
Unveiling 13 Sailboat Hulls: Navigate Waves Like a Pro
Ever wondered why sailboats cut through waves like butter? Dive in and discover 13 hulls that make your sea adventures unforgettable!

A sailboat is only as good as the hull, and it ultimately determines how well you can navigate through the water. The hull of a boat plays a massive role in what type of water you can sail through and your overall speed. So, what are the types of sailboat hulls and how are they different?
The main types of sailboat hulls are planing hulls, displacement hulls, and semi-displacement hulls which offer the best of both worlds. Multi-hull boats such as pontoons and tritoons have even weight distribution and can handle rough waters. Flat-bottom sailboats are the most stable, but they don’t work well in deep waters.
Catamarans and trimarans feature space between each hull which adds stability and protects the deck from water. Choosing a sailboat with the ideal hull for you is essential in finding one that you will keep for years to come. Follow along as we explore the different types of sailboats and see what makes them unique.
Sailboat Hull Types
There are 13 types of sailboat hulls ranging from bilge keels and fin keels to displacement hulls. The ideal sailboat hull varies for you based on factors such as what type of water you’re in and weather conditions. For example, some hulls, such as flat bottoms, are ideal for shallow and smooth water .
On the other hand, semi-displacement hulls are perfect for every application whether you’re in shallow or deep water. Let’s take a look at the different types of sailboat hulls and see how they differ.
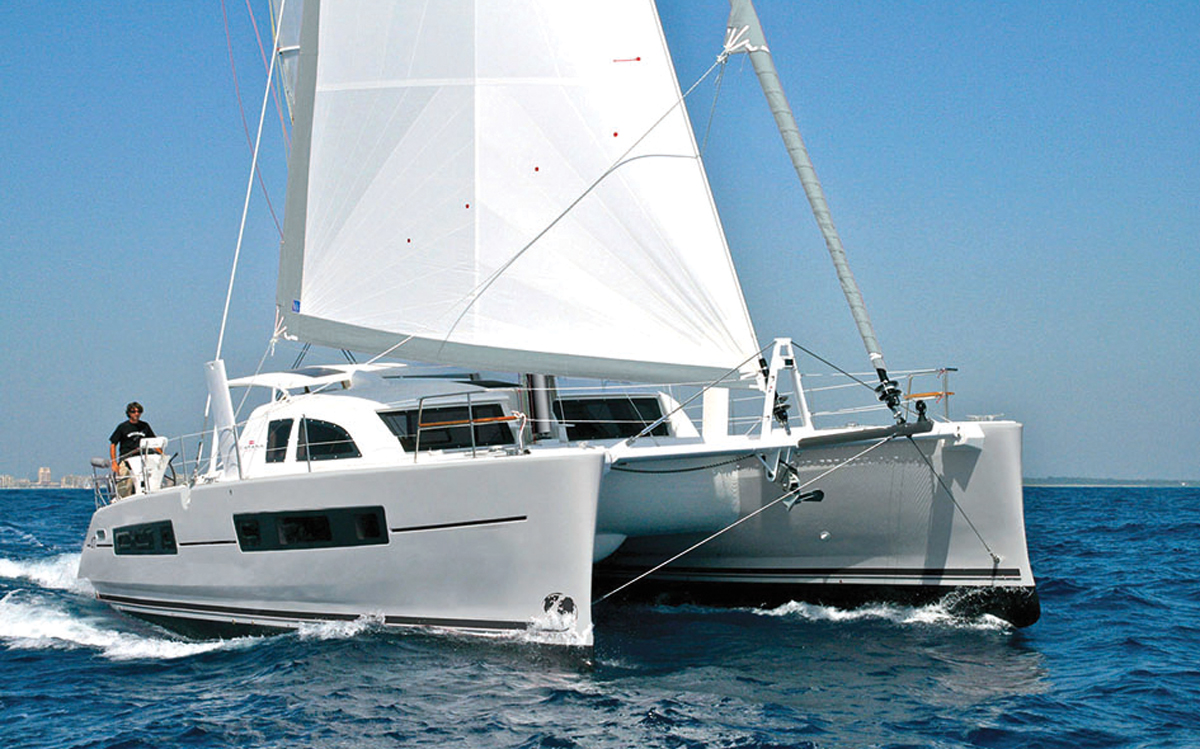
1. Planing Hull

Sail Magazine
Planing hulls are the first of the three major categories of sailboat hulls. You can find planning hulls with 2 different shapes: v-shaped and flat-bottom hulls. Planing hulls sit on top of the water and don’t sink deep like other types .
Many boaters and enthusiasts prefer this design because of how well a boat with planning hulls can move across the water. Most fishing sailboats feature planning hulls because of how smoothly they can glide on the surface whether you’re on an ocean or lake . Boats with planing hulls can also move faster than other types of boats, and that is their main appeal.
2. Displacement Hull

Improve Sailing
Boats with displacement hulls are slower than boats with planing hulls, but that doesn’t mean that they’re bad . While they don’t move as fast, many boaters consider displacement sailboat hulls to be much smoother. This comes in handy if you live in an area with rough waters and strong winds .
A displacement hull is rounded instead of flat at the bottom like a planning hull. The main downside to sailboats with displacement hulls is that you will likely use more fuel than you normally would. That is because the shape isn’t as aerodynamic and you’ll need the extra engine power to move through the water.
3. Semi-Displacement Hull

Seattle Yachts
As the name suggests, semi-displacement hulls combine the best of both worlds between planing and displacement hulls. A semi-displacement hull is both flat and rounded at certain parts providing both speed and stability. They aren’t as fast as a flatter planing hull, but they’re faster than a standard displacement hull .
The unique shape of semi-displacement hulls helps reduce resistance. This alone can help take a load off of your engine and let it work optimally under most water conditions. You also get the benefit of extra storage in most cases because boats with semi-displacement hulls have storage-friendly floor plans.
4. Multi-Hull

Multi-hull boats, such as pontoons and tritoons, are smooth and easy to sail . There are separate hulls on each side of the boat that provide stability and let you power through rough waters. On a pontoon, each hull is a large tube filled with air known as a toon.
Multi-hull boats generally sit higher above the water than most boats because of their unique design. They are popular for fishing, cruising, and entertainment. A key downside to multi-hull boats is that they typically operate loudly because the propeller may not be fully submerged in the water .
5. Monohull

The vast majority of sailboats that you will come across have a monohull . They are easy to sail, transport, and even dock at a marina because of their simple design. As the name suggests, they only feature one hull and are suitable for calm and rough water.
You can save money with a monohull sailboat compared to a multi-hull sailboat like a catamaran. A key advantage to monohull sailboats is that they are incredibly safe. You don’t have to worry about capsizing as much as you would with a multi-hull sailboat.
6. Flat-Bottom

Sailing Magazine
Flat-bottom hulls are essentially the simplest form of planning hulls. You can find flat-bottom hulls on the majority of sailing dinghies, and that’s what they are most suitable for. They aren’t ideal for oceans or rough waters, but flat-bottom sailboats are perfect for rivers and lakes .
Rowboats also feature flat-bottom hulls, and they aren’t known for being particularly smooth. You get less precision with flat-bottom hulls, especially if you have to steer and turn unexpectedly. Otherwise, you won’t have trouble with a flat-bottom sailboat hull if you go out for a quick fishing trip in an area you’re familiar with that has smooth waters.
7. Catamarans

Catamarans feature a unique take on the traditional multi-hull design . They feature 2 hulls with space between them that usually features a deck. Sometimes, the space between each hull features a trampoline or even a small pool or tub.
They aren’t suitable liveaboard boats, but they are perfect for taking out for a day of cruising and fishing. Catamarans are as smooth as possible, but that sometimes comes at the cost of speed. However, they often feature multiple engines which can consume a lot of fuel but also put less strain on each engine.
8. Trimaran

Quiberon 24 Television / Youtube
Trimarans are essentially a step up from catamarans because they feature a third hull. Many people prefer the stability that trimarans offer over catamarans. The extra stability also helps increase the speed that you can cruise at with a trimaran .
They are also safer than catamarans because the multi-hull design allows for perfect weight distribution. That’s not to say that catamarans are unsafe, but the extra hull that trimarans feature is more durable. Most of the weight lies on the center hull and the rest is distributed between the 2 outer hulls .

BlueWater Yacht Sales
Deep v hulls are another type of planing hull, but they are less common than some of the other varieties. Granted, high-end modern powerboats often feature a deep v hull, but they come at a high price. The v design allows the hull to cut into the water easily which lets you easily control the boat in any type of water condition .
Generally, the deadrise goes between 21 and 26 degrees for a deep v hull which is ideal for many boaters. However, boats with deep v hulls are primarily geared toward anglers and aren’t ideal for cruising at high speeds. Deep v hulls are usually made out of aluminum which means that they will be loud as they glide across the water.
10. Bilge Keel

Bilge keel hulls are specifically designed to reduce the risk of a boat rolling . The strange shape of a bilge keel hull lets it stand upright whether you’re on the shore or in shallow waters. This makes them much easier to maintain than many other types of boats.
The bottom of a bilge keel hull features multiple fins in a row that helps ensure a smooth ride. They never feature more than 2 keels which means that they have a shallow draft and you can easily beach them. The one downside to sailboats with a bilge keel hull is that they are difficult to transport to a port because of the bottom.
11. Bulb Keel

Bulb keel sailboats feature a teardrop-shaped ballast that increases the boat’s stability. They are even faster than bilge keel sailboats because of how hydrodynamic they are . Unlike some types of hulls, a bulb keel works just as well on the sea as it does on lakes and rivers.
They feature incredible weight distribution because of the inclusion of an extra ballast. However, you have to be careful with bulb keel sailboats in shallow waters near the shore. They are more susceptible to damage at the bottom so they can be difficult to bring to shore and require precision.
12. Fin Keel
Jordan Yacht Brokerage
Unlike bulb keel and bilge keel hulls, fin keel sailboats are perfect for raising . Fin keel hulls improve the draft of a sailboat which comes in handy when you want to reach high speeds. Some sailors use fin keel sailboats to travel long distances across the water, especially if the weather is in their favor.
They are a perfect happy medium between flat and round-bottomed hulls offering the best of both worlds. Fin keel sailboats are also quite comfortable because of the unique bottom shape that can easily handle choppy waters . With that said, they aren’t ideal for beginners because they can be difficult to steer compared to standard flat-bottom hulls if you are inexperienced.
13. Cathedral Hull

Jeff Clark / YouTube
Cathedral hulls get their name from their appearance which is similar to that of a classic cathedral. The unique appearance is one of the biggest benefits of cathedral hulls because the whole boat takes on that shape. They feature sharp bows and high sterns that are immediately recognizable.
With that said, cathedral-hull sailboats can be difficult to steer compared to flat-bottom or rounded hulls because of their bulky shape . You get plenty of storage with cathedral hulls which makes them perfect for long day trips with many people. They are incredibly stable because of the wide beams and wide berth, so there isn’t a serious risk of capsizing as long as you pack your cargo well.
What Type of Hull is Best For Rough Waters?

Any type of boat with a v-shaped hull is best for rough waters. Whether it’s a deep v or shallow v, this hull design makes it easy to cut through rough water without getting too much on your deck. The last thing that you want is to go through rough waters and take on excess water weight onboard .
They are specifically designed to glide across the water without sinking low which is necessary for choppy waters. Boats with v-shaped hulls also often come with high-performance engines, so they offer the best of both worlds. Generally, deep v hulls are the most precise and smoothest when it comes to rough waters .
They are perfect for keeping course which is essential if you’re in rough waters that can kick you off of your path. You can find many deep v hulls that are made out of fiberglass which is incredibly durable and withstand water exposure. Fiberglass v-shaped hulls are also easy to repair either by yourself or at a professional shop at a low cost.
What is The Most Stable Hull Design?

Flat-bottom hull sailboats have the most stable design for shallow water and multi-hull boats are the most stable in deep water. The inclusion of multiple hulls adds stability in deep water that prevents water from landing on the deck. This can save you expensive repairs and can also prevent your sailboat from capsizing.
Pontoons and tritoons are multi-hull boats and they are specifically popular because of their stability. You can’t find a more stable design than a flat-bottom hull if you plan to cruise in shallow waters . Flat-bottomed hulls are also typically the fastest when you aren’t far from shore, especially if you are in smooth waters.
The box shape of flat-bottomed hulls is conducive to gliding across shallow water. However, they struggle to ride across waves and choppy waters because of the wide surface area. Multi-hull boats such as pontoons and tritoons are the best option if you plan to take your boat out to lakes, rivers, and oceans because they thrive in any scenario.
What is Better Flat Bottom or V-Hull?
Flat-bottom boats are better than v-hull boats for most uses, but v-hulls are better in choppy and deep waters. You can get by with a flat bottom in oceans and lakes alike, but they don’t always do well in deep water. Conversely, v-hull boats can tear through rough and wavey water even at steep depths .
V-hull boats don’t do well in shallow waters and you are more likely to get stuck than you would be with a flat-bottom boat. Of course, you can always have someone push from behind when you depart, but that doesn’t help much when you return to shore. V-hull boats are the better option for deep waters, however, even if you are in rough water .
Flat-bottom boats take on more water than v-hull boats unless you stay in calm waters. It’s always worth choosing a boat that won’t take on water that will weigh it down. However, if you’re looking for a reliable boat with a high capacity, then I would recommend looking into v-hull boats.
What Type of Hull Cuts Through Water?

Displacement hulls are the best at cutting through the water, especially when compared to planing hulls. They don’t rely on a powerful engine to cut through the water because of their design. Displacement hulls displace water once you lower them in from the shore.
This displacement isn’t ideal for speed, but it is perfect for rough waters and strong winds. You can take sailboats with displacement hulls out on the ocean without having to worry about waves . They also work well in freshwater, but they are less necessary because of the lack of waves compared to the ocean.
Otherwise, you can get the best of both worlds with a semi-displacement hull . They aren’t quite as precise as displacement hulls, but they are better at navigating choppy waters than planing hulls. You sacrifice a little bit of speed, but the shape of a boat with a displacement hull lets you power through waves without veering off of your path.
How Long Do Sailboat Hulls Last?
Sailboat hulls last for an average of 15 years, but many of them can last for 20 years or longer. It ultimately depends on how well you maintain them and how often they are in the water. For example, a sailboat that you always keep in the water and rarely store in a dry place may need hull repairs and replacement much sooner .
Sailboat hulls are susceptible to algae damage, and that is more likely if you always keep them in the water. Cleaning the hull of a boat is essential to protect them from algae and examine them for potential damage. Fiberglass is the best material for a boat hull, even compared to aluminum which was the standard for years .
Fiberglass hulls can last for up to 50 years or more with regular cleaning and maintenance. A sailboat’s hull won’t last as long if it suffers damage neglecting maintenance or hits the shore too fast. The best way to increase the longevity of your sailboat is to take it out of the water every once in a while and scrub the hull to remove algae.
How Do You Inspect a Sailboat Hull?

The best way to inspect a sailboat hull is to take it out of the water and clean it . You can easily inspect a sailboat’s hull if it is clean and dry, or else you will mix cracks and dents. Cracks are the most important thing to look out for because it’s best to catch them early on.
You should be concerned if you come across cracks because they can eventually worse and threaten your boat’s structural integrity. This is especially true if you have a sailboat with an aluminum hull that you regularly take out onto saltwater. Aluminum can eventually break down in saltwater so it’s important to inspect it regularly, especially after 10 years or more .
The hull is the first part of a boat that you should inspect because hull damage can cause a boat to sink. Always inspect your boat’s hull if you sail too fast in shallow water because that is when you risk the most trouble. Clean and dry your boat’s hull, then follow along it closely to look for spots that don’t glisten as much. This will indicate a weak point, scratch, tear, or dent.
Fastest Sailboat Hull Design
Multi-hull, trimarans, and flat-bottom boats feature the fastest sailboat hull designs . They are hydrodynamic which lets them glide through the water with minimal resistance. Trimarans move incredibly fast, especially in salt water, as long as they aren’t weighed down with too much cargo.
Careful packing reduces the necessity to haul less cargo because trimarans have incredible weight distribution. However, factors such as water conditions and what type of body of water you are on ultimately play a huge role. Boats move up to 2% faster when in saltwater than in freshwater no matter which type of sailboat hull design you have .
Other factors such as your boat’s capacity and how much cargo you are carrying make a huge difference as well. Any type of boat with a planing hull is a safe bet if you want to move quickly through the water. Avoid sailboats with a displacement hull if you value speed because they often move the slowest.
So, What Are the Types of Sailboat Hulls?
The three main types of sailboat hulls are planing hulls, displacement hulls, and semi-displacement hulls. Bilge keel, bulb keel, and fin keel hulls are similar but have different practical applications between freshwater and saltwater . Trimarans and catamarans feature sturdy hulls that are highly regarded for their even weight distribution and roomy storage.
Multi-hull boats such as pontoons and tritoons sit above the water and can withstand rough waters because of how high they sit. Displacement hulls are the best option if you need to cut through choppy waters and maintain your routing. Otherwise, consider a flat-bottomed hull if you primarily stay in shallow water because of how stable they are.
You may also like...
Jack archer pants review: better than lululemon.
In my quest to find the ultimate pair of travel pants that blend style, comfort, and functionality, I stumbled upon the Jack Archer Jetsetter Pants. Let me tell you...
Win a $500 Flight!
Embark on the adventure of a lifetime! Enter our Dream Journey Sweepstakes for a chance to win a $500 travel voucher, redeemable with any major US airline. Whether it's sandy beaches, bustling cities, or tranquil mountains, your dream destination is just an email away!*
Fisherman's Wharf in San Francisco: Top Eats, Sites, and Local Hacks
Imagine uncovering San Francisco's seaside heartbeat at Fisherman's Wharf—where adventures bob with the tides, flavors beckon, and parking secrets await your discovery. Dive into the ultimate Wharf wanderer's guide.
Beverly Hills Elite: 35 Star-Studded Mansions Revealed
Ever wondered where the stars align and sleep at night? Buckle up, as we take you on an exclusive zip code safari to unveil the plush pads of Beverly Hills' most glittering residents!
2024 Seville Safety Guide: Sun, Siestas & Secure Travels!
Ever dodged a wayward flamenco dancer or a rogue tapa? Fear not in Seville! Let's unravel the mysteries of safety in Spain's city of sun, siestas, and street charm. Stay tuned!
Jet-Setter on a Budget: Unlock Half-Price Student Airfares
Many airlines understand the financial constraints of students and offer special fares to make globetrotting more accessible. In this article, I'll dive into the airlines that provide these coveted student discounts.
Unlock Greek Bliss: Ideal Season Secrets & Fest Frenzy
Discover the best time to visit Greece's whitewashed villages, explore azure seas, immerse in rich history, and delight in Greek cuisine. Plan your dream trip now!
The travel site inspired by travelers and locals alike. Find amazing destinations, unique trip ideas, the best hotels, and most comfortable resorts.
- Yachting World
- Digital Edition

43 of the best bluewater sailboat designs of all time
- January 5, 2022
How do you choose the right yacht for you? We highlight the very best bluewater sailboat designs for every type of cruising

Which yacht is the best for bluewater boating? This question generates even more debate among sailors than questions about what’s the coolest yacht , or the best for racing. Whereas racing designs are measured against each other, cruising sailors get very limited opportunities to experience different yachts in real oceangoing conditions, so what is the best bluewater sailboat?
Here, we bring you our top choices from decades of designs and launches. Over the years, the Yachting World team has sailed these boats, tested them or judged them for European Yacht of the Year awards, and we have sifted through the many to curate a selection that we believe should be on your wishlist.
Making the right choice may come down to how you foresee your yacht being used after it has crossed an ocean or completed a passage: will you be living at anchor or cruising along the coast? If so, your guiding requirements will be space, cabin size, ease of launching a tender and anchoring closer to shore, and whether it can comfortably accommodate non-expert-sailor guests.
Article continues below…

The perfect boat: what makes an ideal offshore cruising yacht?
Choosing a boat for offshore cruising is not a decision to be taken lightly. I have researched this topic on…

European Yacht of the Year 2019: Best luxury cruisers
Before the sea trials began, I would have put money on a Hallberg-Rassy or the Wauquiez winning an award. The…
All of these considerations have generated the inexorable rise of the bluewater catamaran – monohulls can’t easily compete on these points. We have a full separate feature on the best bluewater multihulls of all time and here we mostly focus on monohulls. The only exceptions to that rule are two multihulls which made it into our best bluewater sailboats of 2022 list.
As so much of making the right choice is selecting the right boat for the venture in mind, we have separated out our edit into categories: best for comfort; for families; for performance; and for expedition or high latitudes sailing .
Best bluewater sailboats of 2022
The new flagship Allures 51.9, for example, is a no-nonsense adventure cruising design built and finished to a high standard. It retains Allures’ niche of using aluminium hulls with glassfibre decks and superstructures, which, the yard maintains, gives the optimum combination of least maintenance and less weight higher up. Priorities for this design were a full beam aft cabin and a spacious, long cockpit. Both are excellent, with the latter, at 6m long, offering formidable social, sailing and aft deck zones.
It likes some breeze to come to life on the wheel, but I appreciate that it’s designed to take up to five tonnes payload. And I like the ease with which you can change gears using the furling headsails and the positioning of the powerful Andersen winches inboard. The arch is standard and comes with a textile sprayhood or hard bimini.
Below decks you’ll find abundant headroom and natural light, a deep U-shape galley and cavernous stowage. For those who like the layout of the Amel 50 but would prefer aluminium or shoal draught, look no further.
Allures 51.9 price: €766,000
The Ovni 370 is another cunning new aluminum centreboard offering, a true deck saloon cruiser for two. The designers say the biggest challenge was to create a Category A ocean going yacht at this size with a lifting keel, hence the hull had to be very stable.
Enjoyable to helm, it has a practical, deep cockpit behind a large sprayhood, which can link to the bimini on the arch. Many of its most appealing features lie in the bright, light, contemporary, clever, voluminous interior, which has good stowage and tankage allocation. There’s also a practical navstation, a large workroom and a vast separate shower. I particularly like the convertible saloom, which can double as a large secure daybed or pilot berth.
Potentially the least expensive Category A lift keel boat available, the Ovni will get you dreaming of remote places again.
Ovni 370 price: €282,080

There’s no shortage of spirit in the Windelo 50. We gave this a sustainability award after it’s founders spent two years researching environmentally-friendly composite materials, developing an eco-composite of basalt fibre and recycled PET foam so it could build boats that halve the environmental impact of standard glassfibre yachts.
The Windelo 50 is an intriguing package – from the styling, modular interior and novel layout to the solar field on the roof and the standard electric propulsion, it is completely fresh.
Windelo 50 price: €795,000
Best bluewater sailboat of 2022 – Outremer 55
I would argue that this is the most successful new production yacht on the market. Well over 50 have already sold (an equipped model typically costs €1.6m) – and I can understand why. After all, were money no object, I had this design earmarked as the new yacht I would most likely choose for a world trip.
Indeed 55 number one Sanya, was fully equipped for a family’s world cruise, and left during our stay for the Grand Large Odyssey tour. Whereas we sailed Magic Kili, which was tricked up with performance options, including foam-cored deckheads and supports, carbon crossbeam and bulkheads, and synthetic rigging.
At rest, these are enticing space ships. Taking one out to sea is another matter though. These are speed machines with the size, scale and loads to be rightly weary of. Last month Nikki Henderson wrote a feature for us about how to manage a new breed of performance cruising cats just like this and how she coaches new owners. I could not think of wiser money spent for those who do not have ample multihull sailing experience.
Under sail, the most fun was obviously reserved for the reaching leg under asymmetric, where we clocked between 11-16 knots in 15-16 knots wind. But it was the stability and of those sustained low teen speeds which really hit home – passagemaking where you really cover miles.
Key features include the swing helms, which give you views from outboard, over the coachroof or from a protected position in the cockpit through the coachroof windows, and the vast island in the galley, which is key to an open plan main living area. It helps provide cavernous stowage and acts as the heart of the entertaining space as it would in a modern home. As Danish judge Morten Brandt-Rasmussen comments: “Apart from being the TGV of ocean passages the boat offers the most spacious, open and best integration of the cockpit and salon areas in the market.”
Outremer has done a top job in packing in the creature comforts, stowage space and payload capacity, while keeping it light enough to eat miles. Although a lot to absorb and handle, the 55 offers a formidable blend of speed and luxury cruising.
Outremer 55 price: €1.35m
Best bluewater sailboats for comfort
This is the successor to the legendary Super Maramu, a ketch design that for several decades defined easy downwind handling and fostered a cult following for the French yard. Nearly a decade old, the Amel 55 is the bridge between those world-girdling stalwarts and Amel’s more recent and totally re-imagined sloop designs, the Amel 50 and 60.
The 55 boasts all the serious features Amel aficionados loved and valued: a skeg-hung rudder, solidly built hull, watertight bulkheads, solid guardrails and rampart bulwarks. And, most noticeable, the solid doghouse in which the helmsman sits in perfect shelter at the wheel.
This is a design to live on comfortably for long periods and the list of standard features just goes on and on: passarelle; proper sea berths with lee cloths; electric furling main and genoa; and a multitude of practical items that go right down to a dishwasher and crockery.
There’s no getting around the fact these designs do look rather dated now, and through the development of easier sail handling systems the ketch rig has fallen out of fashion, but the Amel is nothing short of a phenomenon, and if you’ve never even peeked on board one, you really have missed a treat.
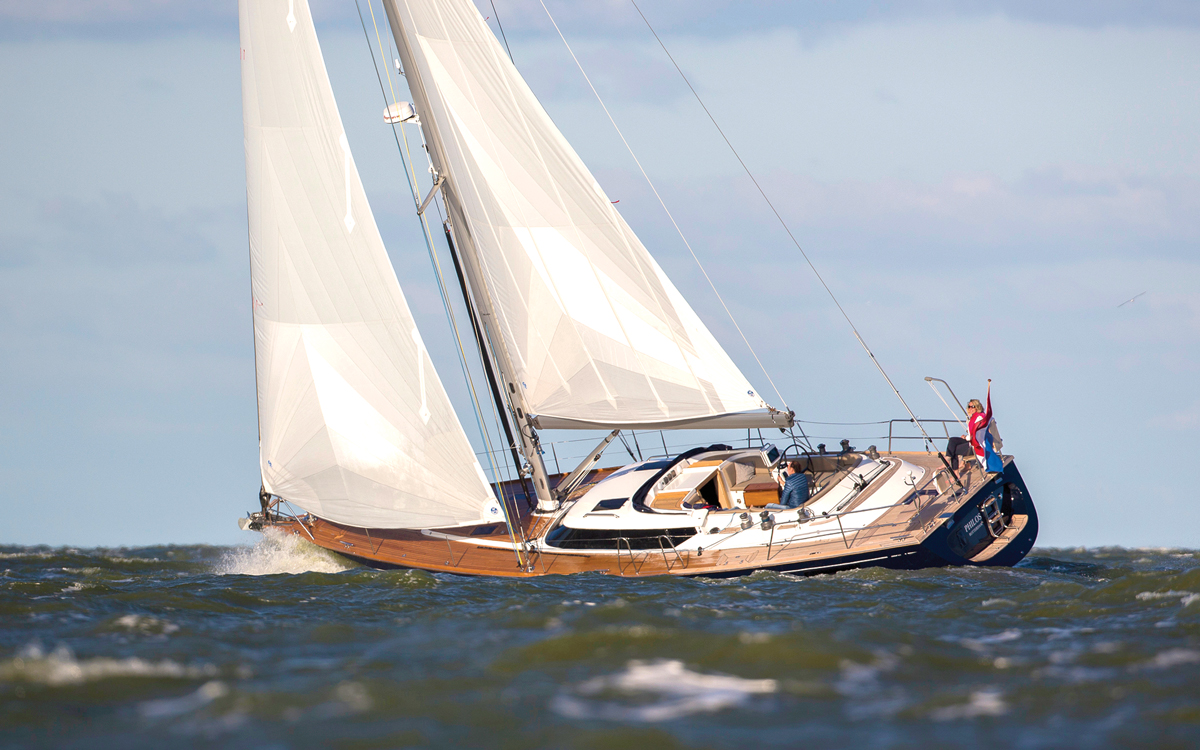

Photo: Sander van der Borch
Contest 50CS
A centre cockpit cruiser with true longevity, the Contest 50CS was launched by Conyplex back in 2003 and is still being built by the family-owned Dutch company, now in updated and restyled form.
With a fully balanced rudder, large wheel and modern underwater sections, the Contest 50CS is a surprisingly good performer for a boat that has a dry weight of 17.5 tonnes. Many were fitted with in-mast furling, which clearly curtails that performance, but even without, this boat is set up for a small crew.
Electric winches and mainsheet traveller are all easy to reach from the helm. On our test of the Contest 50CS, we saw for ourselves how two people can gybe downwind under spinnaker without undue drama. Upwind, a 105% genoa is so easy to tack it flatters even the weediest crewmember.
Down below, the finish level of the joinery work is up there among the best and the interior is full of clever touches, again updated and modernised since the early models. Never the cheapest bluewater sailing yacht around, the Contest 50CS has remained in demand as a brokerage buy. She is a reassuringly sure-footed, easily handled, very well built yacht that for all those reasons has stood the test of time.
This is a yacht that would be well capable of helping you extend your cruising grounds, almost without realising it.
Read more about the Contest 50CS and the new Contest 49CS

Photo: Rick Tomlinson
Hallberg-Rassy 48 Mk II
For many, the Swedish Hallberg-Rassy yard makes the quintessential bluewater cruiser for couples. With their distinctive blue cove line, these designs are famous for their seakindly behaviour, solid-as-a-rock build and beautifully finished, traditional interiors.
To some eyes, Hallberg-Rassys aren’t quite cool enough, but it’s been company owner Magnus Rassy’s confidence in the formula and belief in incremental ‘step-by-step’ evolution that has been such an exceptional guarantor of reliable quality, reputation and resale value.
The centre cockpit Hallberg-Rassy 48 epitomises the concept of comfort at sea and, like all the Frers-designed Hallberg-Rassys since the 1990s, is surprisingly fleet upwind as well as steady downwind. The 48 is perfectly able to be handled by a couple (as we found a few years back in the Pacific), and could with no great effort crack out 200-mile days.
The Hallberg-Rassy 48 was launched nearly a decade ago, but the Mk II from 2014 is our pick, updated with a more modern profile, larger windows and hull portlights that flood the saloon and aft cabin with light. With a large chart table, secure linear galley, heaps of stowage and space for bluewater extras such as machinery and gear, this yacht pretty much ticks all the boxes.

Discovery 55
First launched in 2000, the Discovery 55 has stood the test of time. Designed by Ron Holland, it hit a sweet spot in size that appealed to couples and families with world girdling plans.
Elegantly styled and well balanced, the 55 is also a practical design, with a deep and secure cockpit, comfortable seating, a self-tacking jib, dedicated stowage for the liferaft , a decent sugar scoop transom that’s useful for swimming or dinghy access, and very comfortable accommodation below. In short, it is a design that has been well thought out by those who’ve been there, got the bruises, stubbed their toes and vowed to change things in the future if they ever got the chance.
Throughout the accommodation there are plenty of examples of good detailing, from the proliferation of handholds and grabrails, to deep sinks in the galley offering immediate stowage when under way and the stand up/sit down showers. Stowage is good, too, with plenty of sensibly sized lockers in easily accessible positions.
The Discovery 55 has practical ideas and nifty details aplenty. She’s not, and never was, a breakthrough in modern luxury cruising but she is pretty, comfortable to sail and live on, and well mannered.
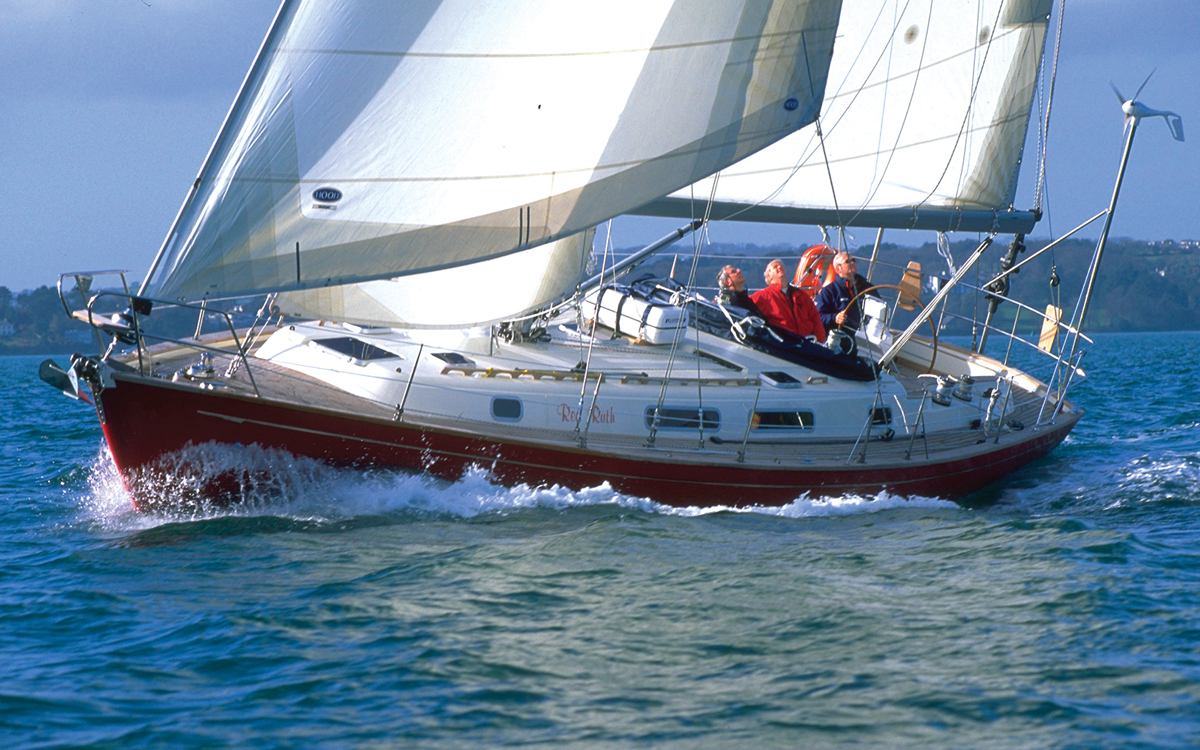

Photo: Latitudes Picture Library
You can’t get much more Cornish than a Rustler. The hulls of this Stephen Jones design are hand-moulded and fitted out in Falmouth – and few are more ruggedly built than this traditional, up-for-anything offshore cruiser.
She boasts an encapsulated lead keel, eliminating keel bolts and creating a sump for generous fuel and water tankage, while a chunky skeg protects the rudder. She is designed for good directional stability and load carrying ability. These are all features that lend this yacht confidence as it shoulders aside the rough stuff.
Most of those built have had a cutter rig, a flexible arrangement that makes sense for long passages in all sea and weather conditions. Down below, the galley and saloon berths are comfortable and sensible for living in port and at sea, with joinery that Rustler’s builders are rightly proud of.
As modern yachts have got wider, higher and fatter, the Rustler 42 is an exception. This is an exceptionally well-mannered seagoing yacht in the traditional vein, with elegant lines and pleasing overhangs, yet also surprisingly powerful. And although now over 20 years old, timeless looks and qualities mean this design makes her look ever more like a perennial, a modern classic.
The definitive crossover size, the point at which a yacht can be handled by a couple but is just large enough to have a professional skipper and be chartered, sits at around the 60ft mark. At 58ft 8in, the Oyster 575 fitted perfectly into this growing market when launched in 2010. It went on to be one of the most popular models from the yard, and is only now being superseded by the newer Rob Humphreys-designed Oyster 565 (just launched this spring).
Built in various configurations with either a deep keel, shoal draught keel or centreboard with twin rudders, owners could trade off better performance against easy access to shallower coves and anchorages. The deep-bodied hull, also by Rob Humphreys, is known for its easy motion at sea.
Some of the Oyster 575’s best features include its hallmark coachroof windows style and centre cockpit – almost everyone will know at first glance this is an Oyster – and superb interior finish. If she has a flaw, it is arguably the high cockpit, but the flip side is the galley headroom and passageway berth to the large aft stateroom.
This design also has a host of practical features for long-distance cruising, such as high guardrails, dedicated liferaft stowage, a vast lazarette for swallowing sails, tender, fenders etc, and a penthouse engine room.

Privilege Serie 5
A true luxury catamaran which, fully fitted out, will top €1m, this deserves to be seen alongside the likes of the Oyster 575, Gunfleet 58 and Hallberg-Rassy 55. It boasts a large cockpit and living area, and a light and spacious saloon with an emphasis on indoor-outdoor living, masses of refrigeration and a big galley.
Standout features are finish quality and solid build in a yacht designed to take a high payload, a secure walkaround deck and all-round views from the helm station. The new Privilege 510 that will replace this launches in February 2020.
Gunfleet 43
It was with this Tony Castro design that Richard Matthews, founder of Oyster Yachts, launched a brand new rival brand in 2012, the smallest of a range stretching to the flagship Gunfleet 74. The combination of short overhangs and centre cockpit at this size do make the Gunfleet 43 look modern if a little boxy, but time and subsequent design trends have been kind to her lines, and the build quality is excellent. The saloon, galley and aft cabin space is exceptional on a yacht of this size.

Photo: David Harding
Conceived as a belt-and-braces cruiser, the Kraken 50 launched last year. Its unique points lie underwater in the guise of a full skeg-hung rudder and so-called ‘Zero Keel’, an encapsulated long keel with lead ballast.
Kraken Yachts is the brainchild of British businessman and highly experienced cruiser Dick Beaumont, who is adamant that safety should be foremost in cruising yacht design and build. “There is no such thing as ‘one yacht for all purposes’… You cannot have the best of all worlds, whatever the salesman tells you,” he says.
Read our full review of the Kraken 50 .

Wauquiez Centurion 57
Few yachts can claim to be both an exciting Med-style design and a serious and practical northern European offshore cruiser, but the Wauquiez Centurion 57 tries to blend both. She slightly misses if you judge solely by either criterion, but is pretty and practical enough to suit her purpose.
A very pleasant, well-considered yacht, she is impressively built and finished with a warm and comfortable interior. More versatile than radical, she could be used for sailing across the Atlantic in comfort and raced with equal enjoyment at Antigua Sailing Week .

A modern classic if ever there was one. A medium to heavy displacement yacht, stiff and easily capable of standing up to her canvas. Pretty, traditional lines and layout below.

Photo: Voyage of Swell
Well-proven US legacy design dating back to the mid-1960s that once conquered the Transpac Race . Still admired as pretty, with slight spoon bow and overhanging transom.

Capable medium displacement cruiser, ideal size and good accommodation for couples or family cruising, and much less costly than similar luxury brands.

Photo: Peter Szamer
Swedish-built aft cockpit cruiser, smaller than many here, but a well-built and finished, super-durable pocket ocean cruiser.
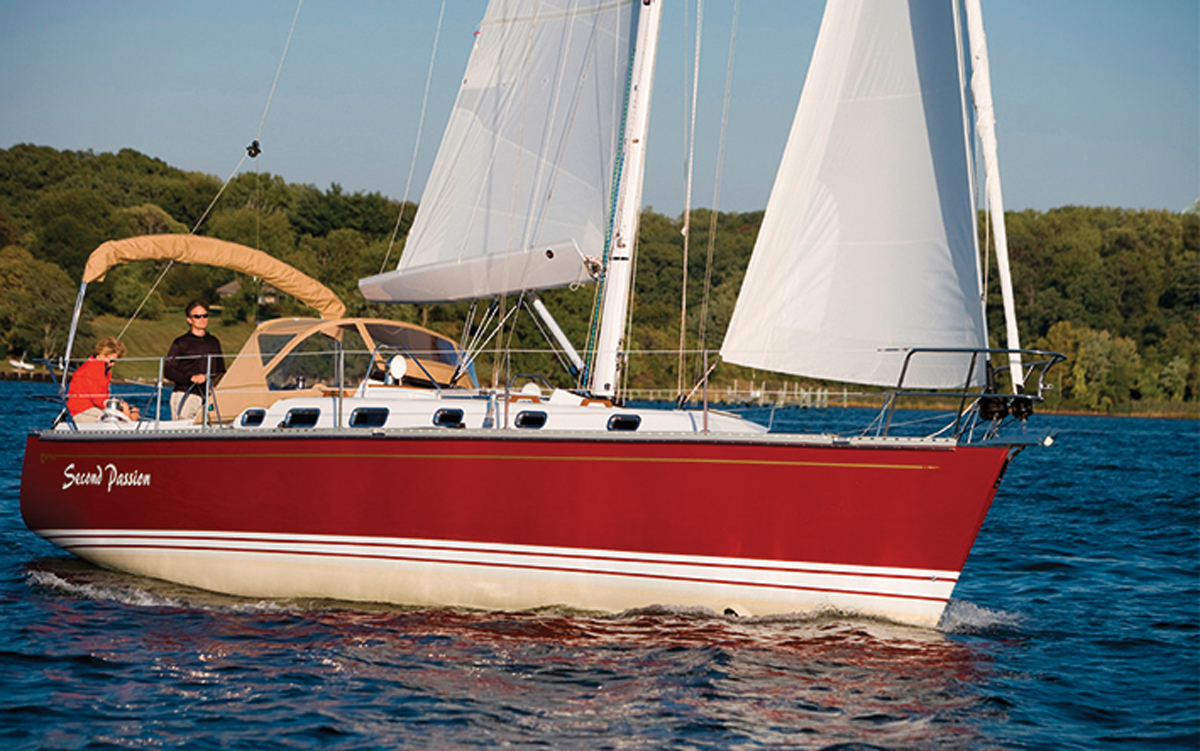

Tartan 3700
Designed as a performance cruiser there are nimbler alternatives now, but this is still an extremely pretty yacht.
Broker ’ s choice

Discovery 55 Brizo
This yacht has already circumnavigated the globe and is ‘prepared for her next adventure,’ says broker Berthon. Price: £535,000 + VAT

Oyster 575 Ayesha
‘Stunning, and perfectly equipped for bluewater cruising,’ says broker Ancasta International. Price: £845,000 (tax not paid)
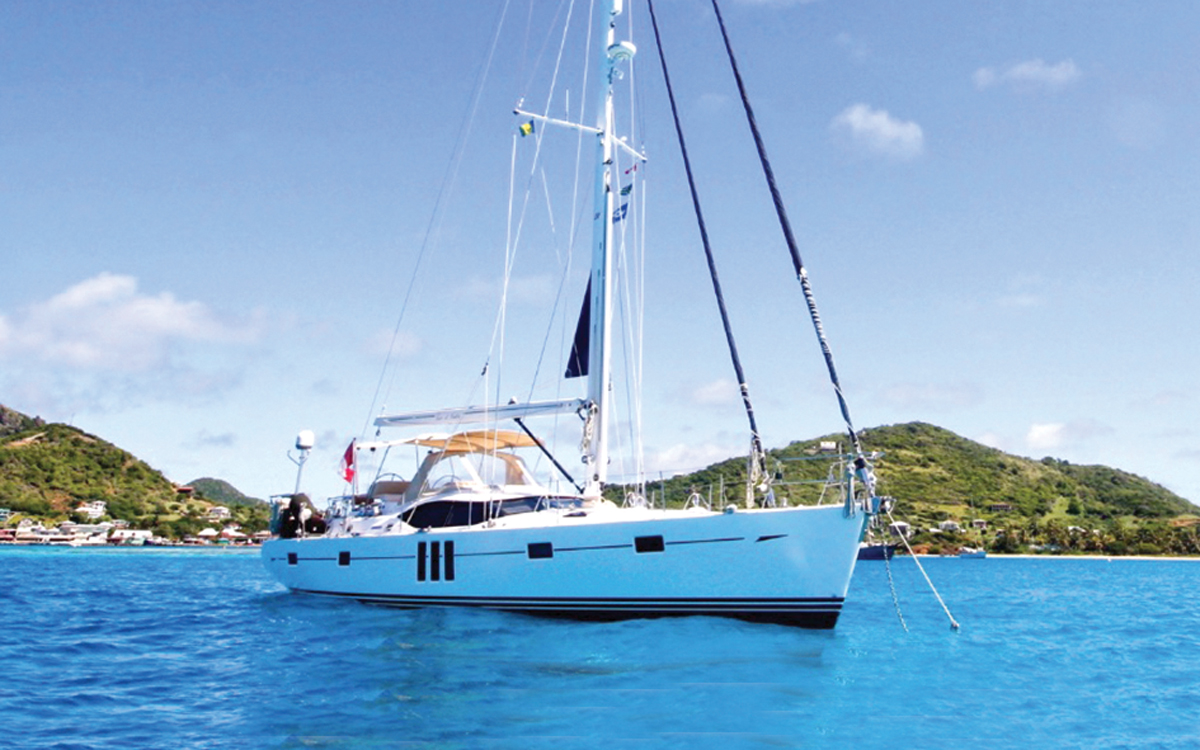

Oyster 575 Pearls of Nautilus
Nearly new and with a high spec, this Oyster Brokerage yacht features American white oak joinery and white leather upholstery and has a shoal draught keel. Price: $1.49m
Best bluewater yachts for performance
The Frers-designed Swan 54 may not be the newest hull shape but heralded Swan’s latest generation of displacement bluewater cruisers when launched four years ago. With raked stem, deep V hull form, lower freeboard and slight curve to the topsides she has a more timeless aesthetic than many modern slab-sided high volume yachts, and with that a seakindly motion in waves. If you plan to cover many miles to weather, this is probably the yacht you want to be on.

Photo: Carlo Borlenghi
Besides Swan’s superlative build quality, the 54 brings many true bluewater features, including a dedicated sail locker. There’s also a cockpit locker that functions as a utility cabin, with potential to hold your generator and washing machine, or be a workshop space.
The sloping transom opens out to reveal a 2.5m bathing platform, and although the cabins are not huge there is copious stowage space. Down below the top-notch oak joinery is well thought through with deep fiddles, and there is a substantial nav station. But the Swan 54 wins for handling above all, with well laid-out sail controls that can be easily managed between a couple, while offering real sailing enjoyment to the helmsman.

Photo: Graham Snook
The Performance Cruiser winner at the 2019 European Yacht of the Year awards, the Arcona 435 is all about the sailing experience. She has genuine potential as a cruiser-racer, but her strengths are as an enjoyable cruiser rather than a full-blown liveaboard bluewater boat.
Build quality is excellent, there is the option of a carbon hull and deck, and elegant lines and a plumb bow give the Arcona 435 good looks as well as excellent performance in light airs. Besides slick sail handling systems, there are well thought-out features for cruising, such as ample built-in rope bins and an optional semi-closed stern with stowage and swim platform.

Outremer 51
If you want the space and stability of a cat but still prioritise sailing performance, Outremer has built a reputation on building catamarans with true bluewater characteristics that have cruised the planet for the past 30 years.
Lighter and slimmer-hulled than most cruising cats, the Outremer 51 is all about sailing at faster speeds, more easily. The lower volume hulls and higher bridgedeck make for a better motion in waves, while owners report that being able to maintain a decent pace even under reduced canvas makes for stress-free passages. Deep daggerboards also give good upwind performance.
With bucket seats and tiller steering options, the Outremer 51 rewards sailors who want to spend time steering, while they’re famously well set up for handling with one person on deck. The compromise comes with the interior space – even with a relatively minimalist style, there is less cabin space and stowage volume than on the bulkier cats, but the Outremer 51 still packs in plenty of practical features.

The Xc45 was the first cruising yacht X-Yachts ever built, and designed to give the same X-Yachts sailing experience for sailors who’d spent years racing 30/40-footer X- and IMX designs, but in a cruising package.
Launched over 10 years ago, the Xc45 has been revisited a few times to increase the stowage and modernise some of the styling, but the key features remain the same, including substantial tanks set low for a low centre of gravity, and X-Yachts’ trademark steel keel grid structure. She has fairly traditional styling and layout, matched with solid build quality.
A soft bilge and V-shaped hull gives a kindly motion in waves, and the cockpit is secure, if narrow by modern standards.

A three or four cabin catamaran that’s fleet of foot with high bridgedeck clearance for comfortable motion at sea. With tall daggerboards and carbon construction in some high load areas, Catana cats are light and quick to accelerate.

Sweden Yachts 45
An established bluewater design that also features in plenty of offshore races. Some examples are specced with carbon rig and retractable bowsprits. All have a self-tacking jib for ease. Expect sweeping areas of teak above decks and a traditionally wooded interior with hanging wet locker.

A vintage performer, first launched in 1981, the 51 was the first Frers-designed Swan and marked a new era of iconic cruiser-racers. Some 36 of the Swan 51 were built, many still actively racing and cruising nearly 40 years on. Classic lines and a split cockpit make this a boat for helming, not sunbathing.

Photo: Julien Girardot / EYOTY
The JPK 45 comes from a French racing stable, combining race-winning design heritage with cruising amenities. What you see is what you get – there are no superfluous headliners or floorboards, but there are plenty of ocean sailing details, like inboard winches for safe trimming. The JPK 45 also has a brilliantly designed cockpit with an optional doghouse creating all-weather shelter, twin wheels and superb clutch and rope bin arrangement.

Photo: Andreas Lindlahr
For sailors who don’t mind exchanging a few creature comforts for downwind planing performance, the Pogo 50 offers double-digit surfing speeds for exhilarating tradewind sailing. There’s an open transom, tiller steering and no backstay or runners. The Pogo 50 also has a swing keel, to nose into shallow anchorages.

Seawind 1600
Seawinds are relatively unknown in Europe, but these bluewater cats are very popular in Australia. As would be expected from a Reichel-Pugh design, this 52-footer combines striking good looks and high performance, with fine entry bows and comparatively low freeboard. Rudders are foam cored lifting designs in cassettes, which offer straightforward access in case of repairs, while daggerboards are housed under the deck.
Best bluewater sailboats for families
It’s unsurprising that, for many families, it’s a catamaran that meets their requirements best of increased space – both living space and separate cabins for privacy-seeking teenagers, additional crew or visiting family – as well as stable and predictable handling.

Photo: Nicholas Claris
Undoubtedly one of the biggest success stories has been the Lagoon 450, which, together with boats like the Fountaine Pajot 44, helped drive up the popularity of catamaran cruising by making it affordable and accessible. They have sold in huge numbers – over 1,000 Lagoon 450s have been built since its launch in 2010.
The VPLP-designed 450 was originally launched with a flybridge with a near central helming position and upper level lounging areas (450F). The later ‘sport top’ option (450S) offered a starboard helm station and lower boom (and hence lower centre of gravity for reduced pitching). The 450S also gained a hull chine to create additional volume above the waterline. The Lagoon features forward lounging and aft cockpit areas for additional outdoor living space.
Besides being a big hit among charter operators, Lagoons have proven themselves over thousands of bluewater miles – there were seven Lagoon 450s in last year’s ARC alone. In what remains a competitive sector of the market, Lagoon has recently launched a new 46, with a larger self-tacking jib and mast moved aft, and more lounging areas.

Photo: Gilles Martin-Raget
Fountaine Pajot Helia 44
The FP Helia 44 is lighter, lower volume, and has a lower freeboard than the Lagoon, weighing in at 10.8 tonnes unloaded (compared to 15 for the 450). The helm station is on a mezzanine level two steps up from the bridgedeck, with a bench seat behind. A later ‘Evolution’ version was designed for liveaboard cruisers, featuring beefed up dinghy davits and an improved saloon space.
Available in three or four cabin layouts, the Helia 44 was also popular with charter owners as well as families. The new 45 promises additional volume, and an optional hydraulically lowered ‘beach club’ swim platform.

Photo: Arnaud De Buyzer / graphikup.com
The French RM 1370 might be less well known than the big brand names, but offers something a little bit different for anyone who wants a relatively voluminous cruising yacht. Designed by Marc Lombard, and beautifully built from plywood/epoxy, the RM is stiff and responsive, and sails superbly.
The RM yachts have a more individual look – in part down to the painted finish, which encourages many owners to personalise their yachts, but also thanks to their distinctive lines with reverse sheer and dreadnought bow. The cockpit is well laid out with the primary winches inboard for a secure trimming position. The interior is light, airy and modern, although the open transom won’t appeal to everyone.
For those wanting a monohull, the Hanse 575 hits a similar sweet spot to the popular multis, maximising accommodation for a realistic price, yet with responsive performance.
The Hanse offers a vast amount of living space thanks to the ‘loft design’ concept of having all the living areas on a single level, which gives a real feeling of spaciousness with no raised saloon or steps to accommodation. The trade-off for such lofty head height is a substantial freeboard – it towers above the pontoon, while, below, a stepladder is provided to reach some hatches.
Galley options include drawer fridge-freezers, microwave and coffee machine, and the full size nav station can double up as an office or study space.
But while the Hanse 575 is a seriously large boat, its popularity is also down to the fact that it is genuinely able to be handled by a couple. It was innovative in its deck layout: with a self-tacking jib and mainsheet winches immediately to hand next to the helm, one person could both steer and trim.
Direct steering gives a feeling of control and some tangible sailing fun, while the waterline length makes for rapid passage times. In 2016 the German yard launched the newer Hanse 588 model, having already sold 175 of the 575s in just four years.

Photo: Bertel Kolthof
Jeanneau 54
Jeanneau leads the way among production builders for versatile all-rounder yachts that balance sail performance and handling, ergonomics, liveaboard functionality and good looks. The Jeanneau 54 , part of the range designed by Philippe Briand with interior by Andrew Winch, melds the best of the larger and smaller models and is available in a vast array of layout options from two cabins/two heads right up to five cabins and three heads.
We’ve tested the Jeanneau 54 in a gale and very light winds, and it acquitted itself handsomely in both extremes. The primary and mainsheet winches are to hand next to the wheel, and the cockpit is spacious, protected and child-friendly. An electric folding swim and sun deck makes for quick fun in the water.

Nautitech Open 46
This was the first Nautitech catamaran to be built under the ownership of Bavaria, designed with an open-plan bridgedeck and cockpit for free-flowing living space. But with good pace for eating up bluewater miles, and aft twin helms rather than a flybridge, the Nautitech Open 46 also appeals to monohull sailors who prefer a more direct sailing experience.

Made by Robertson and Caine, who produce catamarans under a dual identity as both Leopard and the Sunsail/Moorings charter cats, the Leopard 45 is set to be another big seller. Reflecting its charter DNA, the Leopard 45 is voluminous, with stepped hulls for reduced waterline, and a separate forward cockpit.
Built in South Africa, they are robustly tested off the Cape and constructed ruggedly enough to handle heavy weather sailing as well as the demands of chartering.

Photo: Olivier Blanchet
If space is king then three hulls might be even better than two. The Neel 51 is rare as a cruising trimaran with enough space for proper liveaboard sailing. The galley and saloon are in the large central hull, together with an owner’s cabin on one level for a unique sensation of living above the water. Guest or family cabins lie in the outer hulls for privacy and there is a cavernous full height engine room under the cabin sole.
Performance is notably higher than an equivalent cruising cat, particularly in light winds, with a single rudder giving a truly direct feel in the helm, although manoeuvring a 50ft trimaran may daunt many sailors.

Beneteau Oceanis 46.1
A brilliant new model from Beneteau, this Finot Conq design has a modern stepped hull, which offers exhilarating and confidence-inspiring handling in big breezes, and slippery performance in lighter winds.
The Beneteau Oceanis 46.1 was the standout performer at this year’s European Yacht of the Year awards, and, in replacing the popular Oceanis 45, looks set to be another bestseller. Interior space is well used with a double island berth in the forepeak. An additional inboard unit creates a secure galley area, but tank capacity is moderate for long periods aboard.

Beneteau Oceanis 473
A popular model that offers beam and height in a functional layout, although, as with many boats of this age (she was launched in 2002), the mainsheet is not within reach of the helmsman.

Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 49
The Philippe Briand-designed Sun Odyssey range has a solid reputation as family production cruisers. Like the 473, the Sun Odyssey 49 was popular for charter so there are plenty of four-cabin models on the market.

Nautitech 441
The hull design dates back to 1995, but was relaunched in 2012. Though the saloon interior has dated, the 441 has solid practical features, such as a rainwater run-off collection gutter around the coachroof.

Atlantic 42
Chris White-designed cats feature a pilothouse and forward waist-high working cockpit with helm position, as well as an inside wheel at the nav station. The Atlantic 42 offers limited accommodation by modern cat standards but a very different sailing experience.
Best bluewater sailing yachts for expeditions
Bestevaer 56.
All of the yachts in our ‘expedition’ category are aluminium-hulled designs suitable for high latitude sailing, and all are exceptional yachts. But the Bestevaer 56 is a spectacular amount of boat to take on a true adventure. Each Bestevaer is a near-custom build with plenty of bespoke options for owners to customise the layout and where they fall on the scale of rugged off-grid adventurer to 4×4-style luxury fit out.
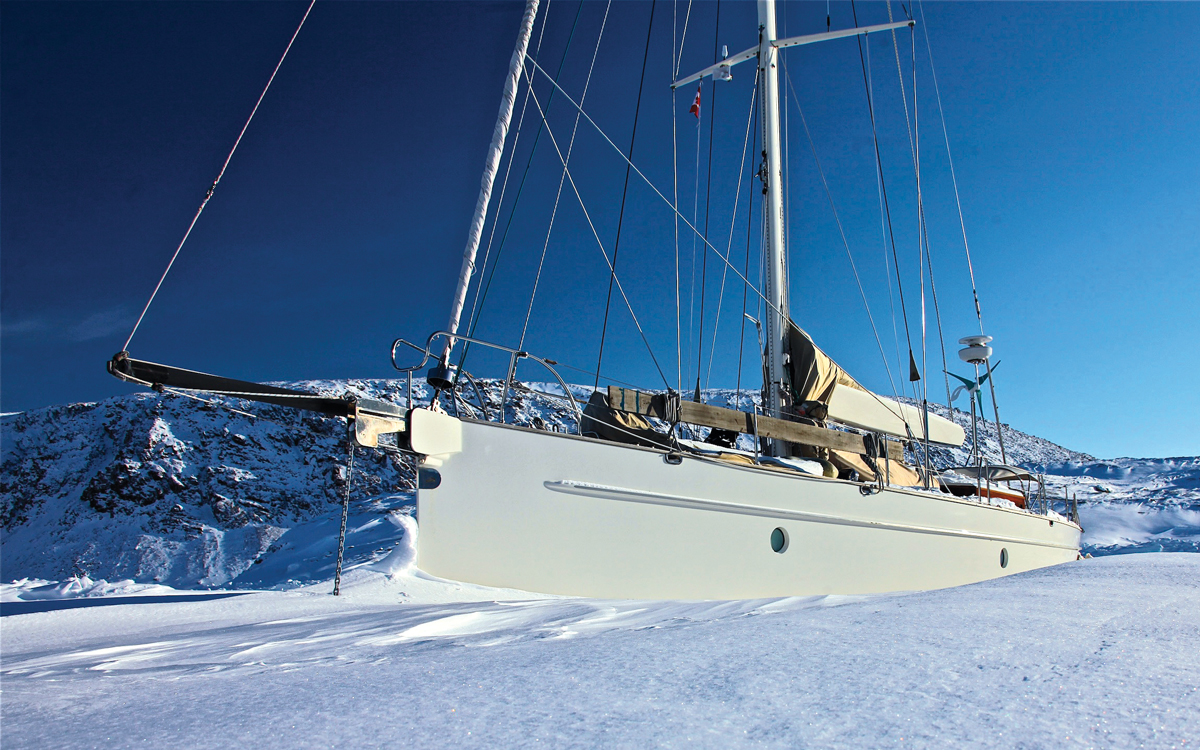

The Bestevaer range began when renowned naval architect Gerard Dijkstra chose to design his own personal yacht for liveaboard adventure cruising, a 53-footer. The concept drew plenty of interest from bluewater sailors wanting to make longer expeditions and Bestevaers are now available in a range of sizes, with the 56-footer proving a popular mid-range length.
The well-known Bestevaer 56 Tranquilo (pictured above) has a deep, secure cockpit, voluminous tanks (700lt water and over 1,100lt fuel) and a lifting keel plus water ballast, with classically styled teak clad decks and pilot house. Other owners have opted for functional bare aluminium hull and deck, some choose a doghouse and others a pilothouse.

Photo: Jean-Marie Liot
The Boreal 52 also offers Land Rover-esque practicality, with utilitarian bare aluminium hulls and a distinctive double-level doghouse/coachroof arrangement for added protection in all weathers. The cockpit is clean and uncluttered, thanks to the mainsheet position on top of the doghouse, although for visibility in close manoeuvring the helmsman will want to step up onto the aft deck.
Twin daggerboards, a lifting centreboard and long skeg on which she can settle make this a true go-anywhere expedition yacht. The metres of chain required for adventurous anchoring is stowed in a special locker by the mast to keep the weight central. Down below has been thought through with equally practical touches, including plenty of bracing points and lighting that switches on to red light first to protect your night vision.

Photo: Morris Adant / Garcia Yachts
Garcia Exploration 45
The Garcia Exploration 45 comes with real experience behind her – she was created in association with Jimmy Cornell, based on his many hundreds of thousands of miles of bluewater cruising, to go anywhere from high latitudes to the tropics.
Arguably less of a looker than the Bestevaer, the Garcia Exploration 45 features a rounded aluminium hull, centreboard with deep skeg and twin daggerboards. The considerable anchor chain weight has again been brought aft, this time via a special conduit to a watertight locker in front of the centreboard.
This is a yacht designed to be lived on for extended periods with ample storage, and panoramic portlights to give a near 360° view of whichever extraordinary landscape you are exploring. Safety features include a watertight companionway door to keep extreme weather out and through-hull fittings placed above the waterline. When former Vendée Globe skipper Pete Goss went cruising , this was the boat he chose to do it in.

Photo: svnaima.com
A truly well-proven expedition design, some 1,500 Ovnis have been built and many sailed to some of the most far-flung corners of the world. (Jimmy Cornell sailed his Aventura some 30,000 miles, including two Drake Passage crossings, one in 50 knots of wind).

Futuna Exploration 54
Another aluminium design with a swinging centreboard and a solid enclosed pilothouse with protected cockpit area. There’s a chunky bowsprit and substantial transom arch to house all manner of electronics and power generation.
Previous boats have been spec’d for North West Passage crossings with additional heating and engine power, although there’s a carbon rig option for those that want a touch of the black stuff. The tanks are capacious, with 1,000lt capability for both fresh water and fuel.
If you enjoyed this….
Yachting World is the world’s leading magazine for bluewater cruisers and offshore sailors. Every month we have inspirational adventures and practical features to help you realise your sailing dreams. Build your knowledge with a subscription delivered to your door. See our latest offers and save at least 30% off the cover price.

Types of Sailboat Hulls

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
Sailboats come in numerous hull shapes. These include single-hull monohulls, along with double and triple-hull multihulls.
There are two main categories of sailboat hulls: monohulls and multihulls. Common monohull types include flat-bottom vessels, fin-keel racers, bulb and bilge keel cruisers, heavy semi-displacement sailboats, and dense full-keel displacement cruisers. Multihull designs include catamarans and trimarans.
In this article, we'll cover the most common types of sailboat hulls along with their best uses. We'll explain the difference between monohulls and multihulls, along with how keel shape influences sailboat performance.
We sourced the information for this article from sailing experts, hull shape guides, and the written wisdom of famous sailboat designers. Additionally, we researched sailboat sales figures to determine the most popular vessel configurations available today.
Table of contents
Importance of Sailboat Hull Design
A sailboat is defined by its rig and hull shape. Sailboat hull shape is one of the deciding factors on how it will handle. Additionally, the shape (and displacement) of a sailboat hull can be used to determine its strengths and weaknesses. Learning about sailboat hull shape can help you understand what kind of boat you need and what your vessel is capable of.
You can easily categorize sailboats based on their hull shape. For example, a heavy deep-draft displacement hull is likely a slow, steady, and comfortable cruiser. In contrast, a sleek flat-bottomed sailboat or catamaran is likely built for speed and could easily outpace even the most nimble displacement cruisers.
The most common kind of sailboat is the monohull. When you think of a sailboat, probably think of a monohull. The term simply means that the vessel has one single hull and nothing more. This is in contrast to multihulls such as catamarans, which are easy to spot and differentiate from traditional designs.
Monohulls are popular because they work. They're easy to build and narrow enough to fit in most marina dock spaces. Monohulls are also generally easy to handle in a variety of conditions, both fair and foul.
One drawback of monohull designs is that they are not quite as stable as most multihulls, though monohulls can recover more easily from a serious roll or capsize. They also cost a lot less, as the vast majority of production sailboats ever constructed were of the same basic single-hull configuration.
Centerboards and Swing Keels
The windward performance of sailboats is greatly improved by the use of a long keel or centerboard. The centerboard is the most simple type of stabilizing device used on sailboats. Usually, the centerboard is simply a long fin that protrudes from the bottom of the hull.
The centerboard keeps the boat on track when the wind is not moving in the boat's direction of travel. This is why sailboats can sail at different angles to the wind without being pushed to the side. A key characteristic of centerboards is that they can be raised and lowered, which is convenient on small boats that need to be trailered or beached.
Swing keels are similar to centerboards in that they can be raised and lowered, though they pivot on a hinge instead of sliding up and down in a truck. Swing keels are either recessed into the hull or held in a housing just below it, which usually also contains much of the boat's ballast. Swing keel designs free up cabin space that would normally be occupied by a bulky centerboard trunk.
Centerboards and most swing keels are an alternative to a permanently affixed keel. They're generally not considered to be as seaworthy as other hull designs, so their use is confined primarily to inland and coastal cruising.
Monohull Sailboat Hull Shapes
When in the water, it's difficult to distinguish between the different types of monohull shapes. In most cases, you have to pull the boat out of the water to figure out what hull shape you're dealing with. Next, we'll go over the most common monohull sailboat shapes and their uses.
Flat-Bottom Sailboats
Flat bottom sailboats are the easiest to build and often the fastest. These vessels have a very shallow draft and are often lightweight, so they slide easily and quickly across the water. Flat bottom sailboats make excellent racing boats and 'gunkholers,' which are primarily used for camping and hopping between shallow Islands.
Flat bottom sailboats usually have centerboards or swing keels, which makes them great for shallow water, beaching, and towing on a trailer. The use of flat bottom sailboats is confined primarily to inland and coastal waters, as a flat bottom does not handle well in swells and rough weather. Flat bottom sailboats pound hard on chop, and they lack the low center of gravity that's necessary for good stability.
Fin Keel Sailboat Hulls
The fin keel is a popular alternative to centerboards, and vessels utilizing this low-profile hull shape have proven to be quite seaworthy. Fin keels are popular on fast racing boats and lightweight cruisers. A fin keel resembles a centerboard, but it usually extends much further from the base of the hull.
The majority of a sailboat's draft comes from the fin keel, as the hulls of these sailboats tend to be rounded and shallow. They resemble flat-bottom designs, but slight rounding significantly increases comfort. Fin keel sailboats are ideal for racing and coastal cruising, and some models can be used for extended offshore passages.
Bulb Keel Sailboat Hulls
A bulb keel sailboat hull usually resembles most fin keel varieties. The hulls of these vessels tend to be shallow and rounded, with a long and thin fin extending from the base of the hull. A bulb keel is essentially just a thin blade with a bulb on the bottom.
Bulb keels are different from fin keels as they usually contain additional ballast weight for stability. The hydrodynamic properties of bulb keels are proven to be efficient. As a result, these boats can also be quite fast. In a direct comparison, a vessel with a bulb keel will likely be more seaworthy than the same sailboat with only a fin keel or a centerboard.
Bilge Keel Sailboat Hulls
The hull shape of a bilge keel sailboat usually resembles that of a bulb or fin keel sailboat, with one major distinction. Instead of one long and thin keel descending from the center of the hull, a bilge keel sailboat has two lengthier fins offset on the port and starboard side.
The idea behind the bilge keel design is that when the vessel heels to one side, one of the two keels will be straightened out. This, in theory, provides better tracking and improves stability. It also distributes ballast evenly on both sides. Bilge keels can also improve motion comfort, and they can reduce the vessel's draft by a small margin.
Bilge keel sailboats offer a balance between seaworthiness and speed. These vessels can be used as bluewater cruisers and coastal cruisers. They can also hold their own in any yacht club regatta.
While a bilge keel sailboat may not be ideal for cruising the North Atlantic during the winter, it can certainly make a safe and comfortable passage maker that can gain a knot or two of speed above its heavier counterparts.
Semi-Displacement Sailboat Hulls
Now, we'll look at some true bluewater cruising designs. The semi-displacement hull features a long and deep keel that runs from about the center of the hull all the way back to the rudder. Semi-displacement hulls get deeper the further back you go, reaching their longest point at the very aft end of the boat.
The offshore benefits of a long and deep keel are numerous, as this hull shape provides an enormous amount of stability and a very low center of gravity. The design itself it's quite old, and it's featured on many classic cruising sailboats and workboats.
Though less common in the modern era than more contemporary fin keel designs, a traditional semi-displacement sailboat offers easy handling and enhanced motion comfort. Semi-displacement hulls tend to have a deep draft and therefore are not ideal for shallow water. They handle confidently in all conditions, though they usually aren't as fast as newer designs.
Displacement Sailboat Hulls
Displacement hulls, also known as full keel hulls, are the bulldozers of the sailboat world. These traditional vessels are deep, heavy, relatively slow, and capable of plowing through the roughest weather conditions.
Displacement hulls have a long keel that begins at the bow and extends all the way after the rudder. Like semi-displacement hulls, full keel sailboats offer excellent motion comfort and confident handling.
Displacement hulls have the best directional stability and downwind maneuvering abilities. Their handling is more forgiving, and they're less jumpy at the helm. Many of these boats heel gently and give the crew more time to respond to changing conditions.
The primary downside to displacement hulls is their high cost and sheer mass. Displacement boats are large and take up a lot of space. They're usually too tall and heavy for trailering, so they tend to remain in the water most of the time.
Displacement hulls aren't made to just sit at the dock or jump around the lake; they're designed for real-deal offshore sailing. They also have the roomiest cabins, as the hull extends further down and longer than any other hull shape.
Now, let's examine multihull sailboat designs and why you may want to consider one. Some of the earliest seagoing vessels had multiple hulls, usually featuring one long hull (occupied by the crew) and a small stabilizing hull off to one side.
Multihulls have only recently become popular, and they make up a decent portion of the modern production boat market. This is because of their numerous design benefits and spacious cabins. Multihulls are almost guaranteed to be more expensive than monohulls (both new and used), and the used market is still saturated with expensive luxury cruising sailboats.
Modern multihull sailboats feature a large pilothouse in the center and plenty of cabin space in each full-size hull. They offer excellent motion comfort and achieve very high speeds. Due to their wide beam, they provide spacious living spaces and excellent stability. Here are the two main types of multihull sailboats.
From above, a catamaran looks like two thin monohull sailboats lashed together and spaced apart. Fundamentally, that's exactly what they are. Except catamarans have a very shallow draft and the capability to reach very high speeds.
Catamarans have two hulls instead of one, and each hull is typically a mirror of the other. They achieve their space using width rather than length, so a 30-foot catamaran has significantly more interior room than a 30-foot monohull.
Their primary drawback is that, due to their width, catamarans usually require two standard dock spaces instead of one. But at sea, they don't heel over dramatically like monohulls, which makes them much more comfortable to eat, sleep, and cook inside of.
Trimarans follow the same basic design principles as catamarans, except they have a third hull in the center. From above, a trimaran looks like a monohull with two smaller hulls lashed to the sides. Unlike a catamaran, the primary living space of a trimaran is in the large center hull. Trimarans are essentially just monohulls with stabilizers on the side, resembling ancient sailing canoes.
Trimarans have the same spatial and stability benefits as catamarans, though they can achieve higher speeds and better sea keeping. This is because of the additional stability provided by the center hall. Trimarans tend to be costlier than catamarans, though many sailors believe that the benefits outweigh the cost.
Best Sailboat Hull Shape for Speed
If we take wave height and weather conditions out of the equation, the fastest sailboats are usually the longest. Sailboats are limited by hull speed and sail plan size regardless of their hull shape. That said, the fastest sailboats tend to be flat bottom monohulls, fin keel monohulls, and trimarans.
Best Sailboat Hull Shape for Motion Comfort
The best sailboat for motion comfort is the catamaran. These wide and seaworthy vessels 'stance up' and minimize rolling. They also come close to completely eliminating heeling.
Wide and stable multihulls are popular because they alleviate some of the most common complaints of sailors. Trimarans are also an excellent choice for comfort, as their stabilizers minimize the effect of rolling in heavy seas.
Most Seaworthy Sailboat Hull Shape
Today, many people consider multihulls to be the most seaworthy design on the market. However, seaworthiness is more than just average stability in rough weather. Many Sailors argue that traditional displacement sailboat hull designs are the most seaworthy.
Displacement hulls have a low center of gravity which improves their knockdown survivability. In other words, in the (rare) event of a displacement boat knockdown, the weight of the keel is more likely to swing the boat back up and out of trouble. Multihulls cannot recover from a knockdown, as they like the pendulum-like recoil ability.
Most Spacious Sailboat Hull Type
The most spacious hull sailboat type is the catamaran. Catamarans have two nearly full-size hulls (one on each side) plus a large central pilothouse that resembles the main cabin of a large powerboat.
Many typical catamarans fit an entire kitchen into the Pilot House along with four private births and two full-sized heads in its hulls. Some mid-size catamarans even come with a bathtub, which is essentially unheard of on equivalent monohulls.
Spaciousness varies on small monohulls. Larger cabins are usually found on bulb and bilge keel designs, as swing keel and centerboard boats need somewhere to hide their skegs. Centerboard boats are the least spacious, as the centerboard trunk must occupy the middle of the cabin space.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Sailboat Parts
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

The Definitive Guide to Sailboat Hull Types

If you’ve ever been on a sailboat or any kind of boat, one of the first parts of the boat you saw was its hull and you might not have even known it.
Simply put, the hull is the bottom part of a boat that rides in and on top of the water. When a sailboat is underwater, it’s accompanied by the keel and the rudder.
Just like knowing the different types of sails , knowing the hull type on your sailboat means you’ll have a better understanding of how your boat operates while it’s out on the water.
All in all, the hull of any boat is meant to keep the boat afloat and to ensure minimum resistance against the water while being propelled forward. Now let’s dive into the different sailboat hull types and even some other types of hulls in boats in general!
Main Sailboat Hull Types
There are two main hull types that we’ll be looking at that encompass the many other types of hulls that vary from these two main types.
Depending on the type of boat you have, you’ll be floating around with one or the other. We’ll take a look at what you can expect if your boat has either of these hull types.
Displacement Hulls
The most common sailboat hull type you’ll find out there is the displacement hull, which is very effective at pushing the water aside and powering through it during forward propulsion.
A displacement hull is often found not only on sailboats, but also fishing, freight, cruise, and other larger boats.
All boats that have a displacement hull will be limited in their speed based on the waterline length of the hull. Regardless of how much power you use, whether it’s from the wind or motor, the maximum speed can’t be increased.
This is why you’ll see people mention the waterline length of a boat’s hull when putting them on the market to sell.
The big advantage of having a displacement hull is that they require far less power to get moving across the water compared to the other main hull type; the planing hull.
What this means is that your boat will be able to cruise for a long time with the same amount of energy, which also allows you to carry more items on board.
Planing Hulls
It’s almost guaranteed that your sailboat won’t have a planing hull since they’re most commonly found on powerboats and personal watercrafts (PWCs), like jet skis.
Planing hulls allow the boat to lift itself out of the water, reducing drag and increasing the speed of the boat.
Almost any boat that’s equipped with a planing hull will be able to attain a speed much greater than a boat with a displacement boat.
The main reason for this is the lift that’s produced when traveling at high speeds which reduces drag on the water.
The maximum speed of a boat with a planing hull is dependent on the horsepower of the engine and how much of the hull can be removed from the water while still cruising.
The biggest advantage of having a planing hull is that your boat will be able to pick up speed quickly and reach a greater maximum speed.
This allows for shorter journey times. However, there needs to be a source of all that energy, which comes directly from a combustion engine. The faster a boat with a planing hull goes, the larger the cost of fuel will be.
How Planing Works
The way planing works is actually pretty interesting, so I thought I’d dive into it a bit. Even though a sailboat is virtually guaranteed not to have one, it’s always nice to know how other boats operate while out on the water.
1. Displacement
Before a boat with a planing hull actually planes, it starts out acting like a displacement hull.
As a matter of fact, a boat with a planing hull needs to reach a certain speed before it starts to produce lift. Before that happens, it’s essentially a displacement hull.
While a boat with a planing hull is picking up speed and lifting itself out of the water, it’s in a plowing mode.
You’ll know when a boat is in plowing mode when the bow of the boat is elevated and the boat is throwing a relatively large wake. The goal, however, is to move from plowing mode to planing mode, which requires further acceleration.
Once the boat with a planing hull reaches a certain speed, it’ll leave plowing mode and enter planing mode.
As I already described, planing is when the hull is gliding across the water with a smaller amount of the hull dragging in the water when compared to the previous modes. Different boats will start planing when reaching different speeds.
Common Sailboat Hull Styles
Now that we’ve gone over the two main types of hulls you’ll find in sailboats and other types of boats, we have a good foundation for the hull styles you’ll commonly see when out on the water.
There are three main hull styles that you’ll see quite often, so let’s take a look at those.
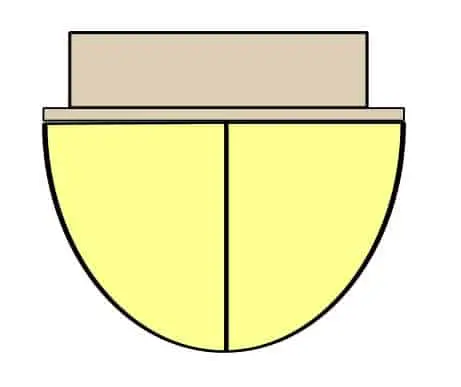
By far the most common hull style you’ll see on sailboats is the monohull, which is simply a single hull.
Traditionally, a sailboat will have a monohull and they can be found all over the place. It’s probably the style of hull that comes to most peoples’ mind when imagining a sailboat.
Monohulls on sailboats are virtually all displacement hulls. As we went over previously, this allows your sailboat to cruise for long stretches and has a greater efficiency compared to planing hulls.
However, most boats that exist on planet earth are monohulls, including powerboats, which can also be of the planing hull type.
When it comes to a monohull on a sailboat, the only way it can keep its stability is to have a proper keel attached to it.
A keel is a wing-like object that sticks out of the bottom of the hull in the water and provides a sailboat with ballast for stability. It’s important to understand how a keel works when operating a sailboat with a monohull since it’s one of the main reasons a sailboat can move forward without tipping.
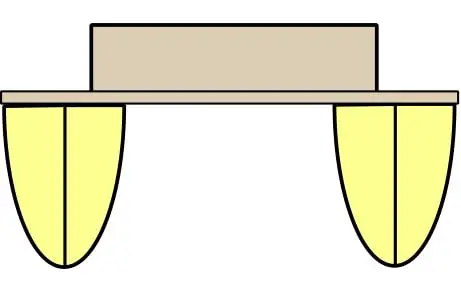
There are certainly a lot of monohull sailboats out there, but there’s no doubt that you’ll also see your fair share of catamarans.
Catamarans are sailboats with two hulls and operate quite differently than their monohull cousin. Catamarans are known to be fast and are likely to outrun most monohull sailboats.
Unlike monohull sailboats, catamarans can be fitted with displacement hulls as well as planing hulls. However, even if they have a planing hull they can still produce a relatively good amount of cruising time and do so rather efficiently.
Catamarans are a bit different than monohulls in the sense that they can reach greater speeds. There are several reasons for this. For one, a catamaran doesn’t need a ballast for stability since the broad stance between the two hulls provides enough stability.
This means there’s no need for a large, heavy keel. Second, they’re often built out of lightweight materials that allow the boat to reach a higher maximum speed compared to heavier sailboats.
Also, if a catamaran has a planing hull, it’ll have the ability to produce lift resulting in reduced drag on the water and even greater speeds.
Unfortunately, catamarans do have the disadvantage of being more likely to capsize in unwanted high-wind situations.
Also, it’s very difficult for a catamaran to recover from capsizing as opposed to a monohull sailboat that has a good ballast from its keel.
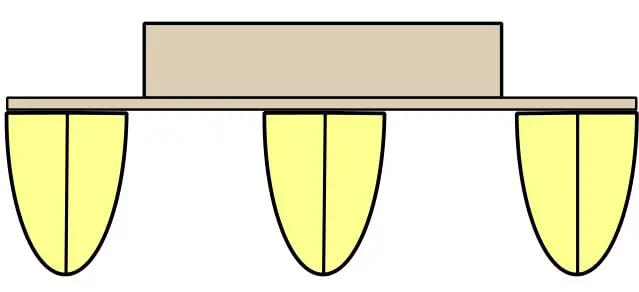
You might have already guessed from the name, but I’ll state the obvious anyway. A trimaran is exactly like a catamaran but with three hulls instead of two.
Often times you’ll see a trimaran look like a monohull sailboat with a pair of hulls attached to its side.
Similar to a catamaran, trimarans can hit speeds much greater than your average monohull sailboat. As a matter of fact, they’re known to be “unsinkable” under the situation that the hulls on the port and starboard side of the central hull are completely filled up with water.
One of the coolest aspects of having a trimaran is that when it has a planing hull and/or a hydrofoil, the trimaran’s central hull will lift completely out of the water.
This gives it the effect that it’s floating across the air, which is the result of lift produced from the planing hull or a hydrofoil. It’s very cool to see this!
Sailboat Hull Bottoms
Apart from the main boat hull styles, like the monohull, catamaran, and trimaran, there are hull bottoms that pop up in the world of boating that can differ in style and function.
These hull bottoms are more of a deeper look at the hulls of a monohull, catamaran, or trimaran, so you can think of them more as a feature of any of the previously mentioned styles of hull.
Flat Bottom
A very common hull bottom for boats that are derived from the planing hull type is a flat bottom hull.
The flat bottom hull is considered to be one of the less stable styles of hulls, especially when confronted with rough waters.
However, you’ll often find them on boats that don’t necessarily ride in these situations, including fishing or taxi areas.
- Good for small lakes and rivers due to having a shallow draft.
- Able to hit relatively high speeds once entering planing mode.
Disadvantages
- Not good at handling choppy waters resulting in a rough ride.
Round Bottom
When it comes to sailboats, you’re most likely going to run into monohull sailboats that have a displacement style hull with a round bottom.
While these are the most common hull bottom for sailboats, they can also be found on smaller boats that are used for fishing, canoeing, and other similar kinds of boats.
- Easily moves through the water due to being a displacement hull type.
- When accompanied by a keel, it produces a great amount of stability from the ballast.
- Without a keel, it can roll when entering and exiting the boat as well as when waves are present.
- Less maneuverable compared to other hull styles.
Deep ‘V’ Bottom
If you’re operating a powerboat, then in all likeliness your boat has a planing hull with a deep ‘V’ bottom.
Since deep ‘V’ bottoms are found on planing hulls, these types of boats will be able to pick up speed quickly and at high maximums. This is the most common setup for powerboats out on the water.
This is the most common type of powerboat hull. This hull type allows boats to move through rough water at higher speeds and they provide a smoother ride than other hull types.
- Provides a smooth ride compared to its flat bottom rival.
- Good at handling rough water.
- Requires more power to plane compared to its flat bottom rival.
- Cannot handle sharp turns very well resulting in potential rolling or banking.
Multi-Chine Bottom
We took a good look at multi-hull styles like the catamaran and the trimaran earlier, which are the exact style of hulls that have a multi-chine bottom.
A multi-chine bottom is a great example of a displacement hull on either a catamaran or trimaran as it’s the most common bottom you’ll find.
- In a multi-hull boat, it has a great amount of stability due to its wide beam.
- In a multi-hull boat, it needs a large area when either tacking or jibing.
Main Parts of a Sailboat Hull
There’s some terminology I threw around while describing the many types of hulls a sailboat and other types of boats have.
As is the case with a lot of activities, learning the terminology is just something you have to do.
Thankfully, the terminology will eventually sink in overtime and eventually you’ll be able to ring off any hull terminology that comes up.
The bow is simply the most forward part of a sailboat and, thus, the very front of the hull.
The stern, conversely to the bow, is the most backward part of a sailboat and, thus, the very end of the hull.
The port side of a hull is the left side. I always remember this with the phrase “I left my port on the table”, with the port being wine.
This just so happens to also be the side where boats will have a red light turned on at night, which is the color of port wine.
The starboard side of a hull is on the right side.
Opposite the port side, in the evening boats will have a green light turned on and will be located on the starboard side of the boat.
Fore is a sailor’s way of saying “forward”.
Aft is a sailor’s way of saying “back”.
A transom is the aft-most (see what I did there?) section of the boat that connects the port and starboard sections of the boat.
The flare of a hull is where the hull starts to form a large angle the closer the hull gets to the deck.
The waterline is the line around the hull where the water touches when under a normal load.
Waterline Length
The waterline length, once referred to as the Load Waterline Length (LWL), is the length of the hull where the waterline is located.
This is not the entire length of the boat.
Length Overall (LOA)
The length overall (LOA) is, you guessed it, the overall length of the boat. This is measured from the tip of the bow to the end of the stern.
The freeboard is the space on the hull of a boat above the waterline and below the deck.
The draft is the length from the bottom-most part of a boat (the tip of the keel on a sailboat) and the waterline.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Basics of Sailboat Hull Design – EXPLAINED For Owners
There are a lot of different sailboats in the world. In fact, they’ve been making sailboats for thousands of years. And over that time, mankind and naval architects (okay, mostly the naval architects!) have learned a thing or two.
If you’re wondering what makes one sailboat different from another, consider this article a primer. It certainly doesn’t contain everything you’d need to know to build a sailboat, but it gives the novice boater some ideas of what goes on behind the curtain. It will also provide some tips to help you compare different boats on the water, and hopefully, it will guide you towards the sort of boat you could call home one day.
Table of Contents
Displacement hulls, semi displacement hulls, planing hulls, history of sailboat hull design, greater waterline length, distinctive hull shape and fin keel designs, ratios in hull design, the hull truth and nothing but the truth, sail boat hull design faqs.

Basics of Hull Design
When you think about a sailboat hull and how it is built, you might start thinking about the shape of a keel. This has certainly spurred a lot of different designs over the years, but the hull of a sailboat today is designed almost independently of the keel.
In fact, if you look at a particular make and model of sailboat, you’ll notice that the makers often offer it with a variety of keel options. For example, this new Jeanneau Sun Odyssey comes with either a full fin bulb keel, shallow draft bulb fin, or very shallow draft swing keel. Where older long keel designs had the keel included in the hull mold, today’s bolt-on fin keel designs allow the manufacturers more leeway in customizing a yacht to your specifications.
What you’re left with is a hull, and boat hulls take three basic forms.
- Displacement hull
- Semi-displacement hulls
- Planing hulls
Most times, the hull of a sailboat will be a displacement hull. To float, a boat must displace a volume of water equal in weight to that of the yacht. This is Archimedes Principle , and it’s how displacement hulled boats get their name.
The displacement hull sailboat has dominated the Maritimes for thousands of years. It has only been in the last century that other designs have caught on, thanks to advances in engine technologies. In short, sailboats and sail-powered ships are nearly always displacement cruisers because they lack the power to do anything else.
A displacement hull rides low in the water and continuously displaces its weight in water. That means that all of that water must be pushed out of the vessel’s way, and this creates some operating limitations. As it pushes the water, water is built up ahead of the boat in a bow wave. This wave creates a trough along the side of the boat, and the wave goes up again at the stern. The distance between the two waves is a limiting factor because the wave trough between them creates a suction.
This suction pulls the boat down and creates drag as the vessel moves through the water. So in effect, no matter how much power is applied to a displacement hulled vessel, it cannot go faster than a certain speed. That speed is referred to as the hull speed, and it’s a factor of a boat’s length and width.
For an average 38 foot sailboat, the hull speed is around 8.3 knots. This is why shipping companies competed to have the fastest ship for many years by building larger and larger ships.
While they might sound old-school and boring, displacement hulls are very efficient because they require very little power—and therefore very little fuel—to get them up to hull speed. This is one reason enormous container ships operate so efficiently.
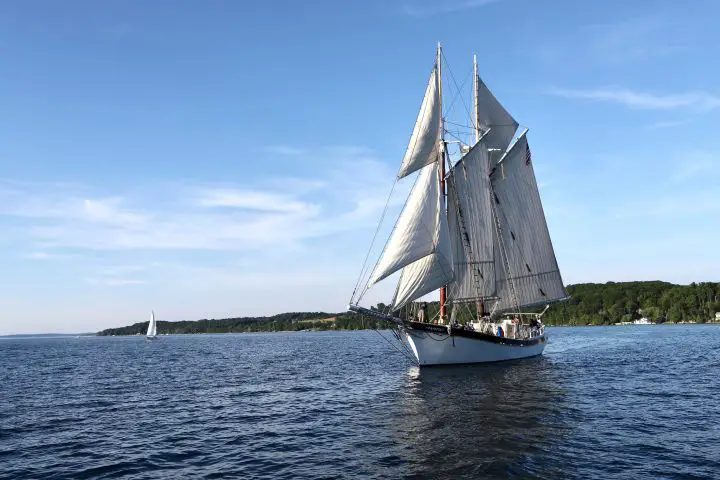

Of course, living in the 21st century, you undoubtedly have seen boats go faster than their hull speed. Going faster is simply a matter of defeating the bow wave in one way or another.
One way is to build the boat so that it can step up onto and ride the bow wave like a surfer. This is basically what a semi-displacement hull does. With enough power, this type of boat can surf its bow wave, break the suction it creates and beat its displacement hull speed.
With even more power, a boat can leave its bow wave in the dust and zoom past it. This requires the boat’s bottom to channel water away and sit on the surface. Once it is out of the water, any speed is achievable with enough power.
But it takes enormous amounts of power to get a boat on plane, so planing hulls are hardly efficient. But they are fast. Speedboats are planing hulls, so if you require speed, go ahead and research the cost of a speedboat .
The most stable and forgiving planing hull designs have a deep v hull. A very shallow draft, flat bottomed boat can plane too, but it provides an unforgiving and rough ride in any sort of chop.
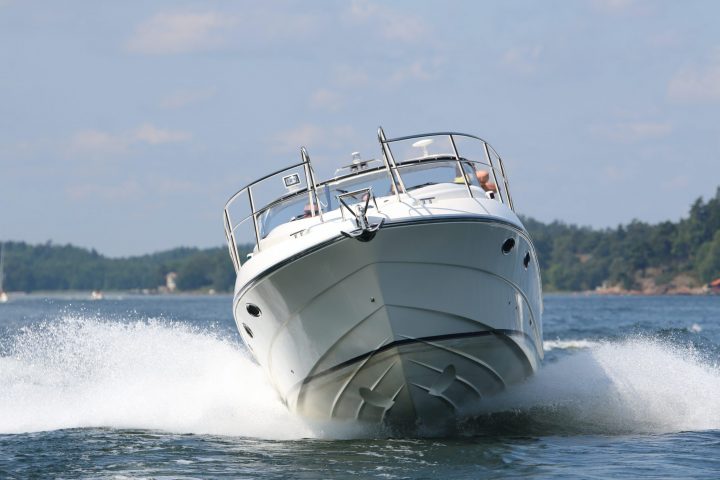

If you compare the shapes of the sailboats of today with the cruising boat designs of the 1960s and 70s, you’ll notice that quite a lot has changed in the last 50-plus years. Of course, the old designs are still popular among sailors, but it’s not easy to find a boat like that being built today.
Today’s boats are sleeker. They have wide transoms and flat bottoms. They’re more likely to support fin keels and spade rudders. Rigs have also changed, with the fractional sloop being the preferred setup for most modern production boats.
Why have boats changed so much? And why did boats look so different back then?
One reason was the racing standards of the day. Boats in the 1960s were built to the IOR (International Offshore Rule). Since many owners raced their boats, the IOR handicaps standardized things to make fair play between different makes and models on the racecourse.
The IOR rule book was dense and complicated. But as manufacturers started building yachts, or as they looked at the competition and tried to do better, they all took a basic form. The IOR rule wasn’t the only one around . There were also the Universal Rule, International Rule, Yacht Racing Association Rul, Bermuda Rule, and a slew of others.
Part of this similarity was the rule, and part of it was simply the collective knowledge and tradition of yacht building. But at that time, there was much less distance between the yachts you could buy from the manufacturers and those setting off on long-distance races.
Today, those wishing to compete in serious racing a building boat’s purpose-built for the task. As a result, one-design racing is now more popular. And similarly, pleasure boats designed for leisurely coastal and offshore hops are likewise built for the task at hand. No longer are the lines blurred between the two, and no longer are one set of sailors “making do” with the requirements set by the other set.
Modern Features of Sailboat Hull Design
So, what exactly sets today’s cruising and liveaboard boats apart from those built-in decades past?
Today’s designs usually feature plumb bows and the maximum beam carried to the aft end. The broad transom allows for a walk-through swim platform and sometimes even storage for the dinghy in a “garage.”
The other significant advantage of this layout is that it maximizes waterline length, which makes a faster boat. Unfortunately, while the boats of yesteryear might have had lovely graceful overhangs, their waterline lengths are generally no match for newer boats.
The wide beam carried aft also provides an enormous amount of living space. The surface area of modern cockpits is nothing short of astounding when it comes to living and entertaining.
If you look at the hull lines or can catch a glimpse of these boats out of the water, you’ll notice their underwater profiles are radically different too. It’s hard to find a full keel design boat today. Instead, fin keels dominate, along with high aspect ratio spade rudders.
The flat bottom boats of today mean a more stable boat that rides flatter. These boats can really move without heeling over like past designs. Additionally, their designs make it possible in some cases for these boats to surf their bow waves, meaning that with enough power, they can easily achieve and sometimes exceed—at least for short bursts—their hull speeds. Many of these features have been found on race boats for decades.
There are downsides to these designs, of course. The flat bottom boats often tend to pound when sailing upwind , but most sailors like the extra speed when heading downwind.

How Do You Make a Stable Hull
Ultimately, the job of a sailboat hull is to keep the boat afloat and create stability. These are the fundamentals of a seaworthy vessel.
There are two types of stability that a design addresses . The first is the initial stability, which is how resistant to heeling the design is. For example, compare a classic, narrow-beamed monohull and a wide catamaran for a moment. The monohull has very little initial stability because it heels over in even light winds. That doesn’t mean it tips over, but it is relatively easy to make heel.
A catamaran, on the other hand, has very high initial stability. It resists the heel and remains level. Designers call this type of stability form stability.
There is also secondary stability, or ultimate stability. This is how resistant the boat is to a total capsize. Monohull sailboats have an immense amount of ballast low in their keels, which means they have very high ultimate stability. A narrow monohull has low form stability but very high ultimate stability. A sailor would likely describe this boat as “tender,” but they would never doubt its ability to right itself after a knock-down or capsize.
On the other hand, the catamaran has extremely high form stability, but once the boat heels, it has little ultimate stability. In other words, beyond a certain point, there is nothing to prevent it from capsizing.
Both catamarans and modern monohulls’ hull shapes use their beams to reduce the amount of ballast and weight . A lighter boat can sail fast, but to make it more stable, naval architects increase the beam to increase the form stability.
If you’d like to know more about how stable a hull is, you’ll want to learn about the Gz Curve , which is the mathematical calculation you can make based on a hull’s form and ultimate stabilities.
How does a lowly sailor make heads or tails out of this? You don’t have to be a naval architect when comparing different designs to understand the basics. Two ratios can help you predict how stable a design will be .
The first is the displacement to length ratio . The formula to calculate it is D / (0.01L)^3 , where D is displacement in tons and L is waterline length in feet. But most sailboat specifications, like those found on sailboatdata.com , list the D/L Ratio.
This ratio helps understand how heavy a boat is for its length. Heavier boats must move more water to make way, so a heavy boat is more likely to be slower. But, for the ocean-going cruiser, a heavy boat means a stable boat that requires much force to jostle or toss about. A light displacement boat might pound in a seaway, and a heavy one is likely to provide a softer ride.
The second ratio of interest is the sail area to displacement ratio. To calculate, take SA / (D)^0.67 , where SA is the sail area in square feet and D is displacement in cubic feet. Again, many online sites provide the ratio calculated for specific makes and models.
This ratio tells you how much power a boat has. A lower ratio means that the boat doesn’t have much power to move its weight, while a bigger number means it has more “get up and go.” Of course, if you really want to sail fast, you’d want the boat to have a low displacement/length and a high sail area/displacement.
Multihull Sailboat Hulls
Multihull sailboats are more popular than ever before. While many people quote catamaran speed as their primary interest, the fact is that multihulls have a lot to offer cruising and traveling boaters. These vessels are not limited to coastal cruising, as was once believed. Most sizable cats and trimarans are ocean certified.
Both catamarans and trimaran hull designs allow for fast sailing. Their wide beam allows them to sail flat while having extreme form stability.

Catamarans have two hulls connected by a large bridge deck. The best part for cruisers is that their big surface area is full of living space. The bridge deck usually features large, open cockpits with connecting salons. Wrap around windows let in tons of light and fresh air.
Trimarans are basically monohulls with an outrigger hull on each side. Their designs are generally less spacious than catamarans, but they sail even faster. In addition, the outer hulls eliminate the need for heavy ballast, significantly reducing the wetted area of the hulls.
Boaters and cruising sailors don’t need to be experts in yacht design, but having a rough understanding of the basics can help you pick the right boat. Boat design is a series of compromises, and knowing the ones that designers and builders take will help you understand what the boat is for and how it should be used.
What is the most efficient boat hull design?
The most efficient hull design is the displacement hull. This type of boat sits low in the water and pushes the water out of its way. It is limited to its designed hull speed, a factor of its length. But cruising at hull speed or less requires very little energy and can be done very efficiently.
By way of example, most sailboats have very small engines. A typical 40-foot sailboat has a 50 horsepower motor that burns around one gallon of diesel every hour. In contrast, a 40-foot planing speedboat may have 1,000 horsepower (or more). Its multiple motors would likely be consuming more than 100 gallons per hour (or more). Using these rough numbers, the sailboat achieves about 8 miles per gallon, while the speedboat gets around 2 mpg.
What are sail boat hulls made of?
Nearly all modern sailboats are made of fiberglass.
Traditionally, boats were made of wood, and many traditional vessels still are today. There are also metal boats made of steel or aluminum, but these designs are less common. Metal boats are more common in expedition yachts or those used in high-latitude sailing.
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Pay My Bill
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter
- Give a Gift

How to Sell Your Boat

Cal 2-46: A Venerable Lapworth Design Brought Up to Date

Rhumb Lines: Show Highlights from Annapolis

Open Transom Pros and Cons

Leaping Into Lithium

The Importance of Sea State in Weather Planning

Do-it-yourself Electrical System Survey and Inspection

Install a Standalone Sounder Without Drilling

When Should We Retire Dyneema Stays and Running Rigging?

Rethinking MOB Prevention

Top-notch Wind Indicators

The Everlasting Multihull Trampoline

How Dangerous is Your Shore Power?

DIY survey of boat solar and wind turbine systems

What’s Involved in Setting Up a Lithium Battery System?

The Scraper-only Approach to Bottom Paint Removal

Can You Recoat Dyneema?

Gonytia Hot Knife Proves its Mettle

Where Winches Dare to Go

The Day Sailor’s First-Aid Kit

Choosing and Securing Seat Cushions

Cockpit Drains on Race Boats

Rhumb Lines: Livin’ the Wharf Rat Life

Re-sealing the Seams on Waterproof Fabrics

Safer Sailing: Add Leg Loops to Your Harness

Waxing and Polishing Your Boat

Reducing Engine Room Noise

Tricks and Tips to Forming Do-it-yourself Rigging Terminals

Marine Toilet Maintenance Tips

Learning to Live with Plastic Boat Bits
- Sailboat Reviews
Practical Sailor Takes a Look at Trends in Modern Boat Design
Is the quest for speed and interior comfort trumping smart design in todays sailboats.

Practical Sailor editors have noticed the increasing tendency in newer-model sailboats to be ill-mannered in gusty conditions. Establishing balance between the sails and the hull is one of the main factors in quality boat design. For correct trim, many things must be considered: the ballast package location, the combined longitudinal center of gravity (LCG), and the longitudinal center of buoyancy. At the same time, to maintain a balanced helm, the keel must promote sufficient lead (the fore and aft distance between the center of effort and the center of lateral resistance). To highlight how these boat design principles play out, Practical Sailor looks at classic sailboats such as the Bill Shaw-designed Pearson 32, Ericson 41, Valiant 40, and Peterson 44, and compares their keel/sail ratios and lead values to more modern sailboat designs such as the Catalina, Hunter, Tartan, and Beneteau.
In the course of taking out boats for testing, Practical Sailor editors have observed an increased tendency for new-model sailboats to be ill-mannered in gusty conditions. We have been watching this trend for several years, and it seems to be becoming more usual than unusual.
In a typical situation, we will be sailing the test boat on the wind in 12 or so knots of breeze and everything is fine. Then, the breeze picks up to about 15 knots and the helm loads up. OK, thats to be expected, so we flatten the main, drop down the traveler, and that takes care of it.
Then we get a puff. Were already on the point of needing to reef, so in the puff, were overcanvassed. Instead of just heeling farther, the boat begins to round up. Fighting it with the helm is hard work, and easing the main so it luffs doesn’t help much.

Photo by Ralph Naranjo
We take in a reef, which usually means we roll in a bit of the jib or a bit of the main, or both, and the helm lightens up. We trim to the new wind and sail along, a bit slower now in the light spots, but then the next gust comes along, and the helm immediately loads up again.
In the worst case weve experienced, the boat rounded up so quickly that it tacked, even though the helm was hard over in the opposite direction. To prove that wasnt a fluke caused by a temporary diversion into a parallel universe, it did the same thing on the other tack.
Practical Sailor editors are old enough to remember a generation of cruising boats that didnt behave in this manner. For sure, there have always been twitchy boats, but most, when hit by a gust, would heel a little more, put some pressure on the wheel or tiller, and once the boat picked up speed, the pressure would come right off. A boat like that will sail for a long time with a loose lashing on the helm.
So, where does this bad habit come from? Several trends in modern cruising yacht design can share the blame. One of them is builders inclination to tilt their designs toward the performance end of the cruisers spectrum. Many recent and current cruising boats, if suitably fitted out with racing sails and the hardware and software to tweak them, could put up an impressive show on the race course.
The sensitivity to trim that accompanies such potential isn’t always suited to cruising shorthanded or with a family, when balance and good manners are key both to enjoyment and, to a degree, safety.
Establishing Balance
Many factors contribute to the balance of a sailboat. The obvious and principal pair are the sails and the hull. When working up a new design, the architect develops these in close association, but both are in turn influenced by other aspects of the boats design as it evolves.
In the standard approach, the designer works up preliminary drawings to express the basic requirements of the design brief, which normally include a desired length, displacement, cabin arrangement, and sailplan to provide the desired performance.
He then sketches out the hull lines (the matrix of contours that define its three-dimensional shape and its volume) to enclose the interior and meet expressed performance goals. The preliminary lines also serve as a basis on which to perform a number of calculations, one of them being the location of the center of buoyancy (CB).
With everything roughed out, the designer then “weighs” every item that will go into the complete boat, from the hull laminate to the toothbrush holder, but excluding the ballast. He combines these weights and their locations on the three axes, X, Y, and Z, to calculate the center of gravity (CG) of the whole package. Computer programs have helped to speed up this process and make volume calculations more accurate, but the process hasn’t changed much.
For the boat to float on its desired lines, the ballast package must then be designed and located to bring the combined longitudinal CG (LCG) of hull and ballast to the same fore-and-aft location as the CB (LCB). Once everything has been resolved satisfactorily, the designer can finalize the lines, carry out the necessary calculations, and establish shape and locations for the keel and the sailplan.
On most boats of current design, the ballast also constitutes the fin keel, and in that role, its location determines the center of lateral resistance (CLR), which in conjunction with the center of effort (CE) of the sailplan, influences how the boat balances under sail.
Even as boat design procedures have evolved from three-dimensional modeling using half hulls, through two-dimensional modeling using pen on vellum, to three-dimensional virtual modeling on computers, the fundamental principles have remained constant. One of the fundamental values used for predicting the proclivities of a boats helm is the dimension termed “lead.” Lead, pronounced “leed,” is the fore and aft distance between the CE and the CLR, expressed as a percentage of the waterline length (DWL).
“Skenes Elements of Yacht Design,” as revised by Francis S. Kinney, and other references for yacht design provide rules of thumb for calculating lead from the sailplan and the hull profile. (See illustration above).
Looking at the diagram, its easy to see how lead is an elusive quantity. First of all, no boat sails with the sailplan as shown-the sails are never flat and on centerline. The traditional range for lead places the CE forward of the CLR by 14 to 19 percent of DWL. This value is lifted from “Skenes,” for years the first reference for any designer. Since that book was written and updated, hull forms have changed, and with them, optimum values for lead.
On designs with fin keels, lead is often calculated with reference to the keel alone. One feature remains constant whatever the design. Moving the centers closer together-reducing lead-increases the tendency to weather helm. Moving them apart reduces that tendency. If the lead is too great, the result may be lee helm, which is generally considered undesirable-and is in fact, rare.
In Kinneys prime years, the 1960s to the 1980s, the basic working sailplan of a sloop included a 150-percent genoa, which would have the effect of moving the CE closer to the CLR. Many designs today have headsails with short or even no overlap and very often a full-battened mainsail with lots of roach. The different aerodynamic characteristics of such rigs might well affect optimum lead, something which designers can only determine through experience. (If a boatbuilder offers an in-mast furling mainsail as an option, its effect on lead will differ from that of the “classic” sailboat.)
The effective CLR can also be very different from that calculated. On a deep-bodied, full-keel hull, that difference simply might be the difference between the geometric center and the center of hydrodynamic pressure of the whole profile.
A sharp bow with a pronounced “chin” might well move the effective CLR forward. On a modern, fin-keeled boat with a shallow, broad canoe body like that of a dinghy, the keel makes a proportionately larger contribution to lateral resistance, so the location of the keel will strongly influence where that resistance operates.
Obviously the rudder, too, is part of the lateral plane, but if our objective is to sail with light to neutral pressure on the helm, under normal conditions, it should not be making a significant contribution to lateral resistance. Its role is to provide a means to change the boats direction and to compensate for the constant fluctuations in the forces applied to the boat in the normal course of sailing. A certain amount of pressure in the form of weather helm helps by providing positive feedback to the helmsman on the state of balance. That said, on many racing hulls, the rudder is designed to contribute lift and has an active role in driving the boat to windward. (It is worth noting that those wide-bodied race boats also tend to have twin rudders.)
Then and Now
Even in the age of computer modeling, yacht design remains a series of compromises. At the moment, it seems the pendulum has swung to a point where high-volume, wide-beam shapes dominate. With them come large rigs to overcome skin drag and its negative effect in light air. As a result, theres a need to sail the vessel as flat as possible or suffer the consequences.
The sailplan and outboard profiles of boats from different eras represent the shift in yacht design that has occurred during recent decades. The modern boats have longer proportional waterlines, indicating higher potential speed. It also means that the boats immersed volume, or displacement, has been distributed over a greater length.
Given two boats of similar displacement like the classic Pearson 32 and the modern Tartan 3400 (above), the Tartan winds up with a shallower canoe body. This also contributes to its being potentially faster and, if both boats had the same draft, would give the keel a slight advantage in span, and therefore effectiveness to windward.
So far so good, but a shallower canoe body forces the cabin sole upward, especially if the belowdecks accommodations are to take full advantage of the wide beam favored in the modern hull. To achieve comparable headroom with its older counterpart, the cabintop has to go up, too, and to ensure sitting headroom on the settees under the sidedeck, so does the freeboard.
Ultimately, the whole deck moves upward. To ensure the boom doesn’t sweep everybody out of the cockpit during an unplanned jibe, the boom too goes up. If sail area is not to be compromised, the entire mainsail goes up, and with it, its center of effort. The bigger the boat, the less pronounced these differences become as the proportions become more relaxed.
Differences are visible, too, between the boats keels; the modern Tartans is smaller in area. While it might be claimed that less wetted surface promises higher sailing speeds in light air, some builders accept a smaller keel to simplify the manufacture of the hull.
In a perfect world, the designer draws a keel to suit the boats sail area and other characteristics, places it to obtain the desired sailing performance, then massages the needed ballast to both fit the keel and trim the boat correctly. The volume of the ballast is usually less than that of the keel, and the builder has to do some intricate laminating work to mold a keel to receive ballast internally or a stub to which to bolt it externally.
On many production boats today, the keels are bolted directly to the bottom of a fair canoe body, a practice which eliminates much labor. The consequence is that the area of the keel is determined by the weight, and therefore the volume, of the ballast. To achieve the desired hydrodynamic properties and mechanical strength-it mustnt bend under the influence of normal sailing loads-a given volume of ballast can be formed into a limited range of shapes. Placing ballast in a bulb at the bottom aids the keels efficiency by creating an endplate effect and raises stiffness by placing ballast low, but it means that the keels lateral plane is sharply reduced.
For a more dramatic representation of how changes in keel design can affect helm balance, compare a Cruising Club of America (CCA) design like the Ericson 41 above, to a modern equivalent with comparable sail area like the Beneteau 46.

When sailing, two boats are subjected to similar forces on the sails. Resisting that side force are the immersed hull, the keel, and the rudder. If the hulls offer similar resistance, the remaining force is shared between the keel and rudder. If one keel is smaller than the other (as is clearly the case here), the effect is to increase the share taken by the rudder.
When the sails are trimmed properly and all is in balance, the rudder will carry a small load. If however, you hit a gust, the rudder must pick up a high proportion of the added side thrust until balance is restored, usually by some adjustment to sail trim.
Simply put, boats of the general modern type are not forgiving in changeable conditions, say, for example when the apparent wind is in the 12- to 18-knot range. At the higher end, youd want to be reefed; at the lower end, probably not.
On a day when you expect the wind to soften rather than harden, youd rather not put in the reef, so that you can maintain speed in the lulls. In the puffs, you want your hands free to ease the traveler and flatten the jib, which is hard to do if the helm is a handful. Compounding the problem on most boats, the mainsail controls are usually not within reach of the helm.
On racing boats, such sensitivity isn’t an issue. On the contrary, sufficient crew are on hand to make adjustments on the fly as quickly and often as needed to keep the boat sailing at her fastest.
Cruising boats are often sailed shorthanded and by crews who are not looking for a constant physical workout. An autopilot might be doing most of the steering, and good balance is helpful in protecting it from having to work too hard-or from being overpowered.
Another striking difference between the older and newer designs is visible in the plan (overhead) view. By 1980, cruising-boat hulls were already becoming beamy relative to boats of the 1960s and 1970s. The current trend is to carry the beam aft, so that in the region of the rudder, its as much as 85 percent of the maximum beam, far wider than the 55 percent to 60 percent once considered acceptable. The principal beneficiary of this extra breadth is the boats interior-builders often offer twin double cabins aft where a generation ago they might have squeezed in a quarter berth and a cockpit locker. The cockpit, too, becomes roomier, and the transom, scooped and sculpted, is transformed into a swim platform and dinghy dock.

Photo by Jarrod Scanlon
All this additional boat aft adds weight aft, in both construction materials and outfit. To compensate, the ballast-that is to say, the keel-has to be fitted farther forward.
The full beam aft does provide a significant boost to the boats ability to carry sail. As the boat heels, the center of buoyancy moves quickly outboard, away from the center of gravity. This lengthens the righting arm, giving a positive contribution toward stability, but it also moves the immersed centerline of the hull away from the static centerline along which both the keel and the rudder are attached. Depending on the hulls shape, this can create a distortion in the immersed volume, which can in turn affect the dynamics acting on it.
Effect of Keel Area
Another factor entering the equation is the area of the keel. This, too, is apparent when comparing the drawings of the older and newer generation boats. Many of the standard tracts on the design of sailing yachts are, lets say, vague on what keel area is adequate or even desirable, although many designers have come up with their own formulas.
Because the keel is reacting in the water to forces generated on the sails by the wind, it makes sense that the area of a fin keel should be related in some way to sail area.
When naval architect Dave Gerr took over as director of the Westlawn Institute of Marine Technology, he found the course materials for sailing yacht design had little detailed explanation on this topic, a gap he subsequently filled. Briefly, he recommends no fin keel should be less that 2.5 percent of the sail area (mainsail 100 percent foretriangle) and need be no more than 5 percent. The smaller value is appropriate for a racing boat with a full crew aboard to trim and tweak the sails to every change in the wind. The larger area is suited to cruising boats, which need to be more forgiving to shorthanded crews.
Current Design Trends
In the past, racing measurement rules have been criticized because the boats designed to compete under them have become type-formed, sometimes with unwelcome consequences in how they handle. We might just as easily level criticism at present-day marketing and manufacturing methods for doing the same to cruising boats.
Lets face it, but for a few differences in sailplans and keel shapes, modern cruising sailboats are quite generic below the sheerline. They are all beamy; they carry their beam aft; they have long waterlines; they have dinghy-like underbodies; and they have spade rudders. The forces that have created this shape have at least as much to do with how many people can sleep and shower in them comfortably as with how the boats will sail.
Dishing out the hull shape in this manner makes it fairly easy to push through the water, but arranging the keel, rudder, and sails so they work in concert has become a more complex problem, exacerbated by having to compensate for extra weight of accommodations aft, something thats less of an issue in raceboats.
The byproduct of these design parameters is zesty performance, a bonus for the marketing department, but speed for its own sake is not the first priority of cruising sailors. In the brochure for the Beneteau 37, the boats polar diagram shows a maximum theoretical sailing speed of over 12 knots in 30 knots of wind. When cruising sailors encounter 30-knot winds, they are more likely to hunker down in the expectation it will blow even harder than they are to set the chute to go surfing. What they want is a boat that will take readily to hunkering, and all the signs indicate those boats are getting fewer in number . . . and they are mostly older designs.
- The Balancing Act
- Pearson 32 vs. Tartan 3400
- Ericson 41 vs. Beneteau 46
- Practical Sailor Design Guide
- The Modern Hull and Helm Balance
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

Island Packet 370: What You Should Know | Boat Review

How To Make Starlink Better On Your Boat | Interview

Catalina 380: What You Should Know | Boat Review
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology

Sailboat Design Evolution
- By Dan Spurr
- Updated: June 10, 2020
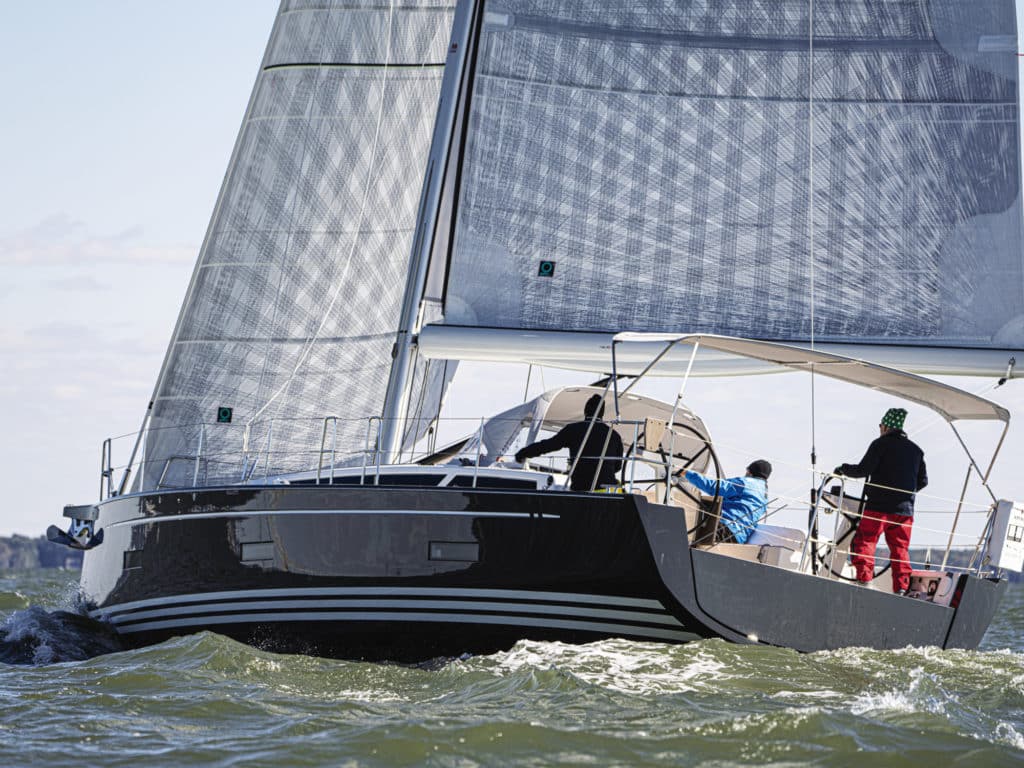

You know the old saying, “The more things change, the more they stay the same”? As a judge for the 2020 Boat of the Year (BOTY) competition at this past fall’s US Sailboat Show in Annapolis, Maryland, I helped inspect and test-sail 22 brand-new current-model sailboats. And I came away thinking, Man, these aren’t the boats I grew up on. In the case of new boats, the saying is wrong: “Nothing stays the same.”
OK, sure, today’s boats still have masts and sails, and the monohulls still have keels. But comparing the Hinckley Bermuda 40, considered by many to be one of the most beautiful and seaworthy boats of the 1960s, ’70s and even ’80s, with, say, the Beneteau First Yacht 53, which debuted at the show, is pretty much apples and oranges.
To get a better sense of what has happened to yacht design, boatbuilding and equipment over the past three, four or even six decades, let’s take a closer look.
Design Dilemmas
At the risk of oversimplification, since the fiberglass era began in the late 1940s and ’50s, the design of midsize and full-size yachts has transitioned from the Cruising Club of America rules, which favored all-around boats (racers had to have comfortable interiors) with moderate beam and long overhangs, to a succession of racing rules such as the IOR, IMS and IRC. All of them dictated proportions, and each required a measurer to determine its rating.

As frustration grew with each (no handicap rule is perfect), alternatives arose, such as the Performance Handicap Racing Fleet, which essentially based one’s handicap on past performance of the same boats in the same fleet. Also, one-design racing became more popular, which spread beyond identical small boats to full-size yachts, popularized in part by builders such as J/Boats and Carroll Marine. The ethos there was: Who cares about intricate rating rules? Let’s just go out and sail fast and have fun!
And that might best sum up the design briefs for the monohulls in this year’s BOTY competition: good all-around performance with comfortable, even luxurious accommodations. Gone are interiors that noted naval architect Robert Perry called “the boy’s cabin in the woods,” deeply influenced by stodgy British designers of the past century and their now-old-fashioned (though sea-friendly, one should note) concepts of a proper yacht, drawn and spec’d by the same guy who designed the hull, deck and rig. Today, dedicated European interior designers are specially commissioned to inject modernity, home fashion colors and textures, amenities, and more light—even dubiously large port lights in the topsides.

Overhangs, bow and stern, have virtually disappeared. Why? It seems largely a matter of style. Plus, the bonus of increased usable space below, not to mention a longer waterline length for a given length overall, which translates to more speed. Former naval architect for C&C Yachts and Hunter Marine, Rob Mazza, recalls that 19th-century pilot cutters and fishing schooners operating in offshore conditions generally had plumb bows, so in a sense, bow forms have come full circle.
Today’s boats are carrying their wide beam farther aft. Gone are the days of the cod’s head and mackerel tail. Wide, flat canoe bodies are decidedly fast off the wind, and might even surf, but they pay a comfort penalty upwind.
These boats have lighter displacement/length (D/L) ratios, which means flatter bottoms and less stowage and space for tanks. The Beneteau 53 has a D/L of 118, compared with the aforementioned Bermuda 40 of 373. Among entries in this year’s BOTY, the heaviest D/L belonged to the Elan Impression 45.1, with a D/L of 195. Recall that when Perry’s extremely popular Valiant 40 was introduced in 1975, the cruising establishment howled that its D/L of 267 was unsuitable for offshore sailing. My, how times have changed!
Perhaps more important, one must ask: “Have the requirements for a good, safe bluewater cruiser actually changed? Or are the majority of today’s production sailboats really best-suited for coastal cruising?”
The ramifications of lighter displacement don’t end there; designers must consider two types of stability: form and ultimate. As weight is taken out of the boat, beam is increased to improve form stability. And with tanks and machinery sometimes raised, ballast might have to be added and/or lowered to improve ultimate stability.
What else to do? Make the boat bigger all around, which also improves stability and stowage. Certainly the average cruising boat today is longer than those of the earlier decades, both wood and fiberglass. And the necessarily shallower bilges mean pumps must be in good shape and of adequate size. That’s not as immediate an issue with a deep or full keel boat with internal ballast and a deep sump; for instance, I couldn’t reach the bottom of the sump in our 1977 Pearson 365.

And how do these wide, shallow, lighter boats handle under sail? Like a witch when cracked off the wind. We saw this trend beginning with shorthanded offshore racers like those of the BOC Challenge round-the-world race in the early 1980s. As CW executive editor Herb McCormick, who has some experience in these boats, says, “They’ll knock your teeth out upwind.” But route planning allows designers to minimize time upwind, and cruisers can too…if you have enough room and distance in front of you. Coastal sailors, on the other hand, will inevitably find even moderate displacement boats more comfortable as they punch into head seas trying to make port.

A wide beam carried aft permits a number of useful advantages: the possibility of a dinghy garage under the cockpit on larger boats; easy access to a swim platform and a launched dinghy; and twin helms, which are almost a necessity for good sightlines port and starboard. Of course, two of anything always costs twice as much as one.
Some multihulls now have reverse bows. This retro styling now looks space-age. Very cool. But not everyone is sold on them. Canadian designer Laurie McGowan wrote in a Professional BoatBuilder opinion piece, “I saw through the fog of faddishness and realized that reverse bows are designed to fail—that is, to cause vessels to plunge when lift is required.” Mazza concurs: “Modern multihulls often have reverse stems with negative reserve buoyancy, and those are boats that really can’t afford to bury their bows.”

McGowan also cites another designer critiquing reverse bows for being noticeably wet and requiring alternative ground-tackle arrangements. The latter also is problematic on plumb bows, strongly suggesting a platform or sprit to keep the anchor away from the stem.
Rigging Redux
If there was a boat in Annapolis with double lower shrouds, single uppers, and spreaders perpendicular to the boat’s centerline, I must have missed it. I believe every boat we sailed had swept-back spreaders and single lowers. An early criticism of extreme swept-back spreaders, as seen on some B&R rigs installed on Hunter sailboats, was that they prevented fully winging out the mainsail. The counter argument was that so many average sailors never go dead downwind in any case, and broad reaching might get them to their destinations faster anyway—and with their lunch sandwiches still in their stomachs.
That issue aside, the current rigging configuration may allow for better mainsail shape. But as Mazza points out, it’s not necessarily simple: “By sweeping the spreaders, the ‘transverse’ rigging starts to add fore-and-aft support to the midsection of the mast as well, reducing the need for the forward lowers. However, spreader sweep really does complicate rig tuning, especially if you are using the fixed backstay to induce headstay tension. Swept spreaders do make it easier to sheet non-overlapping headsails, and do better support the top of the forestay on fractional rigs.”
Certainly, the days of 150 percent genoas are over, replaced by 100 percent jibs that fit perfectly in the foretriangle, often as a self-tacker.
Another notable piece of rigging the judges found common was some form of lazy jacks or mainsail containment, from traditional, multiple lines secured at the mast and boom; to the Dutchman system with monofilament run through cringles sewn into the sail like a window blind; to sailmaker solutions like the Doyle StackPak. This is good news for all sailors, especially those who sail shorthanded on larger boats.
Construction Codas
Improvements in tooling—that is, the making of molds—are easily evident in today’s boats, particularly with deck details, and in fairness. That’s because many of today’s tools are designed with computer software that is extraordinarily accurate, and that accuracy is transferred flawlessly to big five-axis routers that sculpt from giant blocks of foam the desired shape to within thousandths of an inch. Gone are the days of lofting lines on a plywood floor, taken from a table of offsets, and then building a male plug with wood planks and frames. I once owned a 1960s-era sailboat, built by a reputable company, where the centerline of the cockpit was 7 degrees off the centerline of the deck—and they were one piece!

Additive processes, such as 3D printing, are quickly complementing subtractive processes like the milling described above. Already, a company in California has made a multipart mold for a 34-foot sailboat. Advantages include less waste materials.
Job training also has had an impact on the quality of fiberglass boats. There are now numerous schools across the country offering basic-skills training in composites that include spraying molds with gelcoat, lamination, and an introduction to vacuum bagging and infusion.

The patent on SCRIMP—perhaps the first widely employed infusion process—has long ago expired, but many builders have adopted it or a similar process whereby layers of fiberglass are placed in the mold dry along with a network of tubes that will carry resin under vacuum pressure to each area of the hull. After careful placement, the entire mold is covered with a bag, a vacuum is drawn by a pump, and lines to the pot of resin are opened. If done correctly, the result is a more uniform fiberglass part with a more controlled glass-to-resin ratio than is achievable with hand lay-up. And as a huge bonus, there are no volatile organic compounds released into the workplace, and no need for expensive exhaust fans and ductwork. OSHA likes that, and so do the workers.
However, sloppy processes and glasswork can still be found on some new boats. Surveyor Jonathan Klopman—who is based in Marblehead, Massachusetts, but has inspected dozens, if not hundreds, of boats damaged by hurricanes in the Caribbean—tells me that he is appalled by some of the shoddy work he sees, such as balsa cores not vacuum-bagged to the fiberglass skins, resulting in delamination. But overall, I believe workmanship has improved, which is evident when you look behind backrests, inside lockers and into bilges, where the tidiness of glasswork (or lack thereof) is often exposed. Mechanical and electrical systems also have improved, in part due to the promulgation of standards by the American Boat & Yacht Council, and informal enforcement by insurance companies and surveyors.

We all know stainless steel isn’t entirely stainless, and that penetrations in the deck are potentially troublesome; allowing moisture to enter a core material, such as end-grain balsa, can have serious consequences. The core and fiberglass skins must be properly bonded and the kerfs not filled with resin. Beginning in the mid-1990s, some builders such as TPI, which built the early Lagoon cruising catamarans, began using structural adhesives, like Plexus, to bond the hull/deck joint rather than using dozens of metal fasteners. These methacrylate resins are now commonly used for this application and others. Klopman says it basically should be considered a permanent bond, that the two parts, in effect, become one. If you think a through-bolted hull/deck joint makes more sense because one could theoretically separate them for repairs, consider how likely that would ever be: not highly.
Fit-and-Finish
Wide transoms spawned an unexpected bonus; besides the possibility of a dinghy “garage” under the cockpit on larger boats, swim platforms are also possible. In more than one BOTY yacht, the aft end of the cockpit rotated down hydraulically to form the swim platform—pretty slick.
Teak decks are still around, despite their spurning for many years by owners who didn’t want the upkeep. In the 1960s and ’70s, they were considered a sign of a classy boat but fell from favor for a variety of reasons: maintenance, weight and threat of damaging the deck core (the bung sealant wears out and water travels down the fastener through the top fiberglass skin into the core). Specialty companies that supply builders, like Teakdecking Systems in Florida, use epoxy resin to bond their product to decks rather than metal fasteners. And the BOTY judges saw several synthetic faux-teak products that are difficult to distinguish from real teak—the Esthec installed on the Bavaria C50 being one example.

LPG tanks no longer have to be strapped to a stanchion or mounted in a deck box because decks now often incorporate molded lockers specifically designed for one or two tanks of a given size. To meet ABYC standards, they drain overboard. In tandem with these lockers, some boats also have placements or mounts for barbecues that are located out of the wind, obviating the common and exposed stern-rail mount.
Low-voltage LED lights are replacing incandescent bulbs in nearly all applications; improvements in technology have increased brightness (lumens), so some even meet requirements for the range of navigation lights. Advances in battery technology translate to longer life, and depending on type, faster charging. And networked digital switching systems for DC-power distribution also are becoming more common.
Last, I was surprised at how many expensive yachts exhibited at Annapolis had nearly the least-expensive toilets one can buy. Considering the grief caused by small joker valves and poorly sealed hand pumps, one would think builders might install systems that incorporate higher-quality parts or vacuum flushing, and eliminate the minimal hosing that famously permeate odors.
Dan Spurr is an author, editor and cruising sailor who has served on the staffs of Cruising World, Practical Sailor and Professional Boatbuilder. His many books include Heart of Glass , a history of fiberglass boatbuilding and boatbuilders .
Other Design Observations
Here are a few other (surprising) items gleaned from several days of walking the docks and sailing the latest models:
- Multihulls have gained acceptance, though many production models are aimed more at the charter trade than private ownership for solitary cruising. You’d have to have been into boats back in the ’60s and ’70s to remember how skeptical and alarmist the sailing establishment was of two- and three-hull boats: “They’ll capsize and then you’ll drown.” That myth has been roundly debunked. Back then, the only fiberglass-production multihulls were from Europe, many from Prout, which exported a few to the US. There are still plenty of European builders, particularly from France, but South Africa is now a major player in the catamaran market.
- The French builders now own the world market, which of course includes the US. Other than Catalina, few US builders are making a similar impact. In terms of volume, Groupe Beneteau is the largest builder in the world, and they’ve expanded way beyond sailboats into powerboats, runabouts and trawlers.
- Prices seem to have outpaced inflation, perhaps because, like with automobiles, where everyone wants air conditioning, electric windows and automatic transmissions, today’s boats incorporate as standard equipment items that used to be optional. Think hot- and cold-pressure water, pedestal-wheel steering, and full suites of sailing instruments and autopilots.
- More: design , print may 2020 , Sailboats
- More Sailboats

Balance 442 “Lasai” Set to Debut
Sailboat Review: Tartan 455

Meet the Bali 5.8

Celebrating a Classic

Kirsten Neuschäfer Receives CCA Blue Water Medal

2024 Regata del Sol al Sol Registration Closing Soon

US Sailing Honors Bob Johnstone

Bitter End Expands Watersports Program
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

How hull shape affects comfort at sea
- julianwolfram
- September 15, 2021
Understanding how your hull shape responds to waves will keep you and your crew safe and comfortable in a blow, says Julian Wolfram

Understanding how your hull shape responds to waves will keep you and your crew safe and comfortable. Credit: Richard Langdon
There are many desirable attributes sailors want in their cruising yacht.

Julian Wolfram is a physicist, naval architect, former professor of ocean engineering at Heriot-Watt in Edinburgh and a Yachtmaster Offshore who has cruised and raced for 45 years
Stability is obviously a crucial factor, but there are other important factors that should be considered when judging a sailing yacht and the balance of these will depend on the type of cruising envisaged and whether there may be some club racing involved.
Comfort, or seakindliness , is high on many people’s list and a boat that bounces around or slams in a choppy sea is generally shunned by all except hardened racers who will put up with any discomfort in the pursuit of speed.
However, most sailors likes to sail and a boat that can’t maintain a reasonable speed in light winds and frequently requires the use of the engine is also undesirable.
When the wind picks up a bit, a yacht that responds with a good turn of speed is a delight and can make the difference between arriving in daylight and tying up in the dark after a long passage.

A traditional long-keel working boat style cutter – Heard 35. Credit: Graham Snook
Finally, there is course-keeping and manoeuvrability .
A yacht where the helm can be left unattended for a minute or two can be a godsend to a short-handed crew , but the same crew will welcome good manoeuvrability when going into a crowded harbour or marina.
A yacht regarded as being ‘well-found’ is usually a boat that responds slowly and gently to the waves and doesn’t slam when sailing or motor-sailing up wind in a bit of sea, but she may not be the fastest boat out of the blocks.
Comfort depends on low accelerations, and research has shown that the travelling public feel ‘general discomfort’ when accelerations exceed 0.2g (more than 20% of the acceleration due to gravity).

A medium displacement fin and skeg sloop – Hallberg Rassy 352. Credit: Graham Snook/Yachting Monthly
To put this in context, the acceleration at the top of a big, very steep wave can reach 0.5g.
There are international standards on comfort, based on acceleration figures, that have to be met by operators of public transport systems and these are used in the design of manned and unmanned rail and road vehicles.
Whilst we can maintain the smoothness of rails and roads you can’t do the same for the sea, so ferries have ‘operability criteria’ that limit the sea conditions in which they can operate.
Of course bigger vessels are able to operate in more severe conditions than smaller ones. There are also Motion Sickness Indices based on accelerations that predict the number of passengers likely to be ill.
When it comes to small yachts it’s up to the skipper and crew to decide upon the conditions in which they will stay in port.

Light displacement, modern wide hull – Pogo 10.50
This decision should depend, at least in part, on how comfortable the yacht is in a seaway.
Now the comfort of yachts of the same size can be remarkably different. Take yachts of around 35ft or 10.6m long – a common yacht length.
Three examples show how much the displacement can vary for this size of vessel. The Heard 35, a traditional long keel working boat type design, weighs 12.7 tonnes; the Hallberg Rassy 352 , with quite a long keel but separate skeg-hung rudder, weighs 6.7 tonnes; and the Pogo 10.50, which has a very modern wedge-shaped hull with a narrow but deep lifting keel and spade rudder, weighs 3.6 tonnes.
Hull shape: Rolling
Consider these three yachts moored in a line when a fat motor boat goes past with a big wake.
The heave (lifting) force produced by the waves will depend on the yachts’ waterplane area and these will all be roughly the same for all three.
So, initially, they will all experience the same heave force. Now remember Newton’s famous law: force = mass x acceleration. This can be rewritten for boats as:-
Acceleration = Force/Mass (displacement + AV M)
Of course Newton’s Law is usually applied to objects in air, and when a boat moves in water it moves the water around it as well, and this must be accounted for.
This is known as the added virtual mass (AVM) and it will be broadly similar for all these yachts when heaving, and has the beneficial effect of reducing the acceleration.
When it comes to rolling, weight is also an advantage, given careful design and a metacentric height (GM – is the distance from the centre of gravity to the point where the vertical line through the centre of buoyancy, when heeled through a small angle, intersects the centreline. It is a measure of the initial stability or stiffness of a yacht (for small angles, GM multiplied by the angle of heel gives the righting lever) that is not unnecessarily large.

Does your boat slam or hobby-horse over waves? Knowing the difference helps you decide when you’re happy to put to sea and when you’d rather wait. Credit: Richard Langdon
The sail-carrying capacity of a yacht depends on the product of its displacement and GM, so if the displacement is large the GM can be smaller.
A lower GM will lead to lower angular accelerations and a more comfortable rolling motion.
Let’s assume that all the yachts will heel to the same angle when setting full sail in a light breeze on a close reach.
The Heard sets 92 sq. m, with its topsail up, the Hallberg Rassy 64 sq. m and the Pogo 71 sq. m which means the Heard can have a lower GM than the Hallberg Rassy and both can be lower than the Pogo.
Continues below…

How keel type affects performance
James Jermain looks at the main keel types, their typical performance and the pros and cons of each

Hallberg-Rassy 40C: The best sailing boat Hallberg-Rassy has ever built?
The Swedish yard is turbo-charging its range of offshore cruisers, but have they left good old-fashioned seaworthiness behind? Theo Stocker…

Downwind secrets of ocean sailors
How do you choose which sails to set or what course to steer, and can you stop the boat rolling?…

What makes a boat seaworthy?
What characteristics make a yacht fit for purpose? Duncan Kent explores the meaning of 'seaworthy' and how hull design and…
The result is that the Pogo 10 will accelerate nearly twice as quickly as the Heard 35 and about 30% more quickly than the HR352.
So the Pogo 10 motion will be lively whereas the Heard 35 will respond slowly and the HR352 will be somewhere in the middle.
A single wave breaking against the side of the hull will be more noticeable jerk in the Pogo 10 than in HR352 and less noticeable again in the Heard 35.
Interestingly the late Ed Burnett, in discussing the design for his long keeled yacht Nomad , decided against a carbon fibre mast and in favour of a wooden one so as to keep GM smaller and the rolling motion more comfortable.

Credit: Maxine Heath
The reasoning behind this decision is reflected in the diagram above, which shows the estimated roll angles and corresponding angular accelerations for our three yachts whilst on their moorings with waves on the beam.
In a harbour with a 6-knot speed limit the waves generated by passing craft will be between 2m and 6m long, enough to get resonant rolling of the Pogo 10.
But it needs a passing vessel to go at 9 knots to get the Heard 35 to roll.
More significantly, although the maximum roll angles are reasonably similar, the acceleration is much higher for the light Pogo 10.
No wonder racing crews tend to sleep ashore whenever possible. (It should be mentioned that these curves are based on simple linear theory and it is assumed the damping is the same in each case, however these approximations do not affect the broad thrust of the results.)
So in general, for a given length of boat, a greater displacement will result in a more comfortable motion in the sort of waves you might encounter in an anchorage.
Of course the bigger the boat the greater the comfort, and large vessels don’t move much when the fishing boats tear out at 0400!
Hull shape: Pitching
When sailing, of course, the sails will damp out the rolling motion but not the heaving and pitching.
The diagram below shows our yachts going into head seas at 5 knots. Here the wave height is 30cm with a wavelength of 5m.

This goes up to 1.3m when the wavelength is 35m, which is roughly what may happen when the sea rises as the wind increase to Force 6 (25 knots).
The natural period of pitching is larger for a heavy yacht and resonant pitching will occur when driving into longer and generally higher waves than for a lighter yacht.
This is the one occasion when heavy displacement can be a negative in terms of comfort.
The more symmetrical hulls normally associated with heavy displacement have less damping and tend to ‘hobby horse’ in these conditions.
However, they can drive through a short chop comfortably with small accelerations when the light boat is having a more torrid time.
Of all the yacht motions, slamming is often the one that produces the most discomfort and accelerations of over 3g have been measured by Southampton University on racing yachts going upwind.
Slamming was first studied analytically by Theodore Von Karman in connection to seaplane floats in 1929.
Von Karman studied, among other things, the vortex shedding behind slender cylinders, now known as a Karman Street, that gives rise to the strumming vibration of rigging and halyards in high winds.
He showed how important it was to have a ‘V’ shape to the bottom of a seaplane float to reduce the slamming impact on landing. Naval architects call the angle the hull makes with the horizontal at the centreline the ‘dead rise’ .

So a flat bottom has 0° dead rise.
Von Karman showed if you doubled the deadrise angle the impact force should half.
Impact pressure = 1/Tangent of deodorise angle
So, approximately if you increase the deadrise angle from 5o to 10° you halve the impact pressure and significantly reduce the slamming. (This formula doesn’t work when there is no deadrise, i.e. a flat bottom, and Von Karman produced a more complex analysis for this case).
Unfortunately, a trend was started in the 1970s to give sailing yachts flat-bottom bows following the introduction of the International Offshore Rating rule.
The rule wanted to get an estimate of displacement for each yacht without actually weighing it. That was considered too difficult at the time.
So they introduced a complex series of measurements to various points around the hull beneath the waterline including some at the bow.
However, yacht designers soon started to distort the hull shape at the measurement points to kid the rule that a light hull was actually heavier, which gave the yacht a better handicap than would otherwise be the case.

The diagram above shows what was typically done in the bow region to get a lighter boat with lower wetted surface area.
My first personal experience of this trend came in the 1980s when I changed my Trapper 500 for a Westerly Fulmar.
The Fulmar was quicker and had much better accommodation, but it was much more prone to slamming.

A Trapper 500 with V-shaped bow sections
I remember motor-sailing, to catch a tide, down the Irish coast into a short chop when it seemed to slam on every other wave.
The Trapper, on the other hand, rarely slammed even when my kids decided to take a shortcut through overfalls at the top of Skye while I was having an off-watch nap below – it was the pitching that woke me, not any slamming.
The photos show clearly the difference in bow shape.
A ‘V’ or well-rounded bow shape is the best to avoid slamming and if there is any flat area near the bow it should be small to ensure the deceleration on a slamming impact is minimised.

The Westerly Fulmar has a flattened section aft of the bow
If you look at lifeboats and RIBs you will see they have deadrise angles of at least 20o, even at the stern.
Going at high speed in a flat-bottom boat through a steep chop can be an ankle-shattering experience!

Draw a chalk line perpendicular to the centre line and view from ahead to get a sense of your boat’s boat sections. Credit: Julian Woolfram
Drawing a chalk line around the hull mid way between the bow and the keel from the waterline on one side to the waterline on the other side and viewing from the bow will give a good impression of how seakindly, or otherwise, the bow is.
If you have the body plan for the hull look at the shape of the sections near the bow.
Hull shape: Wave slap
Now look at the stern, if it is wide and rises at a shallow angle through the waterline to accommodate a spacious aft cabin, it will probably suffer from ‘wave slap’.
Ideally the angle should be about 17o.
Much steeper, especially on a wide stern, and water flow separation will increase drag; much shallower and there will be wave slap (see below).

I watched a fat little fishing boat going out at a fair lick from an inner berth in Le Crouesty marina last year and nearly half the sailing yacht sterns it passed were slapped on their undersides by its wake.
Not a great way to wake up (excuse the pun) in your sumptuous aft cabin at 0530.
Above and below decks
The other factor to consider in how your crew will experience the seakindliness of any boat is where they are on the boat.
We all know that sleeping in the bow cabin at sea can be like a fairground ride compared to the saloon.
A good sea boat will have this factored into its cockpit and accommodation arrangement, with everything that will be used at sea in the middle third of the boat’s length – heads, chart table, galley and sea berths all need to be here, close to the point of minimum motion just aft of amidships and close to the waterline (see below).

The same is true on deck.
Ideally the helmsman and crew should be able to operate the boat from the forward part of the cockpit and not have to go forward of the mast, or to be perched right at the stern.
While many larger boats, and some boats as small as 30ft, now have twin wheels shoved out to the aft quarters to create more cockpit space and a better view forward, this isn’t the most comfortable place to be.
Tiller steering on small boats is no bad thing as it allows the helm to be much further forward, where there is less motion and more shelter.

Seaberths, galley heads and chart table in the middle third of the boat provide more comfort at sea. Credit: Graham Snook
However, another person’s ideal sea boat may be very different to mine.
It’s just important to understand the difference that their design makes to the conditions you are happy to set out in, understanding when it’s going to be uncomfortable, and how to handle your boat when the wind does get up.

Editor’s Choice: 18 Bluewater Sailboats We Love
Advantages of bluewater sailboats, factors to consider when buying a blue water sailboat, allures 51.9, contest 55cs, discovery revelation 480, grand soleil 42 lc, hallberg-rassy 48mk ii, island packet 349, j/boats j/45, najad 395 cc, outbound 56.

Looking to sail the open seas? Bluewater sailboats are your answer. With their sturdy construction and ability to handle rough conditions, these boats are designed for serious offshore sailing adventures. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of blue water sailboats and provide you with everything you need to know. From their unique features to their advantages and considerations, we will explore it all.
Bluewater sailboats are known for their strength and durability. Built to withstand the challenging conditions of ocean crossings, these boats offer stability and safety on long voyages. Whether you’re planning a solo trip or setting off with a crew, a blue water sailboat is an excellent option to explore the depths.
We will discuss the key characteristics that make blue water sailboats stand out, such as their hull design, rigging, and navigation systems. Additionally, we’ll explore the various types and sizes available to help you find the perfect fit for your sailing aspirations.
So, if you’ve ever dreamed of embarking on a thrilling ocean adventure, join us as we navigate the world of bluewater sailboats and uncover everything you need to know.
Bluewater sailboats are designed to withstand the demanding conditions encountered during long ocean voyages. They possess several key characteristics that set them apart from other types of sailboats.

1. Sturdy Construction
Bluewater sailboats are built with robust materials and construction techniques to ensure their strength and durability. They feature reinforced hulls made of fiberglass, aluminum, or steel, which can withstand the impact of large waves and adverse weather conditions. These boats are designed to handle the constant stresses of offshore sailing without compromising their structural integrity.
2. Seaworthiness
One of the defining characteristics of bluewater sailboats is their seaworthiness. They are designed to handle rough seas and strong winds, providing a stable and comfortable ride even in challenging conditions. The shape of their hulls, with a deep V or modified full-keel design, allows them to cut through waves and maintain stability, minimizing the rolling motion commonly experienced on other types of sailboats.
3. Self-Sustainability
Bluewater sailboats are equipped with systems that enable self-sustainability during long voyages. They typically have large water and fuel tanks, allowing sailors to carry ample supplies for extended periods at sea. In addition, these boats often come equipped with renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines, reducing the reliance on external power sources.
Bluewater sailboats offer numerous advantages for sailors looking to embark on offshore adventures. Here are some of the key benefits of choosing a blue water sailboat for your next sailing journey.
1. Safety and Stability
When sailing across vast oceans, safety is paramount. Bluewater sailboats provide a high level of safety and stability, thanks to their sturdy construction and seaworthiness. These boats are designed to handle adverse weather conditions and rough seas, ensuring the safety of the crew and the vessel. The robust hulls and well-balanced designs make them less prone to capsizing or taking on water, providing peace of mind during long voyages.
2. Long-Distance Capability
Bluewater sailboats are specifically designed for long-distance sailing. They have the capacity to carry ample supplies, including food, water, and fuel, allowing sailors to embark on extended journeys without the need for frequent resupply stops. With their self-sustainability features and efficient hull designs, these boats can cover long distances efficiently and comfortably.
3. Comfort and Liveability
Living aboard a bluewater sailboat for an extended period requires comfort and practicality. These boats are designed with spacious interiors, allowing for comfortable living quarters during long voyages. They often feature multiple cabins, a well-equipped galley, and ample storage space for provisions and personal belongings. The layout and design of blue water sailboats prioritize functionality and convenience, ensuring a comfortable living experience even in the middle of the ocean.
And now… it’s time to discover together our selection of 18 Bluewater sailboats we love!
The Allures 51.9 innovates with its full-beam aft owner’s cabin. This model disrupts the codes of the yard also outside with its cockpit of 6 meters long with sunbath and swim platform for comfort; the navigation space can be protected by a hardtop to navigate in any security. The boat has a length of 51.9 feet (15.8 meters) and a beam (width) of 15.4 feet (4.7 meters). It is equipped with a fixed keel and a composite hull, which provides good stability and seaworthiness. The Allures 51.9 is available in a variety of configurations, including a three-cabin layout with a spacious owner’s cabin and two guest cabins, or a two-cabin layout with a larger owner’s cabin and a smaller guest cabin. It is also equipped with a well-equipped galley, a large saloon, and a navigation station. Allures official website .

In a dynamic evolution and complementary to their range, Amel launched a larger model, with a higher specification and built with attention to details. Riding on the success of the Amel 50 , the Amel 60 is an enhanced version of the new Amel design . The brand’s fundamental characteristics are well represented in this large yacht, with an additional 10 feet increasing her volume as well as her interior and exterior living spaces, while still ensuring ease of use for a small crew.
Signed Berret-Racoupeau, the generous volumes of this large yacht have been designed to allow owners and their guests to fully enjoy life on board, while preserving everyone’s privacy: a large living space in the saloon, an ultra-equipped high-end galley three cabins each with a bathroom, an even larger protected cockpit, opening onto sunbathing areas ideal for relaxation.

The Dutch specialist in semi-custom constructions Contest Yachts presented the brand new 17-metre Contest 55CS at Boot Dusseldorf 2020. Don’t call it “simply” a bluewater yacht. The stunning lines both above and below water from star designers Judel/Vrolijk shall ensure a real sporty character. A newly conceived interior styling now features an even bigger flowing corner radius to the exquisitely finished timber work. There are also now more optional hull windows in up to four stations along the yacht’s length.

Discovery Yachts presented the new Revelation 480 at Boot Dusseldorf 2020 . This is the first model of the new Revelation line and differs from the Southerly line for the fixed keel and the lowered saloon. Yes, the Revelation 480 is a lowered saloon boat based on the well-known Southerly 480. The Revelation 480 combines bluewater capability with a low, sleek coachroof that contributes to an interesting aesthetic. Down below, the single level interior is extremely light and exquisitely furnished.

The Grand Soleil 42 LC is Cantiere del Pardo ’s latest entry model of the bluewater line. Comfort and sailing autonomy are the main features of this 12-meter, designed by Marco Lostuzzi together with Nauta Design and Cantiere del Pardo’s Technical Office.
The 42 LC is available in two versions; standard or sport. The former is equipped with aft benches, and a carbon arch over the cockpit, designed to keep this area free of the mainsheet traveller. The GS 42 LC’s hull guarantees great stability thanks to greater hull volume. The well-proportioned sail plan optimizes the high-performance sailing standards. As with the rest of the Long Cruise range, the Grand Soleil 42 LC is designed to provide greater and more luxurious comfort on board.
The interior layout is available with either two or three cabins, to meet the client’s needs. Both versions include two heads with a shower. In the saloon, a three-seater sofa is found on the starboard side, while the central seat can be transformed into a chart table.

The Hallberg-Rassy 48 MK II is a true bluewater cruiser that offers more natural light, more comfort and more elegance than ever before. With three double cabins and a vast saloon, she offers great space for modern comfort aids. Known far and wide for sturdy construction, superb craftsmanship and signature seaworthiness, Hallberg-Rassy boats are globally respected for their elegant lines and spirited performance.

Hylas Yachts has collaborated with German Frers for over 40 years and built a reputation for yachts that combine ocean sailing capability, classic lines and exquisitely finished interiors. Now the company is staking out new territory with the H60. Still ocean capable, still with an exquisite interior but also embracing some of the contemporary demands of today’s cruising sailors.
Longtime Hylas fans will not be disappointed by her performance. Built using the most advanced construction technologies, the H60 has been designed to excel in all conditions with excellent seakeeping ability. A plumb bow and broad transom make the most of her waterline length underway, providing speed with optimal comfort.
The builder partnered with Milan-based firm Hot Lab , known for their elegant designs in the superyacht world, to offer interiors that immediately set the new Hylas on a new level.

The project of the ICE 70 by ICE Yachts has been realized using the most advanced modeling and analysis software available today. “ Thanks to the new virtual reality ‘tools’ ,” explains Felci Yacht Design , “ we have been able to make the owner and the shipyard participant of many geometric and stylistic choices. It is a yacht with high technological potential, starting from the design of the hull and the appendices “. With this sporty bluewater sailboat, the Italian yard wanted to create a technologically avant-garde boat with large, comfortable indoor and outdoor spaces, which is easy to sail and entirely safe at sea. Like all ICE Yachts models, the ICE 70 is a semi-custom product with which the owner has many possibilities for customization and equipment. ICE Yachts official website

With this model, iconic Island Packet has returned to the Solent-style rig as standard, featuring a mainsail with a working jib and an optional lightweight 170% reacher or asymmetrical that mounts on the integral bow platform and furled with Harken systems. The working jib is fitted with a Hoyt Boom that is self-tending and improves performance with its close sheeting and self-vanging feature, while the large optional reacher or asymmetrical boost performance in light air or when off the wind.
The fully battened mainsail is equipped with a low friction Battcar system and drops easily into a stack pack with an integral cover and lazy jack system. This rigging offers ease of use and versatility in the varied wind or sea conditions and increased speed and maneuverability.

The J/Boats J/45, is a true bluewater sailing yacht, designed and built for the sea by life-long sailors. The J/Boats and J/Composites teams have collaborated to create a special design for discerning sailors seeking an exceptional sailing experience. The J/45 can be sailed solo, cruised by 2-3 couples or large family, and pleasure sailed or raced with room for the whole crew. This is an investment-grade sailboat that won’t require a professional crew to sail, handle or maintain. J/Boats official website

The Kraken 50 is designed to be the short-handed bluewater cruising yacht. Due to her steady motion and stability, her crew will be equally comfortable at sea or in the anchorage, and special consideration has been given in the K50 layouts above and below deck to allow for short-handed ocean passage making. The Kraken 50 features the renowned integral Zero Keel and fully skegged rudder.

N395 CC (centre cockpit) is part of the all-new Najad 395 range, designed in a joint venture by Najad, Farr Yacht Design, and Ken Freivokh Design – superyacht stylist, architects, and interior designers. The N395 CC is characterized by a well-protected large cockpit located close to the center of gravity. It has a well-designed interior and a very comprehensive options list that includes all equipment necessary to tailor the yacht to any individual needs. This model is available in two or three cabin layouts with one or two large heads.

Welcome aboard the newest addition to Outbound’s impressive line of offshore passage makers. The new Outbound 56, built from German Frers timeless and proven design continues to fulfill our single mission of building great offshore yachts. Fast, accommodating and gorgeous, the 56 will take you anywhere your heart desires in style and comfort.

The entry level yacht for the ‘G6’ range of seven models up to the Flagship Oyster 118. Using the latest generation of Oyster hull shapes, developed with Humphreys Yacht Design, the Oyster 565 is designed for family sailing without professional crew.
A generous sail locker and lazarette, headroom and bunk lengths to match the larger Oyster Superyachts, the 565 can be configured with many different cabin layouts – and for the first time in Oyster Yachts – can have the master cabin forward and a dinghy garage in the transom.

The Brittany based yard is well known not only among ocean sailors but also to those who love short-handed sailing and are looking for seaworthy and easily driven bluewater sailboats, both safe and comfortable. This last aspect is where Fora Marine has made great progress in the last few years, shedding some of the spartan image that characterized their products for many years.
What has not changed, and what is still the RM range’s defining characteristic, is the twin-chined hull, made of Okumé plywood impregnated with epoxy resin (the deck is in fiberglass sandwich). Below the hull, the yard offers two options, a single deep keel or double shoal draft keels. The RM are designed by Marc Lombard, probably one of the architects most able to transform the fashionable chine into an important element in cruising design. A chined hull, when properly drawn, gives both better hull shape and interior volumes. ( Read our test )

The Rustler 42 is a classic looking yacht which combines style that is traditional yet modern. Her cruising layout results in a live aboard yacht that has stability and elegance with the same unique sea-kindly characteristics as the Rustler 36. Below the waterline, she looks conservative with a deep canoe body, long fin keel and a big skeg hung rudder.
Below the decks, this yacht has a spacious open plan saloon. The large, finished saloon table can comfortably seat eight. The aft cabin has standing headroom, a full-width double berth and plenty of storage within lockers and a vanity unit with seat. The aft head incorporates a shower unit and a ‘wet lilies’ locker. At the forepeak the grand master cabin has a 6 ft 6 in double V berth.

Signed by German Frers , the Swan 58 needs to combine the spaces of bluewater sailboats with a fast cruiser performances. Key details include a deck featuring soft and rounded shapes, a new cockpit design, a redefined coach-roof style and large swimming platform. The concept is easy: to give the maximum comfort and liveability at rest, together with maximum efficiency for short handed sailing, without losing the capability to race with a full crew.
The interiors of the new Swan 58 , which is fitted with European oak, have been conceived as a combination between luxury and comfortable living spaces, storage and volumes for systems and safety features; we find here a large saloon, a galley with a 360 degree layout and three heads. Various interior styling layouts are available varying woods and materials.

Designed by Tartan naval architect Tim Jackett, the 395 comes out of the Tartan factory in Fairport Harbor and is the perfect example of bluewater sailboats. Her hull shape is an evolution of tried and true concepts proven to deliver great stability and high interior volume while maintaining comforting manners throughout a wide range of sailing conditions. On deck Tartan 395 sports hallmark Tartan design elements such as a traditional cabin house fitted with functional polished stainless steel rectangular portholes.
Like her smaller sister 345, 395’s handcrafted interior is built in maple as standard, with cherry a no-charge option. The lighter maple opens up her interior in ways the darker cherry simply cannot.
Group Beneteau: Record full-year earnings in 2023
The countdown has begun for the new ice 66 rs, lagoon 60, freedom of space and panoramic views, setting sail with swan 51: a milestone in performance cruisers, live your passion, subscribe to our mailing list.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Boat Designs: Exploring Sail Shape, Masts and Keel Types in 2023
- June 4, 2023

When it comes to sail boat designs, there is a wide array of options available, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. From the shape of the sails to the number of masts and the type of keel, every aspect plays a crucial role in determining a sailboat’s performance, stability, and manoeuvrability. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fascinating world of sail boat designs, exploring the various elements and their significance.
Table of Contents
The sail shape is a fundamental aspect of sail boat design, directly impacting its speed, windward performance, and maneuverability. There are several types of sail shapes, including:
1. Bermuda Rig:
The Bermuda rig is a widely used sail shape known for its versatility and performance. It features a triangular mainsail and a jib, offering excellent maneuverability and the ability to sail close to the wind. The Bermuda rig’s design allows for efficient use of wind energy, enabling sailboats to achieve higher speeds. The tall, triangular mainsail provides a larger surface area for capturing the wind, while the jib helps to balance the sail plan and optimize performance. This rig is commonly found in modern recreational sailboats and racing yachts. Its sleek and streamlined appearance adds to its aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice among sailors of all levels of experience.
2. Gaff Rig:
The Gaff rig is a classic sail shape that exudes elegance and nostalgia. It features a four-sided mainsail with a gaff and a topsail, distinguishing it from other sail designs. The gaff, a horizontal spar, extends diagonally from the mast, providing additional area for the mainsail. This configuration allows for a taller and more powerful sail, making the Gaff rig particularly suited for downwind sailing. The Gaff rig offers a traditional aesthetic and is often found in vintage and classic sailboats, evoking a sense of nostalgia for a bygone era of maritime exploration. The distinctive shape of the Gaff rig, with its graceful curves and intricate rigging, adds a touch of timeless charm to any sailboat that dons this rig.
3. Lateen Rig:
The Lateen rig is a unique and versatile sail design that has been used for centuries in various parts of the world. It features a triangular sail that is rigged on a long yard, extending diagonally from the mast. This configuration allows for easy adjustment of the sail’s angle to catch the wind efficiently, making the Lateen rig suitable for a wide range of wind conditions. The Lateen rig is known for its ability to provide both power and maneuverability, making it ideal for small to medium-sized sailboats and traditional vessels like dhow boats. Its versatility allows sailors to navigate narrow waterways and make tight turns with ease. The distinctive silhouette of a sailboat with a Lateen rig, with its sleek triangular sail and graceful curves, evokes a sense of adventure and a connection to seafaring traditions from around the world.
Number of Masts
The number of masts in a sail boat design affects its stability, sail area, and overall performance. Let’s explore a few common configurations:
1. Sloop Rig:
The sloop rig is one of the most popular and versatile sail boat designs, favoured by sailors around the world. It consists of a single mast and two sails—a mainsail and a jib. The sloop rig offers simplicity, ease of handling, and excellent performance across various wind conditions. The mainsail, situated behind the mast, provides the primary driving force, while the jib helps to balance the sail plan and improve manoeuvrability. This configuration allows for efficient upwind sailing, as the sails can be trimmed independently to optimize performance. The sloop rig is commonly found in modern recreational sailboats due to its versatility, enabling sailors to enjoy cruising, racing, or day sailing with ease. Its streamlined design and sleek appearance on the water make it both aesthetically pleasing and efficient, capturing the essence of the sailing experience.
2. Cutter Rig:
The cutter rig is a versatile and robust sail boat design that offers excellent performance, especially in challenging weather conditions. It features a single mast and multiple headsails, typically including a larger headsail forward of the mast, known as the cutter rig’s distinguishing feature. This configuration provides a wide range of sail combinations, enabling sailors to adjust the sail plan to suit varying wind strengths and directions. The larger headsail enhances the boat’s downwind performance, while the smaller headsails offer increased flexibility and improved balance. The cutter rig excels in heavy weather, as it allows for easy reefing and depowering by simply reducing or eliminating the headsails. This design is commonly found in offshore cruising sailboats and has a strong reputation for its reliability and seaworthiness. The cutter rig combines versatility, stability, and the ability to handle adverse conditions, making it a preferred choice for sailors seeking both performance and safety on their voyages.
3. Ketch Rig:
The Ketch rig is a sail boat design characterized by the presence of two masts, with the main mast being taller than the mizzen mast. This configuration offers a divided sail plan, providing sailors with increased flexibility, balance, and versatility. The main advantage of the Ketch rig is the ability to distribute the sail area across multiple sails, allowing for easier handling and reduced stress on each individual sail. The mizzen mast, positioned aft of the main mast, helps to improve the sailboat’s balance, especially in strong winds or when sailing downwind. The Ketch rig is often favoured by cruisers and long-distance sailors as it provides a range of sail combinations suitable for various wind conditions. With its distinctive double-mast appearance, the Ketch rig exudes a classic charm and is well-regarded for its stability, comfort, and suitability for extended journeys on the open seas.
The keel is the part of the sail boat that provides stability and prevents drifting sideways due to the force of the wind. Here are some common keel types:
1. Fin Keel:
The fin keel is a popular keel type in sail boat design known for its excellent upwind performance and stability. It is a long, narrow keel that extends vertically from the sailboat’s hull, providing a substantial amount of ballast to counterbalance the force of the wind. The fin keel’s streamlined shape minimizes drag and enables the sailboat to cut through the water with efficiency. This design enhances the sailboat’s ability to sail close to the wind, making it ideal for racing and performance-oriented sailboats. The fin keel also reduces leeway, which refers to the sideways movement of the boat caused by the wind. This improves the sailboat’s ability to maintain a straight course and enhances overall manoeuvrability. Sailboats with fin keels are commonly found in coastal and offshore racing as well as cruising vessels, where stability and responsiveness are valued. The fin keel’s combination of performance, stability, and reduced leeway makes it a preferred choice for sailors seeking speed and agility on the water.
2. Full Keel:
The full keel is a design known for its exceptional stability and seaworthiness. It extends along the entire length of the sailboat, providing a continuous surface that adds substantial weight and ballast. This configuration offers significant advantages in terms of tracking and resistance to drifting sideways. The full keel’s deep draft helps to prevent leeway and allows the sailboat to maintain a steady course even in adverse conditions. Its robust construction enhances the sailboat’s ability to handle heavy seas and provides a comfortable ride for sailors on extended journeys. While full keel sailboats may sacrifice some manoeuvrability, their stability and predictable handling make them a popular choice for offshore cruising and long-distance voyages. The full keel design has stood the test of time and is often associated with classic and traditional sailboat aesthetics, appealing to sailors seeking reliability, comfort, and the ability to tackle challenging ocean passages with confidence.
3. Wing Keel:
The wing keel is a unique keel design that offers a combination of reduced draft and improved stability. It features a bulbous extension or wings on the bottom of the keel, which effectively increases the keel’s surface area. This design allows sailboats to navigate in shallower waters without sacrificing stability and performance. The wings create additional lift and prevent excessive leeway, enhancing the sailboat’s upwind capabilities. The reduced draft of the wing keel enables sailors to explore coastal areas and anchor in shallower anchorages that would be inaccessible to sailboats with deeper keels. The wing keel is particularly well-suited for sailboats in areas with variable water depths or tidal ranges. This keel design offers the advantages of increased manoeuvrability and improved performance while maintaining stability, making it a popular choice for sailors seeking versatility in a range of sailing environments.
In the vast world of sail boat designs, sail shape, number of masts, and keel types play pivotal roles in determining a boat’s performance and handling characteristics. Whether you’re a recreational sailor, a racer, or a cruiser, understanding these design elements can help you make informed choices when selecting a sailboat.
Remember to consider your specific needs, preferences, and intended use of the boat when choosing a sail boat design. Each design has its strengths and weaknesses, and finding the perfect combination will greatly enhance your sailing experience.
By gaining a deeper understanding of sail boat designs, you can embark on your next sailing adventure with confidence and make the most of the wind’s power.
Related Posts

Sailing Navigation: Exploring Modern Techniques for Navigating the Seas in 2023
- June 10, 2023

Sailing in Different Directions: Harnessing the Wind’s Power in 2023

Sailing Terms Demystified: A Comprehensive Guide to 14 Common Sailing Terminology
- May 28, 2023
Sailboat Keel Types: Illustrated Guide (Bilge, Fin, Full)
The keel type is one of the most important features of your boat. But the different designs can be confusing, so I've set out to create a very clear guide that will help you understand sailboat keels once and for all.
What are the most common sailboat keel types? The most common sailboat keel types are full-length keels, fin keels, bulb keels, wing keels, bilge keels, and lifting keels. Full keels are popular among cruisers, while fin keels are generally used for racing. Bilge keels and lifting keels are typically used in tidal waters, on small fishing boats for example.
In this article, we'll explore the most common keel types together. I'll use diagrams to really hit home the differences of all these keel types, and we'll discuss what keel types are best for liveaboard, ocean cruising, and lake weekend trips. After reading this article, you'll know what to choose - and why.

Sailboat Keels Explained
On this page:, overview of sailboat keel types, keel types: fundamentals, modified full keel, centerboard.
If you just want a quick overview, here's a list with the most common keel types and a short description. More detail will follow below.
The most common keel types
- Full keels run from front to aft and are the most stable keel type, making them the most popular cruising keel.
- Fin keels offer the best performance but are less comfortable. This makes them popular for racing. Fin keels are bolted on to the hull and generally run deep and thin.
- Bulb and wing keels are both variants on the fin keel.
- Bulb keels carry additional ballast in the tip, making them more stable.
- Wing keels have two tips at the end of the keel, which reduces crossflow, improving directional stability.
- Bilge keels are double fin or double full kees, which allows the boat to be beached, making them the most popular keel for tidal waters.
- Lifting keels are moveable keels that can be lowered and raised, allowing the boat to enter shallow waters as well.
- Centerboard keels are a pivoting lifting keel, allowing to sail both coastal and inland waters.
- Leeboards are fins on the sides of flat-bottomed hulls boats, making a keel unnecessary.
Properties of each keel type
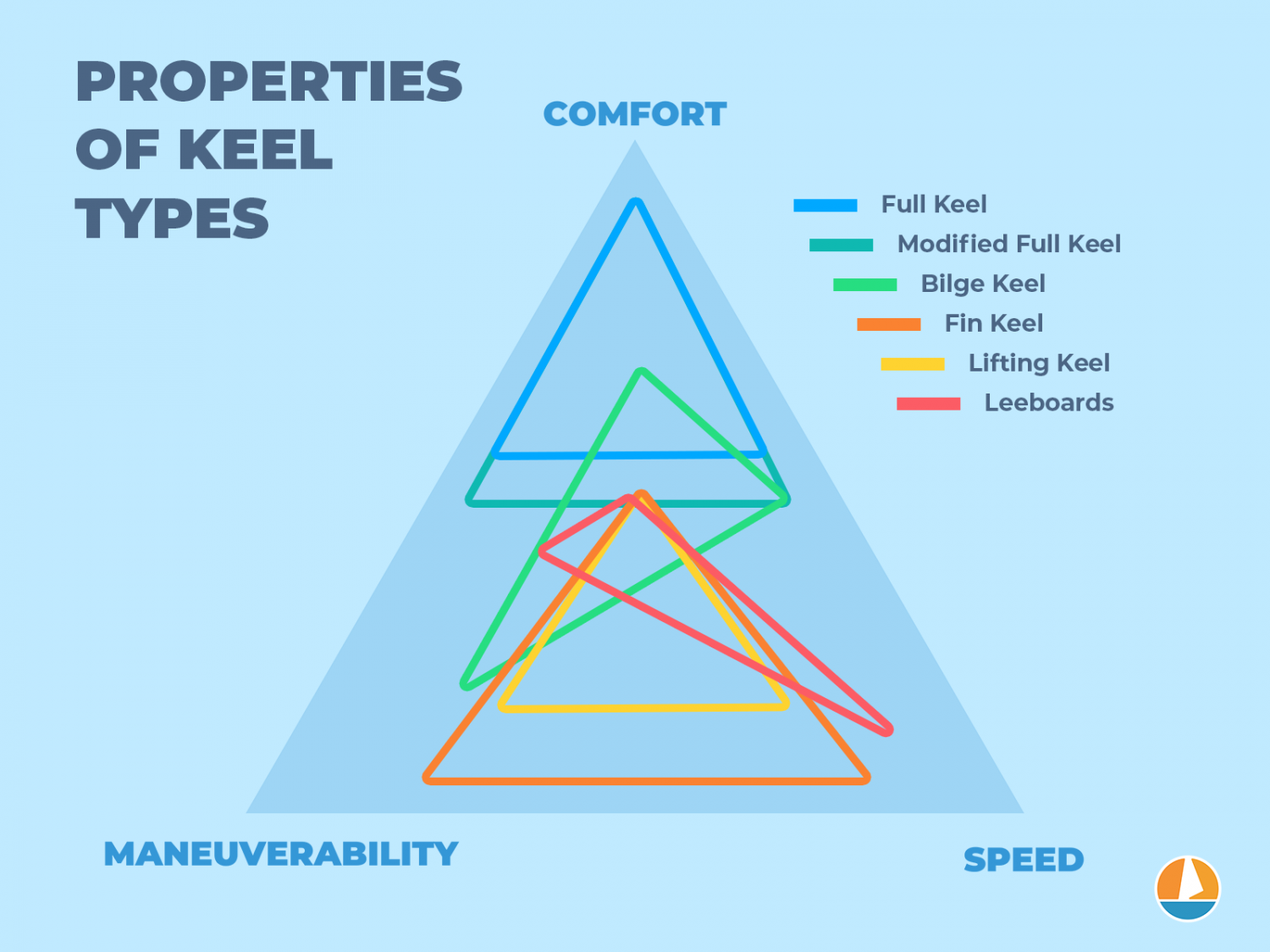
What does a keel do?
What does the keel do? A keel is a vertical blade running down from the hull. It is weighted and acts as a ballast, countering the boat's tendency to heel and preventing it from tipping over. The wetted surface under the waterline reduces slippage to leeward by creating a track, which counters the sideway force of the wind on the sails.
The reason sailboats don't tip over is that the weight of the keel counters the buoyancy of the hull, which means it will pull the boat downward. This downward force reduces heel and prevents the boat from rolling.
A canoe doesn't have a keel. Try stepping into that: it will want to roll.
It counters the horizontal force the wind puts on the sails. Whenever the force on the sails increases, the resistance of the water on the keel increases proportionally.
The heavier the keel, the less heel you'll get.
A keel reduces slippage to leeward. Slippage is simply the amount you fall off course because of the direction of the wind and current. Leeward is the side of the boat behind the wind.
So if you don't have a keel, you will fall off course quite a lot because the wind will push you over the water surface.
You will also heel quite a lot since there is nothing beneath the water surface to counter the force of the wind high up in your sails.
A keel fixes both of these issues and makes sailboats one of the most reliable boats in heavy winds and storms.
You can read on about how keels work here.
Keels can be classified by multiple dimensions. You can look at them from the side or the front. You can also classify them based on properties.
Before I dive into each keel type in-depth and show examples, let's make sure we have the same starting point.
There are essentially two sorts of keels:
Fixed keels
Movable keels.

Fixed keels are keels that are integrated into the hull or bolted on. They can't be moved or lifted.
When looking at fixed keels, you can divide them up further based on the side view. There are three main categories:
Bilge keels
Full keels are more comfortable, provide better stability and protection, but are also slower than fin keels.
Fin keels are less comfortable, provide less stability, are more vulnerable, but they're also a lot faster than full keels.
Bilge keels are double keels: one on each side of the hull. This allows them to be beached, which comes in handy in tidal waters. They are generally a lot slower and less maneuverable compared to fin keels.
Movable keels can be lifted from the water, creating a shoal (shallow) draft, allowing the boat to enter both shallow waters and coastal waters. This makes it a very versatile keel type. There are two main designs:
Lifting keels
Lifting keels can be lowered and raised through a slit in the hull. Examples of lifting keels are the daggerboard and centerboard.
Leeboards are wooden swords attached to the side of the hull and prevent slippage to leeward, but they don't stabilize the boat, nor counter heel by adding ballast.
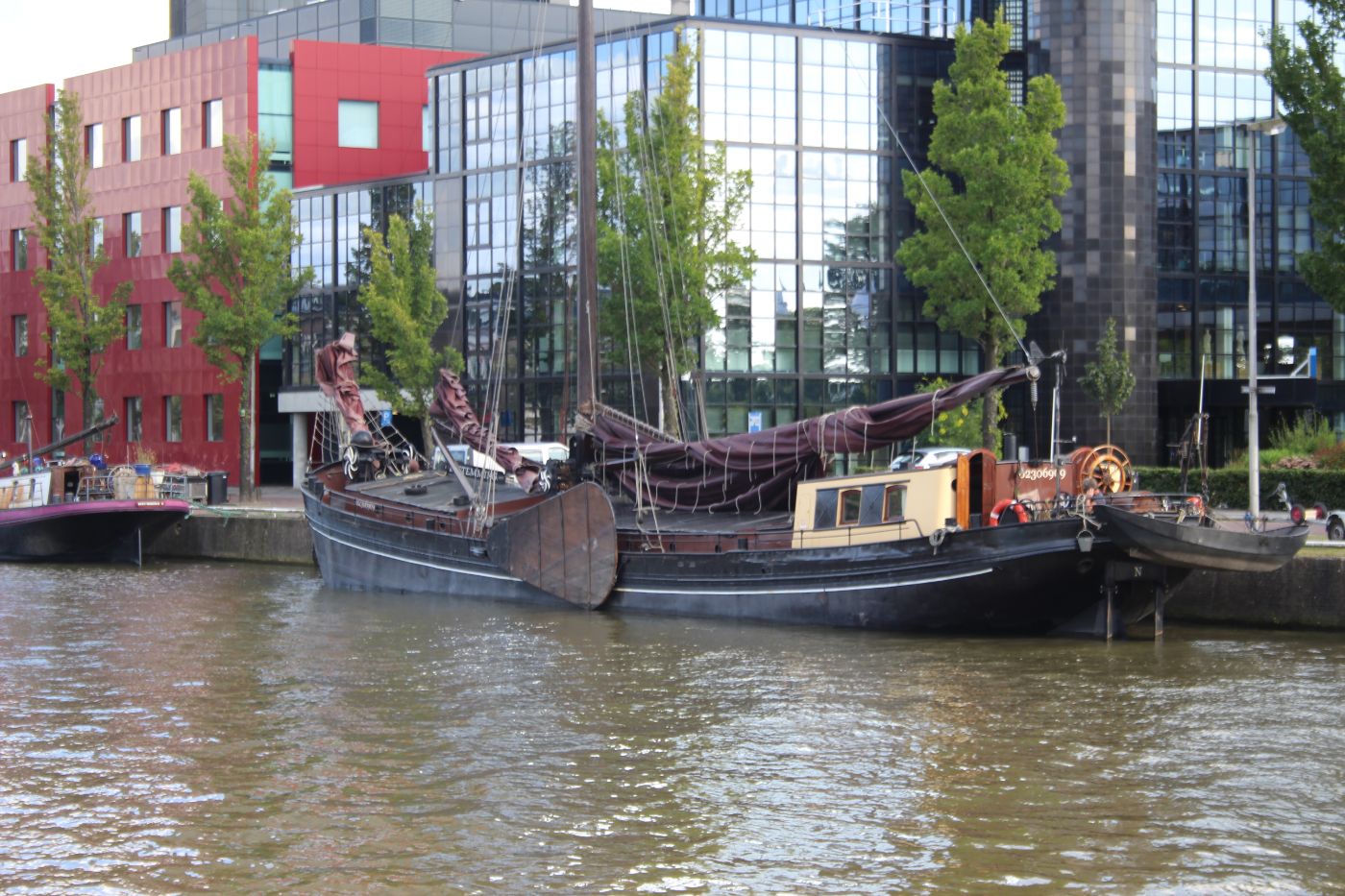

With fin keels, there are different tip designs available. The most common two tip designs are:
These are both variants of the fin keel. Generally, these keel designs are mentioned in one breath with full keels and fin keels, creating confusion on what kind of keel they are. But it's important to understand that they are a sub-category of fin keels.

Rudder design
As with the tip of the fin, there are different rudder designs that may apply to both fin and full keels. The two most common rudder designs are:
Skeg rudder
Spade rudder.
A skeg is a structural part of the keel in front of the rudder that protects the rudder. The keel encompasses the rudder, preventing any rogue ropes, weeds, or rocks from damaging the rudder.
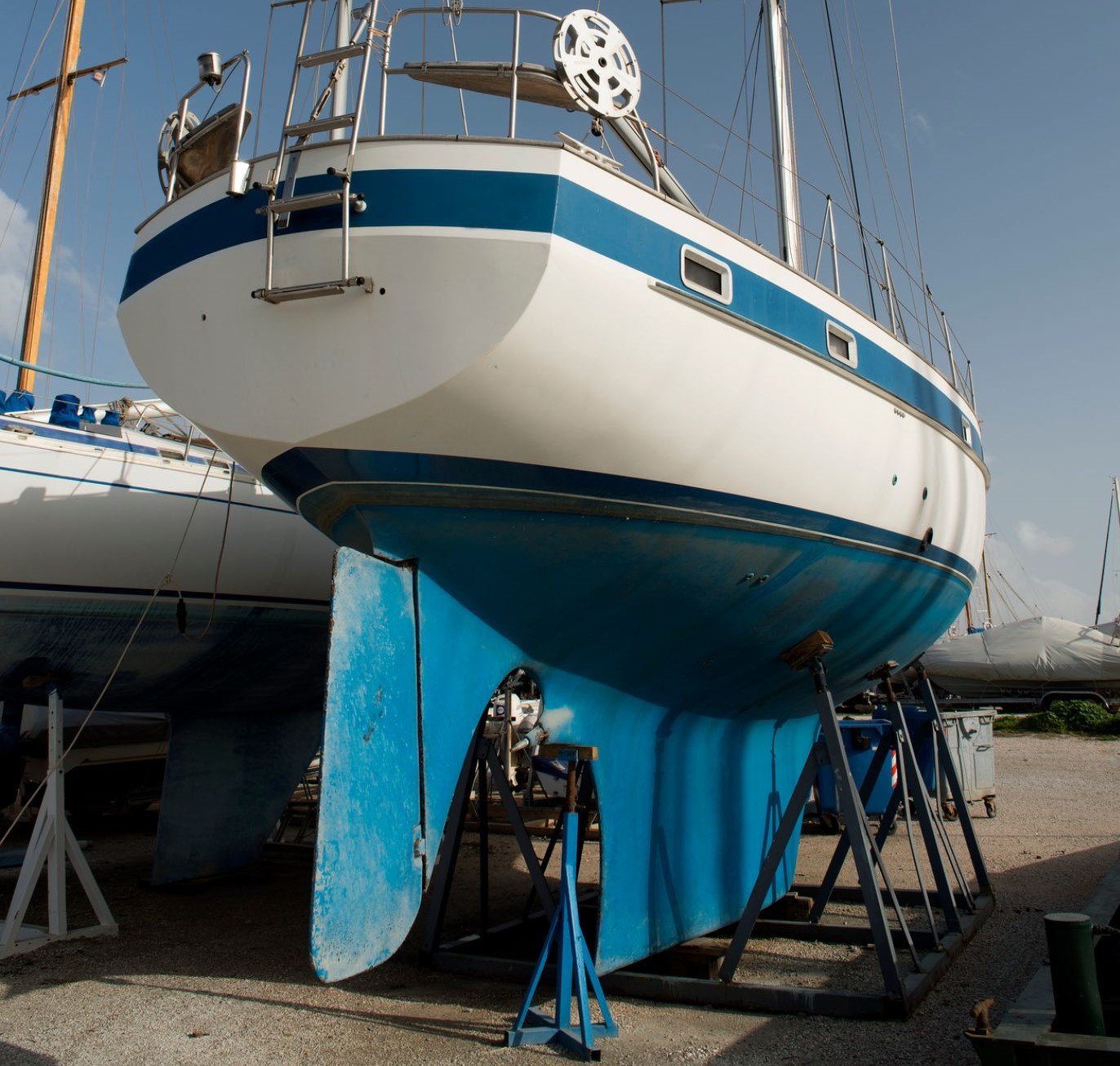

A spade rudder is an unprotected rudder: it doesn't have any structural protection from the keel design. It is simply attached to the hull. This design is very common.
Alright, we understand the big picture. Let's dive into more detail for each keel type and discuss the pros and cons.
Fixed keel Good for cruising and liveaboards Comfortable
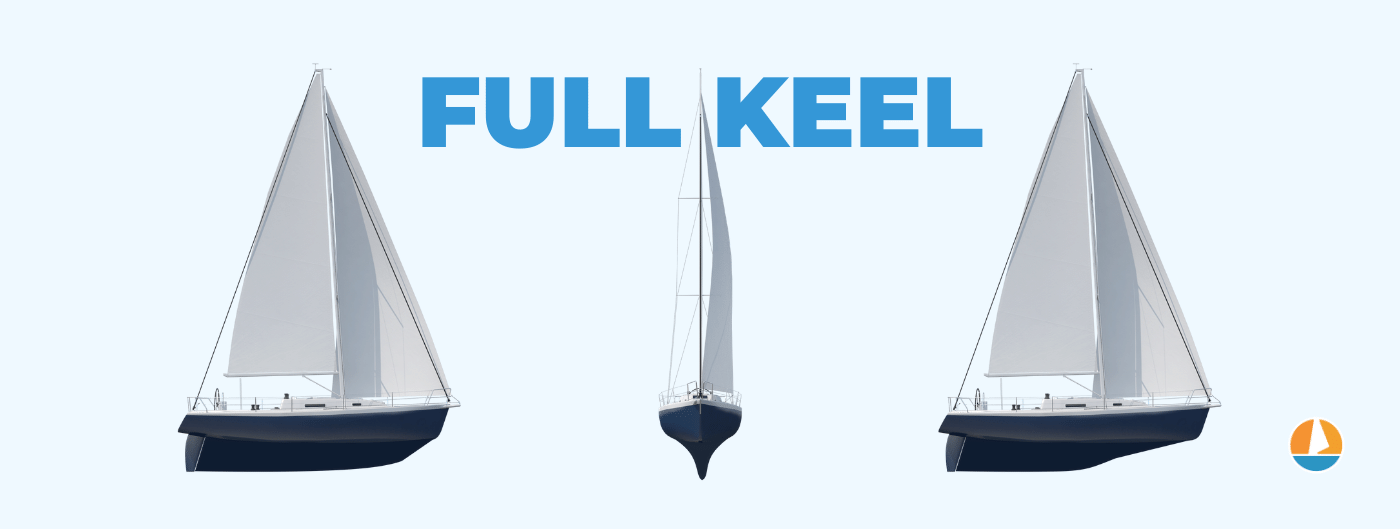
What is a full keel? A full keel runs from front to aft for at least 50% of the hull and is fully integrated into the hull. It has the largest wetted surface of any keel type, and it is also the heaviest. This results in directional stability and reduced heeling, providing the most comfortable ride, but also the slowest.
The wetted surface simply means the amount of water contact area. With such a large wetted surface, it decreases slippage to leeward the most of all keel types, while it counters heeling the most as well.
The full keel is the most comfortable and stable keel type available. However, comfort comes at a price. It delivers the worst performance due to this large wetted area. It is the slowest of the keel types, and it has the worst windward performance.
This makes full keels particularly great for longtime cruisers or liveaboards who prefer comfort over speed, but less ideal for daysailers who need to navigate in and out of slips regularly.
Since it runs for at least 50% of the hull, it doesn't need to run as deep as a fin keel, resulting in a more shoal draft.
Heavier keels result in increased displacement, so a full keel boat will need a larger sail area to compensate for its weight.
For a more detailed discussion on full keel advantages, I recommend reading William's excellent article 5 Surprising Advantages of a Full Keel Sailboat here.
Example sailboats with a full keel:
- Nicholson 22
- Island Packet 380
- Beneteau Oceanis 411 Clipper
- Beneteau First 50
- Jeanneau Sun Shine 38
- Dufour 455 Grand Large
There are a lot of great cruising boats with full keel designs , some of them considered classics.
Full Keel with skeg rudder
Full keels with a skeg rudder design have a protected rudder, thanks to putting a structural part of the keel directly in front of the rudder. This helps with fending off any hazards to the rudder, like floating pieces of rope, rocks, or garbage, and protects it in case of running aground. The skeg design ensures the rudder is nearly impossible to break off.
Fixed keel Good for cruising and liveaboards Faster than a regular full keel

What is a modified full keel? A modified full keel is a full keel with a cutout at the front, reducing the wetted surface slightly, which increases performance without sacrificing too much comfort and stability. After the full keel, it has the best directional stability and the least amount of heel.
The modified full keel is popular among (bluewater) cruisers, thanks to its increased handling and performance. Most modified full keels have a skeg rudder, ensuring it is well-protected.
The slightly reduced weight and wetted surface improve windward performance quite a lot, but it is still one of the most stable keel designs out there.
Example sailboats with a modified full keel:
- Hallberg-Rassy HR 40
- Dufour Arpege 30
- Beneteau Oceanis Clipper 281
- Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 37.2
Fixed keel Good for racing Fast
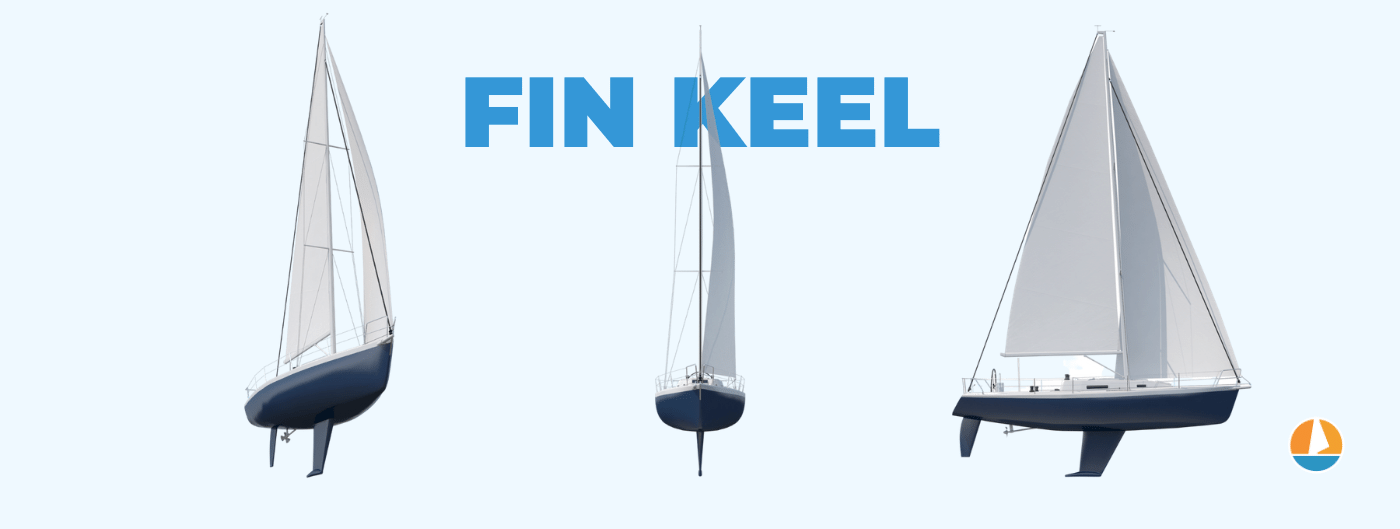
What is a fin keel? A fin keel is a long, weighted blade attached to the bottom of the hull. It is lighter, faster, and more maneuverable than a full keel, but also more vulnerable. The increased distance between ballast and sails provides a lever, reducing the need for a large wetted surface or additional ballast.
Fin keels are generally bolted onto the hull and run deeper and thinner than a full keel. They are also lighter. This helps increasing performance (a lot), making fin keels a lot faster in all situations.
There are some major disadvantages to fin keels, however. Fin keels are a lot less comfortable than full keels and allow for more heel and a less solid track, so less directional stability. Fin keels are also a lot more vulnerable than full keels. They can break off when running aground, or get damaged.
They are very popular among racers and perform better when maneuvering in tight spots, like getting in and out of slips.
Example sailboats with a fin keel:
- Catalina 30
- Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 36.2
Fin keel with skeg rudder
Fin keels with a skeg rudder use a small structural part in front of the rudder to protect it. This design is mostly integrated into the hull, making it less vulnerable, and a great compromise between speed and safety.
Fin keel with spade rudder
Fin keels with a spade rudder have a completely exposed rudder, and typically a fin that is simply bolted on. The keel isn't integrated into the hull, making it more vulnerable and less comfortable.

Fin keel variant Good for cruising Less crossflow
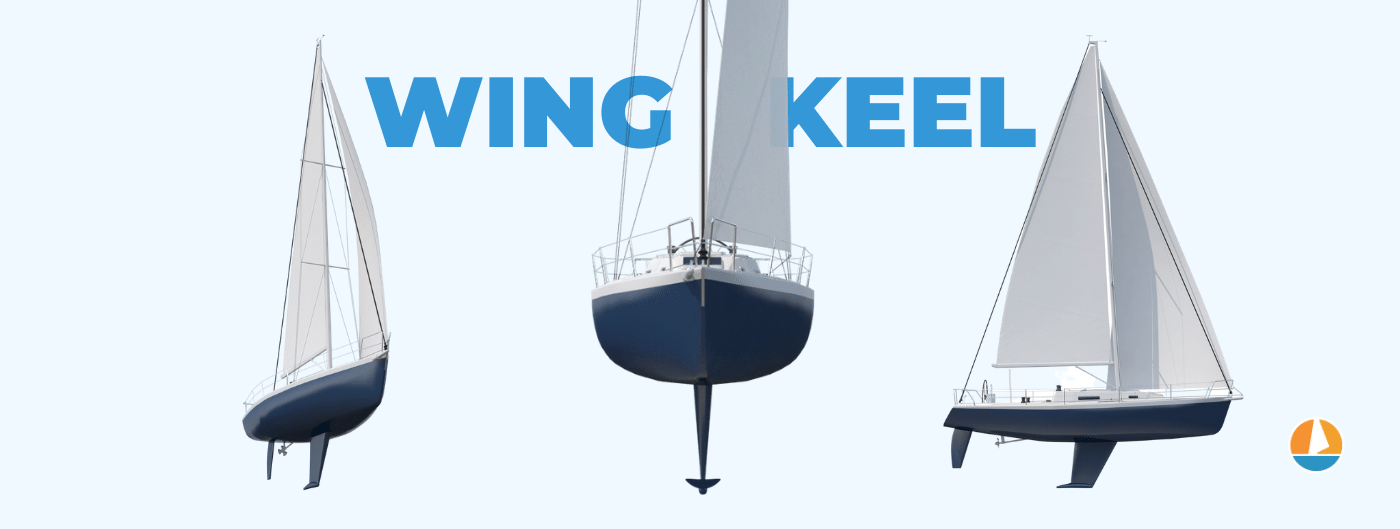
What is a wing keel? A wing keel is a fin keel with a horizontal foil at the tip, which is wing-shaped and generally weighted. Its shape reduces crossflow, improving directional stability, and its ballast decreases heel, resulting in a more comfortable ride. The addition of a wingtip allows for a shorter fin, reducing draft.
Wing keels are good for cruising since this design improves directional stability compared to a regular fin keel or a bulb keel.
We'll discuss the wing keel's advantages and disadvantages in more detail in this article.
Fin keel variant Good for cruising Stability

What is a bulb keel? A bulb keel is a high-aspect-ratio fin keel with additional ballast at the end, which generally has a bulb or teardrop shape. This ballast improves stability and utilizes the distance between force and counterforce as a lever. This design reduces the need for a deep fin, resulting in a shoal draft.
By placing the weight at the largest possible distance from the force on the sails, you need relatively little extra weight for the same reduction in heel, making bulb keels very effective for cruising.
This design reduces the wetted area while increasing the weight of the keel just slightly, which increases sailing comfort big time.
Example sailboats with a bulb keel:
- Bavaria B/One
- Beneteau First 24
Fixed keel Good for racing Can be beached
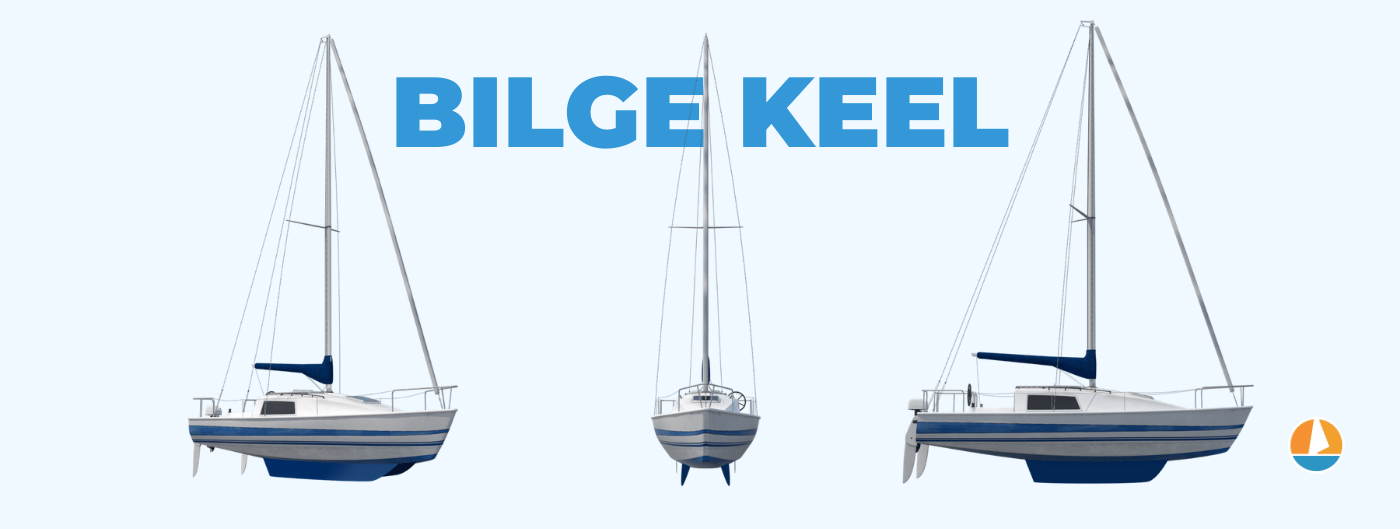
What is a bilge keel? A bilge keel is a twin keel which uses double fins, allowing the boat to be beached and rest on its keel upright. Bilge keels have double the wetted surface, which increases comfort and directional stability while decreasing heel. Modern bilge keels often provide decent windward performance, thanks to better design.
The bilge keel does sacrifice speed compared to the fin keel but doesn't necessarily offer worse performance overall. Older designs performed considerably worse than other keels and were especially slow.

Bilge keels have some major advantages over full keels and fin keels. The most important is that the boat can be beached, making it a popular design in tidal waters. Bilge keels are especially common along the British coastline, where fishermen keep their boats in tidal harbors.
Another major advantage is that the boat can be stored resting on its keels, making dry storage and maintenance a lot easier.
Of course, there are many more pros and cons to the bilge keel , which we go into here.
Example sailboats with a bilge keel:
- Dufour Dynamique 62
- Hunter Duette
- Patagonia Patago 39
- Macwester 27
Lifting keel Good for daysailers Versatile

What is a centerboard? A centerboard is a type of retractable keel that rests on a hinge and can be lowered through a slot in the hull. It folds out like a pocket knife and allows you to increase or reduce the draft of the boat. Centerboards are mostly used on small fishing boats.
The centerboard is a very versatile keel type, allowing you to have both a very shoal draft for inland waters, as well as steadying the boat and reducing heel for larger bodies of water, or even oceans.
I've sailed a Cornish Crabber with a centerboard for a week, and while we stayed inland, having the option to increase the keel depth really came in handy when crossing the IJsselmeer (a former sea in The Netherlands).
There's more to the center
Olaf Roethele
https://www.theyachtmarket.com/en/new-boats/cornish-crabbers/adventure-17/218/
My name is Olaf and I am the owner of a Cornish Crabber 17 Adventure boat.
I would like to ask you if you can imagine to install on this boat a Torqeedo 2.0 Pod motor? Therefore i guess a modification of the keel/skeg is necessary ?!
Best regards from Uruguay,
You completely missed the hybrid planing/water-ballast keel of the Macgregor range
Thanks a lot for this explanation
Roger Bannon
Very well written article which provides an excellent guide for us small wooden boat builders. Thanks.
Leave a comment
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:
- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
Sailboat Design: Stability, Buoyancy and Performance
Simply stated, the first requirement of sailboat design is that the yacht designer's creation is seaworthy; particularly in that it stays afloat and is highly resistant to capsize - but of course we expect rather more than that...
Good sailing performance, particularly to windward, will be high on the list of most sailors' requirements. As will the availability of sufficient space below decks to accommodate the crew and the stores, and all the other sailing paraphernalia.
And the boat must be easy to handle, both under sail at sea and under power in the marina. It must be comfortable, for it's not always just a sailing machine - at times it has to function as a home too.
So a design that successfully incorporates all these requirements won't just happen by accident - but however accomplished your yacht designer, you'll not be able to have everything...
We sailors recognise the stability element of sailboat design as the difference between a 'stiff' boat and a 'tender' one. And whether it's one or the other depends on the relationship between the righting moment applied by the hull and the heeling moment applied by the wind-loaded sails.

As can be seen in the sketch, the righting moment (Gz) is the horizontal distance between the boat's Centre of Gravity (G) and its Centre of Buoyancy (B).
The righting moment increases as the boat heels until a point is reached at which the heeling moment becomes equal to the righting moment, following which any further increase in heeling moment will cause the boat to capsize.
This is best expressed graphically by way of a Gz Curve, which plots Righting Moment against Heel Angle.
This curve establishes the Angle of Vanishing Stability , effectively the point of no return for a sailboat about to capsize, and which is a major factor in allocating any sailboat to one of the four recognised sailboat design categories - Ocean, Offshore, Inland and Sheltered Waters .
If you're planning to buy or charter a sailboat, you should always check its Design Category to make sure that it's suitable for your purposes.
Displacement, Freeboard and the Centre of Gravity
Heavy displacement boats sit lower in the water than light displacement craft, so their cabin soles are deeper below the water line. Lighter displacement boats with their higher cabin soles have to have greater freeboard to provide their occupants with sufficient headroom.
And freeboard has an impact on stability in that it raises the centre of gravity, thereby reducing the righting moment.
To compensate this, any ballast carried by a light displacement boat should always be as low as possible, ideally in a bulb at the foot of the keel - the lower the centre of gravity the better, as it improves the righting moment by maximising the righting lever Gz.
In our medium-to-light sailboat Alacazam, we have gone one stage further by building in a water ballast system .
Performance
Generally light displacement brings performance benefits due to the higher power to weight ratio and reduced hull drag through having a smaller wetted area.
This is borne out by two important design ratios, the Displacement/Length Ratio and the Sail Area/Displacement Ratio.
Length too has an impact on performance, as can be shown by another sailboat design ratio, the Speed/Length Ratio.
It will also come as no surprise that performance is also influenced by the hull shape below the waterline; a slim arrow-like hull offering less resistance that a squat, dumpy one. But what isn't so widely known is that the ideal shape for hullspeed is not the most efficient shape when sailing at less than hullspeed; which is why sailboat designers ponder long and hard over another sailboat design ratio - the Prismatic Coefficient.
Read more about these and other Design Ratios used by today's Yacht Designers...
Recent Articles
'Natalya', a Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 54DS for Sale
Mar 17, 24 04:07 PM
'Wahoo', a Hunter Passage 42 for Sale
Mar 17, 24 08:13 AM
Used Sailing Equipment For Sale
Feb 28, 24 05:58 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
- Sign-up for our newsletter, 'The Sailboat Cruiser' ...
- Identify this month's Mystery Boat...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com

Top 8 Best Boat Design Software in 2024 (Free & Paid)
Written by: 3DSourced
January 16, 2024
Whether you’re a student, a hobbyist, or a professional, finding the right software is the key first step to designing a boat. However, with such a wide range of programs available, you need to make sure you choose the best boat design software for you.
We usually talk about 3D software in relation to 3D printing, but 3D modeling techniques are used across many applications and industries, including boat design. In fact, 3D printing is becoming increasingly prevalent in the boat design industry, with one example being Tanaruz’s 3D printed boats .
Quick Overview
- Free!ship : Best Free Boat Design Software for Linux
- Sailcut CAD : Free Sailboat Design Software
- Bearboat SP : Free Boat Designer for Small Boats & Kayaks
- DELFTship : Intuitive Free Boat Design Tool with Professional Option
- Fusion 360 : Best Free Boat Design Software for Beginners & Mac
- SketchUp : Best Boat Design App for iPad
- Autoship : Best for Naval & Marine Architecture, Best for Windows
- Solidworks : Best for Aluminum Boat Design Software & Best for Yachts
In this guide, we review several 3D ship design software to help you do just that. We’ll take a close look at both free and professional options, so that you’ll be able to find a suitable program regardless of your budget and experience.
Read more: our feature story on 3D printed boats
Best Free Boat Design Software
1. freeship – best free boat design software for linux.
Completely free and open source
Subdivision modeling to design any hull shape
Can export designs in a range of file formats
Can submit support and feature requests
Positive reviews from users
Can be tricky for novices to get used to
Not available on Mac
Unlike most of the boat building software on our list, Free!ship isn’t developed by a company, but rather by an individual called Marven with a desire to make boat design accessible to anyone.
Free!ship is a surface modeling program for designing ships and yachts, using subdivision surfaces modeling rather than NURBs, providing the freedom to design hulls of any shape.
Available on Windows and Linux, you can get started with this free CAD software by automatically generating a basic boat structure to use as a template. You can then easily use the nodes on the structure, as well as a variety of tools like curve, split, collapse, and insert plane, to reshape the design to your liking.
You need to fill in certain parameters, such as:
- Boat length
- Beam length
- Longitudinal and vertical direction
Once you’ve done that, you can view your boat design in four different perspectives and every angle to help you finalize your structure.
Free!ship offers the option to fill out support requests, feature requests, and report bugs. However, bear in mind that design beginners may be better off with a professional free ship design software that has more support options and tutorials available, as you don’t get any training with Free!ship.
2. Sailcut CAD – Free Sailboat Design Software

Specialist sailboat design software
Easy to use node editing
Supports a variety of sail designs
Export designs in different file types including DXF files
Not suitable for designing other boat types
If you’re looking for a free small boat design software specifically geared towards designing sails and sailboats, you can’t go wrong with Sailcut CAD .
This design and plotting software can be used to design the sail, hull, and rail of a boat, in addition to precisely computing panel development in flat sheets.
You can use it for a variety of different sail types, including wing sails, cross cut, twist foot cut, vertical cut, mitre cut, and radicul cut, so it’s a versatile tool that will suit virtually any sailboat designer.
The software provides a base design template that you can then edit and view in a variety of formats, including shaded, wireframe, and development. It provides control over all the key dimensions of your sailboat, such as boat length, gaff round, and seam width.
Sailcut provides documentation that explains how to use it for CAD as well as community mailing lists and a bug tracker where you can report issues.
3. Bearboat SP – Free Boat Designer for Small Boats & Kayaks
Specialist kayak design software
Simple to use
Control all aspects of your design
Multiple view options
Advanced tools like wetting
Not suitable for larger boat designs
Dated interface
Bearboat SP is a specialist kayak design software that can also be used to design other similar types of small boats.
People have been using Bearboat to design kayaks since 1998 – and it’s the most popular program for this specific type of boat design.
It’s a fairly simple, no-frills software that makes it easy to get stuck straight in. You begin by filling in the core boat hull parameters, such as length, stability, and design deplacement, and then just click the ‘create’ button to generate your base kayak template.
From there, you can go about making structural changes to aspects like shape seam, bow and stern seam height, and rockers parameters. You can also easily change dimensions using the nodes on the 2D wireframe design.
There are three viewing options – bird view, side view, and cross-section view – for inspecting your design from different perspectives, as well as options such as changing the color of the wireframe design for easier analysis.
Advanced features include the ability to view the wetted surface and underwater area, and a drag spreadsheet that contains all the parameters of your boat design, making Bearboat SP a well-rounded boat design tool overall.
4. DELFTship – Intuitive Free Boat Design Tool with Professional Option
More up-to-date and intuitive than other free boat design software tools
Impressive model rendering
Professional license and extension options
Perform basic calculations to check buoyancy and other factors
Free version has limited features compared to paid version
DELFTship is another great free boat design software, and offers a somewhat more professional and up-to-date solution versus Sailcut and Free!ship, with more impressive renderings than other free programs.
This 3D hull form modeling program is very intuitive with a range of easy-to-use design features, including lots of nodes that make it simple to edit your base model just by dragging and dropping.
You can inspect your models from five different viewpoints and convert them to wireframes and other formats to better analyze structure. Features like the keel and rudder wizard make it simple to design additional components of your boat.
DELFTship provides an unlimited free version alongside a professional license that costs $160. You can also add on extensions and board stability analysis calculations upon request for additional fees.
Even without the paid license you can still use DELFTship free to perform basic hydrostatic calculations and resistance calculations to help improve the precision of your designs, making this one of the most impressive free boat design tools.
5. Fusion 360 – Best Free Boat Design Software for Beginners & Mac
More beginner-friendly than other boat design software
Lots of learning resources & tutorials
High quality, flexible 3D modeling tool
Impressive renderings
Available on Mac
Not a specialist boat hull design software
Unlike the other programs we’ve covered so far Fusion 360 is a general purpose 3D modeling software that’s not specifically made for boat designing. However, it’s still widely used in boat designing, and its more general nature has some advantages.
For starters, designing a boat is a fairly large and complex task, and the more specialist software like Free!ship and Bearboat SP are complex if you’re new to computer aided design.
While Fusion 360 still has a learning curve, it’s one of the best designed, intuitive, and beginner-friendly 3D modeling software out there. On top of that, it has a huge range of learning resources and tutorials, great support, and a large user community, so it’s very popular among new designers.
In fact, there are a variety of YouTube videos and written tutorials showing how to use Fusion 360 for boat design and for different types of vessels, including yachts and canoes. These include videos showing how to design wooden boats , so it’s a good choice if you’re looking for a plywood boat design software.
Another benefit of Fusion 360 is that, unlike most naval architecture boat design software, it’s available on Mac. It even has iOS and Android apps that allow you to view designs and collaborate via your smartphone or tablet.
Fusion 360 is also free for three years as long as you’re using it non-commercially.
Best Paid Boat Design Software
6. sketchup – best boat design app for ipad.
- Price : $119 a year for the app (free online version available)
3D modeling iPad app
High quality renderings
Intuitive and beginner-friendly
Free online version available
Not specialized for boat design
SketchUp is another general purpose 3D software used for boat design. While it’s not one of the most widely used boat design programs, the reason it’s on our list is that it’s one of the few premier 3D CAD tools that has a fully-fledged mobile app for iPad.
While some programs like Fusion 360 have viewer apps, these don’t have the modeling tools of their desktop counterparts. However, with the SketchUp iPad app, you can enjoy advanced modeling on a tablet, and you can even get creative using an Apple Pencil stylus.
There are a variety of tutorials and videos showing how to design boats with SketchUp, and as a user-friendly software it’s a good option for beginners. SketchUp also boasts high quality renderings for producing 3D boat designs that you can easily share with anyone.
While the SketchUp boat design app has a yearly fee, you can also use the software for free using the online-only version, or choose from a variety of desktop licenses that vary in terms of features and storage.
SketchUp also offers iPhone and Android apps, although these are more stripped back versions more suited to viewing and sharing designs on your mobile.
7. Autoship – Best for Naval & Marine Architecture, Best for Windows
- Price : upon quote
Large software suite that covers the entire boat design pipeline
Used by professional boat manufacturers
Highly intuitive NURBs modeling
Comprehensive testing features and data management
Extensive training and support
Can be used to create load plans
Not available on Mac
Steep learning curve
Autoship is a software suite designed for professional naval and marine architects that provides solutions for every aspect in the boat design process, from modeling to construction and load planning modules for more optimal loading.
In terms of design, Autoship software offers five different CAD/CAM solutions:
- Autoship Pro – a hull design and surface modeling program.
- Modelmaker – for creating 3D models of vessels and components.
- Autohydro Pro – for analyzing hydrostatics and stability of your models.
- Autoplate – a plate design, expansion, and management system.
- Autopower – for resistance and powering predictions.
So, you can create a package with any number of these programs based on your needs. The great thing about Autoship software is all the programs are fully integrated, so any changes made to your model integrate into each solution.
Autoship Pro is the primary design solution in this suite, with a vast array of advanced features for designing vessels. Based on NURBs modeling, the intuitive interface allows you to work in up to four views simultaneously with ten levels of zoom and unzoom for top precision.
Some of the impressive features of this vessel design software include extensive context menus to help speed up operations, the ability to color surfaces so it’s easy to pick out parts in complex designs, curvature displays for curves and surfaces, hydrostatic and resistance calculations, and strength assessment tools.
Overall, with its mix of powerful design, testing, and engineering features, Autoship is one of the most complete boat design software on the market.
8. Solidworks – Best for Aluminum Boat Design Software & Best for Yachts
- Price : upon quote

Solidworks is one of the most advanced 3D CAD/CAM software out there and is widely used across design and engineering industries, from automotive to aerospace as well as boat design.
In fact, this software is used by a number of leading boat manufacturers. One such example is Kvichak Marine Industries, a Seattle-based maker of high quality aluminum vessels, including both passenger and industrial boats.
In this v i deo , the assistant chief engineer explains how Solidworks’ highly precise 3D modeling tools allow them to improve processes by spotting issues quicker and therefore improve efficiency, with the ability to inspect every element from the individual pipes within hulls to the connections within engines.
Solidworks’ extremely advanced and flexible modeling allows you to create any type of boat you like. There’s even an eBook that explains each step in designing a superyacht using Solidworks.
While this software is mostly used by professional companies, there are also numerous YouTube videos showing you how to design a boat with it, so it’s accessible to amateurs.
What is Boat Design Software?
A boat design software is a program used to sketch, plan, and model a boat in 3D. Popular boat design programs include Free!ship, Solidworks, Fusion 360, and Autoship.
What is naval architecture?
Naval architecture is the processing of designing and engineering marine vessels like ships and boats, as well as their parts. Naval architects also work in boat and ship repair.
Do I need special software for designing boats?
You don’t need a special boat design software to design boats and ships. While there are a number of specialist boat design software tools out there, general 3D modeling CAD programs like Fusion 360 and AutoCAD are also used for this purpose.
What Can You Do With Boat Software?
All boat software have different features that determine what you can do with them. For example, certain programs are designed for creating certain types of boats, such as kayaks and sailboats, so this is the first consideration you need to make to find a suitable program.
More expensive programs typically offer a much wider range of features than paid versions. At the top end are industrial solutions like Autoship and Solidworks, which offer extremely high quality and flexible modeling tools and provide support for testing, manufacturing, and engineering processes, so they’re complete solutions.
There are also software like DELFTship and Fusion 360 that provide both free and paid versions, so you can try out the free versions and then upgrade if you want the extra features available on the paid licenses.
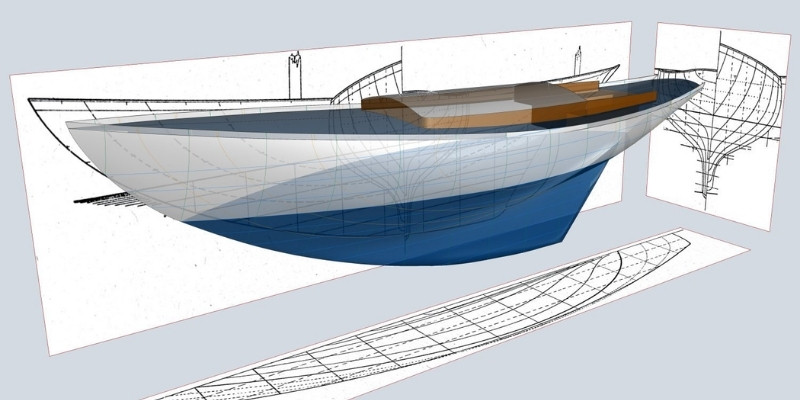
Buying Guide – Things to consider when choosing boat software

Type of Boat
Boats come in all different shapes and sizes, and some software are specially built for designing certain types of boats. For example, Bearboat SP is primarily geared towards kayak designing, while Sailcut is for sailboats.
On the other hand, general 3D modeling software like Fusion 360 and Solidworks are more flexible, so you could use it as a Yacht design software and for other types of boats. The benefits of this are the increased flexibility and beginner-friendliness, but these general programs can lack some of the more specialist features that the likes of Bearboat SP and Sailcut have.
Compatibility
The device you’re using is going to have an impact on what naval architecture software you use, as most programs only work on certain operating systems.
In fact, the majority of boat design software are only compatible with Windows. If you’re looking for a boat design software for Mac, Linux, or iPad, you may be best off using a more general purpose 3D modeling software like Fusion 360 or SketchUp.
3D Rendering & Graphic Quality
Free programs like Free!ship, Sailcut, and Bearboat SP are all great for creating precise boat designs at no expense, but in terms of graphics and 3D model rendering, they’re all very basic.

This isn’t unusual when it comes to free programs, and if you’re not bothered about graphics then it’s no issue. However, if you do want to create higher quality models and renderings – which is especially important if you’re a student or aspiring professional boat designer – then you’ll need a program that provides this, such as Solidworks or Autoship.
Usability & Training
Boat design isn’t exactly a simple process, so if you’re a complete beginner, you’ll want a software that’s easier to get to grips with.
The free boat design software we’ve covered are all fairly simple to use, but the level of intuitiveness and support varies. If you’re a complete newbie to computer design, you may want to go for a widely used modeling software like SketchUp or Fusion 360, both of which boast great support, large communities, and more tutorials than specialist boat structural design software.
Budget & Free Trial
The price of boat design software can vary a lot, from free programs to expensive professional solutions like Solidworks and Autoship that can cost thousands, so bear this in mind. Many paid boat design software offer free trials, so you should definitely take advantage of this to try a program out.
What software is best for basic boat design?
Free!ship, Delftship, and Sailcut are all popular free software that allow you to create basic boat designs.
How do you design a yacht?
If you want to design yachts, the first step is to find a high quality yacht designing software such as Solidworks or Autoship.
How do you become a boat architect / ship designer?
To be a boat architect or ship designer you need to first obtain a relevant degree, such as a BEng or MEng in naval architecture.
How much do yacht architects make?
Yacht and naval architects can make anywhere from $60,000 to $150,000 depending on their experience and position, with the average salary around $75,000.
Autoship, Solidworks, Maxsurf, and OrcaFlex are all popular marine design software that are used in professional ship design.
To become a boat designer you first need a degree in a relevant subject, such as naval architecture, ship science, or marine technology.
The best way to learn how to make a boat hull in Solidworks is by watching one the boast hull design tutorial provided by Solidworks Product Manager Mark Biasotti.
The first step to designing a yacht is finding a suitable CAD software, such as Solidworks or Fusion 360.
Lightning CAD Dock Designer is one of the most popular boat dock design software.
Related posts:
- Top Free CAD Software for 3D Printing For Every Skill Level
- Best 2D & 3D Car Design Software in 2022
- Top Picks For Beginner & Pro Free Furniture Design Software
- Best PCB Design Software
- Free Floor Plan Software
- Garage Design Software
- Great Pool Design Software
Was this content helpful? Give us your feedback here.
Learn More About 3D Sourced

6 Best Large 3D Printers in 2024 (All Budgets)

5 Best 3D Printers for Miniatures & Terrain in 2024

4 Fastest 3D Printers in 2024 (All Budgets)
The 56+ Coolest Things To 3D Print in 2023

44 Common 3D Print Problems – Troubleshooting Issues 2023

13 Best Free 3D Modeling Software (For Beginners) 2024

11 Best 3D Printers in 2024 (All Budgets)

5 Best 3D Printers For Beginners in 2024
Exceptional value with anycubic’s latest 3d printer deals.
40+ 3D Printing Industry Statistics (2024 Update)

22+ Coolest 3D Printed Robotics Projects (2024 Update)

8 Best DIY 3D Printer Kits in 2024 (From $150!)

3D Printing In Space – Top Projects in 2023

Best 3D Printed Shoes in 2023 (Sneakers, Heels & More)

The Best 3D Printer Buyer's Guide Resource & 3D Printer Reviews
[email protected]
3D Printers 3D Scanners 3D Software Guides Rankings Interviews News
Most Popular
Best 3D Printers Best 3D Scanners Best 3D Modeling Software Best 3D Slicers Best Resin 3D Printers Fastest 3D Printers Best Large 3D Printers
Useful Links
About us About the team How we do our reviews Careers Contact Us
Sign up to our newsletter
Privacy policy
Affiliate disclaimer
Editorial policy
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- Email Newsletters
- Boat of the Year
- 2024 Freshwater Boat and Gear Buyers Guide
- 2024 Boat Buyers Guide
- 2024 Water Sports Boat Buyers Guide
- 2023 Pontoon Boat Buyers Guide
- Cruising Boats
- Pontoon Boats
- Fishing Boats
- Personal Watercraft
- Water Sports
- Boat Walkthroughs
- What To Look For
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
- Watersports Favorites Spring 2022
- Boating Lab
- Boating Safety

Six Amazing Boat Hull Designs
- By Dean Travis Clarke
- Updated: October 25, 2016

The American boating consumer bears a remarkable psychological profile when it comes to wants and needs.
A cursory glance at the lines of most boats proves that profiles haven’t changed dramatically over the past 60 or so years. Certainly, construction methods such as resin infusion and injection molding have altered business as usual, and ingredients have also changed to include all manner of space-age composites, epoxies, paints, computer mapping for engines that produces vastly greater horsepower from smaller blocks, and so on. Even propulsion has changed with the advent of pod drives and big outboards. But here’s the weird part: Any time a designer or builder introduces a model that looks significantly different, whether it is Euro-styled or functionally clunky, it fails. It doesn’t matter how well the boat performs, the typical boater rejects it because it doesn’t look like what he knows. We, as an enthusiast niche involving boats, are horribly set in our aesthetic ways.
Look at how well multihulls handle heavy seas. When it comes to seakeeping ability, efficiency and performance, the catamaran has a lot going for it, as anyone who happened to catch some of the most recent America’s Cup racing can attest. And yet, to date, production multihulls have enjoyed only moderate acceptance by boaters.
Here are six of the latest hull-design innovations and technologies being used elsewhere in the maritime world that we will likely never accept for our recreational boats — even though they all work well.

Wave-Piercing Hulls Most accounts cite wave-piercing technology as coming on the scene around the start of the 20th century. However, it has been employed as far back as the times of the Phoenicians and ancient Romans. The design concept consists of a bow with little buoyancy, a hull that slopes inward from the waterline and, ergo, a large reduction in wave-making resistance. While it works well in heavy seas, the drawbacks include reduced interior volume forward and a very wet ride because the waves come up and over the bow as a matter of course. Wave piercers fell out of favor for a period of time due to these same drawbacks but have recently enjoyed a resurgence of popularity because of their dramatic fuel-efficiency gains.

Stepped Hulls OK, this hull form has achieved a certain level of acceptance in our recreational boats, mostly in performance boats or offshore center consoles. But why isn’t it more popular? The stepped bottom has been around as a V-bottom refinement since at least 1912. Steps are grooves in the hull stretching outward from the keel to the chines. Most hulls sport one or two steps per side. And a vessel should really be capable of cruising in excess of about 30 knots for a stepped hull to be worthwhile. Steps work by allowing air to be “injected” against the running surface, breaking contact between part of the hull and the water, which in effect turns the running surface into numerous short, wide planes, rather than one long, narrow one.
How much the hull surface contacts the water directly determines the amount of drag a hull suffers. Steps (also called vents) decrease the amount of hull contacting the water (called the wetted surface), thereby decreasing drag, increasing speed for the same horsepower, and increasing fuel efficiency. It all sounds good. But steps also come with potential drawbacks. Though modern deep-V designs have enough deadrise to counteract the problem in most cases, stepped hulls have been known to suffer from transom slide in sharp turns at speed. They also require attention to loading and trim because the steps need the proper angle of attack to function correctly; they don’t offer an advantage in flat, calm water; and they require a special trailer.
Most owners of stepped-hull vessels are experienced and want to travel at high speeds in moderate to heavy seas, and/or achieve good economy and range. Yet to date, performance and center console builders aside, only Regal Boats, with its FasTrac hulls, and Formula have committed to using steps in production cruisers and sport boats.

Asymmetrical Twin Hulls This unique design concept comes from the drawing board of Larry Graf, the pioneer who put power catamarans on the map here in the U.S. when he founded Glacier Bay Boats in 1987. His new company, Aspen Powerboats, employs a cat design where one hull is narrower (35 percent) than the other. His patent calls it a Power Proa, and it relies on a single engine in only the wider of the two hulls. The hull shapes, alignment and placement compensate for the offset propulsion thrust, allowing the vessel to run straight and true. With only one set of running gear in the water, inherent appendage drag is reduced by 20 percent. Combined with the efficiency of the hull designs, overall fuel efficiency of the Aspen rises to an impressive 70 percent over monohulls of comparable size. Aspen won an award for the best 30- to 39-foot catamaran in the world in 2014.

SWATH A quick glance might lead you to believe that a SWATH (small waterplane area twin hull) vessel is a catamaran. And it is but only to the extent that it has two hulls in the water with a bridge across the top. But that’s where the hulls’ similarities end.
Consider a submarine. Once under the surface, it runs stable, with no roll or pitching from wave action. All that wave energy remains on the sea surface. That basically explains how a SWATH design functions.
If you’ve ever dived under a wave at the beach to avoid being smacked by it, you know that the water beneath the wave is calmer. SWATH minimizes a vessel’s volume where the water meets the air (which is where all the wave energy is at its peak). The bulk of the vessel’s displacement and buoyancy runs beneath the waves, affording amazing stability, even in big seas and at high speeds. Please think of high speeds as a relative term here, as this is not a planing hull. What SWATH does provide, however, are a wide, stable deck and unsurpassed ride quality, especially in rough seas.
Drawbacks to SWATH designs include the fact that each hull must be custom designed. Draft runs deeper than standard hulls (especially planing hulls). The underwater “torpedoes” providing buoyancy must run parallel to the water’s surface, which requires a fairly complex trim-control system. And the underside of the deck must be far enough above the sea surface to avoid waves slamming up into it. Finally, SWATH vessels cost more to design and build than conventional hulls.

Hydrofoils Once the strict province of commercial ferries and a few high-speed military vessels, the most recent America’s Cup has spurred hydrofoil acceptance to new heights. Will it catch on with powerboats?
The hydrofoil design acts exactly like an airplane wing, providing more lift than the drag coefficient the vessel produces, thereby lifting the entire hull out of the water. Only the hydrofoils remain in the water, unaffected by surface wave action. In fact, hydrofoils cut inherent resistance to zero while the hull is out of the water. In the case of power-driven boats, you still suffer drag from the propulsion system (prop, shaft or the like).
The most significant disadvantage to this system on recreational boats is definitely the deployment of the foils. Unless you want the added draft of these struts sticking down below your hull all the time, you must be able to extend and withdraw them — a complex engineering feat. There is at least one recreational powerboat employing hydrofoils: Twin Vee builds a catamaran with foils that don’t actually lift the hulls completely out of the water. It does improve fuel economy and ride stability nonetheless. Still, boats ride more smoothly in a sea and go much faster with hydrofoils. With the dramatic acceptance of this technology in sailing, is it only a matter of time before recreational powerboats incorporate foils into their designs?

Ulstein X-Bow The Norwegian Ulstein Group has been designing offshore vessels since 1917. Presently, it has the notoriety of creating the most advanced bow design in history. The Ulstein X-Bow looks like it might be upside down, but it’s proven itself in more than 100 offshore support vessels to date. The X-Bow allows higher speeds and smoother rides in even the worst seas. Gone are the slamming and vibration that occur when the bow of a ship drops off a wave. It functions better on all points of sea, and its lower hydrodynamic drag substantially decreases fuel consumption. The X-Bow has proven so successful that Ulstein is in the process of creating an X-Stern design now.
You won’t ever see this on small recreational boats, but you can nod knowingly when someone points one out on a mega-yacht in the near future.
- More: Boats

Boat Test: 2024 Nuova Jolly Prince 33 CC

Boat Test: 2024 Starcraft SVX 231 OB CC

Boat Test: 2024 Bass Cat Caracal STS

Boat Test: 2024 Regal 38 Surf

I Learned About Boating From This: Capsize, Rescue and Lessons Learned

Using Hydrofoils to Improve Boat Performance

We Test Interlux Trilux 33 Aerosol Antifouling Paint

- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Boating may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Boating Firecrown . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
- 2024 BOAT BUYERS GUIDE
- SHALLOW WATER FISHING
- Email Newsletters
- Boating Tips
- Boating Safety
- Electronics
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
- Baits & Lures
- Fishing Tackle
- Fishing Travel
- Conservation
- Fishing Knots
- Women in Fishing

The Perfect Boat Hull Designs
- By Chris Woodward
- Updated: May 3, 2012

boat hull shapes
Boats, like cars, often feature a shape that defines them, that makes their purpose expressly obvious. The shapes of a Maserati car and a Yellowfin boat, for instance, say — what else? — speed.
But boat hull designs also carry subtler messages that help boat buyers home in on just the right choice for their fishing style. The width of the chines, the deadrise angle, and the presence of a pad and steps — among other facets — change the comfort and speed of the craft.
What’s in a Shape? “The general philosophy for any planing boat (the category for most trailerable fishing boats) is that the shape of the hull should match its weight,” says Darron Roop, a naval architect and yacht designer based in Virginia Beach, Virginia ( shorebreakmarine.com ). “You want the hull to ride at the right attitude so it handles and tracks better. The second aspect is: Where’s your impact zone? Where’s the boat hitting the water?”
Factors besides hull shape obviously enter the above equations, and Roop is quick to point out that no single design element determines the overall package. In addition, different boats are made for different purposes and different buyers in different locations. But — in general — when tinkering with the running surface of a monohull boat, Roop and others often play with the deadrise angle.
In the fishing world, monohulls comprise flat-bottom skiffs, moderate-V and deep-V boats. Multihull boats have also gained a foothold among anglers because of their deck space and stability at rest. In fact, some designers say power-catamaran hulls are underutilized as fishing boats. The most common error made in building cat hulls, they say, is making the sponsons too wide.
Flat hulls might be easiest to build and have more initial stability per weight, according to the book The Nature of Boats by New York naval architect Dave Gerr ( www.gerrmarine.com ), but they also generally flex more and handle waves rather harshly.
As designers increase the angle of the hull to form a V, they see the vessel’s rough-water ride improve. A standard moderate-V hull carries a deadrise angle of 15 to 20 degrees at the transom. Deep-V’s generally start at 21 degrees and go up to about 26. “At high speed in rough water, deep-V’s pound less than most, and are more stable,” Gerr says. “But as you slow down, they start to flop back and forth more; they’re not as comfortable at slow speed or at anchor.”
A final category is the variable-deadrise hull, wherein the lowest or deepest section of the hull forms a steep angle, and each subsequent section between the longitudinal strakes (the ridges that run fore and aft) angles less and less. The theory is that such a graduated deadrise puts the deepest angle at the keel so that it lessens impact. Flattening the deadrise as it approaches the chines (where the hull bottom meets the sides) should then offer some of the stability benefits of a flatter hull.
Tricks of the Trade With some moderate- and deep-V vessels, the deadrise remains more or less constant from amidships to the transom, though it narrows at the bow. But in many cases, designers create what’s called a modified-V or “warped plane” hull — wherein the deadrise decreases from a high of perhaps 22 degrees amidships to 15 degrees at the transom. A flatter transom allows the boat to travel faster than a deeper hull with the same horsepower. Stated differently: The more deadrise you have, the more power you need to get the same speed.
Lou Codega, a Virginia-based naval architect ( www.loucodegana.com ) who has designed vessels of all sizes — including current Regulator hulls — used a modified deep-V for those popular fishing boats. At the transom, Regulators measure 24 degrees; the deadrise increases almost all the way forward to about 48 or 49 degrees.
“Where you really feel the most impact is at the place where the water hits the boat. That can be anywhere from the bow to 50 percent or 70 percent back toward the stern. That’s the deadrise that the water sees,” he says. “And that’s really where the magic happens. There’s no formula or textbook that says, ‘At this specific point on the hull, you should have 36 degrees deadrise.’ The difference between a good- and bad-riding boat is how you’ve gone from whatever number you have at the transom to the number at the bow.”
Regulators, like many fishing vessels, feature a single chine on each side of the boat . The chine usually forms a sharp angle — as sharp as possible with fiberglass. Inward from the chine is a flat surface — the chine flat — that might measure two to six inches based on the size of the boat.
Chines and the adjacent flat surfaces redirect spray to the side and create lift, Codega says. Beneath the hull, most fishing boats also have strakes that similarly knock down spray but also reduce friction.
“Strakes strip the sheet of water off the hull of the boat,” Codega says. “That reduces resistance and changes trim a little.”
The Speed Creed Some companies take deep-V’s to another level, specifically those builders that make offshore-tournament center-consoles. Wylie Nagler, owner of Yellowfin Yachts ( www.yellowfinyachts.com ) in Sarasota, Florida, entered the tournament mix with a boat-racing background. His Yellowfins feature state-of-the-art-design technology, including a stepped running surface, a flattened pad near the transom and slightly wider, downturned chines.
Yellowfin also takes great care in considering fishing needs. “The old theory was the skinnier the boat, the faster the boat,” Nagler says. “Twenty years ago, people started putting center‑consoles on go-fast boats, and they found that the boat does go fast, but it doesn’t have any room. You need to have some room to have a well-thought-out fishing boat. There’s a ratio of length to beam that doesn’t hamper performance.”
Builders also play with the proportion between chine width (wider chines increase stability at rest), the pad design, and the step size and angle. The pad helps create better stability at speed. “If you look at the back of a conventional-V boat, it will be curved at the bottom or come to a knife edge,” Nagler says. “We have created something that’s 12 to 14 inches wide; it’s a V pad, not a flat pad. It means less deadrise in the keel, but there’s still a little to keep the boat from slapping.”
Steps introduce air, which reduces friction for better efficiency and speed — 25 percent to 30 percent better fuel economy and 15 percent increased speed, Nagler says. But some step designs work and some don’t, he explains, referring to the location of the steps and their angle. “When you’re running fast in a following sea, they can have a tendency to bow steer,” he says. “If a stepped hull is designed correctly, you cannot tell any difference in the handling of the boat from a conventional V bottom.”
Nagler says the steps in a Yellowfin hull are fairly shallow. In addition, rather than running perfectly straight strakes, he staggers them on the steps, which he says creates stability.
Lower and Lighter Most bay boats and flats skiffs feature deadrise angles in the teens; 15 degrees is a fairly typical starting point. A slight angle helps skiffs run a little better in open sounds and in locations such as the mid-Atlantic, where inshore anglers venture outside the inlets.
“If I were selling bay boats from Cape Hatteras to New England only, I might have more deadrise and a sharper entry,” says Roop, who has designed Maverick and Pathfinder boats, among others. “If not, then I’d dial it down a little. A boat is not necessarily going to run worse if it has less transom deadrise. You wouldn’t want to use that one characteristic to drive your opinion.”
Deep-V hulls not aimed for the go-fast crowd often help prove this point. Roop says that in designing Cobia boats — targeting a broader demographic — he dialed down the deadrise angle to 21 degrees, making them flatter boats at the transom to reduce rolling.
“There’s still plenty of deadrise here, so you can run the boat hard and be very comfortable with it,” he says. “The width [of the boat] and the deadrise combine to make it run at the right attitude. That’s why I tell people to go run a boat to find out how it rides. If someone has done a good job designing it, they’ll be more comfortable.”
Outboard boats should run flatter, though in a following sea, they shouldn’t run too flat. Generally, Roop says, the flatter the boat runs, the less vertical acceleration it generates and the more comfortable it will be. However, Cobia boats were not intentionally built to run from wave top to wave top — as some go-fast hulls — but rather they employ a fine entry to slice through the waves for a soft ride.
The bottom line is that many factors work together to make a boat run properly. Don’t assume a specific deadrise number automatically pigeonholes a boat’s performance, Roop says. “My designs are all about finding the right running attitude,” he says. “The hull, the speed, the weight — all things have to dial in to get the attitude.”
- More: Boat Engines , Boating Skills , Center Consoles , Fishing and Boating Tips , fishing boats , Yellowfin Boats

What’s Good Fuel Economy for a Fishing Boat?

Yamaha Releases New 350 Horsepower Outboard

Supersize Center-Consoles Expand Angling Horizons

Things To Look For in a Jig-and-Pop Boat

Toughest Nearshore Game Fish

New Gear: The Siren Connected Boat App

QUICK GUIDE: Surf Fishing Etiquette

Fishing With Crabs as Bait
- Privacy Policy
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Sport Fishing may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Copyright © 2024 Sport Fishing Firecrown . All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
Moskva-Class Cruisers
Separate design teams often attempt to meet a set of ship specifications with completely different, although equally valid, strategies. To fulfill the requirements issued in April 2169 for the successor (NX-223) to the Daedalus class, which was introduced at the end of the Romulan War, Prosser & Ankopitch proposed a ship with an extremely large, spherical command hull attached to a nearly vestigial engineering hull. The proposal from the Mikoyan-Tupolev-Dassault Bureau used a long narrow command hull with a minimal frontal silhouette counterbalanced by an equally long engineering hull.
The engineers at Tezuka-Republic decided that the division of ship's functions between a command/crew hull and an engineering hull was arbitrary and unnecessarily restricted design options. Therefore, rather than gathering all the specified facilities in a single hull, their design TR-223A spread them across two hulls, as in Daedalus , and segregated the SSWR-IV-C warp core to a "bustle" at the extreme aft end of the secondary hull. This bustle could be separated easily and quickly from the rest of the engineering hull in the event of a warp core breach. The now-unpowered warp nacelles would then be shed. In this way, the demands of safety would be met without warp dynamics being degraded either by an excessively large frontal silhouette or by longitudinal warp field imbalance.
Although the Ship Specifications Review Board praised Tezuka-Republic for its creative solution to the problem of admittedly contradictory requirements for extreme safety and improved warp performance, they were forced to disqualify design TR-223A for not precisely meeting contract specifications. Therefore, in October 2171, construction contract NX-223 for Starfleet's new cruiser was awarded to Prosser & Ankopitch for what would become the Wasp class .
However, almost no one was happy with the new Wasp ships. Even before the contract was awarded, voices within Starfleet and within industry had strongly criticized the specifications of April 2169. These critics charged that they would lead to a mediocre, albeit safe, fighting ship. Two separate classes were needed, not a single class that was neither a proper explorer nor a proper warship. When Wasp was finally launched in 2173, her performance during precommisioning trials clearly showed that the critics had been correct. Although the performance problems were related in part to the continuing unavailability of the more powerful Tezuka-Republic Hiryu ("Flying Dragon") mark III warp nacelles, Wasp was obviously not the ship Starfleet had hoped for.
In a second attempt to obtain a reliable and capable warship, new specifications (NX-374) were issued in September 2175, little more than a year after USS Wasp had entered service. Adding to this sense of urgency were intelligence reports suggesting that the Romulans had either developed or otherwise acquired matter/antimatter (M/AM) reactors. This time the specifications put less emphasis upon safety. The original requirement for completely separate command and engineering hulls was eliminated; instead, any hull configuration was allowed as long as the warp core could be quickly separated from the rest of the ship. Furthermore, requirements for speed, acceleration, and maneuverability both under impulse power and under warp power were increased, as were performance levels for target acquisition, tracking, and servicing.
These new specifications were a clear, albeit belated, admission that the critics had been correct all along: one class could not be expected to serve as both an explorer and a main battleship. In fact, starship technology was not considered sufficiently mature for a single ship to adequately fulfill both mission profiles until 2245, when the Constitution -class heavy cruiser was launched. (The controversy continues even today in the wake of the problems of the Galaxy -class explorer.)
Luckily, the designers and engineers at Tezuka-Republic had not been idle since their disappointing loss of the Wasp contract in 2171. Instead, they had spent their time refining design TR-223A so that their new entry (TR-374A) was markedly superior to what had been submitted 5 years earlier. In particular, the new SSWR-V warp reactor allowed the bustle to be made smaller, lighter, and even more easily separable. Therefore, it was hardly surprising when in November 2176 Tezuka-Republic was awarded the production contract over designs from Shimata-Dominquez, Prosser & Ankopitch, Mikoyan-Tupolev Dassault, Monarch R&U, and Thornycroft/Ebisu for what was to become the Moskva class.
However, engineering prowess may not have been the only factor in Tezuka-Republic's winning of the contract. There were accusations that the delay in delivery of the Hiryu warp engines was an attempt by Tezuka-Republic to prevent Wasp from reaching her designed performance levels. While no conclusive incriminating evidence has come to light, the delivery of the long-awaited engines shortly before the scheduled launch of Moskva in December 2177 is certainly suspicious. Tezuka-Republic maintains that if their submission of 2169 had been selected, its performance would also have not have met design specifications without the Hiryu engines. However, critics charge that TR-223A was not as reliant as Wasp on the type of engine used. Furthermore, once the Wasp contract was awarded, and even after Wasp was launched, Tezuka-Republic certainly made no efforts to accelerate delivery of Hiryu.
These controversies were soon rendered moot as the new Moskva class was recognized as a significant advance in starship design. The most important new feature was Moskva's discoid primary hull. Earlier designs had chosen a spherical primary hull for reasons of economy. Simple geometric relationships dictate that a spherical hull has the smallest surface area for a given volume. Therefore, construction costs are lower and shields are more efficient. Furthermore, institutional inertia had led nearly all exploratory cruisers originating until that time from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, the United States Astronautics Agency, the United Earth Space Probe Agency, and its successor organizations to have spherical hulls.

The designers of USS Moskva employed a biconvex disc for several reasons. Their initial motive was to increase hull volume while minimizing both frontal and lateral silhouettes. A warship with large frontal and lateral silhouettes would be at a greater disadvantage in most tactical situations than would be a ship with an increased superior silhouette. However, the discoid hull allowed the traditional radial layout of command hulls to be retained.
More important than these tactical advantages were functional advantages. As was shown with the Wasp class, warp field geometry would have been awkward if a spherical hull with its relatively large frontal area had been used. The discoid hull was also found to channel warp field flow across its upper surface towards the bussard ram scoops of the warp nacelles. This channeling effect improved field efficiency at all power levels and speeds. As the understanding of warp field mechanics was refined, the trend towards saucer-shaped primary hulls would be intensified in later Starfleet vessels.

In most respects, the Moskva class continued design and engineering trends established in the Comet and Daedalus classes introduced at the end of the Romulan War. As in these classes, ship functions were clearly divided between a command/crew hull and an engineering/propulsion hull. The bridge was returned to its customary position atop the command hull and the shuttlecraft bay was again placed in the secondary hull. The fusion reactor was centered along the longitudinal axis of the ship, and impulse thrust ports exited immediately in front of the warp bustle detachment seam.
Weaponry was the then-standard mix of fusion-warhead missiles and lasers. New to this class was an early type of ultraphased pulse laser cannon, two of which were mounted in the chin of the primary hull. Although the on-target energy output of this new weapon approached that of early phasers, its power requirement was higher and its range was substantially less. However, subsequent refinements lead to steady improvement and, ultimately, to the development of true phasers in 2202. Although Moskva -class ships were the first to be fitted with phasers in 2204, lasers were still carried by the Moskva class and later classes until the 2220s. Finally, warp capability was supplied by the long-awaited Hiryu mark III drive units.
The first ship of the new class, USS Moskva (NCC-374), entered service with Starfleet in April 2179. An additional 30 ships (NCC-375 to NCC-404) joined the fleet through 2183. Moskva -class ships gained immediate popularity with officers and crews. First, total laser firepower was increased some 75% over that in the preceding Wasp class. Second, because the ship's mass was more equally distributed along the longitudinal axis than in the Wasp class, Moskva was significantly more maneuverable at both sublight and warp speeds. Finally, the more warp-dynamic design allowed greater cruising and maximum speeds.
The Moskva class had an outstanding safety record. No ships were lost because of mechanical failures. However, an incident occurred aboard USS Johannesburg in 2186 when a faulty nacelle flow monitor falsely indicated a runaway positive feedback power loop within the plasma flow governor. Believing that a catastrophic warp core explosion was imminent, Chief Engineer Roberta Bocharnikov ordered the warp nacelles and warp bustle to be separated. Although unnecessary, these maneuvers were successful in causing the separated warp core to initiate its automatic shut-down routine. The warp core, nacelles, and the rest of the ship were towed to Starbase 13, where they were successfully re-mated. Despite her supreme embarrassment, Bocharnikov oversaw the reassembly and relaunching of Johannesburg and retained her position as chief engineer.
Although most ships of the Moskva class had left front-line service by 2215, some continued to serve as auxiliaries and training vessels until the 2240s. After retirement from active duty, Moskva -class ships were used as testbeds for many emerging technologies owing to the similarities of their layouts to those of succeeding classes. USS Moskva was the site of the first successful ship-to-surface transport of a Human being in 2206, and USS Gato was the first ship to fire photon torpedoes in 2214. In addition, Taurus -class tugs, which entered service in 2182, and Sanford -class repair tenders, which entered service in 2185, were derived from the Moskva class and used the same primary hull and warp drive assembly.
The Moskva -class cruiser USS Aurora (NCC-377), a participant of the Battle of Eohippus IV, is on display at the Starfleet Museum.
Standard displacement: 67,750 t
Crew complement: 160 (27 officers + 133 crew) Weapons: 8 Type VI laser turrets (8 × 1 mounts), 2 Type VII laser cannons (fixed mounts), 2 missile launchers with 36 Spartak missiles Embarked craft: 4 medium cargo/personnel shuttlecraft, 2 light personnel shuttlecraft, 5 fighter/scouts Warp drive: SSWR-V-A spherical cavity M/AM reactor with 2 Hiryu III nacelles Velocity: wf 4.0, cruise; wf 5.0, supercruise; wf 5.2, maximum Units commissioned: 31
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Jail Cells? Morgues? Your Cruise Ship Has Some Surprises for You.
Here are five unexpected features on ships, some of which you hopefully won’t discover on your own.

By Ceylan Yeğinsu
Cruise ships have hidden features that many passengers, particularly first-timers, don’t know about. Some ships are as big as small cities, and while it’s relatively easy to familiarize yourself with a seemingly endless number of amenities — water parks, tattoo parlors, multiple restaurants — there is also an entire ecosystem, often below passenger decks, that is shrouded in mystery.
Here are five things that cruisers may not know about cruise ships:
There’s a morgue …
Cruise ships carry millions of passengers each year, and it is not uncommon for deaths to occur on board. Most vessels are required to have a morgue and additional body bags in the event of an emergency.
The morgue, usually a small stainless steel refrigerated room on the ship’s lowest deck, accommodates between two to 10 bodies, depending on the size of the vessel. When a passenger or crew member dies, officials on the ship will notify the authorities on shore and a medical team will assess the body and move it to the morgue, where it is kept until arrangements are made for repatriation. In most cases, the body will be removed at the next port of call, but sometimes will remain on board until the end of the voyage.
…and a jail
There are no police officers on cruise ships, but most vessels have small jails known as the brig, and unruly passengers could find themselves locked up if the ship’s security team determines that they have violated the cruise line’s code of conduct.
The brig, usually a bare-bones room with a bed and bathroom facilities, does not have iron bars like a traditional jail cell. It is used to detain guests who commit serious crimes like assault or possession of illegal substances. Drunk and disorderly passengers may be put under “cabin arrest,” meaning they cannot leave their cabin without a security escort.
Depending on the circumstances, most passengers put in the brig will stay there until they can be handed over to law enforcement officials.
Many ships don’t have a Deck 13
Many cruise ships do not have a Deck 13 because of the widespread superstition in Western culture that the number is unlucky. Ships with a Deck 13 typically use it for public areas, not cabins.
Some ships, like Royal Caribbean’s Quantum class vessels, have a Deck 13 because the vessels are used mainly for the company’s market in Asia, where the number is not considered unlucky. MSC ships also have a Deck 13, but not a Deck 17, because the cruise line’s founder is Italian and 17 is considered unlucky in Italy.
Cruise lines entertain other superstitions, like appointing godmothers to bless new vessels and ensure the safety of passengers and crew. They also hold naming ceremonies in which a bottle of champagne is smashed against the hull of a new ship for good luck. If the bottle fails to break, the vessel will, according to superstition, have bad luck. These days, cruise lines use mechanical devices to ensure that does not happen.
Hidden pools and facilities for the crew
There are typically more than 1,000 crew members on board large cruise ships, and while they spend most of their time serving passengers, there are several areas on the lower decks designated for them to unwind.
The facilities vary from ship to ship, but there are usually small pools in the ship’s bow exclusively for crew members, as well as restaurants, bars and recreational areas like game rooms and gyms. The designated bar, a central social hub for employees after they have finished their shifts, often hosts live music and events in the evening.
Royal Caribbean’s Icon of the Seas, the world’s largest cruise ship, has an entire “neighborhood” dedicated to its 2,300 crew members, with a clubhouse that has massage chairs and virtual balconies — large screens that show real-time views from outside — as well as a restaurant with portholes looking out to the ocean.
Most ships host A.A. meetings
With all-inclusive beverage packages and countless bars, cruise ships can be a tough environment for guests in recovery. Many cruise lines offer daily Alcoholics Anonymous meetings that are usually scheduled as “Friends of Bill W.,” a reference to William Wilson, who co-founded the A.A. program in 1935.
The meetings are usually held in a quiet place like the library, where guests can feel comfortable and maintain their anonymity. They are also open to other support group members, like Women for Sobriety and Narcotics Anonymous.
Follow New York Times Travel on Instagram and sign up for our weekly Travel Dispatch newsletter to get expert tips on traveling smarter and inspiration for your next vacation. Dreaming up a future getaway or just armchair traveling? Check out our 52 Places to Go in 2024 .
Ceylan Yeginsu is a travel reporter for The Times who frequently writes about the cruise industry and Europe, where she is based. More about Ceylan Yeğinsu
Come Sail Away
Love them or hate them, cruises can provide a unique perspective on travel..
Icon of the Seas: Our reporter joined thousands of passengers on the inaugural sailing of Royal Caribbean’s Icon of the Seas . The most surprising thing she found? Some actual peace and quiet .
Th ree-Year Cruise, Unraveled: The Life at Sea cruise was supposed to be the ultimate bucket-list experience : 382 port calls over 1,095 days. Here’s why those who signed up are seeking fraud charges instead.
TikTok’s Favorite New ‘Reality Show’: People on social media have turned the unwitting passengers of a nine-month world cruise into “cast members” overnight.
Dipping Their Toes: Younger generations of travelers are venturing onto ships for the first time . Many are saving money.
Cult Cruisers: These devoted cruise fanatics, most of them retirees, have one main goal: to almost never touch dry land .
Dyna-Ski Boats custom builds outboard powered water ski boats for recreational skiers and show ski clubs. We have customers all over the world including Malaysia, the Caribbean, Moscow, Russia, the Cayman Islands and Canada. This blog is used to keep readers informed about what is going on at Dyna-Ski and answers questions that are frequently asked. You can also visit www.dyna-ski.com for more information about our boats. Contact Dyna-Ski at [email protected] or call 715-854-7501.
Tuesday, July 2, 2019
Update on things and how to buy a dyna-ski boat, no comments:, post a comment.
trending now

Michael Jackson's son Blanket takes grandma Katherine to court...

Christine Quinn's husband arrested for second time in 33 hours...

Bethenny Frankel threatens to 'f--k up' trolls criticizing the...

Machine Gun Kelly, Megan Fox 'living separately' after she...

Inside Drew Barrymore's very 'normal' and 'simple' New York house...

Erykah Badu rips Beyoncé for copying her, asks Jay-Z to...

Gavin Rossdale admits he doesn’t have ‘a connection’ with...

Aaron Taylor-Johnson, 33, says he married much-older wife Sam,...
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to copy URL
See Mark Zuckerberg’s glossy new $300M, 287-foot superyacht ‘Launchpad’
- View Author Archive
- Follow on Twitter
- Get author RSS feed
Thanks for contacting us. We've received your submission.
All aboard S.S. Facebook.
Mark Zuckerberg has reportedly gifted himself a $300 million megayacht, dubbed “Launchpad,” ahead of his 40th birthday.
The staggering 387-foot-long vessel was seen floating at Port Everglades in Fort Lauderdale, Fla., after arriving at its berth earlier this week, The Sun reported Thursday.

The multi-layered luxury ship’s sleek exterior was designed by Espen Øino International and boasts a steel hull and an aluminum superstructure, according to SuperYacht Times.
Reportedly ranking as the 45th largest yacht in the world, the interiors are just as aesthetically pleasing and reportedly executed by Zuretti Interior Design company, a France-based company specializing in unique and custom yacht design.
The breathtakingly beautiful floater stands out with a navy blue theme matching an American flag perched proudly on its wood-paneled stern.

There are several outdoor areas where the social media maven will be able to relax with his family and the indoor levels feature glass paneling allowing for tons of natural light.
For more Page Six you love…
- Listen to our weekly “We Hear” podcast
- Shop our exclusive merch
There also appears to be a helipad perfect for whenever the Facebook co-founder wants to travel to his vessel by air.
The Feadship-built yacht, built in 2022, can comfortably fit 24 guests aboard, requires a crew of 48, and is said to cost $30 million a year for upkeep and usage, according to Superyachtfan.com .

Want more celebrity and pop culture news?
Start your day with Page Six Daily.
Thanks for signing up!
Please provide a valid email address.
By clicking above you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Want celebrity news as it breaks? Hooked on Housewives?
Boatworld insiders have been buzzing with speculation that Zuckerberg is the owner of the newly minted mega-cruise ever since it made its main voyage from the Netherlands last week.
The tech titan was spotted touring the Russian-commissioned megayacht in early March, though the impressive boat didn’t arrive stateside until this week due to sanctions, according to The Sun.
The website reported that Zuckerberg purchased the pricey yacht – along with its own $30 million partner boat — most likely as an early 40th birthday present to himself.

The boat reportedly traveled to Florida after being granted special permission to be imported just weeks ahead of Zuckerberg’s birthday on May 14.
Zuckerberg’s yacht is just 30 feet shorter than the length of fellow billionaire Jeff Bezos’ 417-foot megayacht Koru, which the Amazon boss snagged for a whopping $500 million.
Zuckerberg’s rep did not immediately respond to Page Six’s request for comment.
Share this article:

Advertisement

COMMENTS
Flat-bottom hull sailboats have the most stable design for shallow water and multi-hull boats are the most stable in deep water. The inclusion of multiple hulls adds stability in deep water that prevents water from landing on the deck. ... Fiberglass is the best material for a boat hull, even compared to aluminum which was the standard for years.
Best bluewater sailboats for comfort. ... The hull design dates back to 1995, but was relaunched in 2012. Though the saloon interior has dated, the 441 has solid practical features, such as a ...
June 15, 2022. Sailboats come in numerous hull shapes. These include single-hull monohulls, along with double and triple-hull multihulls. There are two main categories of sailboat hulls: monohulls and multihulls. Common monohull types include flat-bottom vessels, fin-keel racers, bulb and bilge keel cruisers, heavy semi-displacement sailboats ...
Generally, multihulls and deep-V hulls are considered the most stable hull designs in most situations. In practice, the most stable hull design depends on the specific conditions in which the boat will be used. With large waves, deep hulls tend to be better than multihulls. With different situations, the most stable hull winner changes.
A truly flat-bottomed boat has zero degrees of deadrise. Most powerboat hulls have some deadrise, giving the hull bottom its "V" shape when viewed from the bow or stern. The deep-V hull was developed in the late 1950s and proved to be optimal for high-speed offshore vessels, with transom deadrise of 18 to 24 degrees.
Before that happens, it's essentially a displacement hull. 2. Plowing. While a boat with a planing hull is picking up speed and lifting itself out of the water, it's in a plowing mode. You'll know when a boat is in plowing mode when the bow of the boat is elevated and the boat is throwing a relatively large wake.
Ultimately, the job of a sailboat hull is to keep the boat afloat and create stability. These are the fundamentals of a seaworthy vessel. There are two types of stability that a design addresses. The first is the initial stability, which is how resistant to heeling the design is.
To highlight how these boat design principles play out, Practical Sailor looks at classic sailboats such as the Bill Shaw-designed Pearson 32, Ericson 41, Valiant 40, and Peterson 44, and compares their keel/sail ratios and lead values to more modern sailboat designs such as the Catalina, Hunter, Tartan, and Beneteau. ****.
After a 30 year absence, a veteran marine journalist returns to the US Sailboat Show and discovers the many changes in cruising boat design and construction. By Dan Spurr. Updated: June 10, 2020. The X-Yachts 46 displays the wide beam, twin wheels and open transom that define many 2020 models. Jon Whittle.
Light displacement, modern wide hull - Pogo 10.50. This decision should depend, at least in part, on how comfortable the yacht is in a seaway. Now the comfort of yachts of the same size can be remarkably different. Take yachts of around 35ft or 10.6m long - a common yacht length. Three examples show how much the displacement can vary for ...
Editor's Choice: 18 Bluewater Sailboats We Love. 25,658 11 minutes read. Advantages of bluewater sailboats. Factors to consider when buying a blue water sailboat. Allures 51.9. Amel 60. Contest 55CS. Discovery Revelation 480. Grand Soleil 42 LC.
The sail shape is a fundamental aspect of sail boat design, directly impacting its speed, windward performance, and maneuverability. There are several types of sail shapes, including: 1. Bermuda Rig: The Bermuda rig is a widely used sail shape known for its versatility and performance. It features a triangular mainsail and a jib, offering ...
The most common sailboat keel types are full-length keels, fin keels, bulb keels, wing keels, bilge keels, and lifting keels. Full keels are popular among cruisers, while fin keels are generally used for racing. Bilge keels and lifting keels are typically used in tidal waters, on small fishing boats for example.
Performance. Generally light displacement brings performance benefits due to the higher power to weight ratio and reduced hull drag through having a smaller wetted area.. This is borne out by two important design ratios, the Displacement/Length Ratio and the Sail Area/Displacement Ratio. Length too has an impact on performance, as can be shown by another sailboat design ratio, the Speed/Length ...
Different Types of Boat Hulls: Flat Bottom Hulls : a hull that has almost no deadrise. Deep-V Hulls: a wedge-shaped hull from bow to stern. Modified-V Hulls : the most common hull for small boats. Catamarans : two hulls bridged by a deck. Chines and Strakes : molded strips run lengthwise along the hull bottom and are virtually universal on ...
For almost 20 years, we've called this awards program SAIL Best Boats, but this year, we're refining and renaming this program to better and more fairly represent the boats we've selected. Restricting boats to categories and labels—such as Best Cruising Monohull 30-40 feet and Best Performance Monohull 40-50 feet—doesn't bring our readers the full picture.
Bearboat SP: Free Boat Designer for Small Boats & Kayaks. DELFTship: Intuitive Free Boat Design Tool with Professional Option. Fusion 360: Best Free Boat Design Software for Beginners & Mac. SketchUp: Best Boat Design App for iPad. Autoship: Best for Naval & Marine Architecture, Best for Windows.
With only one set of running gear in the water, inherent appendage drag is reduced by 20 percent. Combined with the efficiency of the hull designs, overall fuel efficiency of the Aspen rises to an impressive 70 percent over monohulls of comparable size. Aspen won an award for the best 30- to 39-foot catamaran in the world in 2014.
A standard moderate-V hull carries a deadrise angle of 15 to 20 degrees at the transom. Deep-V's generally start at 21 degrees and go up to about 26. "At high speed in rough water, deep-V's pound less than most, and are more stable," Gerr says.
The first ship of the new class, USS Moskva (NCC-374), entered service with Starfleet in April 2179. An additional 30 ships (NCC-375 to NCC-404) joined the fleet through 2183. Moskva -class ships gained immediate popularity with officers and crews. First, total laser firepower was increased some 75% over that in the preceding Wasp class.
A quality paint job where the painter turns the boat over and paints the hull bottom and then the deck is the best way to paint a boat. It is also expensive but not as much as Gelcoating an old boat. I think painting and old boat is the best way to go, period! The second guy needs at least $2000 for the stuff to rig a single engine with ...
Cruise ships have hidden features that many passengers, particularly first-timers, don't know about. Some ships are as big as small cities, and while it's relatively easy to familiarize ...
This blog is used to keep readers informed about what is going on at Dyna-Ski and answers questions that are frequently asked. You can also visit www.dyna-ski.com for more information about our boats. Contact Dyna-Ski at [email protected] or call 715-854-7501.
Really no need for a 300 hp. or larger engine as a Dyna-Ski boat is not a go fast hull! It is a water ski boat. I always suggest at least a 175 hp. motor on a 20' but the boat is a decent water ski boat with 150 hp. unless you want to ski with a boat full of people or do a lot of bare foot skiing. If you do go with a 200 hp. or larger motor.
The multi-layered luxury ship's sleek exterior was designed by Espen Øino International and boasts a steel hull and an aluminum superstructure, according to SuperYacht Times. Reportedly ranking ...