial that every system is proven and reliable. To achieve this, Outremer takes particular care with the standard of finish, with its choice of technologies and the selection of brands of equipment they install on their boats. What’s more, every year we conduct a survey among all new Outremer owners to help us consistently improve our liveaboard catamaran construction techniques. This feedback is especially important: it allows us to get closer to building the “perfect boat”!
Combining comfort and pleasure of sailing
Multihulls from the Outremer yard are of course, not racing yachts, but they are among the fastest of cruising boats! Performance is both a source of pleasure for any sailor and also an essential safety factor allowing the crew to have more options when facing weather risks, especially single-handed.
Unparalleled quality of life onboard
One of the keys to successful cruising! The quality of life on board depends essentially on comfort at sea. All the elements which go into making an Outremer are combined to achieve an incomparable quality of life with a comfortable interior: more gentle movement allows for quality sleep, no slamming under the bridgedeck, and reduced pitching, leading to good cooking conditions for whoever is in the galley. Silence on board, the absence of any creaking or groaning, so often found on a sailing catamaran, guarantees unrivaled peace and quiet.
Easy sailing and fun for all
Because the pleasure shared between the crew is the guarantee of harmonious life on board during a blue water sailing journey, Outremer takes everyone’s needs into account: skipper, crew, children, guests… Everyone can enjoy 360° visibility, perfect ventilation, and great ergonomics. And of course, the enjoyment of sailing, feeling a boat which goes fast and well, as seen when using the tiller which is available on Outremer boats, an incomparable way to feel a multihull slipping effortlessly through the water!
Loïck Peyron, 4X sponsor: “The point of sailing is the point of departure and the destination. Between the two, the sailing part is fun, of course, but it’s often too long!”
Architecture
Designing the ideal boat
Naval architects translate specifications into lines and volumes:
- Hull designs carefully studied and optimized; long, to carry the required load and reduce forward resistance. Fine hulls demand, in effect, little power to make the move and allow them to maintain high average speeds under way. Not just that, but also to be able to use only one motor when there is no wind, reducing the amount of noise in the hulls when some of the crew are off watch, and also doubling the range under power.
- Windage is limited for maneuvers in port and for better holding at anchor.
- Centering the weight: a very low center of gravity, and weight distribution around that center of gravity – all these unseen elements add to the quality of sailing and reduce pitching movement.
- Fine bows absorb pitching and help produce high levels of comfort under way.
- Daggerboards for sailing to windward, going faster when close-hauled and being able to reach otherwise inaccessible anchorages. Sailing close-hauled on an Outremer catamaran is worthy of the best monohulls, even in the hardest of conditions.
Catamaran construction principles: how are Outremer multihulls made?
The methodology of the Outremer boatyard: putting forward a blend of high-tech technologies and know-how. Blue water cruising programs require significant safety margins: you need to be able to count on your boat in all circumstances!
Even though the philosophy of the yard of is to reduce weight, this must never be done to the detriment of the structure, and our designers are committed to reinforcing the essential areas: the bows are protected by several watertight crash-boxes, the lower part of the hulls are resistant to collision and knocking, the daggerboard wells are indestructible as the daggerboards act as a fuse, making it insubmersible as a result.
Even though modern composites such as those found in sandwich construction are essential materials for saving weight, an Outremer always has the lower part of the hull built in a very thick monolithic laminate: in the event of collision, no structure in sandwich construction could compete with the strength of an Outremer hull. The structure is completely laminated in the hull, and not simply glued on: there is no backing mold interfering with access to any part of the underwater hull, and all the systems remain visible and accessible.
The stiffness of an Outremer catamaran is incomparable
The main bulkheads are of large dimensions, and so are able to take much greater loads than a cruising multihull might encounter. Inserts in carbon fiber, closed-cell foam, isophthalic resins and high-resistance polyester: everything is designed to guarantee your safety for offshore sailing.
For the furnishings, sandwich panels are used to reduce weight, with wood veneer for warmth and aesthetic appearance. The furnishings do not add to the rigidity, and are insulated from the structural parts to reduce unwanted noise, creaks and groans. Aluminum structures support the floors, which don’t squeak either. No more wedged doors or drawers that won’t shut. For the equipment, we choose brands and makes for their quality, their reliability and their suitability with the boat’s program.
An Outremer is designed to be around for over fifty years
Owners change over time, all with ambitious projects and wanting to replace or add certain equipment to their cruising catamaran! In this respect, we apply four golden rules: every part of the boat and every system installed must be documented, be accessible, able to be checked and be replaceable.
Today, more than three million miles have been sailed by our multihulls on every ocean, most of them cruising tropical seas, though many have seen extreme conditions, ranging from Alaska to Patagonia. The huge amount of experience accumulated by Outremer has allowed us to refine and consolidate our principles of catamaran construction.
- BUILDING RAKU FROM A KIT
- Duflex Kit Construction in 9 Steps
BUILD YOUR RAKU CAT WITH A DuFLEX KIT BY FOLLOWING THESE NINE BASIC STEPS

Step 1. Kit Design
Work with us to finalise the details of the design you have chosen including any design options or additional modules to be included in the kit.
We will determine the laminates, the number of panels required for each laminate, create the cutting files and prepare a quote for the kit if it is not already priced.
Once the design details and pricing are confirmed you are ready to place your order.

Step 2. Unpacking
2. The kit arrives at your workshop door, usually by container, as a stack of 1.2m x 2.4m routed composite panels ready to be joined. The shipment will normally include additional reinforcements, resins, and ancilary products as specified.
Unpack the shipment and stack the panels out of the way of the space where the panels will be joined.
If you have purchased a joined kit many of the panels will already be joined up to the length that can be shipped in a container (12m).

Step 3 Joining the Panels
Set up the work space where the panels are to be joined.
The panels have a scarf join called a Z join that facilitate the join without needing tapes.
The joining can be done with a heated Z press that cures the epoxy join quickly. Alternatively they can be joined with clamping pressure.
If the panel are are being joined with the Z press you will need an elevated work bench the full length of the longest panels you are using. (image below).
If you are joining them with a clamping technique the space can be on the factory floor.
A nesting booklet is provided with the kit to show how the panels are joined (right)

Joining the panels with clamping pressure

Panels are being joined into a single long panel by painting the surfaces of the scarf join with epoxy screwing through plywood battens that have a release film applied to one side.
Joining the panels with the Z Press

Step 4 Stacking Joined Panels
Once the joins are cured the panels are stacked to one side until they are needed for the job. The inividual parts should not be cut free of the panels until they are required.
Bulkhead and floor panels will be needed before the hull sides and cabin top so they should be left to the front of the stack wherever possible.

Step 5. Separating the Parts
When assembly is ready to begin the individual parts are separated from the panels by cutting the joining tabs. It is likely you will be building onto moulded hull bottoms that have been built from strip planking or another method of building moulded components. The process for building moulded components is described in another article.

Step 6. ASSEMBLY
As the joined panels are assembled onto the job you will need to apply glass tapes to the joins as specified in your plans.
Panels can be surfaced and coated inside and out with high build while they are on the workshop floor to minimise fairing time once they are assembled to the boat. The paint on the panels shown here has been kept back from the edges to provide a good bond for the tapes.

Smaller items such as steps, seats and dagger cases are nested into the kit and for the more complex parts diagrams are provided to assist with the assembly process.

Step 7. Interior
Interior kits can be ordered with the primary kit, or they can be ordered later when final decisions have been made about the interior arrangement.
A compromise solution is to order the interior as a set of plain planels that can be cut to shape on site after finalising the layout.

Step 8 Fairing, Painting, Hardware Installation
8. The DuFLEX construction process goes a long way to minising the amount of fairing that has to be done, but inevitably any boat that has not come out of a female mould will require some level of fairing and surface preparation prior to painting.
The fillers and resin systems required for the fairing work are normally supplied as part of the kit.
Hardware installation is the same as for any other form of construction using high density core inserts or consolidated laminate in way of fittings.

Step 9. Sailing
Go Sailing. This Barefoot 40 Catamaran was built entirely with a Duflex kit in Foam/Glass and Epoxy resin systems from ATL Composites

DuFLEX Kits are manufactured and supplied world wide by ATL Composites
atlcomposites.com.au
And in Europe by VDL Composites
www.vonderlinden.de/her/28/vdL-Composites-GmbH
For more information on DuFLEX and associated Products
atlcomposites.com.au/category/27/DuFLEX

Join the Newsletter

- Scroll to top

How To Build A Catamaran? (A Step-By-Step Guide)

Are you excited about the prospect of building your own catamaran? With a little research, planning, and the right tools, you can turn your vision into reality in no time.
In this step-by-step guide, well show you how to make the most of this incredible boatbuilding project.
From selecting the materials and planning the design to constructing the hulls and deck and outfitting the boat, well walk you through everything you need to know to build a catamaran of your own.
So, grab your tools and lets get started!
Table of Contents

Short Answer
Building a catamaran requires careful planning and a lot of patience.
The first step is to decide on the design and the materials you will use.
You will need plans for the project, along with lumber and other materials such as fiberglass and epoxy.
The next step is to build the catamaran frame, which involves cutting and fitting the wood pieces together to form the hulls and decks.
Finally, you will need to attach the decking, add the rig and sails, and finish the project with paint and varnish.
Benefits of Building a Catamaran
Building a catamaran can be a very rewarding experience.
Not only will you have the satisfaction of creating something with your own hands, but you will also have a boat that is uniquely yours.
Catamarans offer many benefits over traditional monohull boats, making them an ideal choice for those looking for a reliable and efficient ride.
These benefits include greater stability, more space, improved fuel efficiency, and greater speed.
Stability is one of the biggest advantages of catamarans.
The two hulls provide a wider base that helps to keep the boat from rocking and rolling in rough waters.
This makes for a much smoother and safer ride, even in choppy waters.
Additionally, the two hulls create an open area between them that is perfect for storing equipment, making it ideal for longer trips.
Catamarans are also more fuel efficient than monohulls.
This is because the two hulls provide lift, allowing the boat to glide through the water more easily.
This means you won’t need to use as much fuel to power your boat, allowing you to save money in the long run.
Finally, catamarans are faster than monohulls.
This is due to the increased surface area of the two hulls, which allows the boat to move more easily through the water.
This makes them ideal for those who want to travel quickly and efficiently.
Overall, building a catamaran can be a fun and rewarding experience.
With the right materials and tools, you can create a boat that is unique to you and offers many benefits over traditional monohull boats.
With the right planning and construction process, you can create a catamaran that will be the envy of your peers.
Selecting the Materials

Selecting the right materials is a crucial step in building a catamaran.
The type of material you choose will depend on the size and type of catamaran you are building, as well as your budget and experience.
Catamarans are typically constructed from wood, aluminum, or fiberglass.
Each of these materials has unique advantages, so it is important to research the pros and cons of each before making a decision.
Wood is the traditional material used to build catamarans and is often the most cost-effective option.
Wooden catamarans are strong and stable, and they can be custom-built to any size or shape.
However, wood requires a lot of maintenance and can be susceptible to rot and water damage.
Aluminum is a great option for larger catamarans, as it is lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
It is also relatively easy to work with and can be welded together to create a strong and durable structure.
However, aluminum is a more expensive material and is not as flexible as wood or fiberglass.
Fiberglass is the most popular material for building catamarans, as it is lightweight, strong, and resistant to corrosion.
Fiberglass is also relatively easy to work with and can be shaped to create unique designs.
However, fiberglass is also the most expensive option and can be difficult to repair if damaged.
Once you have selected the material, it is important to purchase the right amount for the project.
Make sure to measure the catamaran carefully and purchase enough material to account for any mistakes or waste.
It is also important to purchase high-quality materials that will last for years.
With the right materials, you can build an amazing catamaran that you will enjoy for years to come.
Planning the Design
When planning the design of your catamaran, youll need to consider a variety of factors, including the size, shape, and type of material youll be using.
Consider the size and weight of the catamaran and the type of water it will be used in.
Youll also need to think about how the catamaran will be used, such as for recreational or commercial purposes.
When it comes to the shape of the catamaran, the most common design is the two-hulled V-shape.
This shape is ideal as it offers stability and is easy to maneuver.
However, depending on the type of use, other shapes, such as the three-hulled catamaran, may be better suited.
The material you choose for your catamaran will also play a role in the design process.
Common materials used to build catamarans are wood, fiberglass, aluminum, and composites.
Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, so its important to research and select the best material for your project.
Finally, when planning the design, youll need to consider the outfitting of the boat.
This includes items such as decking, seating, and a helm station.
Make sure to think about the type of equipment youll need for your catamaran, and consider how it will be installed.
By taking the time to plan the design of your catamaran, you can ensure that you get the best possible outcome.
Doing your research, selecting the right materials, and choosing the right outfitting will all help you create an amazing catamaran that will last for years to come.
Constructing the Hulls and Deck

Constructing the hulls and deck of a catamaran is perhaps the most important and time-consuming step in building a catamaran.
You will need to plan the design of the hulls and deck carefully to ensure that your catamaran is strong, stable, and seaworthy.
When constructing the hulls, you will need to use strong and light materials that are suitable for marine environments.
Fiberglass is a good choice for this, as it is strong and lightweight.
You will need to cut and shape the fiberglass to fit the shape of the hulls, and you will need to use a strong adhesive to bond the pieces together.
The deck of the catamaran will need to be strong and stable enough to support the weight of the passengers and cargo.
You will need to construct the deck out of marine-grade plywood, and you will need to use a strong adhesive to bond the pieces together.
You may also need to add extra support beams to the deck for added strength.
Once the hulls and deck have been constructed, you will need to sand and finish them to ensure a smooth and watertight surface.
You may need to use a sealer or primer to protect the wood and fiberglass from the elements.
Finally, you will need to attach the hulls and deck together.
This can be done with bolts, screws, or other fasteners.
You may also need to use a water-resistant sealant to ensure a watertight connection between the hulls and deck.
Outfitting the Boat
Outfitting a catamaran is an essential part of the build process.
Once the hulls and deck are constructed, you’ll need to ensure that all the necessary components are in place for a successful voyage.
This includes items such as masts, sails, rudders, and outriggers.
It is critical to ensure that the boat is outfitted with the right components for its size and purpose.
For example, if you are building a small catamaran for speed and agility, you’ll need to outfit it with a light and responsive mast and sail.
If you are building a larger craft for comfort and luxury, you’ll need to outfit it with a heavier and more resistant mast and sail.
Additionally, you’ll need to select the right outriggers and rudders for the catamaran’s size and purpose.
Outfitting a catamaran can be a complex process, and it is important to do the research and plan ahead.
Taking the time to select the right materials and components will ensure that your boat is outfitted for success.
Additionally, it is important to use quality materials and components to ensure a safe and successful voyage.
With careful planning and quality components, you can outfit your catamaran for a successful journey.
Acquiring the Right Tools

When it comes to building a catamaran, having the right tools can make all the difference.
To get started, you’ll need a variety of hand tools, including saws, drills, sanders, and screwdrivers.
You’ll also need power tools like routers, biscuit joiners, and angle grinders.
It’s also important to have safety equipment like safety glasses, ear protection, and respirators.
You’ll also need a variety of measuring tools, such as rulers, calipers, and tape measures.
Finally, you’ll need a selection of glues, adhesives, epoxies, and sealants.
With the right tools, you’ll be able to complete your catamaran project safely and efficiently.
Researching and Planning Your Build
Researching and planning your build are essential steps in the process of building a catamaran.
The first step is to become familiar with the design and construction of catamarans.
Start by researching different types of catamarans, from the small and lightweight recreational boats to the larger and more luxurious cruising vessels.
Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of catamarans and determine which type is best suited to your needs.
Once you have a good understanding of the different types of catamarans, you can begin researching the materials and tools you will need for your project.
You will need to choose the type of wood you will use for the boats hulls and deck, as well as the type of fiberglass and resin you will use for the hulls and deck.
You will also need to choose the type of engine you will use and the type of rigging and sail you will use.
Once you have selected the materials and tools you will need for your project, you will need to create a plan for the construction of your catamaran.
You will need to determine the size and shape of your boat, the types of joints you will use to construct the hulls and deck, and the type of engine and rigging you will need.
You should also plan out the sequence of construction steps, so that you can build the catamaran in the most efficient way.
Finally, you will need to research the best ways to protect your catamaran from the elements.
You will need to determine what type of paint or varnish to use on the hulls and deck, and you will need to research the most effective ways to protect your boat from the sun, wind, and water.
By taking the time to research and plan your build, you will be able to create a catamaran that is well-built, efficient, and beautiful.
With the right research and planning, you can create an amazing catamaran that will be the envy of your friends.
Final Thoughts
Building a catamaran is a rewarding experience that can be achieved with the right approach and materials.
With a clear plan, the right tools, and a good understanding of woodworking and fiberglass techniques, you can build an amazing catamaran to share with your family and friends.
So what are you waiting for? Get started on your own catamaran build today and all the rewards that come with it!
James Frami
At the age of 15, he and four other friends from his neighborhood constructed their first boat. He has been sailing for almost 30 years and has a wealth of knowledge that he wants to share with others.
Recent Posts
Does Your Boat License Expire? Here's What You Need to Know
Are you a boat owner looking to stay up-to-date on your license requirements? If so, youve come to the right place! In this article, well cover everything you need to know about boat license...
How to Put Skins on Your Boat in Sea of Thieves? (Complete Guide)
There is a unique sense of pride and accomplishment when you show off a boat you customized to your exact specifications. With Sea of Thieves, you can customize your boat to make it look like your...
Time For a Catamaran Adventure
Isn't Time For Yours?
Building Your Own Catamaran
Building your own catamaran is another option to getting into your own boat. In this page we will go over the advantages, considerations, and a detailed history and journal of our boat-building adventure with Light Wave . We hope this will give you a clear picture of what lies ahead if you go this route, including:
- Construction methods
- 9 essential design features
- Review of the four leading catamaran designers for home builders
- Construction times
- Budget: How much did it cost to build a basic cruising catamaran?
- Layout of our catamaran, LightWave , and lots of pictures
- Carllie’s article from September 2000 Multihulls Magazine: “The Boat Builder’s Wife “
- Equipment outfitting
- Radio and communication outfitting
- Dinghy selection and considerations
- Having a boat custom-built for you
Because of the huge dollars needed to buy a new or even a used catamaran, we would never have gotten a catamaran if we hadn’t built it ourselves.
Let’s start by saying that building any type of larger boat, especially a catamaran, can be one of the most intellectually and physically challenging things you will ever do.
It has been said that building a large boat is the closest a man can come to giving birth to a baby. In other words there is going to some discomfort and pain along the way; you will question yourself on whether this was such a good idea; it’s very difficult to reverse the decision; and though friends will support you, you will be on your own most of the time with your significant other if he/she is game.
Know your boat
You will intimately know every part of your boat. You will know where every wire, hose, bolt, bulkhead, rib, and support is because you installed them!
Pride of ownership
We have often thought what it would be like to just buy a boat from a manufacturer, and know that while owners who have spent a lot of cash (or future life to pay off the lien) their often possessive and competing-with-the Joneses could not begin to compare to our quiet glow of happiness and akinship we feel with Light Wave .
Our boat is like part of the family. So much time was spent on her that we have a major emotional investment. Every time we see our vessel – from a distance at anchor or approaching her in our marina, we say, “What a pretty boat! I can’t believe we built it!” Then that sense of accomplishment settles back in and we feel we have indeed earned the privilege of all of the beautiful experiences we have had sailing, cruising, exploring the beautiful BC Coast and much further a field (or should we say “an ocean”?).
You will be able to pay for the materials as you go and “donate” your time to the cause.
Get a newer design
Many of the production boats that are out there are designs of many years ago because the manufactures have to recoup their capital investment on the mold and production setup. When you build your own you have much newer designs to draw from.
Details on Our Boat Building Adventure
We had sailed our first boat Wave Dancer for five years and had many adventures on the British Columbia coast. In May 1996, I had just returned from a little one-week solo trip in the Gulf Islands of BC when I bought the book, The Cruising Multihull by Chris White (Future link to book review on our web site).
This is the book that got me going (Carllie was not yet convinced). I must have read it a half dozen times over the next 6 months, each time becoming more convinced that this was the way to go for our next boat. It was really still pre-internet web site days so I wrote to all the designers that were listed in the back of the book. Over the next several weeks packages of information started appearing in the mailbox (there is just something about getting packages in the mail – I guess it’s the anticipation). I would pour over these preliminary printed pages with pictures and accommodation layouts. Next, I put a few dollars down to buy the information packages and study plans from the top prospects.
I waited patiently for the study plans. It was like the night before Christmas when I was kid. Oooh the wait! Finally they came, and again I carefully scrutinized the next level of detail. Things were getting a little more serious. The top contenders were:
- Richard Woods
- Chris White
- James Wharram
Click here to read my comments and reviews on their catamaran designs as well as those of Jeff Schionning.
I remember initially drooling over the Atlantic 42 by Chris White, still one of my favorite designs. It seemed to be so seaworthy (by the way if I run into about $800,000 USD any time soon, I am going to buy an Atlantic 55). The most important piece of advice that came out of the material was from Richard Woods:
“Build the smallest boat you‘d be happy with it.”
Axiom #1: The hours to build a catamaran is in almost in direct proportion to its weight.
Which brings us to Axiom #2:
Axiom #2: It takes about 1 hour to create 1 pound of finished boat.
In our case we spent 3,500 hours ( click here for full details on the construction hours ) to build a 4,000 lb. boat (just a little less than 0.9 hours per pound). If a boat’s empty weight is 8,000 lbs., it will probably take about 6,000 hours to build.
When you think about it, you can only mix and handle so much material per hour. More boat weight, more material, more hours. Sure there are some economies of scale on a bigger boat, but usually the systems become more complex and these take longer to install.
This decision process took 8 months and I figured we’d launch in 6 months. It was now January of 1997. Little did we know it would be 26 months and 3,500 hours between the two of us until we launched on June 5, 1999. We ordered the full plans and we were off and running.
We were ready to build, but where would we start the process? First of all, we live in a tiny 480 sq. ft. apartment in Vancouver. Back-yard building wasn’t exactly an option so I found a small garage nearby that we rented for 5 months.
After about 4 months in the garage, I had made all the small parts and it was time to build the hulls. This meant that we had to go larger facilities. We found space at Shelter Island Marina and Boatyard in Richmond. This is the biggest boat yard in the Vancouver area with dozens of commercial and private projects, big and small, under way.
We were out of money by then, so we sold our first boat so we could buy resin and fiberglass. It was a traumatic time as we said goodbye to our beloved Wave Dancer . We were now committed. We than had all the foam for the hull cores, barrels of resin, and huge rolls of matting and roving needed for the fiberglass skins delivered to our “domed stadium”. We kicked ourselves many times that we didn’t take a picture of this raw material stacked in one corner of the empty shed, so we could later show “before” and “after” photos. It was time to build the hulls.
Over the next several months we proceed to join the hulls with the beams I had built in the garage, and then to install the cuddy cabin, cockpit, and decks. By the spring of 1998, it was staring to look like a catamaran. Through the spring and summer of 1998, we continued with the major structural components: mini-keels, hatches, stairs, and interior. Then we went on to the very laborious work of fairing the boat before painting. Don’t under estimate that job!
By October 1998 we were ready to prime the boat and start painting. I really thought this would go quickly. I forgot that I would have to do two more complete sandings to sand off and finish the two layers of primer application. In addition we had to fill countless pinholes – a laborious process somewhat like hiking up a mountain – each time you get to what you think is the top, you see another summit!
The boat seemed to get bigger and bigger. Believe me, there is a lot of surface area on a catamaran. I clearly remember that last sanding: I had reached the end of my physical and mental endurance – I was exhausted. I was ready to move on to the next phase – any phase but more sanding!
We now started spray-painting the hulls bright yellow. It was around this time we decided on our boat name of Light Wave . The painting took over a month: the hulls being the easy part, it was the topsides, the nonskid, and all the masking and prep that seemed to take forever. Happily, the worst of the dust was gone.
By March 1999 we were in the home stretch. The center bridge deck cabin was completed so we took a week off from our paid jobs and lived on the boat in the shed so we could work all day and not waste time commuting. March, April and May were frantic months as we finished all the final touches: engine installation, rudders, windows, deck fittings, electrical, plumbing, mast, and rigging. See our outfitting page (for more details on what we picked and why, and things we would do differently now.
Initially, our electronic systems were relatively basic but included GPS and autopilot see the following link for all our electronic outfitting choices and reasoning for more details.
It was May 22, 1999 and we decided that Saturday, June 5th would be “Launch Day” so we could send invitations to all of our friends. On the Friday night before Launch Day, we still had a number of final things to do, many of them outside. Unfortunately it was pouring rain. We were tired and very wet but the boat had to go into the water next day so we persevered on till everything was ready.
The moment of truth came as Light Wave was lowered into the water. While still in the slings of the Travelift, I jumped aboard to check for leaks. Of course there weren’t any! More food and laughs and tours of the boat for all attending. It was a great day.
Emotionally drained that night, we slept in Light Wave in the water for the first time. It was another week before we actually went out for our first trip as we had to sell the shed, setup sails, and install some final deck hardware.
To sum it up, building a catamaran was a great experience. We learned a lot. Carllie and I grew closer together through it all. We had a great time doing it. We had a beautiful catamaran to show for it. Now it was time for a catamaran adventure !
[email protected]

The Best Advanced Build System in the World
The schionning advanced build system are one of the simplest ways to build your own boat, or have a custom design built faster and more accurately by a professional. utilising duflex panels with a balsa core, large sheets are joined on their long edge to form full length hull panels, bulkheads etc similar to a giant jigsaw puzzle. once you release the tabs, your full size pieces are ready to be assembled., a pre-cut advanced build system does not only benefit the home builder, but streamlines a professional build as quantities are accurate and wastage is minimised. when having a vessel built overseas, a kit reduces the chances of local materials not being available, or delays during your project, and ensures there are no mistakes., read on below to gain a more solid understand of how the schionning advanced build system go together, where are you building.
Schionning Designs is partnered with a number of leading composite manufacturing companies with varying CNC capabilities, as well as supplying resins, hardeners, cloths and fillers. Our partners are located in different parts of the world, so where you are planning to build your boat will have an impact on which composite company is best to supply your kit.
Listed below are our composite manufacturering partners, ATL Composites located in Australia, VDL Composites located in Germany, and PBT Technologies located in South Africa.

ATL Composites (Australia)

VDL Composites (Germany)

PBT Composites (South Africa)
Starting the process.

THE KIT PROCESS
MATERIAL CHOICES

TECHNICAL INFORMATION

RECOMMENDED EQUIPMENT

Catamaran Plans: Design, Build and Sail your own Multi-Hull Boat
Table of Contents
Why Build a Catamaran: The Benefits of Multi-Hull Boats
Building a catamaran offers many benefits over traditional monohull boats. One of the main advantages of catamarans is their stability. With two hulls instead of one, catamarans have a lower center of gravity, which makes them less likely to tip over in rough waters. This makes them ideal for families with children, or for anyone who wants to feel more secure while on the water.
Another benefit of catamarans is their increased speed and efficiency. The two hulls of a catamaran can displace more water than a single hull, which means they can move through the water faster and with less resistance. This makes them ideal for racing or for anyone who wants to cover more ground in less time. Additionally, Catamarans are also known for their space, as the twin-hull design provides more room for living and storage than a monohull.

Catamarans also offer more flexibility in terms of design. The two hulls of a catamaran can be configured in many different ways, which allows for a wide range of customization options. For example, one hull can be used for sleeping quarters, while the other can be used for storage or as a cockpit. This makes catamarans ideal for long-term cruising or for anyone who wants to create a unique and personalized boat.
Finally, catamarans are also more environmentally friendly than monohulls. Because they are more efficient, they can move through the water with less fuel consumption, which reduces their carbon footprint. Additionally, many catamaran designs incorporate solar panels and other renewable energy sources, which makes them ideal for anyone who wants to minimize their environmental impact while enjoying the water.
Designing Your Own Catamaran: Tips and Tricks
Designing your own catamaran can be a challenging but rewarding experience. Before you begin, it’s important to consider your needs and goals for the boat. Are you planning to use it for racing, cruising, or a combination of both? How many people will be on board? What kind of conditions will you be sailing in? Answering these questions will help you to determine the size, shape, and features of your catamaran.
One important tip when designing your catamaran is to keep it simple. While it can be tempting to add a lot of bells and whistles, the more complex your design, the more difficult and expensive it will be to build and maintain. Instead, focus on creating a functional and efficient boat that meets your needs.

Another tip is to take into account the materials you will be using. Different materials have different properties and costs, so it’s important to choose the right ones for your design. For example, wood is a traditional and affordable material, but it requires more maintenance than fiberglass. On the other hand, composites materials are more expensive but offer great weight to strength ratio.
Finally, it’s important to consult with experts and professionals during the design process. There are many resources available, such as online forums, books, and classes, that can help you to learn more about catamaran design and construction. Additionally, you should consider consulting with naval architects, boat builders, and other experts who can offer guidance and feedback on your design. They can help you to refine your ideas and ensure that your boat is safe and seaworthy.
Materials and Tools Needed for Building a Catamaran
Building a catamaran requires a variety of materials and tools. The materials you will need will depend on the design of your catamaran and the type of construction you choose. Common materials used in catamaran construction include wood, fiberglass, composites, aluminum, and PVC. Each material has its own unique properties and benefits, so it’s important to choose the right one for your project.
When it comes to tools, you will need a basic set of hand and power tools to complete your catamaran project. These include saws, drills, sanders, and other tools that are commonly used in woodworking or metalworking. Additionally, you will need specialized tools such as a router, a band saw, and a vacuum bagging system if you are building with composites materials.

In addition to the above tools, you will also need safety gear, such as goggles, respirators, and ear protection. Building a catamaran can be a challenging and time-consuming process, so it’s important to take the necessary precautions to protect yourself and others. Additionally, it’s important to have a well-ventilated workspace, as some of the materials and chemicals used in catamaran construction can be harmful if inhaled.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Building a Catamaran
Building a catamaran can be a complex and challenging process, and it’s easy to make mistakes if you’re not careful. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when building a catamaran:
One of the most common mistakes is not properly planning and designing your catamaran. This can lead to problems later on in the construction process, such as not having enough room for your intended use or not being able to fit certain components. It is important to take the time to carefully plan and design your catamaran, taking into account your needs, goals and the materials you will be using.
Another common mistake is not properly preparing your materials. This can include not properly storing or protecting the materials from the elements, or not properly cutting or shaping the materials before assembly. Proper preparation of materials is essential to ensure that your catamaran is strong and durable.
A third mistake is not using the right tools or not using them properly. This can lead to problems such as not being able to cut or shape the materials correctly, or not being able to assemble the boat properly. It’s important to research and invest in the right tools for the job, and to learn how to use them properly before starting the construction process.

Another common mistake is not properly securing and aligning the components during assembly. This can lead to problems such as leaks, or the boat being unstable on the water. It’s important to take your time and to work carefully to ensure that everything is properly aligned and secured.
Finally, not following safety guidelines is a mistake that should be avoided. This can include not wearing protective gear, not having proper ventilation, or not taking the necessary precautions to protect yourself and others. Building a catamaran can be a challenging process, but it’s important to prioritize safety to prevent accidents or injuries.
After completing the construction of your catamaran, there are several important steps to take before launching it. These include finishing the exterior and interior of the boat, and performing necessary safety checks.
Finishing and Launching Your Catamaran
Finishing the exterior of your catamaran involves tasks such as painting, varnishing, or applying gel coat. This step is important to protect the boat from the elements and give it a professional look. It’s important to use the right type of paint or finish for the materials you used in the construction, and to follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Similarly, finishing the interior of your catamaran involves tasks such as installing cabinetry, flooring, and other finishing touches. This step is important to make the boat more comfortable and functional. You can add amenities such as a kitchen, a bathroom, and a sleeping area.
After the finishing is done, it’s important to perform safety checks on your catamaran before launching. This includes checking the boat’s systems such as electrical, plumbing, and navigation. You should also check that all the safety equipment is in place and working properly. This includes life jackets, flares, and fire extinguishers.

Once all the necessary steps are completed, you will be ready to launch your catamaran. Launching a catamaran is a complex process that requires coordination between the boat owner, the marina, and other professionals. The boat should be launched in a protected area with calm waters, and with the help of a crane or a trailer. It’s important to have a plan in place for launching and to be aware of the local laws and regulations.
Finally, after the catamaran is launched, it’s important to test the boat and make any necessary adjustments before taking it out on the water. This includes testing the systems, checking for leaks and making sure that the boat is stable on the water. After this, you can finally enjoy your new catamaran!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Design Dynamics
Open Bridgedeck Catamaran
Configuration & Basic Types
Amultihull, just as any other type of boat, presents a series of compromises, and this applies to overall hull, deck and configuration as well. Concessions often have to be made because of space, performance or construction costs. In addition, the intended usage will be a significant factor in determining the shape and size of the vessel. Successful cruising designs will balance all parameters and only you, as a sailor, will know which type of catamaran will be suitable for your needs.
A monohull 's characteristics, largely determined by the beam-to-length ratio of the hull and its displacement, will vary very little from another ballasted boat, as there is only so much volume you can fit into a single hull. This will establish the amount of accommodations, which will not greatly differ from one monohull to another, setting a stark contrast to a catamaran, where intended parameters vary so much more.
Basically, we can break down the major design considerations into: overall configuration,
If one thinks of an open bridgedeck-type of catamaran, images of Hobie Cats on one end of the spectrum, and giant-open ocean racing multihulls on the extreme end, come to mind. They have no fixed coachhouse roof and some of them, especially the small beach cats, only have nets strung between the hulls. Larger examples have partial composite platforms, which stiffen the structure and allow for cockpit seats and helm stations. Since without a solid coachhouse there is less boat to build, these multihulls will be generally lighter and have better aerodynamic properties than full bridgedeck-type cats.
Although few manufacturers and designers have attempted to build open bridgedeck catamarans for cruising, only the most die-hard campers will find them useful for liveaboard applications. Typical examples are the older MacGregor 36, Stiletto 27 and 30, the French KL27 and Corneel designs, which could be sailed hard by lifting a hull (something that you try to avoid when cruising with a fully decked-out boat). Some of these vessels even featured a tiny removable doghouse which provided some shelter for the crew. On smaller open bridgedeck multihulls the only living quarters are found in the confines of the hulls. Even on larger types, they are cramped and not conducive to long-term cruising. The advantages of these sporty vessels,
Copyright © 2006, 2008 by Gregor Tarjan. Click here for terms of use.
Basic Catamaran Configurations

especially in sizes below 30 feet, is their lower cost, trailerability and lively performance. However, attention has to be paid that they not be overloaded or else one could easily turn a cat into a t they are big moneymakers and are considered the workhorses of the sea.
A large exception to the class 1 type of configuration is found in sizes above 30 feet, which could be considered as class 2. Manufacturers such as Maine Cat and a few other custom multihulls such as the Shuttleworth successfully combine an open-deck plan with a certain degree of cruising comfort. In order to provide some shelter for the crew, large semi-rigid biminis are erected. Not only are these afterthoughts unsightly and do no justice to the beauty of these boats, but they also add a considerable amount of drag, contradicting the nature of these athletic multihulls.
Large charter boats or "Day Boats," as they are called, also utilize the open bridgedeck layout to maximize cockpit space. These machines can entertain up to 80 passengers and are found in holiday resorts around the world. Correctly managed and marketed,
Partial Bridgedeck Catamaran
These are often referred to as cruising/ racing types and, unfortunately, very few existing manufacturers still make them. Designs such as the older Edel and Outremer catamarans had a rigid deck and a small coachhouse, which was completely separate from the hulls. My own Outremer 43 "Flo" was of that category. She was a great sailboat and provided ample room for our family cruises along the U.S. East Coast. Similar to the class 1 vessels, the bridge decks of these types of catamarans are also shorter fore and aft, and the accommodations are simple.
Partial bridgedeck catamarans usually place simple sitting arrangements and nav-stations on the main deck. The balance of the layout, below The Broadblue range of cruising catamarans are examples of full-length bridgedeck multihulls, providing plenty of volume for cruisers.

above The Blubay 72 is a state-of-the-art, maxi-sized racer-cruiser featuring a separate saloon pod. She will cruise at close to 28 knots.
below The Gemini 105Mc, seen here in the Patagonian channels, is a popular full bridgedeck catamaran which, in capable hands, can be taken to the world's most remote areas.
such as the galley, heads and berths are often situated in the hulls. Most of the time, these multihulls only have sitting or crouching headroom in the saloon, unless the cabin sole is dropped significantly, compromising the underwing clearance. The Edel 35 was particularly notorious for her low bridge deck, although hundreds of them were built.

Advantages are good looks and light weight overall structure, but the fact that one can only access the hull compartments via the cockpit poses limitations for serious cruising or live-aboard applications.
Some years ago when Outremer was looking for a substitute for its 40 footer, I was asked to design an open bridgedeck type and came up with a compact 38' racer/cruiser with low profile and tiller steering. Unfortunately, lack of demand prevented the project from being realized and the Outremer 42 was born. However, I feel that a properly designed class 2 multihull is a fantastic compromise for the average weekend sailor. It is unfortunate that presently no manufacturer builds one.
Bridgedeck Catamaran
Probably the majority of production and custom cruising catamarans belong to this category, which is the focus of this book. A bridgedeck multihull maximizes the use of space and features a solid deck with a coachhouse that spans the entire width of the cockpit. There is one main entrance into the boat via large sliding doors, and access into both hulls is through companionways leading down from either side of the large saloon. Bridgedeck catamarans are ideal for cruisers or liveaboard sailors. These vessels feature ample payload-carrying capacity and provide good protection for the crew. Helm locations are usually behind the coach roof bulkhead or in some rare cases on the aft end of the hulls behind the cockpit.
These class 3 multihulls contain all the comforts of home and feature a spacious

saloon, galley, and navigation station on the main deck. The coachhouse acts as a centralized core, spanning both hulls, which are usually reserved for heads, sleeping cabins and storage. Unlike any other type of boat, monohull and multihull combined, the class 3 cruising catamaran has an unrivalled "homey" feel to it. The wide cockpits are protected by biminis which integrate seamlessly into the coachroof. This not only looks good but creates an inside-outside space that is both practical and unique.
Large bridgedeck cats have the capacity and volume to carry most of the items you would find in your home. From dishwashers to the generators that power them, you can actually have it all. However, the desire to load up too much sometimes overburdens the vessel, compromising its performance.
On vessels larger than 40 feet, headroom is sufficient, although individuals 6 feet and taller might have to make compromises in the forward part of the saloon or in the extremities of the hulls. Designers try to balance the need for ample bridgedeck clearance and place the cabin sole high enough to avoid underwing pounding created by waves. Low, good-looking silhouettes can be found on larger catamarans, although some manufacturers have the "no holds barred" approach and make their boats look like a toolbox. Although this maximizes space, the chunky appearance is detrimental to the performance of the boat as it increases air drag. Finally, square coachhouses make catamarans look rather unattractive.
Some builders elect to pull the solid bridge deck all the way from bow to stern.
above This recently launched Yapluka 72' catamaran is seen here in full cruising trim and serves her owner-couple as a liveaboard world voyager and mobile office.
Bridgedeck pounding caused by waves is one of the drawbacks of low underwing catamarans. Moderate displacement, full-volume bow and stern sections, and a high and long bridgedeck will minimize, if not eliminate, annoying wave slap under the saloon sole. Although bridgedeck height is a very important parameter, it is a misconception that it is the only design feature to look for. One has to consider weight as well as its distribution and support by the hulls, especially in the extremities. Heavy, low bridgedeck multihulls might make great liveaboard vessels, but they should only be taken to sea by masochists.
below A partial bridgedeck cat, such as the older Outremer 43, was a swift boat but had the disadvantage of separate saloon and hull access.
Parameters Contributing to Bridgedeck Pounding

This book would not be complete without the mention of the new breed of luxury yacht: the Multihull Supercat. These magnificent vessels usually measure in

This is beneficial for stiffening the structure and making the most out of the available deck space. The Gemini catamaran is a very successful design which employs this layout. Yet designers who try to put too much weight into the ends must be careful. These types frequently suffer from excessive pitching in a seaway and display mediocre performance under sail.
Superyacht Catamaran
This book would not be complete without the mention of the new breed of luxury yacht: the Multihull Supercat. These magnificent vessels usually measure in excess of 100' and can sail on free wind energy at more than 30 knots without any heel. They feature living rooms the size as found on monohull superyachts twice their size, and require neither a dozen crew to run them nor large diesel engines. Very few builders in the world specialize in these types of vessels, yet their ideal application as large eco-expedition vessels, corporate entertainment platforms, or ultimate private yachts is unquestionable. Blubay Yachts of France seems to be on the forefront of this group as they have gained invaluable experience by being the only builder that has built a succession of composite superyacht multihulls upwards of 100'.
The world market for extravagant pleasure boats has been steadily growing, yet the catamaran platform for luxury sailing vessels has only recently been recognized.
Modern composite materials and highlevel engineering utilizing Finite Element Analysis now permit the construction of large structures such as multihulls, which was not possible 10 or 20 years ago. The aeronautical and automobile racing industry have contributed considerably to the design and engineering of complex composite structures from which super-catamarans have greatly benefited. The use of aluminum has been the classic hull and superstructure material for large vessels around 60' and it is still a strong and economical build alternative. With the advance of composite technology experienced builders (usually French yards) are developing lighter, stronger and increasingly sophisticated super-yachts, providing clients alternatives that were unheard of just years ago.
Large catamarans, with their wide and stable platforms are becoming recognized as ideal structures for lavish, as well as exciting, pleasure boats. Their vast living accommodations and privacy layout make them ideal for people looking for an alternative to deep draft and heavy monohulls. In addition, their low-profile underbodies permit access to shallow harbors. The new generation of research vessels and oceanographic laboratory ships are frequently large catamarans. They project the image of eco-friendliness and efficiency as they are propelled by clean wind energy. Their shallow draft allows access to reefs and remote anchorages. Their wide aft platforms provide superior storage facilities for large dive tenders and even ideal helicopter landing pads. The demand for these types of superyacht catamarans worldwide is steadily growing.
below Large luxury yachts, such as this 100' catamaran, can easily accommodate several dozens of guests in ultimate comfort while, at the same time, they can sail at double-digit speeds. With world oil prices steadily rising, they very well might become the new breed of mega-yacht.

Continue reading here: Catamaran Design Guide
Was this article helpful?
Recommended Programs

Myboatplans 518 Boat Plans
Related Posts
- How Much Payload Do A Cruizing Catamaran Need
- Bridge Clearance - Maintaining Boats
- How Are Catamaran Masts Fixed Down
- Configuration Types - Catamarans Guide
- Hull Hydrodynamics and Design
Readers' Questions
How to build a catamaran free plans?
There are a number of online sources that provide free plans for building a catamaran, such as: The Boat Plans Collection: <a href="http://www.theboatplanscollection.com/catamaran-plans/" >http://www.theboatplanscollection.com/catamaran-plans/</a> Boat Design Net: <a href="https://www.boatdesign.net/forums/multihulls/free-catamaran-plans-54219.html" >https://www.boatdesign.net/forums/multihulls/free-catamaran-plans-54219.html</a> DIYCatamaran: <a href="https://www.diylargecatamaran.com/category/plans/" >https://www.diylargecatamaran.com/category/plans/</a> Multihulls 4 U: <a href="https://www.multihulls4u.com/diy-catamaran-plans/" >https://www.multihulls4u.com/diy-catamaran-plans/</a> BoatBuilderCentral: <a href="https://boatbuildercentral.com/category/boat-plans/power-catamaran.html" >https://boatbuildercentral.com/category/boat-plans/power-catamaran.html</a> Before beginning the project, be sure to read and understand all instructions, diagrams, and safety guidelines that are included in the plans. Additionally, consider consulting with a professional boat builder in the case of any questions or doubts.

The challenge of building a trimaran from beachcat hulls
Hi Mike! Let me first say I appreciate the depth of information on your web site :)
I've been ‘oogling’ it for years. But now I have a question regarding the potential of building a trimaran out of some old 18' cat hulls. How would you suggest I proceed and what might I expect from the result ?
….. Josh from Kalispell, MT.
ANSWER : Tks Josh … always pleased to hear my work is proving of value to others.
I first need to say that using cat hulls is not a perfect fit for either the vaka (center hull) or even the amas (floats) but sometimes we can make something work as a fun project. The vaka will be the biggest challenge. I could briefly answer your question with just a list of do’s & don’ts , but I think a more detailed reply will give you some specifics and cover a broader range of related questions, so here we go.
First step is to make a weight estimate starting with what a ship designer would call the “Lightship weight” (boat ready to sail, but no supplies, crew or their personal equipment). You then need to decide what weight you wish to tack-on to form the Design Displacement . This we call the ‘Deadweight’. The very minimum would be for solo day sailing .. say 200 lbs added to the Lightship weight, but for an 18footer, this will likely be more like 350lbs as an absolute minimum.
So let’s assume the boat and its rig and gear weigh 550 lbs. Now with 350lbs added, the required Design displacement will now be 900lbs. The volume to support that will be 900/64 = 14 cu.ft. (1 cuft displaces 64 lbs of seawater, or use 62.4 for fresh water)
The difficulty with a trimaran over a beachcat, is that there is initially only ONE hull to provide this buoyancy volume, compared to two for a catamaran, so right away, one can see why a single catamaran hull is WAY too small for a vaka. Let’s say these are your 3 hulls.
Place the widest one with most volume in the center.
Obviously, if you kept the hull in this level position, your trimaran would be dragging 3 hulls through the water with far more drag than for a catamaran.
So you need to lower the central hull, so that it will support your 900 lbs .. requiring 14 cu.ft volume under the waterline. It will clearly not have the volume needed so what can be done ? There are 3 basic ways to go. You can lengthen it, widen it, or sink it deeper. Using all three would be best if designing a new vaka but I suggest that sinking it deeper will be the easiest, as you can then just raise the sides. But you will probably need some frames to support the deeper hull section as the hull will now have to accept more hydrostatic pressure.
It will now look more like this:
You can either raise the sides (C) or a better solution would be to combine this with side extensions (D) to give yourself some form of central cockpit as well as more width to later attach your cross beams (akas). Exactly how deep this central hull will need to go, will decide how practical this whole ‘conversion’ will be, and it’s quite possible you will need to do some major surgery to this central hull (or build a new one) to get the buoyancy volume you need. If you are not already familiar with how to calculate this, I suggest you study this page from the design section.
https://www.smalltridesign.com/Trimaran-Articles/design/simpsons-rule.html
A very rough idea of the sectional area (marked as ‘buoyancy’ in the above sketch) can be obtained by assuming a Block Coefficient* of 0.5. For this, double your required volume and divide by your waterline length .
- Block Coefficient is the ratio of actual hull volume to an encompassing ‘block’, that has dimensions equal to: your waterline length: your waterline beam: and underwater water depth (design draft)..
So in this case, this will be 2 x 14 / 17.5 or 1.60 sqft, which will roughly require a beam and draft of (1.60 0.5 ) or 1.265 ft for both waterline beam and for draft .
If your hull is much smaller, you either have to go deeper than 1.3ft draft OR find ways to widen that hull to get the cross-sectional area you need. (Typically, a central trimaran hull has a waterline width of about double that of the ama beam).
Moving forward .. let’s assume you now have chosen your best workable solution for the vaka.
As far as the overall beam is concerned, the issues involved and a way to select a suitable beam is already explained in this Q&A from earlier this month.
We now need to connect the amas with the main hull using beams. As I understand you are planning to use a similar folding system to my W17 and using my design of fiberglass hinge and latch , I will explain what you will need.
Beam and latch strength will be defined by the maximum righting moment that the ama can apply, plus a safety factor.
As a safety factor, it is common to apply the full buoyancy of the ama (when fully underwater) to the main beam ... and multiply by the Beam Lever (shown here), which might be ~4ft in this case. IF the full ama volume is say 800 lbs, then the bending moment on the beam would be 3200 lbs.ft
Once you have fixed the hinge location, you can calculate the bending moment at the hinge, using the same 800 lbs (just assumed for this example) but with a smaller lever. Let’s assume it is 2.5ft in this case, so the Bending Moment will now be 2.5 x 800 or 2000 ft lbs. This would mean that IF your vertical distance between the upper hinge and the lower latch is 5” deep (0.42ft), that the latch will need to take 2000/0.42 or 4762 lbs in tension, for the hinge to be as strong as the beam. This shows the important value of 'beam depth' with a hinge system.
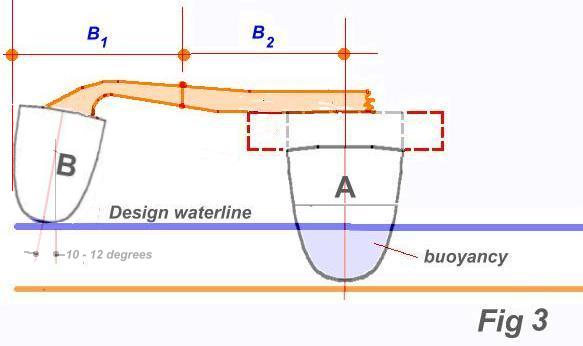
There will also be a download on the upper hinge, due to whatever crew weight you place on the flying windward ama (plus the weight of the ama and outer beam itself). With a large volume ama, this download is typically about 70-80% of the upload, so the hinge is a little less stressed in tension than the lower latch, but with a small ama, it could be the reverse, so you need to do the maths..
In Fig 3. note that I show the amas inclined out at 10-12 degrees. If this is not done, they are more side-loaded when heeled and this adds an unnecessary load to their beam attachment as well as making the ama more resistant to push through the water, so personally, I consider some outward angle is essential.
In addition to their location in the above sectional view, the outer hulls that will work as amas, also need to be positioned in profile view , relative to the central hull.
In the sketch below, they are shown with slight lift of the bow that some designers in the past have incorporated with the assumption of less resistance and 'to ride over the waves'. In the 1970’s many amas were then banana shape d and even back then, Hobie 16 hulls were sometimes used as trimaran floats. Having sailed on one a few times, I found such boats (like Newick’s Tremolino for one) were very jittery in any seaway, were very wet, and also pitched excessively. Even using the straighter and therefore more suitable H18 hulls, their stability role for a trimaran is still compromised if installed as shown here in Fig 6.
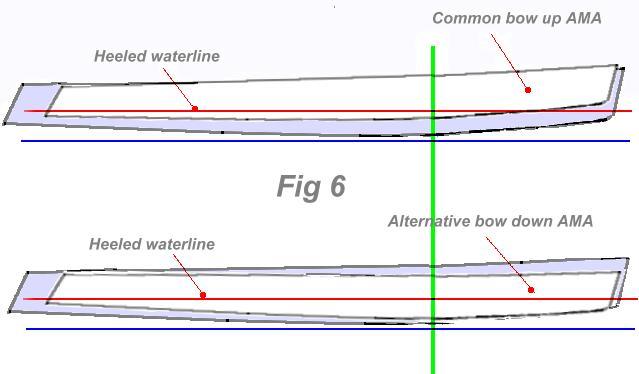
Just compare these two sketches in Fig 7 that both show an identical assumed heeled water line (in red) and you can see that IF the bow of the ama is raised that the ama will not give any bow lift UNTIL the whole bow drops, severely increasing the risk of pitch-poling, so unless the bow is very full with a wide vee, its more effective and safer to actually LOWER the buoyancy of the ama bow so that it quickly immerses, to provide more effective lift when heeled.
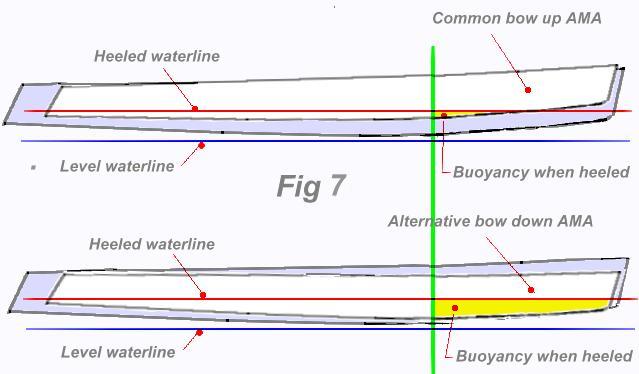
So what can be done to make the beachcat hull more like this ama? The bow is deep and narrow, not vee’d. Think of the Hazelett mooring buoy that is a vertical tube. While it still offers buoyancy, it moves very little in waves. When a bow is like that, its not easily launchied in the air to only fall again, over and over again. It just stays quiet and cuts horizontally through waves and it certainly increases the waterline length. Early rockered amas, had short waterline lengths and were also vee’d … two things I advise against. After all, we are ’sailing’ on this ama and need it to act like an efficient boat hull. But as it would be complicated to deepen the forefoot of an existing beachcat hull, its easier to lower the bow as shown above and then raise the deck forward of the forward beam.
As a picture is a 1000 words …, check out what I would do. 3 days of 4 hours could see both done if you plan your work.
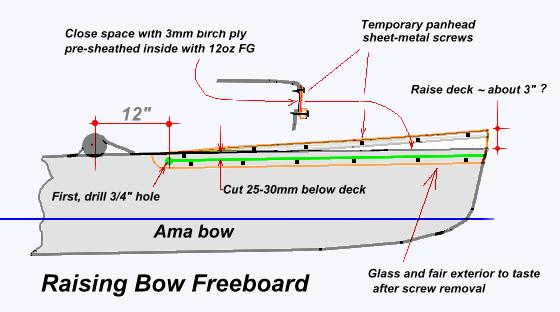
You might find a collision bulkhead inside that will need cutting across, but it should not be hard to raise that with rigid foam, so that the raised deck can be bonded to it and keep it watertight. The ¾” holes in the sides will stop the end of the cut from splitting and cracking, and will be filled and covered over by the fill piece.
This should give one enough to make the important decisions and calculations, but as can be seen, catamaran hulls are not ideally interchangeable with Trimaran hulls, so their use like this will always be a compromise.
You also have to decide which hull will hold a centerboard or daggerboard. It’s much easier to reach one in the center hull, but this is your choice and dilemma. Either can be made to work but do not use ama boards unless you are operating in deep water, or you may end up IN the water while trying to adjust them from an ama, especially in rough water.
As far as the end result , it depends on so many things that it’s hard to predict. But it could be made to perform quite well in relatively flat water and give you some fun at least … but it will not be a dry boat like the W17, nor as comfortable or have as low leeway, as the round hulls are just not as ideal for slicing waves with minimum disturbance as the W17 hulls are. While rounded hulls are very effective in lowering surface friction, they seldom slice waves as well and certainly do not provide the leeway resistance of the W17 hulls.
It's also frequently forgotten (or just not understood) that often, the greatest resistance from a small boat is wave resistance or wave making … being the most critical in the 4 to12kt range. Optimizing for this range with non-round hulls can more than make up for their added skin drag. See this article for more on this, where there is a chart showing what proportion of residuary (wave) resistance applies at what speed.
Hope this helps to get you going in the right direction, and good luck with your project.
Also note that there was an earlier question of using the reverse ... Trimaran hulls for a Catamaran and as my graph showing the proportion of residuary resistance versus the total is also there, it may be of some interest too.
Mike ... March 2022
"New articles, comments and references will be added periodically as new questions are answered and other info comes in relative to this subject, so you're invited to revisit and participate." —webmaster
"See the Copyright Information & Legal Disclaimer page for copyright info and use of ANY part of this text or article"

Professional BoatBuilder Magazine
An aluminum expedition catamaran.
By Dieter Loibner , Apr 5, 2022

With 110′ LOA, a 35′ beam, and 45′ (33.5m, 10.6m, and 13.7m) of bridge clearance, the H-2 catamaran seeks to make a case for U.S. custom boatbuilding.
Hauling toys beyond the horizon is the raison d’être for a rugged go-anywhere catamaran designed and built in the U.S., a notable exception in the world of big yacht projects.
Gunboat might have left town, but there’s another big catamaran under construction in its old facility in Wanchese, North Carolina. It’s called H-2 , short for Hippocampus 2 , a stout 110-footer (33.5m) that liberally and intentionally quotes from the expedition/workboat vernacular. It’s built from aluminum and was conceived to go to the back of the beyond, where adventure beckons and Vessel Assist doesn’t operate. Aside from commodious and cushy accommodations, the boat offers grid autonomy, ocean-crossing range, and cargo capacity to match the mission of hauling a 26 ‘ (7.92m) tender, a 17 ‘ (5.8m) skiff, a two-person submarine, a four-seat ATV on the main deck, and a small helicopter on the flight deck aft.
The boat was commissioned by Brian Schmitt, 67, a real estate executive in the Florida Keys, who pilots his own plane to commute to the Bahamas, where he keeps Hippocampus , his current 57 ‘ (17.37m) cold-molded wood/epoxy catamaran. I asked him about the jump from 57 ‘ to 110 ‘ . “I never thought I’d have the ability to do that in my own boat until probably the last few years,” he replied, adding that “it would be 120 ‘ [36.58m] if I had to do it today.”

Its predecessor, Hippocampus, built in wood/epoxy, was launched in 2003. At 57′ (17.37m), it is about half as long as H-2, but with 22,500 miles under its keels, it was a useful starting point for designing the new vessel.
Wearing shorts and a shirt with the new boat’s name and logo to our meeting, Schmitt talked openly about his project, which he manages as attentively as his real estate brokerage with 130 agents. Communication is his thing, responding to e-mail questions in near real time (in ALL CAPS) and talking to contractors directly. No project manager.
A passionate diver who habitually explores remote and exotic locales, Schmitt said he was happy with the first Hippocampus , which has three staterooms and cruises at 15 knots on twin 370-hp Yanmars. “It was the vehicle that got our 17 ‘ tender wherever we needed it.” But running the little boat 60 or 70 miles a day lost its charm. “One of the things I wanted was a twin-engine tender that would have more room for dive gear. That ended up being a 26 ‘ Calcutta, so I needed a bigger mother ship.”
With accelerating climate change, the carbon footprint of ships and large yachts is under scrutiny, but hydrocarbons still win when speed, range, and payloads are priorities. While H-2 doesn’t break the mold there, Schmitt pointed to the project’s virtues as a U.S. domestic build. “You can’t complain about global warming when you’re flying around in your G500 jet that’s contributing more CO2 emissions than anybody else in the world,” he said. “You can’t complain about all the boats being built in Germany, The Netherlands, and Italy, and then go buy a boat [there].” Schmidt wanted to build locally, keeping jobs and money in the U.S. Besides, he noted, this approach simplified communications and enabled him to personally check on progress during COVID. Perhaps most importantly, he could pick a team of trusted and compatible mates to turn his dream into a boat.

The vast build hall left vacant when Gunboat left Wanchese, North Carolina.
He selected John Marples, a fellow pilot, inventor, and multihull specialist for the design and Felix Herrin to build H-2 . Both men had worked for him on Hippocampus , and their familiarity helped when meeting today’s challenges, such as damaging trade tariffs that drove up aluminum prices, and a pandemic that killed millions, wreaked havoc on global supply chains, and caused labor shortages in industrial sectors. These factors have conspired to delay H-2 ’s launching by roughly two years and counting.
Advantage Aluminum
A key decision early on was to build in aluminum, which promised a robust structure but required extra steps to deal with corrosion and noise mitigation. “Construction was reduced to something simple—a V-bottom deadrise model, stretched out,” Marples explained. “There wasn’t any benefit to round bilges on an aluminum boat. You’d have to add internal structure to support the flat panels, and it drives the cost and difficulty of construction way up. We’re talking about a speed-to-length ratio of 2 or less, which is not a big deal. His current boat would do a speed/length of about 3, so the extra length means that you’re never really pushing the boat that hard, so shape was not a huge consideration.”
Marples and Herrin go back at least three decades to their mutual acquaintance with naval architect and boatbuilder Dave Dana, who assisted Marples with the hull design for Admiral Pete , a catamaran passenger ferry still serving Puget Sound. Herrin works with different construction materials, but having built crew boats for Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) at Sea Force in Palmetto, Florida, he has spent considerable time with aluminum.

Taking a break during IBEX 2021 are builder Felix Herrin (left) and owner Brian Schmitt. H-2 is their second joint project with designer John Marples.
The structural components on H-2 are 5083-H32 alloy aluminum plate and extrusions of 6061-T6 alloy. Scantlings, materials, and weldment comply with the American Bureau of Shipping’s (ABS) 2016 design guidelines for pleasure motoryachts. Hulls and wing structures have transverse frames and bulkheads spaced on 36 “ (0.91m) centers. Those frames are supported by substantial centerline vertical keels (CVKs) welded atop twin 3 “ x 8 “ (76mm x 203mm) solid extruded-aluminum-bar keels. Intermediate subframes in the forward and aftermost hull compartments strengthen the hulls for operating in ice. Schmitt indicated he wants to traverse the Northwest Passage. For the same reason, there’s 3⁄8 “ (10mm) plate running the length of the boat above and below the waterline.
The topside and underwing plating is primarily ¼ “ (6mm), with areas of 5⁄16 “ (8mm) to strengthen slamming zones in the bow. The main deck plating is also 1/4 “ while the foredeck plate is specified at 5⁄16 “ . The bottom plating is 5⁄16 “ in the aft two-thirds of the hull and 3⁄8 “ forward. “We built all the frames and bulkheads first, then scarfed together the keel sections [and] lined those up on the bunks that we built on,” Herrin explained. “We welded the CVK on top of the keel, then started installing frames.”

Hulls and wing structure have transverse frames and bulkheads on 36″ (0.91m) centers. The hulls are supported by centerline vertical keels.
Herrin said he changed aluminum suppliers midway through the project, sourcing from Bayou Metal Supply , an ISO 9001:2015–certified distributor in Slidell, Louisiana. “We sourced the material from Greece and from domestic suppliers,” said Taylor Smith, who handles Bayou’s sales. Tariffs, he said, did not slow down business much, but the aluminum cost more. “Felix sent cut files. We had the material in inventory, we cut it, processed it on a router, and shipped it on time. Everything flowed well.”
Naval and structural engineering and detailing was contracted out to Van Gorkom Yacht Design in Portsmouth, Rhode Island. “My first responsibility was looking at structures,” Geoff Van Gorkom said. “Given that this is an aluminum yacht, we can do literally all the structures in 3D and have all the metalwork precut before it came into the yard. All the frames and longitudinals and all the primary structure were precut, which saved huge amounts of time.” Van Gorkom said he uses Rhino 3D and some of the numerous modules such as Orca 3D for hydrostatics and hydrodynamics, and 2D AutoCAD to produce construction details.

Helping save time and money, 3D-modeling allowed frames, longitudinals, and the primary structure to be cut before being sent to the building site.
Van Gorkom observed that H-2 is not a fussy high-performance vessel that needs minimum weight to achieve maximum speed. Besides ABS guidelines that address torsional loads in catamaran structures, he also consulted A.L. Dinsenbacher’s paper “A Method for Estimating Loads on Catamaran Cross-Structure” ( Marine Technology , Vol. 7, No. 4, October 1970) to estimate load conditions in beam and quartering seas. “This is going to be a very stiff boat. It’s going to be a very strong boat simply because it has to be, and that was one of the criteria that Brian put out there right from the very start of the project. The boat is sturdy and stout, a strong expedition yacht.”
Van Gorkom also engineered the setup for a folding deck crane housed under a flush hatch in the helideck on the port side to launch and retrieve the two-man submarine or the ATV. “It’s basically an enclosure that opens up, so the crane extends out,” he explained. “It comes up on a telescoping pipe to swing out and pick up something from the side of the boat.” It required support from beams on each side of the crane and cutting a slot in the helideck for the lifting bridle so the loads can move inboard or outboard. On the starboard side, the 5,500-lb (2,492-kg) Calcutta tender is an even heavier load moved by twin overhead beam cranes. The 17 ‘ Twin Vee is launched and retrieved from the foredeck with a 2,500-lb-capacity (1,153-kg) crane.
Catamarans are known to be weight-sensitive, so how will H-2 handle the weight of all the toys and high superstructure? The arch over the flybridge is 33 ‘ (10.05m) above waterline, Van Gorkom confirmed. “Add another 10 ‘ [3.05m] for the radar, mast, etc., so a comfortable bridge clearance would be around 45 ‘ [13.7m].” Marples conferred with Van Gorkom about the effect of the added weight on the center of gravity, which was deemed “almost imperceptible,” Marples remembered. A quick calculation suggests that a 5,500-lb deck load is equal to only 1.57% of a full-load displacement given as 350,000 lbs (158,550 kg).
High Power, Low Noise
Van Gorkom hired engineers at HydroComp to evaluate the design’s hydrodynamics and propulsion systems, including the influence of hull-shape parameters and demi-hull spacing on resistance. HydroComp also offered a speed-power prediction to aid with engine selection and recommended optimum shaft rpm and propeller parameters. Technical director Donald MacPherson, who prepared the report, outlined the process and findings: “Particularly interesting for this project was the use of its novel analytical distributed volume method [ADVM] for the vessel’s resistance modeling. This 2D technique (between parametric methods and CFD) uniquely allows for assessment of the influence of local sectional area curve regions (such as ‘shoulders’ or inflections) in wave-making drag. It also directly evaluates the effects of catamaran hull spacing.” HydroComp helped optimize the hulls by identifying the regions that contribute most to wave-making drag, and securing a 3% reduction in total drag at the design speed by making what MacPherson called “very minor changes to the immersed volume distribution.”

Rob Ayers works on the installation of the starboard engine’s Evolution Marine Shaft System that will be fitted with a 36″ (0.91m) five-blade propeller.
That simulation was mapped to benchmark performances of four similar catamarans, and the process was run for two design variants, followed by a propulsion simulation for partial-load conditions. The hull-spacing study concluded that the originally designed 35 ‘ (10.7m) beam remained suitable despite the boat being 20 ‘ (6.1m) longer than originally drawn. The chosen propulsion system comprises two MTU 10V 2000 M96, 1505-mhp diesels with ZF 3000 flange-mounted marine gears, providing an estimated top-speed range of 20–22 knots, cruising speeds of 12–15 knots, and 10–13 knots for long-range voyaging. Actual performance will be established during sea trials.
The recommended propeller specifications developed by HydroComp were for five-blade models with 36 “ diameters. HydroComp applied PropElements, a wake-adapted propeller-analysis tool, to determine the advisability of installing a nozzle or shroud to restrict transmission of pressure pulses to the hull and to create a more uniform inflow. This would reduce interior noise but would increase appendage drag and power demand. Schmitt said he will wait to see if cavitation or prop noise is an issue before making a final decision.
He invested heavily in noise and vibration mitigation, knowing that an aluminum boat won’t provide the natural sound-dampening of a wood/epoxy structure like that of his first Hippocampus . Consulting with Soundown of Salem, Massachusetts, Schmitt wanted to replicate what worked well on his old boat, starting with the Evolution Marine Shaft System, in which the prop shaft runs in an oil-filled tube and uses roller and needle bearings instead of standard water-lubricated bearings. “You have a lot less shaft noise, but one of the primary benefits of an integral thrust bearing is that it transmits all the thrust directly into the hull, as opposed to pushing on the gearbox or the engine and gearbox combination,” said Sam Smullin, Soundown’s marketing and quality assurance manager. “It allows for a much softer engine mounting, so you reduce the noise from the shaft itself and get a much quieter engine installation, which reduces structure-borne noise.” Because of the relative weight sensitivity of catamarans, Smullin said, “it’s particularly important to do a really good job on the driveline.” His father, Joseph Smullin, president of Soundown and J&A Enterprises Inc., an engineering firm for noise and vibration control, estimated that this could reduce driveline noise levels by 5 dBA to 10 dBA compared to a conventional system.

Clemente Perez, one of Herrin’s build crew, works on the interior. The extensive sound and thermal insulation includes foam sprayed into the cavities.
Soundown also looked at the two 38-kW Northern Lights gensets, which have double-isolation mounts to reduce structure-borne noise. The firm also recommended structural changes to ensure that the mount foundations were as stiff as possible.
Energy from propulsion or generator engines invariably transmits to the boat structure and then resonates through big, flat panels like bulkheads, decks, ceilings, and liners, causing the familiar vibrating rattle. To dampen those vibrations, Herrin said he used Roxul, a lightweight, semi-rigid stone-wool insulation for fire resistance and sound control. His crew also sprayed cavities with Dow Froth-Pak, a quick-cure polyurethane foam for thermal insulation, and installed Sylomer (a microcellular PUR-elastomer) between the structural components and the floors, walls, and panels. “We glued the Sylomer, which is kind of a spongy foam, to the structure of the boat, and then the plywood of the subfloors and walls are glued to that,” Herrin explained, adding that this created a floating interior without any fasteners.
The plywood, called QuietCore, is a composite sandwich panel comprising marine plywood skins and an acoustic damping layer that converts acoustic energy into small amounts of heat that are dissipated. Soundown claims that an 18mm (0.7 “ ) QuietCore bulkhead can reduce noise transmission by up to 10 dBA, an audible reduction 50% greater than with regular marine plywood of equal thickness.
Electricity for a Small Town
Going off grid on H-2 does not mean anyone will suffer, as long as the electrical system keeps powering the boat’s myriad house loads—hydraulic Maxwell windlasses and thrusters; a Webasto air-conditioning system; two full-size stand-up freezers, two refrigerator freezers, and two under-counter refrigerators in the galley, all by Vitfrigo; Krüshr compactors for recyclables and garbage; Headhunter sewage-treatment system; Alfa Laval fuel-polishing system; two FCI watermakers; a complete set of Garmin navigation electronics with full redundancy; and a Böning vessel control and monitoring system.

Two Northern Lights 38-kW gensets are the heart of H-2’s AC system, which also includes a 37-kW Atlas inverter to connect to shore power in foreign ports.
Much of the AC side was designed and specified by Ward’s Marine Electric in Fort Lauderdale, Florida, in cooperation with OceanPlanet Energy of Woolwich, Maine, and principal Bruce Schwab, who helped design and integrate the DC components. “Today there’s a big trend in the industry to use shore-power converters as inverters and superlarge lithium-ion battery banks to provide power, at least temporary power, for major loads like air-conditioning, chiller plants, and things like that,” said Ward Eshleman, chairman of Ward’s Marine Electric. “So, rather than using only smaller inverters and synchronizing them and stacking to get additional kW, the trend for the larger vessels is to use shore-power converters as inverters. There is an inverter bus in the main switchboard.”
True to its go-anywhere mission, H-2 was fitted with an Atlas 37-kW inverter to connect to shore power in places that do not serve 60 Hz, 240V single-phase power. “We can take anything from 90V to 400V and pretty much anything from below 50 Hz to the 60 Hz and single- or three-phase,” Herrin explained.
Eight GTX24V315A-F24 lithium-ion batteries from Lithionics are split between a house bank that can run all DC loads for at least 24 hours, and an emergency bank to operate critical DC loads—display screens, radios, nav lights—for 24 hours. The boat is equipped with 10 Solara Ultra-S 160W panels paralleled in two groups of five each, connected to two Victron SmartSolar MPPT 100/50 solar controllers to charge the house bank. Given enough sunshine, solar and battery power should be “capable of running lights and refrigeration but not air-conditioning or heating,” Schmitt said. “Since we will likely spend most of our time in the tropics, we did not believe that solar power alone could do the job we needed.”
OceanPlanet Energy specified four Victron Buck-Boost DC-DC converters, two for each engine, to help charge the house bank from the starter batteries without having to modify the engines’ stock alternators, which would have voided the warranty. “The converters activate based on the input voltage from the starting batteries,” Schwab explained. “With lower rpm, the alternators would not produce enough current to feed both converters without the starting-battery voltage dropping, turning the converters off. Then the voltage will rise, the converters turn on again, drop the voltage, turn off…over and over. Staggering the input voltage cut-in, hopefully starting the converters one at a time, will more smoothly supply power to the house bank across the engine/alternator rpm range.”

OceanPlanet Energy specified the DC system including DC/DC converters and hefty battery banks to power house loads and critical electronics.
There are two 4,500-watt 240V split-phase engineroom-ventilation fans connected to two Victron Quattro 5-kW 24V inverter-chargers configured for 240V/120V split-phase AC loads. They can accept AC inputs from two sources (shore power or generators) and automatically connect to the available source. “In the event of a grid failure or power disconnect, they take over the supply to the connected AC loads by inverting from the Lithionics house-battery bank,” Schwab said.
“It’s more complicated than that,” according to Herrin. “Typically, we’re going to be operating with the A-bus and the B-bus tied together, so we can power everything with one generator. The B-bus actually passes current through the Victron inverter-chargers on its way to the load. We have the ability to split the A-bus and the B-bus and run the A-bus on one generator and the B-bus on the other in the few instances we’re exceeding the capacity of one of the generators. If we lose both generators, then the essential loads are still going to be carried,” meaning engine vents or water pumps.
Redundancy and emergency backups also figured largely in the deliberations of John McKay, manager of the Switchgear Systems Division at Ward’s Marine Electric and point man for this project.
One of his challenges was limiting the voltage drop in the estimated 53 ‘ (16.2m) cable run between engines, which in an emergency allows the starboard engine to be started from the port battery and vice versa. “For a starter group, you can allow a 20% voltage drop,” McKay said and noted that starting the engines requires 720 amps, while the gensets needed only 200 amps. “I was keeping the 720-amp current between 7% and 11% voltage drop, getting up to some pretty good-sized copper. Some sections of the run were 240mm2 [500MCM] cable.” Knowing that the boat is capable of going to high latitudes, McKay recalled his youth and the frigid winter mornings in Massachusetts, “where you can crank a diesel all day long at a low rpm, and it’ll never start. You just need to turn it over one or two times at a higher rpm, and it’ll be running. So, I was making certain that the starter was going to crank at the highest rpm possible and not lose it all to voltage drop.”
Protecting Assets and Finishing the Job
No matter how fast or how far H-2 will travel, corrosion caused by galvanic current between dissimilar metals, by stray currents or by electric fault, is an enemy that needs to be kept in check. That’s the calling of Ted Schwartz, who runs Electro-Guard (Mount Shasta, California). He’s one of the country’s foremost experts on cathodic protection, and also served on ABYC’s E2 Cathodic Protection Project Technical Committee.
“We designed the system and supplied all the equipment and steered them through the installation,” Schwartz said. It’s a 15-amp impressed-current-cathodic-protection (ICCP) system, model 715 A-2, with three anodes and two reference cells. Regarding the boat’s Evolution shaft system with driveshafts running inside an oil-filled tube, Schwartz said: “It was a real challenge because you can’t actually make contact with the propeller shaft on the inside of the boat.” He consulted with Soundown and found a solution. “At the coupling on the inboard end of the tube, a bit of the shaft stuck out through the seal,” Swartz said. “There’s this coupling that Soundown built that fastens to the shaft, and we asked them to provide a surface on that coupling where we could put our silver slip rings on [to provide an electrical connection] to protect props and shafts.”
Every anode can deliver up to 5 amps of current using its own current controller that receives a signal from the main controller, which determines exactly how much current each anode will put out. The entire system consists of three anodes, three current controllers, the main controller, and a separate monitoring station connected to the controller by signal cable. Later, Schmitt also ordered a backup system employing aluminum sacrificial anodes.
On catamarans, the company installs a reference cell aft near the prop of each hull, and an anode on the aft section of each hull, and one anode amidships on the inboard side on one hull.

Chromate, two layers of epoxy, copious amounts of fairing compound, and various primers rendered the surface fair and ready for a yacht-quality paint job.
At the time of this writing, the vessel had been shot with chromate and two layers of epoxy before approximately 500 gal (1,893 l) of fairing compound and 325 gal (1,230 l) of various primers rendered the surface fair and ready for a yacht-quality Alexseal paint job with 35 gal (132.5 l) light ivory, 24 gal (91 gal) stark white, and 2 gal (7.6 l) cordovan gold. Parallel to the exterior, construction was on the home stretch with installation of the crew quarters and the saloon overhead. On the systems side, pressure checks were performed for hydraulics and plumbing.
Since H-2 is a much larger and more complex vessel than the original Hippocampus , with a multitude of systems that need to be managed, monitored, and maintained, I was curious how many crew Schmitt was planning to hire to help run his new boat. He said he consulted with captains and headhunters, and “the consensus is three or possibly four at most. I just completed my 100-Ton Masters and will build time on the new boat as well. We won’t charter and are not accustomed to being cooked for or served or having our beds made and all that. So mostly I’m looking for a qualified captain and engineer to maintain the systems.”
Little surprise that a hands-on operator like Schmitt does not want to cede too much of the game he loves to play. But as big, bold, and broad-shouldered as H-2 will be when she finally emerges from the old Gunboat shed in Wanchese, the proud owner is quick to remind anyone that it’s still “a vehicle to get the toys wherever.”
H-2 : The Designer’s View
H-2 ’s owner, the adventurous Brian Schmitt, has dived into deep caves to see submerged caverns, hand-fed large sharks that would normally view him as food, and spent years in his off-time exploring Caribbean archipelagos in Hippocampus, his current 19-year-old 57 ‘ (17.4m) power catamaran. Nearing retirement age, he gave the order for his “ultimate” yacht.

The foldable hydraulic deck crane to launch and retrieve a two-man electric submarine or an all-terrain vehicle required cutting a slot in the helicopter deck for the lifting bridle.
The first talk about the new design was between the owner, the builder, and me. As we discussed the mission of the boat, it became clear that it would fall into the category of expedition vessel with more guest staterooms, more range, and more room for equipment than his old boat. Brian defined the function of the vessel as a carrier for a 26 ‘ (7.92m) twin-outboard catamaran, an outboard skiff, a small car, and a small helicopter, which needed a flight deck. This vessel was to be used with family and guests while also serving as an operations base for outbound travel by air, land, or sea.
Aside from commodious accommodations, a key requirement was comfortable motion on rough seas. This was to be a catamaran, like his current boat, which offers extensive real estate afloat in a seagoing vessel. The only restriction for the new design was a beam no greater than 35 ‘ (10.6m) to fit the largest Travelift.
The trade-off for overall beam width involves room versus roll motion. A wider catamaran responds more quickly to roll in seaways but with less amplitude, whereas a narrower beam rolls more slowly with slightly more amplitude. The slower roll is preferable as long as overall roll stability is maintained. Roll in catamarans is unlike roll in single-hulled vessels. Because the vessel is supported by two buoyancy chambers (hulls) with distance between them, motion has little to do with roll inertia, but rather with response of the hulls to the seaway. Each hull responds to a passing wave independently by heaving (up/down) and rolling, which is a circular motion around the center of gravity (CG) that translates to lateral motion when standing above the CG, especially high up on the bridge. Power catamarans, unlike sailing catamarans, do not require wide hull spacing to generate righting moment (to support a sail plan), so they can have closer hull spacing, which still preserves sufficient stability, slows wave-response roll characteristics, and takes up less space in port.
One of the expected routes for this vessel is the Northwest Passage over the top of North America. Boats venturing there can expect floating ice, so we added thicker hull plating at the waterline and an ice-separation chamber on the cooling water intakes. We also designed the hull to give the propeller protection by positioning it behind a deep canoe-stern afterbody with no exposed shaft. A rudder horn, below the propeller extending aft from the hull, adds support for the rudder and protection for the prop. This configuration is useful as a hedge against the possibility of grounding. In fact, this boat can be careened on the beach between tides if necessary for repairs. The hull includes a strong, deep, vertical keel structure that allows for blocking anywhere along its length.
Speed and range became the largest determinates of the design. A maximum range of 4,000 miles at 15 knots (enough to cross the Atlantic Ocean) was proposed. Catamarans are easily driven at modest speeds due to lack of significant wave resistance by narrow hulls. A preliminary speed prediction analysis showed that we would be in the ballpark with about 1,400 hp (1,050 kW) and 5,000 gal (18,925 l) of diesel per hull. The final installed fuel capacity is 12,500 gal (47,313 l).

The general arrangement plan shows crew quarters in the hulls, three guest cabins, office, saloon, and galley on the main deck and owner’s suite on the bridge deck level.
A totally new design normally goes through a lengthy proposal and critique cycle between designer and client, especially if the client is knowledgeable and involved. The vessel’s first iteration started at 90 ‘ (27.43m) LOA, but it became evident that it needed more length to relieve a number of ills. After adding 10 ‘ (3.05m) we saw improvements, but it wasn’t until the 110 ‘ (33.5m) length proposal that we felt all the requirements had been satisfied: more slender hull shape, more open interior space, and better placement of machinery and tankage. The flight deck for the helicopter became larger, and the forward superstructure fairings gave the boat a sleeker look. And at 110 ‘ we achieved an efficient length versus waterline beam ratio that reduced wave drag and fuel consumption at the target cruise speed.
While beam remained at 35 ‘ , lightship displacement increased significantly to 230,000 lbs (104,190 kg). Accommodations now include crew quarters for four persons in the bows; three double guest cabins and a ship’s office forward; a large saloon amidships with adjacent galley, and a dive and a storage locker aft on the main deck. The upper deck is arranged with a full-width-bridge steering station forward, protected by a Portuguese bridge, and a master stateroom with en suite bathroom aft. The flight deck extends aft of the master stateroom. Access to the upper deck is by either a staircase from the foredeck, an interior staircase adjacent to the ship’s office, or by stairs from the starboard side deck.
The largest variable weight on the boat is fuel, so the tankage is located amidships to minimize its influence on trim. Engine and machinery rooms aft of the tankage take up the remaining spaces all the way to the transoms. Other amenities include a utility area aft of the crew quarters port side with storage and washing machines, and a walkway through the tank spaces and enginerooms to the boarding decks at each transom. Another late addition is the flying bridge to aid with shallow-water operation by improving the vantage point to see coral heads and other obstructions. Its protective bimini serves as a mounting platform for lights and antennae.
—John R. Marples
Read more Construction , Design , Drawing Board , Yards articles

- Van der Werff’s Curved Wood
A Dutch yard adopts composite panel molding technology to build boats from preshaped wooden hull sections.

- Departures: Carl Chamberlin
Passionate, competent, considerate, modest, and thoughtful is how designer and boatbuilder Carl Chamberlin is remembered by those who knew him. He died last November at age of 75 in Port… Read more »

- SAFE Boats Regains Small-Business Status with Employee Ownership
More than 20 years ago, Professional BoatBuilder ran a feature titled “God, Country and Fast Boats” (No. 85, page 64) about SAFE Boats International (SBI), a Bremerton, Washington–based manufacturer of aluminum boats…. Read more »

Recent Posts
- Find out how 3D printing can help your boatbuilding with MASSIVIT
- SNAME Powerboat Symposium Is Back
- Companies (85)
- Construction (106)
- Design (161)
- Drawing Board (10)
- Education (25)
- Environment (16)
- Events (21)
- Materials (50)
- Obituary (18)
- People/Profiles (49)
- Products (16)
- Propulsion Systems (32)
- Racing (16)
- Repair (37)
- Rovings (317)
- Short Cuts (3)
- Sponsored Partner News (14)
- Systems (80)
- Task Sheet (1)
- Uncategorized (26)
- Wood to Glass (7)
ProBoat.com Archives

A Trusted Source For Boating Information Since 2019
Catamaran hulls- everything you need to know.
- Post Written By: Boater Jer
- Published: July 17, 2022
- Updated: July 19, 2022

Disclaimer: You might notice that we recommend products in some articles. We may earn a commission for referring you if you click the link and buy a product.
We only recommend products we’ve tried/tested/own (that’s why you won’t find thousands of affiliate links on my site). If you have experience with one of the products we’ve mentioned, please share your experiences in the comments at the end.
Advertisement

Catamaran hulls are not like normal boats but provide increased stability. Let’s take a look at these incredible boats and how their hulls create one of the most versatile watercraft available today.
The Tamil Cholas used catamarans to ferry their troops to invade Malaysia, Indonesia, and Burma. The early paravars or fishing communities in the southern part of Tamil Nadu used two-hulled boats to fish. Polynesian seafarers were also early users of the catamaran, utilizing the watercraft to get to hard-to-reach islands. ( source )
Although the catamaran hull concept is a relatively new introduction to modern boat design , the boat has been in use since the 5th century. It was used for fishing, traveling, and transporting people and supplies.
Parts Of A Catamaran
Here are the basic parts of the modern sailing catamaran:
- Hulls are what sets this boat apart from the rest. The catamaran has two hulls, while the monohull, as the name suggests, has only one hull. Most of the advantages of this boat are hinged on these two hulls.
- The bridge deck connects the two catamaran hulls.
- On top of the catamaran hulls and the bridge deck is the deck . It is where owners attach most of the equipment in a boat.
- You can locate the berth, the galley, and other living amenities in the cabin .
- The cockpit is where you find the navigation equipment of the boat . It is where you control the catamaran’s rudder, sails, and engine.
Types Of Catamaran

The modern catamaran is far more different than its crude ancestor. Instead of tree cutouts, catamarans are now carbon fiber or fiberglass. Here are the different types of catamarans:

Based On function
Pontoons are usually present on rivers and lakes and sometimes even on oceans, but they only travel near the shore.
In a catamaran pontoon-type boat, the pontoons serve as storage areas, where you will find the onboard motors. They are useful for water leisure activities such as short water trips, tubing, wakeboarding, and water skiing.
Some pontoons may also serve as houseboats. They provide a broader, more stable platform ideal for a floating house. Plus, the space is bigger, and most of it is above water. It offers a better viewing option than a monohull. ( Source )
Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull is a catamaran-type boat that the United States Navy initially used for military purposes. They provide the water stability that is necessary when transporting heavy military equipment.
One example of a military SWATH catamaran is the Spearhead class EPF. It is as long as a World War II escort destroyer, yet it is twice as fast at 43 knots. It can reach that speed because of its two separate hulls.
Because of their innate speed, SWATH catamarans can become patrol boats in lakes and rivers. They can easily outrun and outmaneuver standard watercraft.
Nowadays, there are SWATH cruise ships and other non-military variations. ( Source )

Based On Design
- Sailing Catamaran
The smaller sailing catamarans do not have auxiliary engines, so the owner can propel the boat by harnessing the wind using the sails. It’s a popular choice for people with very little or no sailing experience because they are light and easy to use.
The larger sailing catamarans are for group charters and long-distance cruising. They have become so popular lately that they now outnumber monohulls in tropical locations all over the world. They have a last, a headsail, and a mainsail. And the twin hulls have one engine each.
- Power Catamaran
Unlike their sailing cousins, the powered catamarans do not have sails. They have massive engines which provide high speed. Their twin hulls are stronger and can carry and protect the large motors.
The smaller “powercats” are used mainly for fishing. The bigger ones are rented out for charters and cruises.
Catamaran Hulls Performance
Thanks to the catamaran hulls, the boat offers many advantages over other boat types.
- Because its dual-hull design provides a broader base, it offers more water stability than monohull boats. It makes the cat (catamaran) a popular choice for fishing expeditions and cruises.
- Riding a catamaran is ideal for people who feel seasick whenever they ride boats. The twin hulls prevent the boat from moving from side to side. The hulls allow the boat to travel smoothly, even on moderately choppy waters.
- The catamaran is the best choice when storing provisions and other household items with less heeling and bobbing.
- The twin hulls’ stability is ideal for many activities such as cooking and partying.
- Cats offer more moving space because of their broader base, thanks to dual hulls.
- With a catamaran, you have two great options on where to hang out. You can do it on the spacious deck or below the galley.
- Compared to a monohull of the same size, the catamaran can accommodate more equipment and people.
- The living area in a catamaran is above the water line. This feature provides more natural light, a greater view of the outside, and better air circulation.
- Since catamarans do not have keels, they can anchor on shallow waters, something that most monohulls will not be able to do. This ability of catamaran boats is impressive, especially if you are going around areas with many reefs and small islands.
- Catamaran hulls allow the boat to cut through the waves easier and faster. It means they require less engine power than their monohull counterparts.
- Because it has two engines and two rudders, the catamaran can easily maneuver in very tight spaces.
- Because they do not carry heavy keels, catamarans can sail faster than monohulls.
- The catamaran’s stability, speed, and weight make it a safer option than the monohull. It can sail in shallow waters, make a 360 degrees maneuver effortlessly, and carry more provisions.
Disadvantages Of A Catamaran
Like any other boat type, the catamaran also has drawbacks and limitations. Here are some of them:
- The catamaran hulls prevent the boat from sailing as fast as the monohull upwind. The two hulls cause drag, and this slows the boat considerably.
- Because of its bigger size, looking for a docking site can be more difficult and costlier than a monohull.
- For hardcore sailing fans, the experience of sailing with a catamaran will never be able to match that of sailing with a monohull. To them, the challenge of true sailing is just not there with a catamaran.
What Are The Hulls Of The Catamaran Called?
According to the Online Etymology Dictionary, the Tamil word கட்டுமரம், which is pronounced as kattumaran, is where the word catamaran takes its name. The word means “pieces of logs tied together”. Through the years, the term has evolved into what is now a catamaran in English.

What Are The Characteristics Of A Catamaran Hull?
- Both hulls of a catamaran complement each other to achieve very minimum water resistance.
- Because of this, it takes less energy to propel a catamaran, whether via an engine or sails.
- The catamaran hulls provide stability to the boat. The twin-hull significantly reduces bobbing.
- The catamaran’s ability to keep steady on the water makes it an ideal vessel for cooking, dining, and storing provisions.
Are Catamarans Good In Rough Water?
Catamarans are amazingly stable in rough water. The catamaran’s design and build, which provides stability, are factors why it is one of the best boats to use when the waters are choppy.
Yes, catamarans are relatively more expensive than monohulls. Nevertheless, since single-hull boats are less expensive, their resale value is also cheap.
If you add all the advantages that a catamaran offers – safety, comfort, and speed- it does not come out expensive.
patekphilippe.io

Share this post with your friends
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Join us in our love for all things water. And Adventure.
A Guide to Cruising Catamaran Manufacturers In 2022
Advertisement So, you finally decided that a multi-hull will serve you way better than a single-hull but can’t choose which one of the catamaran manufacturers on the market will provide you with your dream vessel. Well, I’ve done a ton of research on the top 13 current manufacturers, so you don’t have to. Leopard Lagoon

How Fast Can Canoes Go? We Find Out (With World Records).
Advertisement Sliding over the glass-like stillness of a peaceful morning lake, a ride in the canoe is an incredible experience. The mist rising slowly off the water and wildlife waking to the coming day can be a nearly magical experience for the canoeist. However, it may not be only about peace and tranquility. If you

How Shallow A Flat Bottom Boat Can Go & More About Jon Boats
Advertisement Ranger RB190 Camo, picture courtesy of Ranger. When you’re shopping for a Jon boat, knowing the capabilities is essential to choosing the right watercraft. You know Jon boats have a flat bottom hull, but just how deep does the water need to be for the boat to travel safely? Since a boat is a

Rope Types Every Boater Should Know
Rope can come in a variety of sizes, colors, and types. It can be made from any fibrous, stringy, and obviously long-stranded materials. For boating, depending upon the purpose of the rope, there are a variety of different types that you will encounter.

Can A Bass Boat Pull A Skier?
Answering the question with facts about water skiing and bass boats, we dive into the mods required and the considerations of water skiing behind a bass boat.

How Long Does A Kayak Last? 5 Awesome Materials Examined
Advertisement If you’re wondering: “How long does a kayak last?” you’ve come to the right place for answers about kayaks of various materials. Kayaks and canoes are expensive things. Some cost hundreds of dollars, so it is understandable to want your investment to last for a lengthy period. Some investigation is required to establish the

Boat Information By Type
© 2023 Boating.Guide, A Hyperwave Media Group Ltd. Publication.
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The primary use for pre-preg in boating is high performance race boats. With catamarans, pre-preg may be used high load parts, like Gunboat does for foils and rudders. 4. Industry Examples. Across the catamaran building industry you'll find almost all the above techniques and materials used, though some are less common.
If you were to build a 40-foot (12.1-meter) catamaran, your cost of materials would range between 20-30% of the total cost. Therefore, for $300,000 total, the boat's materials would range between $60,000 and $90,000. The hull tends to range between 15-35% of the total build.
Have you ever wondered the processes that go into Catamaran design and building a Catamaran? Maybe. Maybe not.However for those of you who are contemplating ...
Here's a short explainer on sailing catamaran hull design and the theory behind our own hulls. We have a quite distinctive and unusual design for a high perf...
The first step to building your dream catamaran begins with a strongback - this is a square frame used to position the temporary frames that will be used to form the hull shape. ... Once both hulls are turned the tops of the bulkheads will be used to join the two hulls, and then the bridgedeck component will be installed underneath. STEP 6.
STEP 1. The first step to building your dream catamaran begins with a strongback - this is a square frame used to position the temporary frames that will be used to form the hull shape. This frame will be set up and must be square and accurate, a string or laser level can be used to achieve this.
Building a catamaran hull is a great way to get out on the water and experience the joys of sailing. Catamarans are known for their stability and speed, making them a great choice for those who want to get out on the water with confidence. With the right plans and materials, anyone can build a catamaran hull and create a beautiful and seaworthy ...
Building a bridge deck and the structures around a pair of hulls is a lot more difficult to design and build than a single hull, and we'll explore a little about why. Part 1: Forces on the Hulls Load and force calculations on a boat hull isn't a simple calculation, and even monohulls take a lot of designing to build a shape which performs ...
Outremer catamaran construction principles: our mission is to build safe, seaworthy, comfortable, easy to handle performance catamarans for your offshore sailing journey. ... Hull designs carefully studied and optimized; long, to carry the required load and reduce forward resistance. Fine hulls demand, in effect, little power to make the move ...
Building a catamaran boat requires a lot of patience and skill. The first step is to choose the right materials for the hull, such as fiberglass, wood or aluminum. Then, you will need to build the frame of the boat, which includes the crossbeams and the main hull.
Step 1. Kit Design. Work with us to finalise the details of the design you have chosen including any design options or additional modules to be included in the kit. We will determine the laminates, the number of panels required for each laminate, create the cutting files and prepare a quote for the kit if it is not already priced.
The next step is to build the catamaran frame, which involves cutting and fitting the wood pieces together to form the hulls and decks. Finally, you will need to attach the decking, add the rig and sails, and finish the project with paint and varnish. Benefits of Building a Catamaran. Building a catamaran can be a very rewarding experience.
Axiom #1: The hours to build a catamaran is. in almost in direct proportion to its weight. Which brings us to Axiom #2: Axiom #2: It takes about 1 hour to create. 1 pound of finished boat. In our case we spent 3,500 hours ( click. here for full details on the construction hours) to build a 4,000 lb. boat.
The larger TRI's and CAT's have full radius hulls.With no lofting you build right away. The DESIGNER'S book TRIMARAN and CATAMARAN CONSTRUCTION is part of the plans (over 21') and covers all phases of construction. Plans are leased to build ONE boat, NO time limit. Tri-Star designs are proven designs, sailing the seven seas since 1964.
The Best Advanced Build System in the World. The Schionning Advanced Build System are one of the simplest ways to build your own boat, or have a custom design built faster and more accurately by a professional. Utilising DuFlex panels with a balsa core, large sheets are joined on their long edge to form full length hull panels, bulkheads etc ...
Why Build a Catamaran: The Benefits of Multi-Hull Boats. Building a catamaran offers many benefits over traditional monohull boats. One of the main advantages of catamarans is their stability. With two hulls instead of one, catamarans have a lower center of gravity, which makes them less likely to tip over in rough waters. This makes them ideal ...
Although few manufacturers and designers have attempted to build open bridgedeck catamarans for cruising, only the most die-hard campers will find them useful for liveaboard applications. Typical examples are the older MacGregor 36, Stiletto 27 and 30, the French KL27 and Corneel designs, which could be sailed hard by lifting a hull (something ...
Catamaran and Trimaran Boat Plans make it a reality to build your own catamaran or trimaran. Multi-hulled sailing vessels are a special class of boat. ... There are some unique challenges building a multi-hull sail boat, the extra beam added by each hull for instance can create storage issues while under construction. Hartley boat plans make ...
Place the widest one with most volume in the center. Obviously, if you kept the hull in this level position, your trimaran would be dragging 3 hulls through the water with far more drag than for a catamaran. So you need to lower the central hull, so that it will support your 900 lbs .. requiring 14 cu.ft volume under the waterline.
An Aluminum Expedition Catamaran. With 110′ LOA, a 35′ beam, and 45′ (33.5m, 10.6m, and 13.7m) of bridge clearance, the H-2 catamaran seeks to make a case for U.S. custom boatbuilding. Hauling toys beyond the horizon is the raison d'être for a rugged go-anywhere catamaran designed and built in the U.S., a notable exception in the world ...
Hulls are what sets this boat apart from the rest. The catamaran has two hulls, while the monohull, as the name suggests, has only one hull. Most of the advantages of this boat are hinged on these two hulls. The bridge deck connects the two catamaran hulls. On top of the catamaran hulls and the bridge deck is the deck.
Sunreef says its new Eco Explorer 40m can accommodate 10 guests aboard, who can be taken care of by a crew of seven. Its motors deliver a cruising speed of 10 knots and a top speed of 14 knots ...