

Type Of Sails: A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
Last Updated on September 29, 2023 by Boatsetter Team
If you are approaching sailing and sailboats from a very beginner’s perspective , then the concept of different kinds of sails can be a strange one. We often believe we see one kind of sailboat with one kind of sail, and our simple minds lead us to believe you are only meant to move them around, and you will get to where you need to go.
However, you would not have landed on this article if you did not suspect that there was more to sails and sailboats. So here, you can have a kind of in-depth, kind of summarized review of the different kinds of sails and the most popular sail and mast configurations out there.
It is also important to understand why there are so many different kinds of sails. When you are out on the water, different weather conditions can occur. Your sail acts as a motor of some sort, moving your sailboat forwards, but your sail is also highly dependent on the wind conditions around it. This is why having different kinds of sails can help you navigate your weather conditions and turn them to your own advantage while sailing.
Different sails also come with different danger levels in case of strong wind, so knowing what kinds you might need to watch out for is also extremely important. So, without further ado, let us get into it.
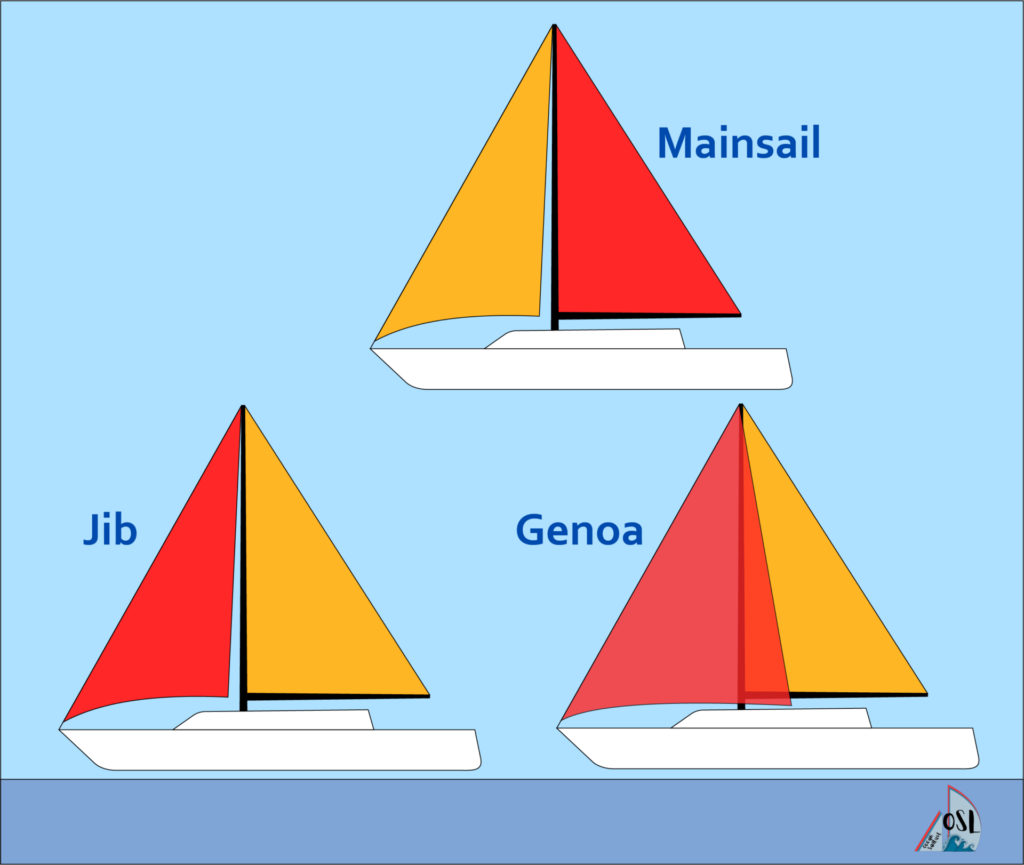
You may have heard of this one before or seen it portrayed in movies and TV shows. As the name suggests, the mainsail is the most popular kind of sail on any sailboat, and they are found behind the mast. They are also attached to the boom. Because they take up so much space on your sailboat, they are also one of the most important sails to take care of and keep an eye on.
Since the mainsail is such a large sail, it does not require too strong a wind to propel it forward , as its large surface area will easily catch a breeze. At the same time, the fact that it can be moved around by moving the boom makes it, so it is easy to steer. This makes it so that the mainsail is the most important sail on your sailboat.
Headsail/Jib

The headsail, or the jib, is likely the second most popular kind of sail found on sailboats. This is because it often accompanies the mainsail, the most popular kind. On all sailboats , the headsail is put at the front of the mast over the sailboat’s bow . It is always a smaller sail than the mainsail.
The fact that the headsail is smaller can be especially useful if you are caught in strong winds. In this situation, you likely do not want to use your mainsail (or trim it as much as possible) to move slower and not be thrown around by the winds. Smaller sails catch less wind, meaning they do not propel your boat as strongly as larger sails.
Having a good headsail can be an incredible safety measure, especially if the seas you are trying to sail are known to be wild and unpredictable.
You may have seen a genoa sail before if you have been around boats or have ever lived in a coastal town. This kind of sail is a large sail that you can attach to the front of the forestay (similarly to the headsail). This is a larger sail than the headsail and can even cover the mainsail either partially or completely. For this reason, the genoa also used to be called an “overlapping jib.”
You should use a genoa if you are sailing through either light or medium winds and if your sailboat is at a dead run point of sail (this means that the wind is coming directly from the rear. If you attempt to use a genoa sail in stronger winds , you might start going too fast and put yourself and your boat at risk since it is such a large sail. So, it is important to be careful .

The spinnaker is the most whimsical kind of sail since it is a large and colorful kind. They are also often symmetrical, which means they are more appropriate for reaching different points of sail, such as the running point of sail. They are lighter sails, and they do not cover the mast as the genoa sail does. You do not attach a spinnaker to the forestay and instead let it stretch out past the boat’s bow.
The large surface area of the spinnaker means that you have to be even more careful than with others on the kind of conditions you choose to use this sail in. If the winds are too strong, you could be putting yourself and your passengers at serious risk using this sail, so you should choose to use it only at times when the wind is low or in seas that are known for their low winds and tranquility.
As the name suggests, the gennaker sail mixes the genoa sail and the spinnaker sail. These kinds of sails are more recent inventions. They are as large as the spinnaker sail, but they are not symmetrical. Unlike the genoa or the headsail, they are also not meant to be attached to the forestay, like the spinnaker sail.
The usefulness of this sail is that if the winds change from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, then sailors do not have to resort to using a spinnaker from a genoa, instead of being able to take advantage of different winds while still using the same sail as they were before. This kind of sail is still only meant for lighter and milder winds , but there is more flexibility with the gennaker than the genoa and the spinnaker sails.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
There are many different ways to place the sails we have learned about in the above section. We have compiled a list of some of the most popular ones so you can understand how these sails can be used to make a sailboat move through the oceans.

A sloop is by far the most popular configuration. It features a single mast, double sail (the mainsail and the headsail), and mast configuration. The headsail is located from the forestay on the mast to the top of it. The type of headsail used can also vary from a genoa, a spinnaker, or a gennaker sail.
Fractional Rig Sloop
A fractional rig sloop also features a single mast with a double sail setup similar to a sloop. However, what makes the fractional rig sloop different is that the forestay does not reach the top of the mast. This means the headsail is constricted to a smaller amount of surface than on a regular sloop, making it so that your sailboat captures less wind and moves slower .
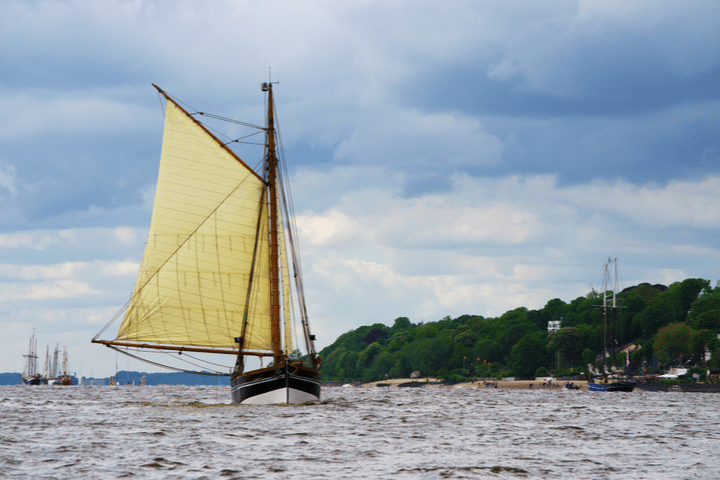

Cutters are interesting because they’re like a sloop but with a second forestay. This can be useful because it allows them to carry two headsails (a mainsail and one of the jibs). Cutters are good for cruising because they offer a range of wind options, giving you more time to get from place to place.
This is a less common mast configuration than previous others on this list. This is because a ketch features two masts. There is a larger mast fit for the mainsail and the headsail and a smaller mast between the mainmast and the stern (the rear) of the boat. This kind of mast configuration is more commonly found among Northern European freighters or fishing boats. This mast configuration is also called the mizzen mast.
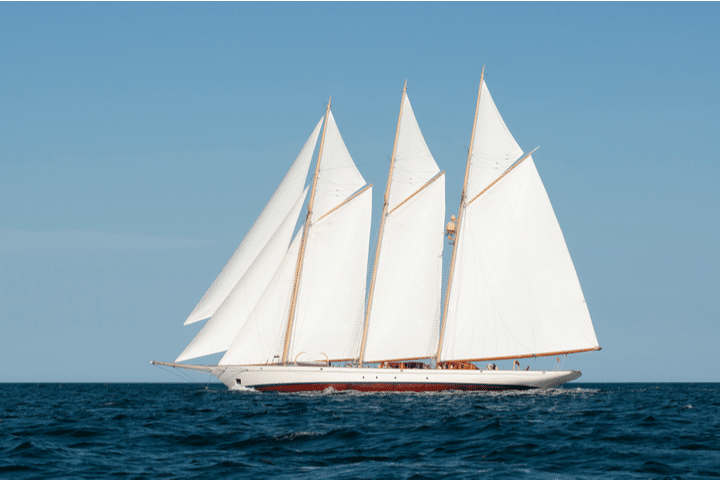

A schooner mast configuration features two or more masts. This is similar to the previous configuration, the ketch. It also features multiple sails. While a ketch’s aft mast (also known as the rear mast) is higher than the forward mast, a schooner’s aft mast is shorter than the forward mast. A schooner can also have up to six masts (although two are the most common). These are the main differences between the two.
This one is quite similar to a ketch mast configuration (mentioned above). The only real difference between them is that the mizzen mast is put directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post in a yawl.
A cat sail will have one mast and one sail. The mast is put at the bow of the sailboat. This kind of mast configuration is often found on smaller boats, more specifically on dingy boats. Boats with the cat mast configuration are also often called catboats.
Final Verdict
Having the appropriate kind of sail on your sailboat is incredibly important. At the same time, being aware of the kinds of sails that there are and the kind of sail and mast configuration can make you into a more well-rounded and informed sailor. With that in mind, we hope that you leave this article feeling more confident in your skills when you are out at sea.

Boatsetter empowers people to explore with confidence by showing them a world of possibility on the water. Rent a boat, list your boat, or become a Boatsetter captain today.
Browse by experience

Explore articles

Boatsetter Teams up With Owners to Help Protect & Preserve Our Waterways

How Carlos Looks Ahead as Boating's Busy Season Gets Underway

10 Best Pontoon Boats 2024

Key West Boat Races: 2022 World Offshore Championships
Sail Types: A Comprehensive Guide to 8 Types of Sails
Sailboats come in all shapes and sizes. And that means there are many types of sails on the market! For those who might not know, sails are made of canvas and use wind power to propel sailboats through the water.
Understandably, different sails are required for different types of sailboats . And sailboats are categorized by the number of hulls they have. Monohulls have a single-hull design, catamarans have two hulls, and trimarans have three. Generally, sailors use catamarans for upwind sailing (but they can be used to sail downwind in certain conditions).
The type of sail you'll need for your sailboat depends on the kind of sailboat you have. Additionally, sails are highly dependent on the wind and weather conditions. Therefore, it's always a good idea to have different types of sails on board to navigate the ever-changing weather conditions.

8 Types of Sails for Sailboats
As mentioned, you should carry multiple sails when sailing to prepare for various weather conditions. Here's a brief overview of the types of sails for sailboats:
1. Mainsails
The mainsail is the largest and most important sail. Therefore, it's probably the first sail to come to mind when you think of camping. Typically, it's situated directly behind the mast — connected to the boom — and uses wind energy to move the vessel. The mainsail plays a significant role in tacking and gybing, making it essential for any voyage.
Since the mainsail is a larger sail, it doesn't require wind to propel it forward. And the fact that it can be moved by moving the boom makes it uber-easy to operate.
Learn More About Sailing
2. Headsail
The headsail often accompanies the mainsail, though it is smaller in size. Regardless of your sailboat type, the headsail is positioned at the front of the mast – over the sailboat's bow.
Because headsails are small, they are helpful when navigating through windy conditions. Smaller sails catch less wind, preventing them from propelling your boat as strongly as larger sails. Additionally, headsails help lift, balance, and protect the vessel from inclement weather conditions.
While the term 'headsail' refers to any sail in front of the mast, the jib is the most common type of headsail. (And when a jib is so large that it overlaps the mast, it's called a genoa.)
Learn More About Sailboats
3. Genoa
The genoa is a large sail that attaches to the front of the forestay. (In this instance, it's similar to a headsail.) However, the genoa is larger than the headsail and overlaps the mainsail partially or completely to help the boat go faster.
Genoa sails are useful when sailing through light or medium wind. You can also use it when the wind comes directly from the rear. If you use a Genoa sail during high winds, you'll probably start sailing too quickly and put yourself and your boat at risk.
4. Spinnaker
The spinnaker is a large and whimsical (often colorful) sail. Spinnaker sails are usually symmetrical, allowing them to reach different points of sail. Generally, these are lighter sails and don't cover the mast like the genoa.
Because spinnaker sails are on the larger side, you have to be incredibly careful with them. Don't use them in rough conditions. Instead, save them for sailing in low winds and calm seas.
5. Gennaker
As the name suggests, the Gennaker sail combines a spinnaker and a Genoa sail. They are as large as the spinnaker, although they're not symmetrical.
They come in handy whenever the wind changes from a pure dead run to a reaching point of sail, as sailors can navigate various wind types with the same sail. It's still only meant for lighter and milder winds, but it's more versatile than the spinnaker and genoa.
6. Light Air Sails
Light air sails are useful in calmer conditions when the headsail and mainsail alone aren't cutting it. They include:
- Code Zero : A code zero sail is a gennaker sail ideal for sailing in light to mild winds. It's designed to create lift and boost boat speed whenever regular sails don't generate enough power. For that reason, many racers and cruisers use code zero sails to improve performance and gain control in various situations.
- Windseeker : This small, special sail is reserved for no wind or light wind. Essentially, it helps boats remain maneuverable in extremely calm conditions. And for that reason, it's valuable to long-distance sailors.
7. Storm Jib
Storm jibs can be used as a headsail whenever the weather is particularly rough and windy. Because it functions as a safety seal, it prevents boats from capsizing by reducing the sail area exposed to the wind. Therefore, it's a necessary sail for every sailor.
Read Next: Boating in Inclement Weather
During strong winds and storms, sailors can raise a trysail — a small, triangular sail near the boat's stern — for better control and stability. Generally, sailors do this whenever the mainsail becomes too large and challenging to maneuver.

Join Our Newsletter!
Get community news, buying bargains, and how-to guides at your fingertips.

Types of Sails: A Comprehensive Guide
In the enchanting world of sailboat dynamics, where the dance between wind and water takes center stage, the significance of sails cannot be overstated. Like the wings of a bird, these meticulously crafted sails unfurl to catch the slightest whisper of breeze, converting it into a powerful forward thrust that carries us through the vast expanse of the ocean. They are the very essence of a sailboat, the conduits through which dreams and aspirations set sail.
Join us on a captivating voyage as we unfurl the secrets of the myriad types of sails adorning the mastheads of sailboats across the globe. From the grandeur of the mainsail, proudly dominating the skyline, to the nimble headsails that steer with precision, and the enigmatic mizzensails that add an extra touch of finesse, we shall embark on a comprehensive exploration of the diverse array of sail types.
Different Types of Sails on a Sailboat: Why Use Different Sails at All?
Different sail types for different wind conditions.
Triangular sails, such as the mainsail and jib, are commonly used on modern sailboats to optimize performance when sailing upwind. The shape of these sails helps to create lift, which propels the boat forward even against the wind’s direction. The mainsail is attached to the mast at the front edge and a boom at the bottom. Jibs, on the other hand, are headsails that are attached to a stay near the bow of the boat.
Balloon sails, like spinnaker sails, are designed for downwind sailing and catching more wind to increase boat speed when sailing with the wind behind it. These types of sails have a large surface area that allows them to catch more wind than triangular sails. Spinnaker sails can come in different shapes depending on their intended use and can be flown from a spinnaker pole or directly from the bow.
Sail Plans: Different Combinations for Different Boats
Sail plans refer to how different types of sails are arranged and combined on a sailing craft. Sail plans can vary depending on specific design features and intended use of boats. For example, some boats may have multiple masts with several triangular-shaped sails attached while others may only have one mast with one triangular sail (mainsail) and one square sail (spinnaker). The combination of different types of sails can also affect how easy it is to handle a boat under certain conditions.
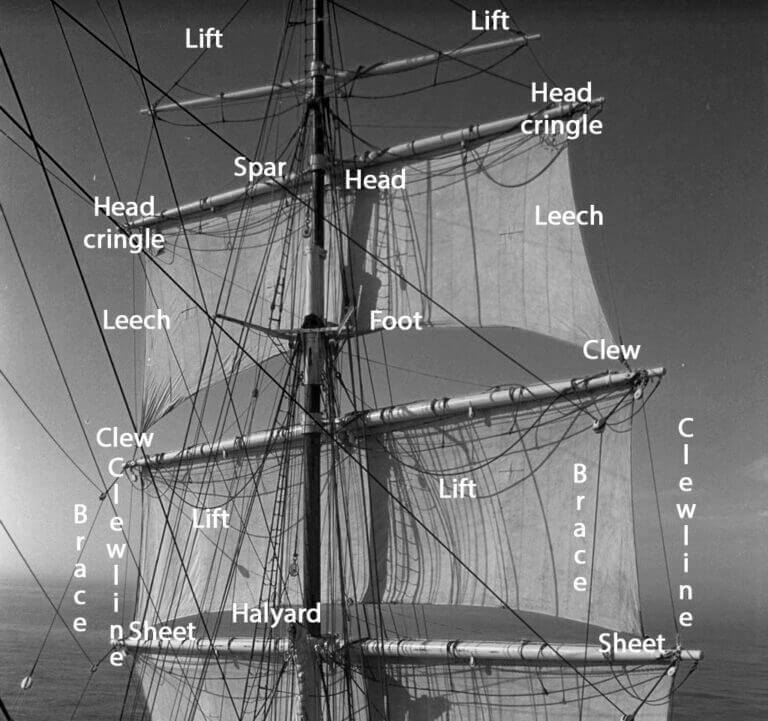
Understanding Sail Anatomy
Head, tack, foot, luff, leech, and clew. These are the different parts that make up a sail’s anatomy. But what exactly are they and why are they important? In this section, we’ll take a closer look at each part and how it contributes to the performance of a sailboat.

The Head: The Top of the Sail
Starting from the top, we have the head of the sail. This is where the halyard (the rope or wire used to hoist the sail) is attached. The head determines how high or low the sail sits on its mast. A higher head means more power but less control over the sail’s shape. Conversely, a lower head provides better control but less power.
The Tack: The Lower Front Corner of the Sail
Next is the tack which is found at the lower front corner of most sails. It’s where one end of a line called a “sheet” attaches to control how much wind enters through this corner of your sail. Adjusting your sheet will affect your boat’s speed and direction.
The Foot: The Bottom of the Sail
At the bottom edge of any sail lies its foot which helps determine its overall shape and size. Generally speaking, longer feet result in larger sails that provide more power while shorter feet result in smaller sails with better maneuverability.
The Luff: The Forward Edge of the Sail
The forward edge of any sail is called its luff which runs along its mast track or forestay depending on what type of rigging you have set up on your boat. It helps maintain proper airflow over your sails by keeping them from flapping around too much in high winds.
The Leech: The Back Edge of Your Sail
Opposite from your luff is your leech – or back edge – which helps create lift by allowing air to flow smoothly over your sail. A longer leech will result in a more powerful sail, while a shorter one will provide better control and maneuverability.
The Clew: The Bottom Back Corner of Your Sail
Lastly, we have the clew which is found at the bottom back corner of most sails. It’s where the other end of your sheet attaches to control how much wind enters through this corner of your sail. Adjusting your sheet here can affect how well you’re able to steer your boat.
Primary Sail Types
The main sail is attached to the main mast and boom and can be adjusted to match the wind conditions. Its main purpose is to keep the boat steady and under control by providing stability to the stern (back) of the vessel.
There are several variations of mainsails that sailors can choose from depending on their needs. One popular type of mainsail is an in-mast furling mainsail. This type of sail can be easily furled and unfurled by pulling a line, making it ideal for short-handed sailing or cruising. Another variation is a slab reefing mainsail, which has horizontal strips called battens that help maintain its shape. Finally, there is also a boom furling mainsail, which uses a roller system inside the boom to make it easier to handle.
A headsail is any sail located forward of the mast on a sailing vessel. These sails are designed to work in conjunction with the main sail to provide optimal performance under varying wind conditions. There are several types of headsails available, each with its own unique characteristics and purposes.
One popular type of headsail is known as a genoa. This large foresail extends beyond the mast and overlaps with the main sail, providing additional power when sailing upwind or reaching across wind angles. Genoas come in various sizes ranging from 110% up to 150%, depending on how much overlap you want.
Another common type of headsail is called a jib. This smaller foresail does not overlap with the main sail but instead works in conjunction with it. The jib is typically used in higher wind conditions when a smaller sail area is needed to maintain control of the boat.
A staysail is a smaller sail located between the mast and the forestay. This type of headsail is typically used on larger boats to provide additional power when sailing upwind or reaching across wind angles. Staysails are often used in conjunction with other sails, such as a genoa or main sail.
Finally, there is also a mizzensail, which is located aft of the main mast on ketches and yawls. This sail provides additional power when sailing downwind or reaching across wind angles. Mizzensails come in various sizes and can be either fully battened or free-flying.
Lightwind Sails
Spinnaker sails are a type of downwind sail that can be used to increase boat speed when sailing in light winds. They are typically used in wind conditions below 10 knots, which are considered light air sails. Spinnakers come in two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical.

Symmetrical vs Asymmetrical Spinnaker
The symmetrical spinnaker is designed to sail directly downwind or with the wind coming from behind the boat. It is shaped like a balloon, with equal amounts of material on both sides of the sail. The sail is attached to a spinnaker pole, which extends out from the mast and holds the sail away from the boat.
Asymmetrical spinnakers, on the other hand, are designed for sailing at angles off the wind. They have an uneven shape, with more material on one side than the other. This design allows them to be flown without a spinnaker pole, making them easier to handle for smaller crews.
Another type of downwind sail is called a gennaker. Gennakers are similar to asymmetrical spinnakers but have a hybrid characteristic between a spinnaker and a genua. They are designed for reaching or running downwind at higher speeds than traditional cruising chutes or asymmetric spinnakers.
For those who prefer an even more user-friendly option than asymmetrical spinnakers or gennakers, parasailors might be what you’re looking for! A parasailor combines aspects of both a traditional spinnaker and a parachute into one easy-to-use package. The unique design of this sail makes it ideal for use in light winds when other sails may not perform well enough.

Finally, there’s another type of upwind/downwind sail called the code zero. Code zeros are designed to be used in light winds when sailing upwind, but they can also be used for reaching and running downwind. These sails have a flat shape that allows them to generate lift even in very light wind conditions.
Heavy Weather Sails
Heavy weather sailing is a challenging and potentially dangerous activity. The use of heavy weather sails, such as trysails, is crucial to ensure the safety of sailors and their vessels.
A trysail is a small triangular sail made of heavy-duty material, typically spinnaker cloth or other lightweight fabric. It is designed to be used in stormy weather conditions when winds are high and the seas are rough.
The role of a trysail is to provide an alternative source of propulsion when the main sail or jib cannot be used. In addition, it helps reduce the heeling effect on the vessel caused by strong winds. Trysails are rigged using a separate halyard and can be set up quickly when needed.
A trysail should be used in severe weather conditions when winds exceed 40 knots or more. It is recommended that sailors practice setting up their trysail before they need it so that they can do it quickly and efficiently in an emergency situation.

Another type of heavy weather sail that every sailor should have on board is a storm jib. This sail is typically much smaller than a regular jib and made from heavier materials such as Dacron or nylon. Its purpose is to provide additional stability during high wind speeds and rough seas.
The features of a storm jib include its size, shape, and weight distribution. It has a large luff (the leading edge) which allows it to be hoisted higher up on the rigging than other sails. This helps keep the boat stable during high-speed sailing in strong winds.
A storm jib should be used in extreme weather conditions where wind speeds exceed 50 knots or more. When using this sail, it is important to ensure that the halyard is properly tensioned and that the sail is sheeted in tightly. This will help prevent any unnecessary movement or fluttering of the sail.
Overview Common Sail Types
100% of mainsail
Light – High
100% of foretriangle
Moderate – High
triangular, overlapping
110% – 150% of foretriangle
Light – Moderate
60% – 80% of foretriangle
Close Reach – Broad Reach
Lightwind, Downwind
balloon shape, free flying
200% of mainsail (or even more)
Broad Reach, Running
parachute shape
100% of spinnaker
80% – 85% of spinnaker
Lightwind, Upwind
75% of spinnaker
30% – 60% of mainsail
Mainsail, heavy weather
17.5% of mainsail (or less)
Headsail, heavy weather
max. 65% of the hight of the foretriangle
Unconventional Sails
Wing sails are a type of sail design that is not commonly used in traditional sailboat designs. They are essentially vertical airfoils that generate lift and propulsion by directing the wind over the surface of the sail. Wing sails have become increasingly popular in modern sailing craft, particularly in high-performance racing boats.
One of the main advantages of wing sails is their ability to produce a significant amount of power with very little heeling force. This means that they can be used effectively in high-wind conditions without causing the boat to tip over. Additionally, wing sails are highly efficient at sailing upwind, which allows sailors to point higher into the wind than with other types of sails.
While wing sails may seem like a relatively new concept, they have actually been around for quite some time. The first recorded use of a wing sail was by German engineer Wolfgang Zimmermann in 1959. Since then, many different variations on the design have been developed and tested.

Kite sails are another unconventional type of sail that has gained popularity in recent years. Unlike traditional downwind sails such as spinnaker or parasailors, kite sails are flown from a line attached to the bow of the boat and do not require a mast or boom.
Sail Materials and Technology
Traditional sail materials.
Sails have been used for thousands of years to harness the power of the wind and propel boats across water. Traditional sail materials were flax, hemp, or cotton. These natural fibers were woven together to create a strong, yet flexible material that could withstand the harsh conditions at sea. However, as technology advanced and sailors began to demand more from their sails, new materials were developed.
Modern Sail Materials
Modern sailboats use synthetic materials such as polyester, nylon, or laminated fabrics for their sails. These materials are lightweight and incredibly strong, allowing sailors to achieve greater speeds with less effort. They are also more durable than traditional sail materials and can withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight and saltwater.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations

The sloop rig is one of the most popular sail plans for modern sailboats. It features a single mast and one headsail, like a jib or genoa. The mainsail is typically triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast using a backstay to support it. The jib or genoa is attached to the forestay that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat.
Another popular sail plan is the cutter rig, which also features a single mast but has two headsails – an overlapping jib and a smaller staysail. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support.
Moving onto two-masted rigs, we have ketch rig, which features a main mast and a shorter mizzen mast located in front of the rudder. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support, while the mizzen sail is generally smaller and triangular or quadrilateral in shape.
Lastly, we have the yawl rig which is similar to the ketch rig but has its shorter mizzenmast located aft of the rudder. The mainsail is still triangular in shape and hoisted up the main mast with a backstay for support, while the mizzen sail is generally smaller and triangular or quadrilateral in shape.
Conclusion: Understanding the Different Types of Sails
Understanding the Different Types of Sails is crucial for any sailor who wants to optimize their performance and safety on the water. Whether you’re racing, cruising or simply enjoying a day out on your sailboat, having the right sails for the conditions can make all the difference.
Ultimately, understanding the different types of sails is essential for any sailor looking to improve their skills on the water. By selecting the right sail for your boat and conditions, you can optimize your performance while staying safe and comfortable during your time at sea.
So whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, take some time to explore the various types of sails available and find the ones that work best for you. With a little knowledge and experience under your belt, you’ll be well on your way to mastering this exciting sport!
Similar Posts

How do Boats Float? Exploring the Science Behind Buoyancy
Sailboats float because the average density of the boat is less than the density of water. When boats displace as much water as it weights, this is known as the buoyancy force generated by Archimedes’ principle. If you’ve ever wondered how do boats float and therefor enable us to embark on thrilling water adventures, you’ve…

How Does a Marine Toilet Work?
Have you ever wondered how a marine toilet works? If you’re planning to embark on a boating adventure or just curious about the mechanism of a marine toilet, this article is for you. Marine toilets work similarly to the ones on land with a bowl, a seat, and a flushing mechanism that uses water. However,…

Advantages of Catamaran Sailboat Charter
A catamaran sailboat charter is an exciting way to explore the beauty of the sea. Whether you are an experienced sailor or a first-timer, booking a catamaran sailboat charter has a lot of advantages that you can enjoy. In this article, we will discuss the advantages of booking a catamaran sailboat charter, so that you…

Monohulls vs. Catamarans: Which One is Best for You?
If you’re considering purchasing a sailboat, you might be wondering which type of vessel is best suited for your seafaring adventures. Fear not, for we’re here to help you weigh the differences between monohulls vs. catamarans to make an informed decision. Now, before we dive into the nitty-gritty details of hull design, sail handling, and…

Whats the Difference between Standing Rigging and Running Rigging?
Running rigging refers to the movable lines and ropes used to control the position and shape of the sails on a sailboat. Standing rigging, on the other hand, refers to the fixed wires and cables that support the mast and keep it upright. As the sun rises on another day, we find ourselves immersed in…

What is a Keel?: The Backbone of a Ship
As ships sail through tumultuous seas, their stability and maneuverability are tested to the fullest extent. The intricate design and engineering that go into a ship’s construction ensure that it can withstand the forces of nature and navigate through any challenging conditions. One of the most critical components of a ship’s design is the keel,…

The Different Types Of Sails And When To Use Them – Complete Guide

Sail forms an integral part of a sailboat. When you sail on the open water and observe other boats (in various sizes), you’d have noticed how each boat type has a specific model of sail. If you’re a beginner in boating, you must know that there are a ton of different sails and they each have their own purpose.
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker.
While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily differentiate between them and choose the ideal model based on your purpose. This article guides you on this aspect. Let’s begin!
Different Types of Sails & When To Use Them
1. mainsail.
Mainsail is by far the most widely spotted sail model, and it’s usually fixed to the boom and fitted behind the mast. This offers the highest mileage to your sailboat, thereby maximizing speed and performance.
You can use a mainsail if:
- You’re concerned about the performance
- You need to go faster and utilize all wind power
- You need to steer your boat irrespective of the wind’s status
- You’ve a large boat and can offer adequate space to this sail.
This mainsail displays a wide surface area to make the most out of the available wind condition. As a result, you can steer your boat quite easily. However, the downside is its size. It is very large and hard to store if you need to take it down for some reason.
Check out my other article all about maintaing sails!
2. Headsail
Similar to a mainsail, it’s very easy to spot a head sail. Just look at the bow of the boat and see if there is a sail. If you see one then yes that’s a headsail. Also called a jib or genoa, a headsail is smaller in size compared to a mainsail and attaches in front of the mast to the forestay. The Foresail will not have a boom for the clew of the sail to attach to. The clew will be attached to the foresails sheet. It can be used without the mainsail in certain conditions but for the most part the two sails are used together. The foresail is always forward of the main.
The headsail comes in many different forms such as a jib, genoa, spinnaker or storm jib. The most common headsail is a jib or genoa.
You can use a headsail if:
- Your sailboat is set up for it.
- You don’t want to use the mainsail at this time.
- Your mainsail is not usable.
The biggest advantage of a headsail is the option to protect yourself even if the wind turns unpredictable or wild. This all depends on the type of headsail you are using.
So, what are the different types of headsails? Let’s take a look!
As more boaters chose to use a headsail for their boats, the jib was introduced as one of its forms. The Jib is a form of headsail that is attached to a shackle present on the deck’s front region.
The Jib is a sail that does not go past the mast when it is raised and in use. If it goes past the mast then you probably have a genoa.
You can use a jib if:
- You are out for a normal day of sailing in moderate wind speeds
- You have a roller furling. Which is a sail that wraps up around itself.
Some weather conditions can make maneuvering harder or tighter than usual. As a result, it’s essential to use a jib in such cases. It functions well with boats containing a roller furling as the jib handles different positions and tackles the movement of the boat at ease.
2.2 Genoa
Just when you’ve got acquainted with the jib, genoa comes into the picture as a larger version of the jib. If you’re boating along a coastal region, the genoa sail is the one widely used and is attached to the front area of the deck as well.
Here’s a quick trick to find out if a boat has a genoa sail. This genoa is usually larger than a Jib. This means that the genoa effortlessly overlaps and extends itself beyond the mast, thereby covering the mainsail as well.
You should use a genoa sail if:
- You’re planning to sail in minimum wind conditions. Less wind means you need more sail.
- You find the wind to originate from the rear area.
- You own a large boat. Remember that genoa can partially or completely cover the mainsail too. Larger sails for larger boats!
While it’s great for sailing in regular conditions, there are downsides associated with it. A genoa can put you in a dangerous situation if you are sailing in high wind conditions and don’t have the ability to furl in the sail. Furling in the sail will reduce the area of the sail and catch less wind.
Genoas do come in many sizes as well such as 110% or 120%.
The next section of the sail list are ones that aren’t necessary but can be helpful in certain situations. Let’s look at specialty sails!
3. Specialty Sail
While headsails and mainsails are quite commonly used, there are also specialty sails in the market to address specific requirements. Some of the widely seen specialty sails are spinnakers, storm jibs, and code zeros.
3.1 Spinnakers
Spinnaker is a sail dedicated to downwind and is quite large. Think of a beautifully covered parachute.
It’s easy to spot spinnakers as they resemble kites or parachutes. However, it crosses the bow of the boat and isn’t attached to the forestay.
Unlike the genoa sail that covers the mast, a spinnaker fails to do so. The advantage of a spinnaker is the surface area. When the wind is light, the spinnaker can catch a lot more wind giving you more speed. The Spinnaker is usually fixed to three points – pole, halyard, and sheet.
You should use a spinnaker if:
- You have minimal wind on a run.
- You are trying to harness as much wind power as you can.
While it has a wide surface area, the downside is its inability to steer the boat during strong wind conditions. It can even put the passengers at risk when the wind is at high speeds.
Make sure you have experience before trying out the spinnaker.
3.2 Storm Jibs
Storm jib is another type of specialty sail meant exclusively for rough weather. It’s a tiny, triangular structure that helps during offshore racing or cruising. Just think of it as a smaller jib.
You should use a storm jib if:
- You’re going to sail in heavy weather conditions.
- You anticipate high wind speeds.
- You’re going to be in an offshore race and they are an approved sail type.
Note: In the case of an offshore racing requirement, it’s critical to take prior permission from the regulatory authority for using a storm jib.
3.3 Code Zeros
Code zero is another updated version of a spinnaker that’s meant to be a combination of genoa and gennaker sails. It resembles the look of a genoa but is a lot bigger.
You should use a code zero if:
- You’re looking for an overlapping flying headsail.
- You’re sailing only in light air conditions.
- You’re looking for an alternative to a Genoa.
Having said that, a code zero or a screecher does the job of a genoa with better efficiencies.
3.4 Trysail
Trysail is another type of specialty sail that’s tiny, triangular, and can be fixed right above a gooseneck on the sailboat.
The Trysail is less known in the market as most boaters go ahead with common mainsails and headsails. It’s essential to acknowledge trysail as a front-and-aft mainsail model. It offers excellent performance and contains a permanent pennant in it.
You should use a trysail if:
- You’re sailing in heavy weather conditions.
- You’re looking for a storm replacement.
- You are experienced with using them.
The quadrilateral sail in a trysail is usually turned and bent to a mast, and this helps in heading the vessel during windy conditions.
3.5 Gennakers
If you’ve been able to spot genoa and spinnaker in the past, identifying a gennaker is incredibly easy. A gennaker is a hybrid sail form that is small, slow, and requires no pole attached to the mast.
You should use a gennaker if:
- You’re looking for a smaller version of a spinnaker.
- You’ve no space to fix a pole to the mast.
- You require the sail to be easily manageable.
- You’re sailing in a region requiring minimum downwind levels.
Choosing a hybrid sail has a lot of benefits as it combines the usefulness of 2 sail models. However, being aware of their cons is critical to planning a safe sail.
As you begin using these sails, you can also look for better customizations. There are drifters, wind seekers, and other jib types that are meant to handle different wind conditions.
How Many Sails On A Sailboat ?
In general, a sailboat contains two sails. Two sails is the typical setup for the best performance of the boat during different wind conditions. It’s essential to pick your two sails based on your sailing plan.
Why Are There Two Sails On A Sailboat?
A sailboat uses two sails because the wind left over by the first sail is easily caught by the second sail. This helps in steering the sailboat to a better extent and gives the sailboat more power.
Final Thoughts
Sails are one of the major assets of a sailboat. From managing wind to maximizing the performance and longevity of a sailboat, the type of sails you use, plays a huge role. From the various sail types listed in this article, you can choose the best model that fits your sailing routine. Just make sure to remember to check and make sure they are the correct size for your vessel.
Make sure to plan ahead and have the right sails for your sailing weekend. Cheers!
Boatlifehq owner and author/editor of this article.
Recent Posts
How to Repair a Sailboat Hull: Step-by-Step Guide
Maintaining your sailboat's hull is crucial for ensuring its longevity and performance on the water. Hull damage can occur due to various reasons, such as collisions, grounding, or general wear and...
10 Steps For Anchoring Your Sailboat
Anchoring a sailboat is a fundamental skill every sailor must master. Proper anchoring ensures your boat remains secure, preventing it from drifting and potentially causing damage. Whether you're...
The different types of sails and their uses
Discover the different types of sails and their uses to optimize your sailing performance and enjoy the freedom and fulfillment of exploring the open sea.
The Different Types of Sails and Their Uses
Sailing is an incredible way to explore the world, spend quality time with family, and embrace the freedom of the open sea. As you embark on your sailing adventure, it’s essential to understand the different types of sails and their uses. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to navigate your journey confidently.
Table of Contents
Introduction to sails, symmetrical spinnakers, asymmetrical spinnakers, sail materials and construction.
Sails are the driving force behind any sailing vessel, harnessing the power of the wind to propel the boat forward. They come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, each designed for specific sailing conditions and purposes. Understanding the different types of sails and their uses will help you make informed decisions when selecting sails for your boat and optimizing your sailing performance.
The mainsail is the primary sail on a sailing vessel and is typically hoisted on the aft side of the mast. It is a triangular sail with its leading edge (or luff) attached to the mast and its foot running along the boom. Mainsails are essential for providing the boat with forward propulsion and play a significant role in steering and balancing the vessel.
There are two primary types of mainsails: full-batten and partial-batten. Full-batten mainsails have horizontal battens that run the entire width of the sail, providing additional support and shape. Partial-batten mainsails have shorter battens that only extend partway across the sail. Full-batten mainsails tend to hold their shape better and last longer, while partial-batten mainsails are lighter and easier to handle.
Headsails are sails that are set forward of the mast and are used in conjunction with the mainsail to provide additional propulsion and balance. There are several types of headsails, each with its unique characteristics and uses.
A jib is a triangular sail that is set forward of the mast and is attached to the forestay, a wire that runs from the masthead to the bow of the boat. Jibs come in various sizes, with smaller jibs being more suitable for strong winds and larger jibs providing more power in light wind conditions. Jibs are essential for upwind sailing, as they help to direct the airflow around the mainsail, increasing its efficiency.
A genoa is a type of jib that is larger than a standard jib, extending past the mast and overlapping the mainsail. Genoas are designed to provide maximum sail area and power in light to moderate wind conditions. They are particularly useful for upwind sailing, as their large size helps to generate more lift and drive the boat forward. However, genoas can be more challenging to handle than smaller jibs, especially in strong winds or when tacking.
Spinnakers are large, lightweight sails designed for downwind sailing. They are typically set forward of the jib and are not attached to the forestay. Instead, they are held out by a pole called a spinnaker pole, which is attached to the mast and the sail’s clew (the lower aft corner of the sail). Spinnakers are used to catch the wind from behind, providing significant power and speed when sailing downwind.
A gennaker, also known as a cruising spinnaker or code zero, is a hybrid sail that combines the characteristics of a genoa and a spinnaker. Gennakers are designed for reaching and downwind sailing and are typically set on a furling system, making them easier to handle than traditional spinnakers. They provide more power than a genoa in light wind conditions and are more stable and easier to control than a spinnaker.
Downwind Sails
Downwind sails are designed specifically for sailing with the wind coming from behind the boat. These sails are typically larger and lighter than upwind sails, allowing them to catch more wind and generate more power. There are two main types of downwind sails: symmetrical spinnakers and asymmetrical spinnakers.
Symmetrical spinnakers are large, balloon-shaped sails that are designed for sailing directly downwind. They are symmetrical in shape, with the sail’s centerline running vertically down the middle of the sail. Symmetrical spinnakers are held out by a spinnaker pole, which is attached to the mast and the sail’s clew. This allows the sail to catch the wind from behind, providing maximum power and speed when sailing downwind.
Asymmetrical spinnakers, also known as gennakers or A-sails, are designed for reaching and downwind sailing at angles that are not directly downwind. They are asymmetrical in shape, with a longer luff (leading edge) and a shorter leech (trailing edge). Asymmetrical spinnakers are typically set on a furling system and do not require a spinnaker pole, making them easier to handle than symmetrical spinnakers. They provide more power and stability than a genoa in light wind conditions and are more versatile than a symmetrical spinnaker.
Storm Sails
Storm sails are small, heavy-duty sails designed for use in extreme weather conditions. They are used to replace the standard sails when the wind is too strong, providing better control and reducing the risk of damage to the boat and its rigging. There are two main types of storm sails: storm jibs and trysails.
A storm jib is a small, heavy-duty jib that is used in place of the standard jib in strong winds. It is typically set on the inner forestay, closer to the mast, providing better balance and control. Storm jibs are designed to withstand high wind loads and are made from durable materials, such as heavy-duty Dacron or laminate fabrics.
A trysail, also known as a storm trysail or storm mainsail, is a small, heavy-duty sail that is used in place of the standard mainsail in extreme weather conditions. It is typically set on a separate track on the mast, allowing it to be hoisted independently of the mainsail. Trysails are designed to provide better control and balance in strong winds and are made from durable materials, such as heavy-duty Dacron or laminate fabrics.
Sails are made from various materials, each with its unique characteristics and performance attributes. The most common sail materials include Dacron, laminate fabrics, and high-performance fibers, such as carbon and aramid.
Dacron is a durable, low-stretch polyester fabric that is widely used for cruising sails. It is relatively inexpensive and provides good performance in a wide range of conditions. Laminate fabrics are made by sandwiching layers of polyester or high-performance fibers between layers of Mylar film. These sails are lighter and more resistant to stretch than Dacron sails, providing better performance and shape retention. High-performance fibers, such as carbon and aramid, are used in racing sails and offer the highest levels of strength, durability, and performance.
Sail construction techniques also play a significant role in the performance and durability of a sail. Cross-cut sails are made from panels of fabric that are sewn together horizontally, following the natural lines of the fabric’s weave. This construction method is relatively simple and inexpensive but can result in a sail that is more prone to stretch and distortion. Radial-cut sails are made from panels of fabric that radiate out from the corners of the sail, distributing the loads more evenly and providing better shape retention and performance.
Understanding the different types of sails and their uses is essential for any sailor looking to optimize their sailing performance and enjoyment. By selecting the appropriate sails for your boat and the conditions you’ll be sailing in, you’ll be better prepared to navigate the open sea and embrace the freedom and fulfillment that comes from choosing an unconventional path.

Sail Rigs And Types - The Only Guide You Need

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
A well-designed sailboat is a thing of pure beauty. Whether you're a proud owner of one, a guest on one, or a shore-side admirer, you'll fall in love with the gliding sails, the excitement of a race, and the eco-friendly nature of these sophisticated yet magnificent vessels. With good sails, great design, and regular maintenance, sails and rigs are an important part of a sailboat.
If you’re thinking about going sailing, one of the first things you have to understand is the variety of modern sail plans. Unlike old sailboats, modern sailboats don't need huge, overlapping headsails and multiple masts just to get moving. In the past, when sailboats were heavy, keels were long, the only way to get the boat moving was with a massive relative sail area. You needed as much square footage as you could just to get your sailboat moving. But with the invention of fiberglass hulls, aluminum or composite masts, high-tensile but low diameter lines and stats, and more efficient sails, sailboats no longer need to plan for such large sail plans.. Still, there are various rig styles, from the common sloop, to the comfortable cat-rig, to the dual masted ketch and schooner, there are various sail types and rigs to choose from. The most important thing is to know the different types of sails and rigs and how they can make your sailing even more enjoyable.
There are different types of sails and rigs. Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The mainsail is generally fore-and-aft rigged and is triangular shaped. Various conditions and courses require adjustments to the sails on the boats, and, other than the mainsail, most boats can switch out their secondary sail depending on various conditions.. Do you want to sail upwind or go downwind? You cannot hoist just any sail and use it. It's, therefore, of great importance to understand how and when to use each sail type.
In this in-depth article, we'll look at various sail types and rigs, and how to use them to make your sailing more enjoyable.
Table of contents
Different Sail Types
It is perhaps worth noting that a sailboat is only as good as its sails. The very heart of sailing comes in capturing the wind using artfully trimmed sails and turning that into motion. . Ask any good sailor and he'll tell you that knowing how and when to trim the sails efficiently will not only improve the overall performance of your boat but will elevate your sailing experience. In short, sails are the driving force of sailboats.
As such, it's only natural that you should know the different types of sails and how they work. Let's first highlight different sail types before going into the details.
- Jib - triangular staysail
- Spinnaker - huge balloon-shaped downwind sail for light airs
- Genoa - huge jib that overlaps the mainsail
- Gennaker - a combination of a spinnaker and genoa
- Code zero - reaching genoa for light air
- Windseeker - tall, narrow, high-clewed, and lightweight jib
- Drifter - versatile light air genoa made from particularly lightweight cloth
- Storm jib - a smaller jib meant for stormy conditions
- Trysail - This is a smaller front-and-aft sail for heavy weather
The mainsail is the principal sail on a boat. It's generally set aft of the mainmast. Working together with the jib, the mainsail is designed to create the lift that drives the sailboat windward. That being said, the mainsail is a very powerful component that must always be kept under control.
As the largest sail, and the geometric center of effort on the boat, the mainsail is tasked with capturing the bulk of the wind that's required to propel the sailboat. The foot, the term for the bottom of any sail, secures to the boom, which allows you to trim the sail to your heading. The luff, the leading edge of the sail, is attached to the mast. An idealized mainsail would be able to swing through trim range of 180°, the full semi-circle aft of the mast, though in reality, most larger boats don’t support this full range of motion, as a fully eased sail can occasionally be unstable in heavy breeze.
. As fully controlling the shape of the mainsail is crucial to sailing performance, there are many different basic mainsail configurations. For instance, you can get a full-batten mainsail, a regular mainsail with short battens, or a two-plus-two mainsail with two full-length battens. Hyper-high performance boats have even begun experimenting with winged sails which are essentially trimmable airplane wings! Moreover, there are numerous sail controls that change the shape by pulling at different points on the sail, boom, or mast. Reefing, for instance, allows you to shorten the sail vertically, reducing the amount of sail area when the boat is overpowered.
Features of a Mainsail
Several features will affect how a particular sail works and performs. Some features will, of course, affect the cost of the sail while others may affect its longevity. All in all, it's essential to decide the type of mainsail that's right for you and your sailing application.
Sail Battens, the Roach, and the Leech
The most difficult part of the sail to control, but also the most important, are the areas we refer to as the leech and the roach. The roach is the part of the sail that extends backwards past the shortest line between the clew, at the end of the boom, and the top of the mast. It makes up roughly the back third of the sail. The leech is the trailing edge of the sail, the backmost curve of the roach. Together, these two components control the flow of the air off the back of the sail, which greatly affects the overall sail performance. If the air stalls off the backside of the sail, you will find a great loss in performance. Many sail controls, including the boom vang, backstay, main halyard, and even the cunningham, to name a few, focus on keeping this curve perfect.
As for parts of the sail itself, battens control the overall horizontal shape of the sail. Battens are typically made from fiberglass or wood and are built into batten pockets. They're meant to offer support and tension to maintain the sail shape Depending on the sail technology you want to use, you may find that full battens, which extend from luff to leech, or short battens, just on the trailing edge, are the way to go. Fully battened sails tend to be more expensive, but also higher performance.
Fully Battened Mainsails
They're generally popular on racing multihulls as they give you a nice solid sail shape which is crucial at high speeds. In cruising sailboats , fully battened mainsails have a few benefits such as:
- They prevent the mainsail from ragging. This extends the life of the sail, and makes maneuvers and trimming easier for the crew.
- It provides shape and lift in light-air conditions where short-battened mainsails would collapse.
On the other hand, fully-battened mainsails are often heavier, made out of thicker material, and can chafe against the standing rigging with more force when sailing off the wind.
Short Battens
On the other hand, you can choose a mainsail design that relies mostly on short battens, towards the leech of the sail. This tends to work for lighter cloth sails, as the breeze, the headsail, and the rigging help to shape the sail simply by the tension of the rig and the flow of the wind. The battens on the leech help to preserve the shape of the sail in the crucial area where the air is flowing off the back of the sail, keeping you from stalling out the entire rig.
The only potential downside is that these short battens deal with a little bit of chafe and tension in their pockets, and the sail cloth around these areas ought to be reinforced. If your sails do not have sufficient reinforcement here, or you run into any issues related to batten chafe, a good sail maker should be able to help you extend the life of your sails for much less than the price of a new set.
How to Hoist the Mainsail
Here's how to hoist the mainsail, assuming that it relies on a slab reefing system and lazy jacks and doesn't have an in-mast or in-boom furling system.
- Maintain enough speed for steeragewhile heading up into the wind
- Slacken the mainsheet, boom vang, and cunningham
- Make sure that the lazy jacks do not catch the ends on the battens by pulling the lazy jacks forward.
- Ensure that the reefing runs are free to run and the proper reefs are set if necessary.
- Raise the halyard as far as you can depending on pre-set reefs.
- Tension the halyard to a point where a crease begins to form along the front edge
- Re-set the lazy jacks
- Trim the mainsail properly while heading off to your desired course
So what's Right for You?
Your mainsail will depend on how you like sailing your boat and what you expect in terms of convenience and performance. That being said, first consult the options that the boatbuilder or sailmakers suggest for your rig. When choosing among the various options, consider what you want from the sail, how you like to sail, and how much you're willing to spend on the mainsail.
The headsail is principally the front sail in a fore-and-aft rig. They're commonly triangular and are attached to or serve as the boat’s forestay. They include a jib and a genoa.
A jib is a triangular sail that is set ahead of the foremost sail. For large boats, the roto-furling jib has become a common and convenient way to rig and store the jib. Often working in shifts with spinnakers, jibs are the main type of headsails on modern sailboats. Jibs take advantage of Bournoulli’s Principle to break the incoming breeze for the mainsail, greatly increasing the speed and point of any boat. By breaking the incoming wind and channeling it through what we call the ‘slot,’ the horizontal gap between the leech of the jib and the luff of the mainsail, the jib drastically increases the efficiency of your mainsail. It additionally balances the helm on your rudder by pulling the bow down, as the mainsail tends to pull the stern down. .
The main aim of the jib is to increase the sail area for a given mast size. It improves the aerodynamics of the mainsails so that your sailboat can catch more wind and thereby sail faster, especially in light air
Using Jibs on Modern Sailboats
In the modern contexts, jib’s mainly serve increase the performance and overall stability of the mainsail. The jib can also reduce the turbulence of the mainsail on the leeward side.
On Traditional Vessels
Traditional vessels such as schooners have about three jibs. The topmast carried a jib topsail, the main foresail is called the jib, while the innermost jib is known as the staysail. The first two were employed almost exclusively by clipper ships.
How to Rig the Jibs
There are three basic ways to rig the jib.
Track Sheets - A relatively modern approach to the self-tacking jib, this entails placing all the trimming hardware on a sliding track forward of the mast. This means that on each tack, the hardware slides from one side of the boat to the other. This alleviates the need to switch sheets and preserves the trim angle on both sides, though it can be finnicky and introduce friction.
Sheet up the Mast - This is a very popular approach and for a good reason. Hoist the jib sheet up the mast high enough to ensure that there's the right tension through the tack. Whether internally or externally, the sheet returnsto the deck and then back to the cockpit just like the rest of the mast baselines. The fact the hardware doesn't move through the tacks is essential in reducing friction.
Sheet Forward - This method revolves around ensuring that the jib sheet stays under constant pressure so that it does not move through the blocks in the tacks. This is possible if the through-deck block is extremely close to the jib tack. Your only challenge will only be to return the sheet to the cockpit. This is, however, quite challenging and can cause significant friction.
Dual Sheeting - The traditional method, especially on smaller dinghies, though it is not self-tacking. This requires a two ended or two separate sheet system, where one sheet runs to a block on starboard, and the other to port. Whenever you tack or gybe, this means you have to switch which sheet is active and which is slack, which is ok for well crewed boats, but a potential issue on under-crewed boats.
Another important headsail, a genoa is essentially a large jib that usually overlaps the mainsail or extends past the mast, especially when viewed from the other side. In the past, a genoa was known as the overlapping jib and is technically used on twin-mast boats and single-mast sloops such as ketches and yawls. A genoa has a large surface area, which is integral in increasing the speed of the vessel both in moderate and light winds.
Genoas are generally characterized by the percentage they cover. In most cases, sail racing classes stipulate the limit of a genoa size. In other words, genoas are usually classified by coverage.
Top-quality genoa trim is of great importance, especially if the wind is forward of the beam. This is because the wind will first pass over the genoa before the mainsail. As such, a wrongly sheeted genoa can erroneously direct the wind over the mainsail,spelling doom to your sailing escapades. While you can perfectly adjust the shape of a genoa using the mast rake, halyard tension, sheet tension, genoa car positioning, and backstay tension, furling and unfurling a genoa can be very challenging, especially in higher winds.
That being said, here are the crucial steps to always keep in mind.
- Unload and ease the loaded genoa sheet by going to a broad reach
- Do not use the winch; just pull on the furling line
- Keep a very small amount of pressure or tension on the loaded genoa sheet
- Secure the furling line and tighten the genoa sheets
- Get on the proper point of sail
- Have the crew help you and release the lazy genoa sheets
- Maintain a small tension while easing out the furling line
- Pull-on a loaded genoa sheet
- Close or cleat off the rope clutch when the genoa is unfurled
- Trim the genoa
To this end, it's important to note that genoas are popular in some racing classes. This is because they only categorize genoas based on the fore-triangle area covered, which essentially allows a genoa to significantly increase the actual sail area. On the contrary, keep in mind that tacking a genoa is quite a bit harder than a jib, as the overlapping area can get tangled with the mast and shrouds. It's, therefore, important to make sure that the genoa is carefully tended, particularly when tacking.
Downwind Sails
Modern sailboats are a lot easier to maneuver thanks to the fore-and-aft rig. Unfortunately, when sailing downwind they catch less wind, and downwind sails are a great way of reducing this problem. They include the spinnaker and the gennaker.
A spinnaker will, without a doubt, increase your sailing enjoyment. But why are they often buried in the cabin of cruising boats? Well, the first few attempts to rig and set a spinnaker can be difficult without enough help and guidance. Provided a solid background, however, spinnakers are quite straightforward and easy to use and handle with teamwork and enough practice. More importantly, spinnakers can bring a light wind passage to life and can save your engine.
Spinnakers are purposely designed for sailing off the wind; they fill with wind and balloon out in front of your sailboat. Structured with a lightweight fabric such as nylon, the spinnaker is also known as a kite or chute, as they look like parachutes both in structure and appearance.
A perfectly designed spinnaker should have taut leading edges when filled. This mitigates the risk of lifting and collapsing. A spinnaker should have a smooth curve when filled and devoid of depressions and bubbles that might be caused by the inconsistent stretching of the fabric. The idea here is that anything other than a smooth curve may reduce the lift and thereby reduce performance.
Types of Spinnakers
There are two main types of spinnakers: symmetric spinnakers and asymmetric spinnakers.
Asymmetric Spinnakers
Flown from a spinnaker pole or bowsprit fitted to the bow of the boat, asymmetric spinnakers resemble large jibs and have been around since the 19th century. The concept of asymmetric spinnaker revolves around attaching the tack of the spinnaker at the bow and pulling it around during a gybe.
Asymmetric spinnakers have two sheets just like a jib., These sheets are attached at the clew and never interact directly with the spinnaker pole. This is because the other corner of the spinnaker is fixed to the bowsprit. The asymmetric spinnaker works when you pull in one sheet while releasing the other. This makes it a lot easier to gybe but is less suited to sailing directly downwind. There is the loophole of having the asymmetric spinnaker gybed to the side opposite of the boom, so that the boat is sailing ‘wing-on-wing,’ though this is a more advanced maneuver, generally reserved for certain conditions and tactical racing situations.
On the contrary, the asymmetric spinnaker is perfect for fast planing dinghies. This is because such vessels have speeds that generate apparent wind forward. Because asymmetrics, by nature, prefer to sail shallower downwind angles, this apparent wind at high speeds makes the boat think that it is sailing higher than it really is, allowing you to drive a little lower off the breeze than normal. . In essence, the asymmetric spinnaker is vital if you're looking for easy handling.
Symmetric Spinnakers
Symmetric spinnakers are a classic sail type that has been used for centuries for controlling boats by lines known as a guy and a sheet. The guy, which is a windward line, is attached to the tack of the sail and stabilized by a spinnaker pole. The sheet, which is the leeward line, is attached to the clew of the spinnaker and is essential in controlling the shape of the spinnaker sail.
When set correctly, the leading edges of the symmetric spinnaker should be almost parallel to the wind. This is to ensure that the airflow over the leading edge remains attached. Generally, the spinnaker pole should be at the right angles to the apparent wind and requires a lot of care when packing.
The main disadvantage of this rig is the need to gybe the spinnaker pole whenever you gybe the boat. This is a complicated maneuver, and is one of the most common places for spinnakers to rip or get twisted. If, however, you can master this maneuver, you can sail at almost any angle downwind!
How to Use Spinnaker Effectively
If you decide to include the spinnakers to your sailboat, the sailmaker will want to know the type of boat you have, what kind of sailing you do, and where you sail. As such, the spinnaker that you end up with should be an excellent and all-round sail and should perform effectively off the breeze
The type of boat and where you'll be sailing will hugely influence the weight of your spinnaker cloth. In most cases, cruising spinnakers should be very light, so if you've decided to buy a spinnaker, make sure that it's designed per the type of your sailboat and where you will be sailing. Again, you can choose to go for something lighter and easier to set if you'll be sailing alone or with kids who are too young to help.
Setting up Spinnakers
One of the main reasons why sailors distrust spinnakers is because they don't know how to set them up. That being said, a perfectly working spinnaker starts with how you set it up and this revolves around how you carefully pack it and properly hook it up. You can do this by running the luff tapes and ensuring that the sails are not twisted when packed into the bag. If you are using large spinnakers, the best thing to do is make sure that they're set in stops to prevent the spinnakers from filling up with air before you even hoist them fully.
But even with that, you cannot fully set the spinnaker while sailing upwind. Make sure to bear away and have your pole ready to go as you turn downwind. You should then bear away to a reach before hoisting. Just don't hoist the spinnakers from the bow as this can move the weight of the crew and equipment forward.
Used when sailing downwind, a gennaker is asymmetric sail somewhere between a genoa and a spinnaker. It sets itself apart because it gennaker is a free-flying asymmetric spinnaker but it is tacked to the bowsprit like the jib.
Let's put it into perspective. Even though the genoa is a great sail for racing and cruising, sailors realized that it was too small to be used in a race or for downwind sail and this is the main reason why the spinnaker was invented. While the spinnakers are large sails that can be used for downwind sail, they are quite difficult to handle especially if you're sailing shorthanded. As such, this is how a gennaker came to be: it gives you the best of both worlds.
Gennakers are stable and easy to fly and will add to your enjoyment and downwind performance.
The Shape of a Gennaker
As we've just noted, the gennaker is asymmetrical. It doesn't attach to the forestay like the genoa but has a permanent fitting from the mast to bow. It is rigged exactly like a spinnaker but its tack is fastened to the bowsprit. This is fundamentally an essential sail if you're looking for something to bridge the gap between a genoa and a spinnaker.
Setting a Gennaker
When cruising, the gennaker is set with the tack line from the bow, a halyard, and a sheet that's led to the aft quarter. Attach the tack to a furling unit and attach it to a fitting on the hull near the very front of the sailboat. You can then attach the halyard that will help in pulling it up to the top of the mast before attaching it to the clew. The halyard can then run back to the winches to make the controlling of the sail shape easier, just like when using the genoa sail.
In essence, a gennaker is a superb sail that will give you the maximum versatility of achieving the best of both a genoa and a spinnaker, especially when sailing downwind. This is particularly of great importance if you're cruising by autopilot or at night.
Light Air Sails
Even though downwind sails can be used as light air sails, not all light air sails can be used for downwind sailing. In other words, there's a level of difference between downwind sails and light air sails. Light air sails include code zero, windseeker, and drifter reacher.
A cross between an asymmetrical spinnaker and a genoa, a code zero is a highly modern sail type that's generally used when sailing close to the wind in light air. Although the initial idea of code zero was to make a larger genoa, it settled on a narrow and flat spinnaker while upholding the shape of a genoa.
Modern boats come with code zero sails that can be used as soon as the sailboat bears off close-hauled even a little bit. It has a nearly straight luff and is designed to be very flat for close reaching. This sail is designed to give your boat extra performance in light winds, especially in boats that do not have overlapping genoas. It also mitigates the problem of loss of power when you are reaching with a non-overlapping headsail. Really, it is closer to a light air jib that sacrifices a little angle for speed.
In many conditions, a code zero sail can go as high as a sailboat with just a jib. By hoisting a code zero, you'll initially have to foot off about 15 degrees to fill it and get the power that you require to heel and move the boat. The boat will not only speed up but will also allow you to put the bow up while also doing the same course as before you set the zero. In essence, code zero can be an efficient way of giving your boat about 30% more speed and this is exactly why it's a vital inventory item in racing sailboats.
When it comes to furling code zero, the best way to do it is through a top-down furling system as this will ensure that you never get a twist in the system.
Generally used when a full size and heavier sail doesn't stay stable or pressurized, a windseeker is a very light sail that's designed for drifting conditions. This is exactly why they're designed with a forgiving cloth to allow them to handle these challenging conditions.
The windseeker should be tacked at the headstay with two sheets on the clew. To help this sail fill in the doldrums, you can heel the boat to whatever the apparent leeward side is and let gravity help you maintain a good sail shape while reaching.The ideal angle of a windseeker should be about 60 degrees.
Though only used in very specific conditions, the windseeker is so good at this one job that it is worth the investment if you plan on a long cruise. Still, you can substitute most off the breeze sails for this in a pinch, with slightly less performance gain, likely with more sacrifices in angle to the breeze.
Drifter Reacher
Many cruising sailors often get intimidated by the idea of setting and trimming a drifter if it's attached to the rig at only three corners or if it's free-flying. But whether or not a drifter is appropriate for your boat will hugely depend on your boat's rig, as well as other specific details such as your crew's ability to furl and unfurl the drifter and, of course, your intended cruising grounds.
But even with that, the drifter remains a time-honored sail that's handy and very versatile. Unlike other light air sails, the drifter perfectly carries on all points of sails as it allows the boat to sail close-hauled and to tack. It is also very easy to control when it's set and struck. In simpler terms, a drifter is principally a genoa that's built of lightweight fabric such as nylon. Regardless of the material, the drifter is a superb sail if you want to sail off a lee shore without using the genoa.
Generally stronger than other regular sails, stormsails are designed to handle winds of over 45 knots and are great when sailing in stormy conditions. They include a storm jib and a trysail.
If you sail long and far enough, chances are you have or will soon be caught in stormy conditions. Under such conditions, storm jibs can be your insurance and you'll be better off if you have a storm jib that has the following features:
- Robustly constructed using heavyweight sailcloth
- Sized suitably for the boat
- Highly visible even in grey and white seas
That's not all; you should never go out there without a storm jib as this, together with the trysail, is the only sails that will be capable of weathering some of nature's most testing situations.
Storm jibs typically have high clews to give you the flexibility of sheet location. You can raise the sail with a spare halyard until its lead position is closed-hauled in the right position. In essence, storm jib is your insurance policy when out there sailing: you should always have it but always hope that you never have to use it.
Also known as a spencer, a trysail is a small, bright orange, veritably bullet-proof, and triangular sail that's designed to save the boat's mainsail from winds over 45 knots and works in the same way as a storm jib. It is designed to enable you to make progress to windward even in strong and stormy winds.
Trysails generally use the same mast track as the mainsail but you have to introduce the slides into the gate from the head of the trysail.
There are two main types of rigs: the fore-and-aft rig and the square rigg.
Fore-and-aft Rig
This is a sailing rig that chiefly has the sails set along the lines of the keel and not perpendicular to it. It can be divided into three categories: Bermuda rig, Gaff rig, and Lateen rig.
Bermuda Rig - Also known as a Marconi rig, this is the typical configuration of most modern sailboats. It has been used since the 17th century and remains one of the most efficient types of rigs. The rig revolves around setting a triangular sail aft of the mast with the head raised to the top of the mast. The luff should run down the mast and be attached to the entire length.
Gaff Rig - This is the most popular fore-and-aft rig on vessels such as the schooner and barquentine. It revolves around having the sail four-cornered and controlled at its peak. In other words, the head of the mainsail is guided by a gaff.
Lateen Rig - This is a triangular fore-and-aft rig whereby a triangular sail is configured on a long yard that's mounted at a given angle of the mast while running in a fore-and-aft direction. Lateen rig is commonly used in the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean.
Square Rigged
This is a rig whereby the mainsails are arranged in a horizontal spar so that they're square or vertical to the mast and the keel of the boat. The square rig is highly efficient when sailing downwind and was once very popular with ocean-going sailboats.
Unquestionably, sailing is always pleasurable. Imagine turning off the engine of your boat, hoisting the sails, and filling them with air! This is, without a doubt, a priceless moment that will make your boat keel and jump forward!
But being propelled by the noiseless motion of the wind and against the mighty currents and pounding waves of the seas require that you know various sail types and how to use them not just in propelling your boat but also in ensuring that you enjoy sailing and stay safe. Sails are a gorgeous way of getting forward. They remain the main fascination of sailboats and sea cruising. If anything, sails and boats are inseparable and are your true friends when out there on the water. As such, getting to know different types of sails and how to use them properly is of great importance.
All in all, let's wish you calm seas, fine winds, and a sturdy mast!
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Sailboat Parts
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
Guide to Understanding Sail Rig Types (with Pictures)
There are a lot of different sail rig types and it can be difficult to remember what's what. So I've come up with a system. Let me explain it in this article.
What are the different types of sail rig? The sail rig is determined by the number of masts and the layout and shape of sails. Most modern ships are fore-and-aft rigged, while old ships are square-rigged. Rigs with one mast are sloops and cutters. Ketches, yawls, brigs, and schooners have two masts. Barques have three masts. Rigs can contain up to seven masts.
'Yeah, that's a gaff brig, and that a Bermuda cutter' - If you don't know what this means (neither did I) and want to know what to call a two-masted ship with a square-rigged mainsail, this article is definitely for you.
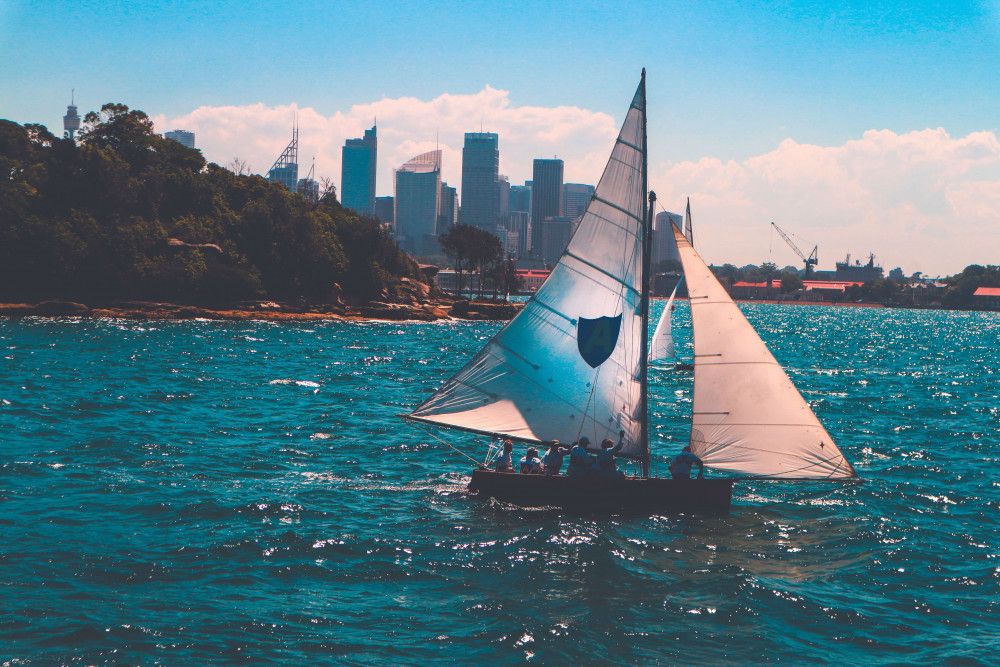

On this page:
More info on sail rig types, mast configurations and rig types, rigs with one mast, rigs with two masts, rigs with three masts, related questions.
This article is part 2 of my series on sails and rig types. Part 1 is all about the different types of sails. If you want to know everything there is to know about sails once and for all, I really recommend you read it. It gives a good overview of sail types and is easy to understand.

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)
First of all, what is a sail rig? A sail rig is the way in which the sails are attached to the mast(s). In other words, it's the setup or configuration of the sailboat. The rig consists of the sail and mast hardware. The sail rig and sail type are both part of the sail plan. We usually use the sail rig type to refer to the type of boat.
Let's start by taking a look at the most commonly used modern sail rigs. Don't worry if you don't exactly understand what's going on. At the end of this article, you'll understand everything about rig types.
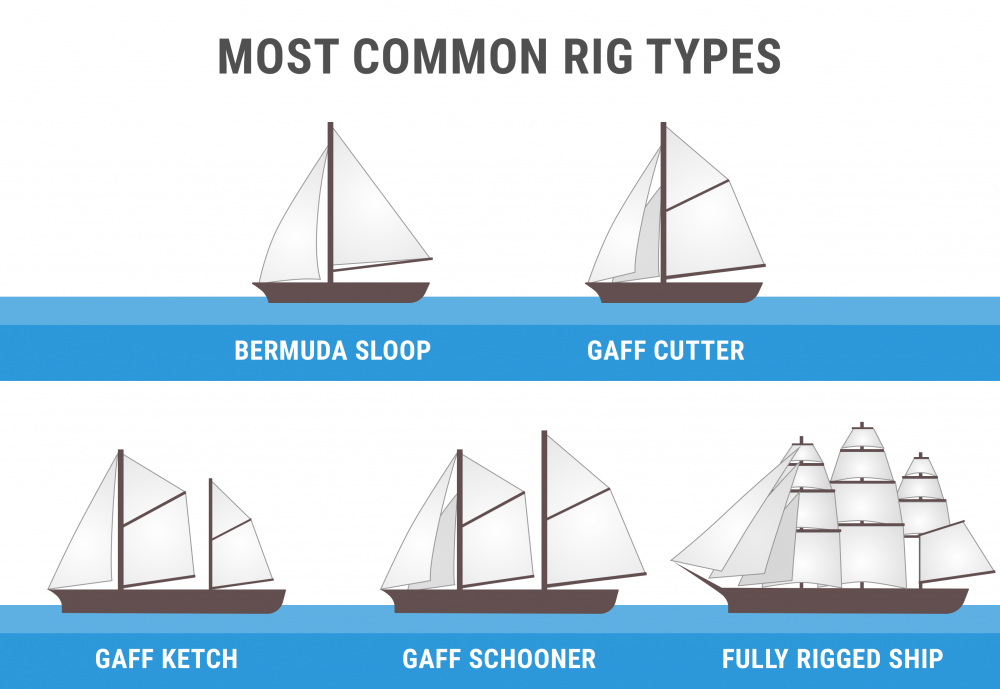
The sail rig and sail plan are often used interchangeably. When we talk of the sail rig we usually mean the sail plan . Although they are not quite the same. A sail plan is the set of drawings by the naval architect that shows the different combinations of sails and how they are set up for different weather conditions. For example a light air sail plan, storm sail plan, and the working sail plan (which is used most of the time).
So let's take a look at the three things that make up the sail plan.
The 3 things that make up the sail plan
I want to do a quick recap of my previous article. A sail plan is made up of:
- Mast configuration - refers to the number of masts and where they are placed
- Sail type - refers to the sail shape and functionality
- Rig type - refers to the way these sails are set up on your boat
I'll explore the most common rig types in detail later in this post. I've also added pictures to learn to recognize them more easily. ( Click here to skip to the section with pictures ).
How to recognize the sail plan?
So how do you know what kind of boat you're dealing with? If you want to determine what the rig type of a boat is, you need to look at these three things:
- Check the number of masts, and how they are set up.
- You look at the type of sails used (the shape of the sails, how many there are, and what functionality they have).
- And you have to determine the rig type, which means the way the sails are set up.
Below I'll explain each of these factors in more detail.
The most common rig types on sailboats
To give you an idea of the most-used sail rigs, I'll quickly summarize some sail plans below and mention the three things that make up their sail plan.
- Bermuda sloop - one mast, one mainsail, one headsail, fore-and-aft rigged
- Gaff cutter - one mast, one mainsail, two staysails, fore-and-aft rigged
- Gaff schooner - two-masted (foremast), two mainsails, staysails, fore-and-aft rigged
- Gaff ketch - two-masted (mizzen), two mainsails, staysails, fore-and-aft rigged
- Full-rigged ship or tall ship - three or more masts, mainsail on each mast, staysails, square-rigged
The first word is the shape and rigging of the mainsail. So this is the way the sail is attached to the mast. I'll go into this later on. The second word refers to the mast setup and amount of sails used.
Most sailboats are Bermuda sloops. Gaff-rigged sails are mostly found on older, classic boats. Square-rigged sails are generally not used anymore.
But first I want to discuss the three factors that make up the sail plan in more detail.
Ways to rig sails
There are basically two ways to rig sails:
- From side to side, called Square-rigged sails - the classic pirate sails
- From front to back, called Fore-and-aft rigged sails - the modern sail rig
Almost all boats are fore-and-aft rigged nowadays.
Square sails are good for running downwind, but they're pretty useless when you're on an upwind tack. These sails were used on Viking longships, for example. Their boats were quicker downwind than the boats with fore-and-aft rigged sails, but they didn't handle as well.
The Arabs first used fore-and-aft rigged sails, making them quicker in difficult wind conditions.
Quick recap from part 1: the reason most boats are fore-and-aft rigged today is the increased maneuverability of this configuration. A square-rigged ship is only good for downwind runs, but a fore-and-aft rigged ship can sail close to the wind, using the lift to move forward.
The way the sails are attached to the mast determines the shape of the sail. The square-rigged sails are always attached the same way to the mast. The fore-and-aft rig, however, has a lot of variations.
The three main sail rigs are:
- Bermuda rig - most used - has a three-sided (triangular) mainsail
- Gaff rig - has a four-sided mainsail, the head of the mainsail is guided by a gaff
- Lateen rig - has a three-sided (triangular) mainsail on a long yard
The Bermuda is the most used, the gaff is a bit old-fashioned, and the lateen rig is outdated (about a thousand years). Lateen rigs were used by the Moors. The Bermuda rig is actually based on the Lateen rig (the Dutch got inspired by the Moors).
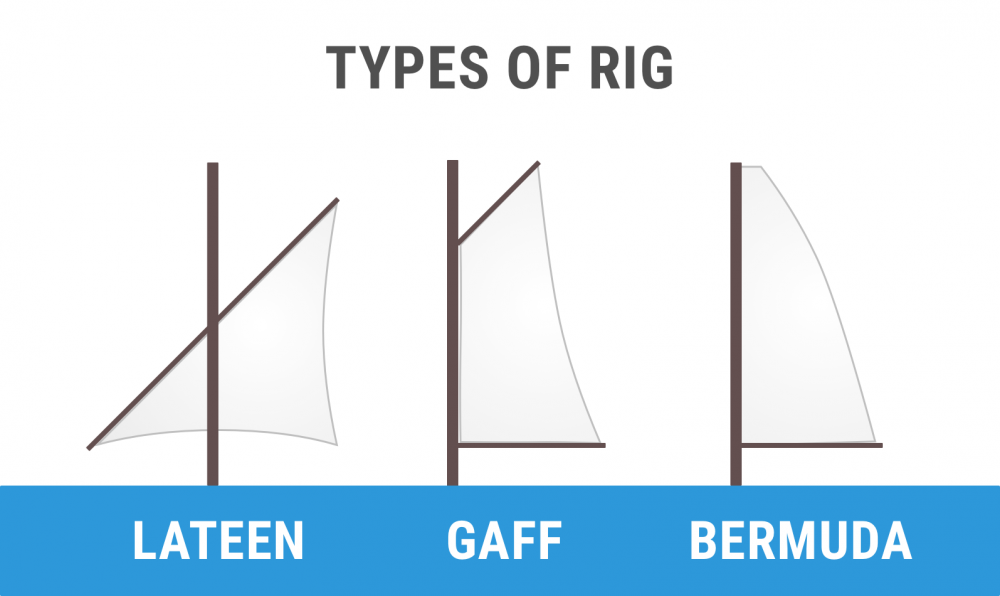
Other rig types that are not very common anymore are:
- Junk rig - has horizontal battens to control the sail
- Settee rig - Lateen with the front corner cut off
- Crabclaw rig
Mast configuration
Okay, we know the shape of the mainsail. Now it's time to take a look at the mast configuration. The first thing is the number of masts:
- one-masted boats
- two-masted boats
- three-masted boats
- four masts or up
- full or ship-rigged boats - also called 'ships' or 'tall ships'
I've briefly mentioned the one and two mast configurations in part 1 of this article. In this part, I'll also go over the three-masted configurations, and the tall ships as well.
A boat with one mast has a straightforward configuration because there's just one mast. You can choose to carry more sails or less, but that's about it.
A boat with two masts or more gets interesting. When you add a mast, it means you have to decide where to put the extra mast: in front, or in back of the mainmast. You can also choose whether or not the extra mast will carry an extra mainsail. The placement and size of the extra mast are important in determining what kind of boat we're dealing with. So you start by locating the largest mast, which is always the mainmast.
From front to back: the first mast is called the foremast. The middle mast is called the mainmast. And the rear mast is called the mizzenmast.
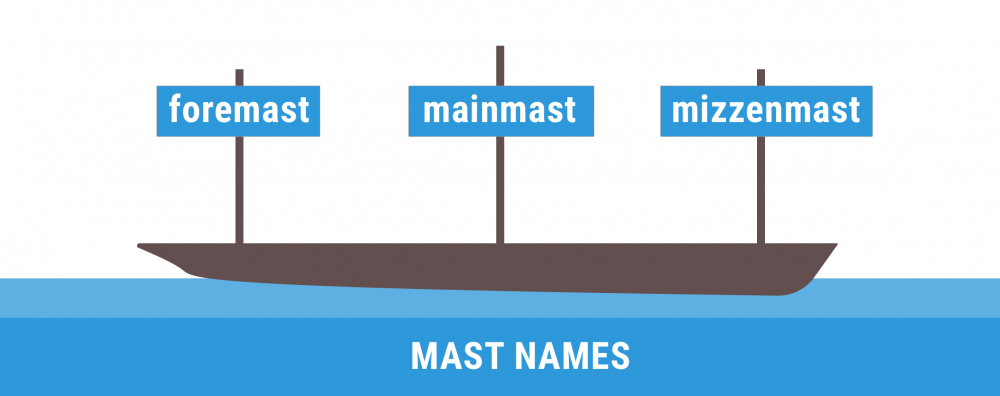
What is the mizzenmast? The mizzenmast is the aft-most (rear) mast on a sailboat with three or more masts or the mast behind the mainmast on a boat with two masts. The mizzenmast carries the mizzen sail. On a two-masted boat, the mizzenmast is always (slightly) smaller than the mainmast. What is the purpose of the mizzen sail? The mizzen sail provides more sail area and flexibility in sail plan. It can be used as a big wind rudder, helping the sailor to have more control over the stern of the ship. It pushes the stern away from the wind and forces the bow in the opposite way. This may help to bring the bow into the wind when at anchor.
I always look at the number of masts first, because this is the easiest to spot. So to make this stuff more easy to understand, I've divided up the rig types based on the number of masts below.
Why would you want more masts and sail anyways?
Good question. The biggest advantage of two masts compared to one (let's say a ketch compared to a sloop), is that it allows you to use multiple smaller sails to get the same sail area. It also allows for shorter masts.
This means you reduce the stress on the rigging and the masts, which makes the ketch rig safer and less prone to wear and tear. It also doesn't capsize as quickly. So there are a couple of real advantages of a ketch rig over a sloop rig.
In the case of one mast, we look at the number of sails it carries.
Boats with one mast can have either one sail, two sails, or three or more sails.
Most single-masted boats are sloops, which means one mast with two sails (mainsail + headsail). The extra sail increases maneuverability. The mainsail gives you control over the stern, while the headsail gives you control over the bow.
Sailor tip: you steer a boat using its sails, not using its rudder.
The one-masted rigs are:
- Cat - one mast, one sail
- Sloop - one mast, two sails
- Cutter - one mast, three or more sails

The cat is the simplest sail plan and has one mast with one sail. It's easy to handle alone, so it's very popular as a fishing boat. Most (very) small sailboats are catboats, like the Sunfish, and many Laser varieties. But it has a limited sail area and doesn't give you the control and options you have with more sails.
The most common sail plan is the sloop. It has one mast and two sails: the main and headsail. Most sloops have a Bermuda mainsail. It's one of the best racing rigs because it's able to sail very close to the wind (also called 'weatherly'). It's one of the fastest rig types for upwind sailing.
It's a simple sail plan that allows for high performance, and you can sail it short-handed. That's why most sailboats you see today are (Bermuda) sloops.
This rig is also called the Marconi rig, and it was developed by a Dutch Bermudian (or a Bermudian Dutchman) - someone from Holland who lived on Bermuda.
A cutter has three or more sails. Usually, the sail plan looks a lot like the sloop, but it has three headsails instead of one. Naval cutters can carry up to 6 sails.
Cutters have larger sail area, so they are better in light air. The partition of the sail area into more smaller sails give you more control in heavier winds as well. Cutters are considered better for bluewater sailing than sloops (although sloops will do fine also). But the additional sails just give you a bit more to play with.
Two-masted boats can have an extra mast in front or behind the mainmast. If the extra mast is behind (aft of) the mainmast, it's called a mizzenmast . If it's in front of the mainmast, it's called a foremast .
If you look at a boat with two masts and it has a foremast, it's most likely either a schooner or a brig. It's easy to recognize a foremast: the foremast is smaller than the aft mast.
If the aft mast is smaller than the front mast, it is a sail plan with a mizzenmast. That means the extra mast has been placed at the back of the boat. In this case, the front mast isn't the foremast, but the mainmast. Boats with two masts that have a mizzenmast are most likely a yawl or ketch.
The two-masted rigs are:
- Lugger - two masts (mizzen), with lugsail (a cross between gaff rig and lateen rig) on both masts
- Yawl - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast is much taller than mizzen. Mizzen without a mainsail.
- Ketch - two masts (mizzen), fore-and-aft rigged on both masts. Main mast with only slightly smaller mizzen. Mizzen has mainsail.
- Schooner - two masts (foremast), generally gaff rig on both masts. Main mast with only slightly smaller foremast. Sometimes build with three masts, up to seven in the age of sail.
- Bilander - two masts (foremast). Has a lateen-rigged mainsail and square-rigged sails on the foremast and topsails.
- Brig - two masts (foremast), partially square-rigged. The main mast carries small lateen-rigged sail.
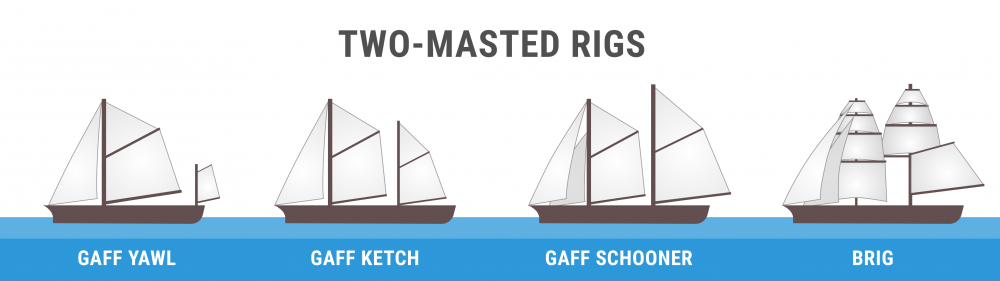
The yawl has two masts that are fore-and-aft rigged and a mizzenmast. The mizzenmast is much shorter than the mainmast, and it doesn't carry a mainsail. The mizzenmast is located aft of the rudder and is mainly used to increase helm balance.
A ketch has two masts that are fore-and-aft rigged. The extra mast is a mizzenmast. It's nearly as tall as the mainmast and carries a mainsail. Usually, the mainsails of the ketch are gaff-rigged, but there are Bermuda-rigged ketches too. The mizzenmast is located in front of the rudder instead of aft, as on the yawl.
The function of the ketch's mizzen sail is different from that of the yawl. It's actually used to drive the boat forward, and the mizzen sail, together with the headsail, are sufficient to sail the ketch. The mizzen sail on a yawl can't really drive the boat forward.
Schooners have two masts that are fore-and-aft rigged. The extra mast is a foremast which is generally smaller than the mainmast, but it does carry a mainsail. Schooners are also built with a lot more masts, up to seven (not anymore). The schooner's mainsails are generally gaff-rigged.
The schooner is easy to sail but not very fast. It handles easier than a sloop, except for upwind, and it's only because of better technology that sloops are now more popular than the schooner.
The brig has two masts. The foremast is always square-rigged. The mainmast can be square-rigged or is partially square-rigged. Some brigs carry a lateen mainsail on the mainmast, with square-rigged topsails.
Some variations on the brig are:
Brigantine - two masts (foremast), partially square-rigged. Mainmast carries no square-rigged mainsail.
Hermaphrodite brig - also called half brig or schooner brig. Has two masts (foremast), partially square-rigged. Mainmast carries a gaff rig mainsail and topsail, making it half schooner.
Three-masted boats are mostly barques or schooners. Sometimes sail plans with two masts are used with more masts.
The three-masted rigs are:
- Barque - three masts, fore, and mainmast are square-rigged, the mizzenmast is usually gaff-rigged. All masts carry mainsail.
- Barquentine - three masts, foremast is square-rigged, the main and mizzenmast are fore-and-aft rigged. Also called the schooner barque.
- Polacca - three masts, foremast is square-rigged, the main and mizzenmast are lateen-rigged.
- Xebec - three masts, all masts are lateen-rigged.
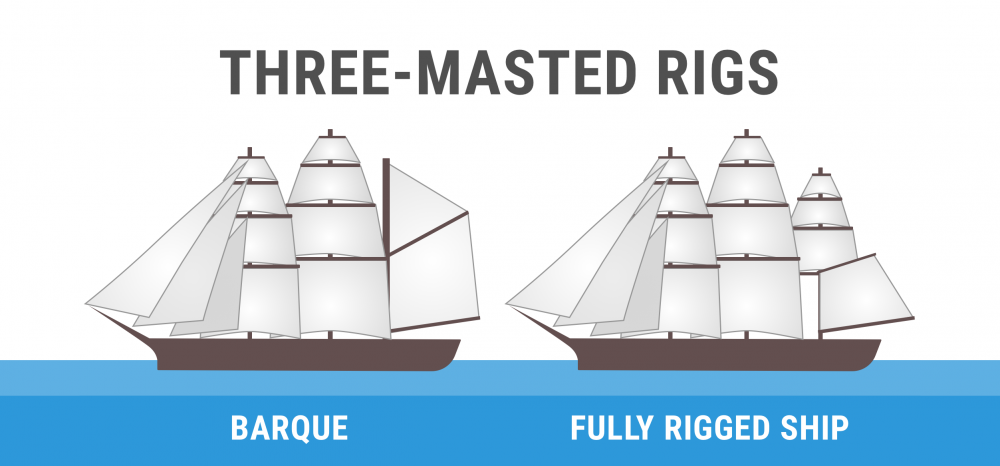
A barque has three or four masts. The fore and mainmast are square-rigged, and the mizzen fore-and-aft, usually gaff-rigged. Carries a mainsail on each mast, but the mainsail shape differs per mast (square or gaff). Barques were built with up to five masts. Four-masted barques were quite common.
Barques were a good alternative to full-rigged ships because they require a lot fewer sailors. But they were also slower. Very popular rig for ocean crossings, so a great rig for merchants who travel long distances and don't want 30 - 50 sailors to run their ship.
Barquentine
The barquentine usually has three masts. The foremast is square-rigged and the main and mizzenmast fore-and-aft. The rear masts are usually gaff-rigged.
Faster than a barque or a schooner, but the performance is worse than both.
The polacca or polacre rig has three masts with a square-rigged foremast. The main and mizzenmast are lateen-rigged. Beautiful boat to see. Polacca literally means 'Polish' (it's Italian). It was a popular rig type in the Mediterranean in the 17th century. It looks like the xebec, which has three lateen-rigged masts.
Fun fact: polaccas were used by a Dutch sailor-turned-Turkish-pirate (called Murat Reis).
The xebec is a Mediterranean trading ship with three masts. All masts are lateen-rigged. I couldn't find any surviving xebecs, only models and paintings. So I guess this rig is outdated a long time.
A boat with three or more masts that all carry square-rigged sails is called a ship, a tall ship, or a full-rigged ship. So it's at this point that we start calling boats 'ships'. It has nothing to do with size but with the type of rigging.
More sails mean less stress on all of them. These ships use a lot of sails to distribute the forces, which reduces the stress on the rigging and the masts. Square sails mean double the sail area in comparison to triangular sails.
They are quite fast for their size, and they could outrun most sloops and schooners (schooners were relatively a lot heavier). The reason is that tall ships could be a lot longer than sloops, giving them a lot of extra hull speed. Sloops couldn't be as large because there weren't strong enough materials available. Try making a single triangular sail with a sail area of over 500 sq. ft. from linen.
So a lot of smaller sails made sense. You could have a large ship with a good maximum hull speed, without your sails ripping apart with every gust of wind.
But you need A LOT of sailors to sail a tall ship: about 30 sailors in total to ie. reef down sails and operate the ship. That's really a lot.
Tall ships are used nowadays for racing, with the popular tall ship races traveling the world. Every four years I go and check them out when they are at Harlingen (which is very close to where I live).
Check out the amazing ships in this video of the tall ship races last year near my hometown. (The event was organized by friends of mine).
What is the difference between a schooner and a sloop? A schooner has two masts, whereas the sloop only has one. The schooner carries more sails, with a mainsail on both masts. Also, sloops are usually Bermuda-rigged, whereas schooners are usually gaff-rigged. Most schooners also carry one or two additional headsails, in contrast to the single jib of the sloop.
What do you call a two-masted sailboat? A two-masted sailboat is most likely a yawl, ketch, schooner, or brig. To determine which one it is you have to locate the mainmast (the tallest). At the rear: schooner or brig. In front: yawl or ketch. Brigs have a square-rigged foremast, schooners don't. Ketches carry a mainsail on the rear mast; yawls don't.
What is a sloop rig? A sloop rig is a sailboat with one mast and two sails: a mainsail and headsail. It's a simple sail plan that handles well and offers good upwind performance. The sloop rig can be sailed shorthanded and is able to sail very close to the wind, making it very popular. Most recreational sailboats use a sloop rig.
What is the difference between a ketch and a yawl? The most important difference between a ketch and a yawl are the position and height of the mizzenmast. The mizzenmast on a yawl is located aft of the rudder, is shorter than the mainmast and doesn't carry a mainsail. On a ketch, it's nearly as long as the mainmast and carries a mainsail.
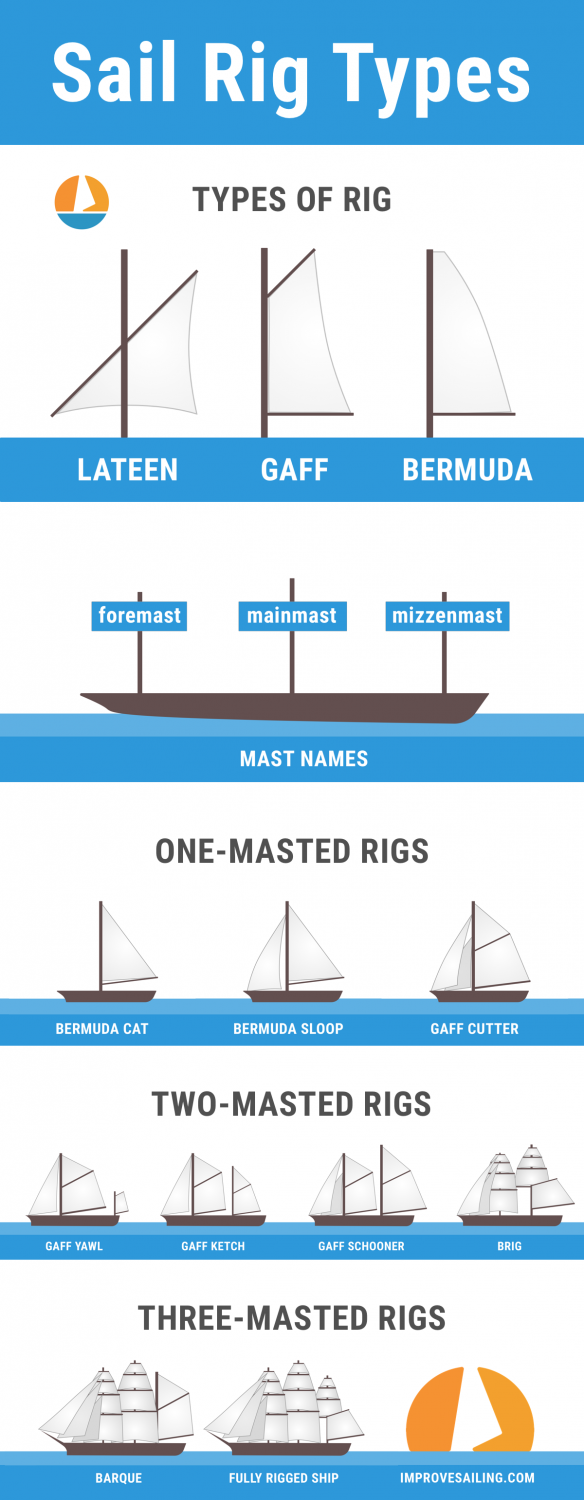
There are a wonderful lots of DIY changeability shows on the cable airwaves these days.
Rick the rigger
There are SO many errors on this site it really should be taken down.
First major mistake is to say you are no longer afraid of the sea.
One that truly gets up my nose is the term ‘fully’ rigged ship. It’s a FULL rigged ship!! Your mast names are the wrong way round and just because there may be 3 it doesn’t automatically mean the one in the middle is the main.
I could go on and totally destroy your over inflated but fragile ego but I won’t. All I will say is go learn a lot more before posting.
Shawn Buckles
Thanks for your feedback. If you like to point out anything more specific, please let me know and I will update the articles. I’ve changed fully-rigged to full-rigged ship - which is a typo on my part. I try to be as concise as I can, but, obviously, we all make mistakes every now and then. The great thing about the internet is that we can learn from each other and update our knowledge together.
If you want to write yourself and share your knowledge, please consider applying as a writer for my blog by clicking on the top banner.
Thanks, Shawn
Well, I feel that I’ve learned a bit from this. The information is clear and well laid out. Is it accurate? I can’t see anything at odds with the little I knew before, except that I understood a xebec has a square rigged centre mainmast, such as the Pelican ( https://www.adventureundersail.com/ )
Hi, Shawn, You forgot (failed) to mention another type of rig? The oldest type of rig known and still functions today JUNK RIG!
Why are so many of the comments here negative. I think it is wonderful to share knowledge and learn together. I knew a little about the subject (I’m an Aubrey-Maturin fan!) but still found this clarified some things for me. I can’t comment therefore on the accuracy of the article, but it seems clear to me that the spirit of the author is positive. We owe you some more bonhomme I suggest Shawn.
As they say in the Navy: “BZ” - for a good article.
Been reading S.M. Stirling and wanted to understand the ship types he references. Thank you, very helpful.
This site is an awesome starting point for anyone who would like to get an overview of the subject. I am gratefull to Shawn for sharing - Thanks & Kudos to you! If the negative reviewers want to get a deeper technical knowledge that is accurate to the n-th then go study the appropriate material. Contribute rather than destroy another’s good work. Well done Shawn. Great job!
Good stuff Shawn - very helpful. As a novice, it’s too confusing to figure out in bits and pieces. Thanks for laying it out.
First of all I have to say that Rick ‘the rigger’ is obviously the one with the “over inflated but fragile ego” and I laughed when you suggested he share his knowledge on your blog, well played!
As for the content it’s great, hope to read more soon!
Alec Lowenthal
Shawn, I have a painting of a Spanish vessel, two masted, with. Lateen sails on both masts and a jib. The mainsail is ahead of the main mast (fore) and the other is aft of the mizzen mast. Would this be what you call lugger rig? I have not seen a similar picture. Thanks, Alec.
Thank you for your article I found easy to read and understand, and more importantly remember, which emphasises the well written.. Pity about the negative comments, but love your proactive responses!
This vessel, “SEBASTIAN” out of Garrucha, Almería, España, was painted by Gustave Gillman in 1899.
Sorry, picture not accepted!
Thank you for a very informative article. I sail a bit and am always looking for more knowledge. I like the way you put forth your info and I feel if you can’t say anything positive, then that person should have their own blog or keep their opinions to their-self. I will be looking for more from you. I salute your way of dealing with negative comments.
Thank you for a great intro to sailing boats! I searched different sailboats because I use old sails tp make bags and wanted to learn the difference. Way more than I ever expected. Thanks for all the work put in to teach the rest of us.
Your description of a cutter is lacking, and your illustrations of “cutters” are actually cutter-rigged sloops. On a true cutter, the mast is moved further aft (with more than 40% of the ship forward of the mast). A sloop uses tension in the backstay to tension the luff of the foresail. The cutter can’t do this.
Also, a bermuda-rigged ketch will have a line running from the top of the mainmast to the top of the mizzenmast.
wow great guide to rig types! thanks
Interesting guide, however I am confused about the description of the brig. You say the main mast on a brig can have a lateen sail, but in your picture it looks like a gaff sail to me. How is it a lateen sail?
Hi Shawn, thank you for taking the time to share this information. It is clear and very helpful. I am new to sailing and thinking of buying my own blue water yacht. The information you have supplied is very useful. I still am seeking more information on performance and safety. Please keep up the good work. Best Regards
mickey fanelli
I’m starting to repair a model sailboat used in the lake I have three masts that have long been broken off and the sails need replacement. So my question is there a special relationship between the three masts I do have reminents of where the masts should go. they all broke off the boat along with the sails I can figure out where they go because of the old glue marks but it makes no sense. or does it really matter on a model thank you mickey
Cool, total novice here. I have learnt a lot. Thanks for sharing - the diagrams along with the text make it really easy to understand, especially for a beginner who hasn’t even stepped on a sailing boat.
Daryl Beatt
Thank you. Cleared up quite a few things for me. For example, I was familiar with the names “Xebecs” and “Polaccas” from recent reading about the Barbary War. I had gathered that the two Barbary types were better suited to sailing in the Med, but perhaps they were less able to be adaptable to military uses,(but one might assume that would be ok if one plans to board and fight, as opposed to fight a running gun duel). Specifically, the strangely one sided August 1, 1801 battle between the USS Enterprise under Lt. John Sterett and the Polacca cruiser Tripoli under Admiral Rais Mahomet Rous. On paper both ships seemed nearly equal in size, guns and crew, but pictures of the battle are confusing. While the Enterprise is usually rendered as the familiar schooner, the polacca Tripoli has been pictured in radically different ways. Thus the Wikipedia picture by Hoff in 1878 used to illustrate the Battle shows a Brig design for Tripoli, indicating 77 years later, polaccas were no longer common.
Lee Christiansen
I am curious as to what you would call a modern race boat with a fractional jib,not equipped for full masthead hoist? Thanks Lee
Thanks Guy: The information and pictures really eliminate a lot of the mystery of the terminology and the meanings. Also appreciate the insight of the handling idiosyncrasies “hand” (staff) requirements to manage a vessel for one that has not been on the water much. I long to spend significant time afloat, but have concern about the ability to handle a vessel due to advancing age. The Significant Other prefers to sit (in AC comfort)and be entertained by parties of cruise line employees. Thanks again for the information.
Gordon Smith
Your discussion made no mention of the galleon, a vessel with either square-rigged Fore and Main masts and a shorter lateen-rigged Mizzen, or, on larger galleons, square-rigged Fore and Main masts, with a lateen-rigged Mizzen and a lateen-rigged Bonaventure mast, both shorter than either the Fore or Main masts. Also, it was not uncommon for a galleon to hoist a square-rigged bowsprit topsail in addition to the usual square-rigged spritsail.
Leave a comment
You may also like.
What's that sail for? Generally, I don't know. So I've come up with a system. I'll explain you everything there is to know about sails and rigs in this article.

17 Sailboat Types Explained: How To Recognize Them

Different Types of Sailing and Racing Explained

How Are Sail Numbers Assigned? (And how to pick yours)

Boat Sailor
Type of sails: a comprehensive guide to sails.

As an avid sailing enthusiast and advisor, I am excited to share a complete guide to different types of sails for sailboats. Choosing the right sail is crucial for optimizing sailing performance and ensuring safety in various weather conditions. In this article, we will explore the main type of sails, their advantages, and when to use them effectively. So let’s set sail and delve into the world of sails!
The Main Types of Sails
Mainsail: The Backbone of Sailing
The mainsail, being the largest and most essential sail on a sailboat, plays a central role in driving the vessel forward. It is a fore-and-aft rigged sail attached to the mast and the boom. Mainsails are incredibly versatile and suitable for various wind conditions, making them the go-to sail for most situations. They are easy to steer, even in light winds, making them ideal for relaxed cruising.
Headsail/Jib: Your Go-To Sail for Safety
The headsail, also known as a jib , is a smaller sail located forward of the mast. Its primary purpose is to maintain stability and balance the boat in strong winds. When the wind picks up, the mainsail can become overpowering, and that’s when the headsail steps in to ensure safe and controlled sailing. It’s like having a safety net during rough weather conditions.
Genoa: Power and Versatility Combined
The genoa is a type of headsail that offers more sail area and power compared to a standard jib. It’s perfect for boosting speed and maneuverability, especially in light winds. Genoas are incredibly versatile, making them an excellent choice for sailors who want to get the most out of their sailboat in various conditions.
Sailing Ship Rigs: A Historical Perspective
In the era of the “golden age of sail,” different sail plans were used on sailing vessels to optimize their performance and accommodate smaller crews.

Fore and Aft Rig
The fore-and-aft rig, consisting of sails aligned along the length of the boat, includes popular designs like schooners and sloops. These rigs required smaller crews and were well-suited for coastal and fishing trades.
Square topsail schooners with athwart sails were also prevalent during that time. They were used for cargo ships and long voyages, but their complex rigging required larger crews to handle the sails effectively.
The Golden Age of Sail
This period marked the peak of sailing ship technology and saw remarkable advancements in shipbuilding and sail design. It’s a fascinating chapter in the history of sailing that continues to inspire sailors to this day.
Type of Sails Names: Decoding the Terminology
Mainsail and Foresail
The mainsail, as mentioned earlier, is the principal sail that catches the wind to move the boat forward. Foresail is a general term that includes various sails positioned near the bow of the sailboat, such as the jib and genoa.
Genoa and Jib
The genoa and jib are both types of foresails. The genoa is larger and overlaps the mainsail, providing additional power and efficiency. The jib, on the other hand, is smaller and is used when the wind is stronger.
Staysail and Spinnaker
Staysails are triangular sails set between masts and stays, used to improve stability and balance. Spinnakers are large, balloon-shaped sails used for downwind sailing, providing an extra boost of speed.
Choosing the Right Sail for Different Conditions
Sailing in Light Winds
In light winds, the mainsail is your best friend. It’s highly efficient and capable of catching even the slightest breeze, propelling the boat forward smoothly.
Sailing in Strong Winds
When the wind picks up, it’s time to rely on the headsail or jib. These sails provide a reduced surface area, preventing the boat from becoming overpowered and ensuring a controlled sail.
Navigating Challenging Weather
Different weather conditions call for different sails. Understanding the intricacies of each sail and when to use them will help you navigate through challenging weather with ease.
Type of Sails Materials: Quality Matters
Traditional Canvas Sails
Traditional canvas sails, made of materials like cotton or linen, were commonly used in the past. While they offer a classic charm, their performance and durability have limitations compared to modern sail materials.
Modern Sail Materials
Today, sail manufacturers utilize advanced materials like Dacron, Mylar, and Kevlar. These materials offer superior strength, low stretch, and better shape retention, contributing to improved sailing performance.
Pros and Cons of Each Material
Understanding the pros and cons of different sail materials will help you make an informed decision when purchasing or maintaining your sails.
Understanding Sail Shapes and Configurations
The Science of Sail Shape
Sail shape is crucial for maximizing performance and efficiency. Properly trimmed sails allow you to sail efficiently, whether you’re sailing upwind or downwind.
Balancing Performance and Stability
Finding the right balance between performance and stability is essential. Adjusting sail shape and trim can significantly impact your sailing experience.
Fine-Tuning Sail Trim
Sail trim is an art form. Mastering the art of fine-tuning sail trim will make you a more skilled sailor and enhance your overall sailing experience.
The Evolution of Sail Designs
From Classic to Cutting-Edge
Sail design has come a long way. From classic traditional sails to modern, innovative designs, sailmaking has witnessed significant evolution.
How Technology Impacted Sail Design
Technological advancements have revolutionized sailmaking, resulting in more efficient, aerodynamic, and performance-oriented sails.
Innovation in Sailmaking
Sailmakers are continually exploring new materials and construction techniques to create sails that are lighter, stronger, and more efficient than ever before.
Sailing Techniques: Getting the Most Out of Your Sails
Tacking and Gybing
Tacking and gybing are essential sailing maneuvers used to change the direction of the boat and optimize the use of wind.
Maximizing Speed
To get the most out of your sails, understanding how to trim them properly and sail at optimal angles is crucial for achieving higher speeds.
Safety Precautions
Sailing is exhilarating, but safety should always be a top priority. Understanding safety procedures and precautions will ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
Maintaining and Storing Sails
Sail Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance are essential to prolong the life of your sails and keep them in top condition.
Storing Sails Properly
When not in use, storing sails correctly can prevent damage and maintain their performance over time.
Extending the Lifespan of Sails
With proper care and attention, you can extend the lifespan of your sails, making them a worthy investment.
Sustainable Sailing: Eco-Friendly Sail Materials
The Impact of Traditional Sails on the Environment
Traditional sail materials, while charming, may have a more significant environmental impact compared to modern, eco-friendly alternatives.
Eco-Friendly Sail Options
Eco-conscious sailors can explore sustainable sail materials that minimize environmental harm without compromising performance.
Embracing Sustainable Practices
As sailors, we have a responsibility to protect the oceans and environment. Embracing sustainable practices in sailing is essential for the well-being of our planet.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide to different type of sails, I hope you now have a deeper understanding of the critical role sails play in sailing. Choosing the right sail and mastering sail techniques will elevate your sailing experience to new heights. Remember, sailing is an ever-evolving journey of learning and adventure.
Which sail is best for light winds?
The mainsail is the most suitable sail for light winds as it can efficiently catch even the slightest breeze and keep the boat moving smoothly.
What is the purpose of a genoa?
The genoa is a type of sails that provides additional power and versatility, making it an excellent choice for boosting speed and maneuverability in various wind conditions.
What sail material is most durable?
Modern sail materials like Dacron and Kevlar offer superior strength and durability compared to traditional canvas sails made of cotton or linen.
How do I maintain my sails?
Proper care and maintenance, including regular cleaning and inspection, will help prolong the life of your sails and ensure they perform optimally.
Are there eco-friendly sail options?
Yes, eco-conscious sailors can opt for sustainable sail materials that minimize environmental impact, contributing to a greener and more sustainable sailing experience.

Michael Thompson
Embarking on a lifelong love affair with the sea, I found solace and exhilaration in the art of sailing. From navigating treacherous waters to harnessing the wind's untamed power, my passion has evolved into a mission to inspire others. Join me on a voyage of discovery as we explore the vast horizons of sailing's timeless allure.
More to Explore

Spiridakos Sailing Cruises: An Unforgettable Adventure

Sailing in the Caribbean

Sailing Greek Islands

Types of Sails on Sailboats: A Comprehensive Guide
Sailboats come in many shapes and sizes, but all have one thing in common: sails. The type of sail used on a boat can make a big difference in how it performs on the water. Understanding the different types of sails and their advantages and disadvantages can help sailors choose the right sail for their boat and the conditions they will be sailing in.
One of the most common types of sails is the mainsail. This sail is attached to the mast and boom and is used to catch the wind and propel the boat forward. Mainsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including full-batten, partial-batten, and no-batten designs. Each design has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the type of sailing the boat will be doing.
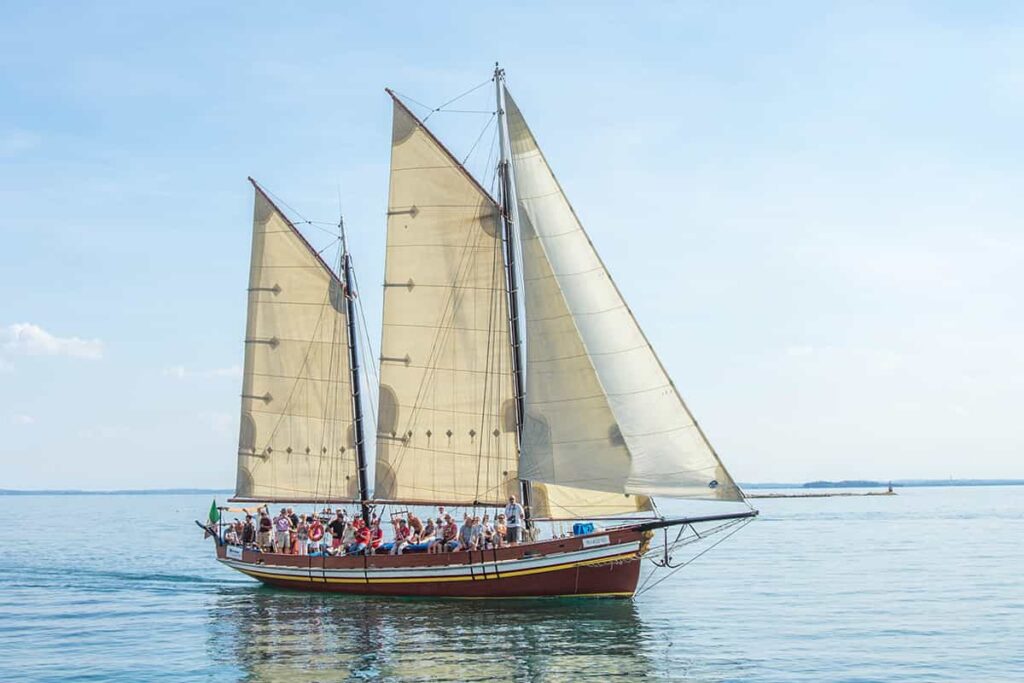

Another important sail on a sailboat is the headsail. This sail is located at the front of the boat and is used to catch the wind from the side. Headsails come in many different shapes and sizes, including genoas, jibs, and spinnakers. Choosing the right headsail can make a big difference in how the boat performs , especially in heavy wind conditions.
Basic Types of Sails
Sails are an essential part of any sailboat. They are used to harness the wind to propel the boat forward. There are several types of sails available for sailboats , and each serves a different purpose. Here are the three basic types of sails:
The mainsail is the most critical sail on a sailboat. It is a large, triangular sail that is hoisted up the mast. The mainsail is the primary source of propulsion for the boat and is used to control the boat’s direction. The mainsail is attached to the boom, which is a horizontal spar that runs along the bottom of the sail. The boom helps to control the mainsail’s shape and angle to the wind.
The mainsail can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the mainsheet, the traveler, and the boom vang. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
The jib is a smaller sail that is located at the front of the boat. It is a triangular sail that is attached to the forestay, which is a wire that runs from the top of the mast to the bow of the boat. The jib is used to balance the boat and to help control its direction. It is often used in conjunction with the mainsail to provide additional power and control.
The jib can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the jib sheet and the jib halyard. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
The spinnaker is a large, colorful sail that is used for downwind sailing. It is a symmetrical sail that is attached to the boat’s mast and bow. The spinnaker is used to catch the wind and provide additional power to the boat. It is often used in racing and can help to increase the boat’s speed and performance.
The spinnaker can be adjusted using a variety of controls, including the spinnaker sheet and the spinnaker halyard. These controls allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s shape and angle to the wind, which can help to optimize the boat’s speed and performance.
Specialty Sails
While many sailors may be familiar with the standard mainsail and jib combination, there are a variety of specialty sails that can be used for specific purposes. These sails can be particularly useful for racing, cruising, or for handling difficult weather conditions.
The genoa is a type of jib that is larger than the standard jib and overlaps the mainsail. This sail is particularly useful for upwind sailing as it provides more power and lift than a standard jib. The genoa is also useful for light wind conditions where a larger sail area is needed to catch the breeze.
A storm sail is a heavy-duty sail that is designed for use in strong winds and heavy seas. These sails are typically smaller than the standard mainsail and jib, and are made from heavy-duty materials such as Dacron or Kevlar. The storm sail is used to reduce sail area and provide better control in difficult conditions.
The gennaker is a hybrid between a spinnaker and a genoa. This sail is designed for downwind sailing and is particularly useful in light wind conditions. The gennaker is typically made from a lightweight nylon material and is larger than a spinnaker, but smaller than a genoa. This sail is particularly popular with cruising sailors as it provides a comfortable and stable ride in light wind conditions.
Sail Materials
Sailboats are equipped with sails made from a variety of materials. The type of sail material used depends on the intended use of the sailboat, as well as the budget of the sailor. The following are some of the most common sail materials used on sailboats today:
Dacron is a synthetic material that is commonly used in sails. It is durable, easy to handle, and relatively inexpensive. Dacron sails are ideal for cruising and recreational sailing, as they are not designed for racing or high-performance sailing.
Dacron sails are available in a variety of weights, with heavier sails being more durable and lighter sails providing better performance. Dacron sails are also available in a variety of colors, allowing sailors to customize the look of their sailboat.
Kevlar is a high-performance synthetic material that is commonly used in racing sails . Kevlar sails are lightweight, strong, and have a low stretch rate, making them ideal for high-performance sailing. However, Kevlar sails are more expensive than Dacron sails and require more maintenance.
Kevlar sails are available in a variety of weights and colors, allowing sailors to customize the look and performance of their sailboat.
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a high-performance material that is commonly used in racing sails. Carbon fiber sails are extremely lightweight and have a low stretch rate, making them ideal for high-performance sailing. However, carbon fiber sails are the most expensive option and require the most maintenance.
Carbon fiber sails are available in a variety of weights and colors, allowing sailors to customize the look and performance of their sailboat.
In conclusion, the type of sail material used on a sailboat depends on the intended use of the sailboat and the budget of the sailor. Dacron is the most common sail material used for cruising and recreational sailing, while Kevlar and carbon fiber are used for racing and high-performance sailing.
Sail Shapes
Sail shape is an important factor in determining the performance of a sailboat. Different sail shapes are designed for different wind conditions, and the choice of sail shape can greatly affect a boat’s speed and maneuverability. Here are three common sail shapes:
Bermuda Rig
The Bermuda rig is the most common sail shape on modern sailboats. It consists of a triangular mainsail and a smaller jib or foresail. The triangular shape of the mainsail allows for efficient wind capture, while the jib helps to balance the boat and control the sail’s shape. The Bermuda rig is versatile and can be used in a wide range of wind conditions, making it a popular choice for cruising and racing sailboats .
The gaff rig is an older sail shape that was commonly used on sailing vessels in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It features a four-sided mainsail with a gaff spar at the top, which provides additional sail area. The gaff rig is less efficient than the Bermuda rig, but it has a distinctive appearance and can be used in light to moderate wind conditions. Gaff-rigged sailboats are often seen in traditional and classic boat regattas.
The lateen rig is a triangular sail shape that is commonly used on small boats and traditional sailing vessels in the Mediterranean and Middle East. It consists of a single, triangular sail that is mounted on a long, diagonal spar called a yard. The lateen rig is efficient in light to moderate winds and is particularly well-suited to sailing downwind. It is often used on small sailing dinghies and traditional wooden boats.
- Recent Posts
- Sustainable and Luxurious: Discovering Split’s Yachting Paradise – April 26, 2024
- MarineTraffic vs VesselFinder: Which Is Better Vessel Tracking Service? – February 14, 2024
- Port Costs: A Comprehensive Guide to Port Dues and Fees for Cargo Ships – February 12, 2024
About the author
I worked as an officer in the deck department on various types of vessels, including oil and chemical tankers, LPG carriers, and even reefer and TSHD in the early years. Currently employed as Marine Surveyor carrying cargo, draft, bunker, and warranty survey.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest posts

Marine Satellite Internet: How Ships Keep Connected
Some boaters take leisurely trips to the lake while others venture into the ocean, far removed from the rest of civilization. Thankfully, marine satellite internet helps ships stay connected.

What to Wear on a Boat
Sailing on a ship requires extensive preparation. In addition to understanding its components and how to operate it, people must also know what to wear on a boat.

What Happens if a Ship Loses Power?
A power outage is among the worst issues for maritime professionals. What happens if a ship loses power?

Most Popular Types of Sails on a Sailboat

Learning about how there were different types of sails on sailboats for me was a bit strange at first. I thought something along the lines of “Don’t you just need to put some fabric on some polls and grab the wind?” Obviously, there’s far more to it than that.
So what are the most popular types of sails on sailboats? The mainsail, headsail (or jib), genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker are the most popular types of sails on sailboats. There are also a number of different configurations when considering the type of sail and mast in use including a sloop, fractional rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner, yawl, and cat.
Simply put, different sailboat sails serve different purposes when out on the water.
The sail is kind of like the “engine” of your sailboat (of course, sailboats can have actual engines) in that it’s the main source of forward propulsion.
So, it’s important to know when best to use either type of sail and why including the many different names of sails on a ship.
Types of Sails
There are a number of reasons why you’d want to use one sail over another, but the most important points to consider have to do with the point of sail you’re sailing in and the wind strength.
Maybe you need downwind sails, square sails, or a triangular sail. Maybe a unique sail shape, sail cloth, or sail area. With that in mind, let’s check out the different sail types!
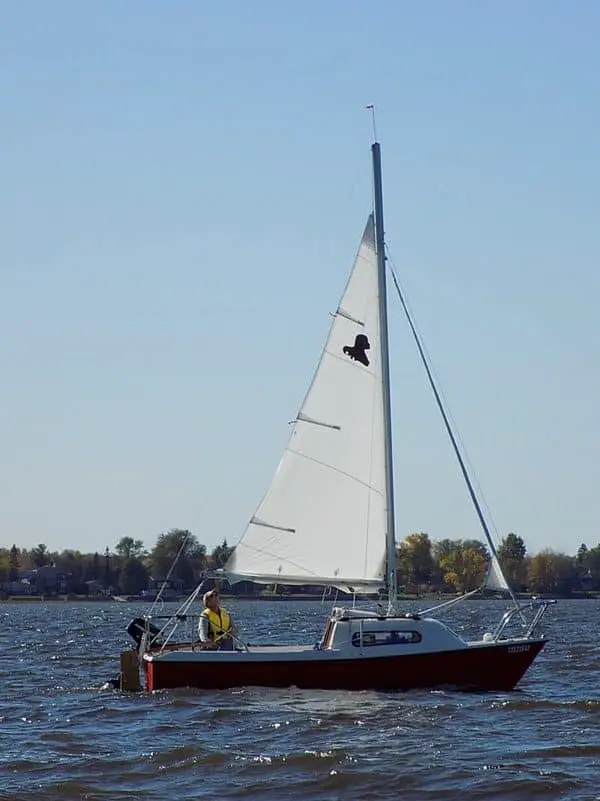

The mainsail is by far the most popular type of sail on sailboats and is often the first image that comes to mind when thinking about a sailboat.
Mainsails are found behind the mast and attached to the boom, which makes it a common part of the sailboat to keep an eye on as it takes up a lot of real estate on a boat with sails especially during a sail tack.
Mainsails are able to cover a lot of surface area with respect to incoming winds, especially since they’re attached to the boom.
The fact that they have a large surface area means they don’t require very strong winds to provide good forward propulsion on a sailboat.
Also, since the position of the mainsail can be easily configured thanks to the boom, all points of sail are achievable.
Headsail/Jib

The headsail (or jib) is probably the second most popular type of sail on sailboats since it usually accompanies the mainsail.
The headsail is always placed at the front of the mast and can cover a good amount of the bow of the sailboat. It’s also smaller than a mainsail, making it more portable and easy to work with.
Headsails aren’t as big as mainsails, therefore they have a smaller surface area which results in the fact that they’re not capable of catching as much wind as a mainsail.
This is an important point though since if the current wind is exceptionally strong and your mainsail has been trimmed as much as possible, being able to put away your mainsail and depend on your headsail alone is an excellent strategy to reduce speed.
When the wind is just too strong to keep your mainsail out, putting it away and using only your headsail is a great option.
You won’t be grabbing as much wind as with the mainsail and you’ll be able to have a much more enjoyable (and safer!) sailing experience.
One of the most picturesque sailing images one can conjure up is the one with a sailboat using a genoa sail (see the image above on the right).
A genoa is a type of large jib that’s attached to the front of the forestay just like a headsail.
One of the main differences with the genoa sail is that it’s bigger than the normal headsail and oftentimes extends behind the mast partially or completely covering the mainsail. It actually used to be called an “overlapping jib”.
Using a genoa sail means you have light to medium winds and your sailboat is more or less in a dead run point of sail (wind coming directly from the rear or sailing downwind).
Since the surface area of a genoa sail is so large, it’s important only to use it when winds are relatively low. Otherwise, you’ll be moving exceptionally fast resulting in a potentially risky situation.
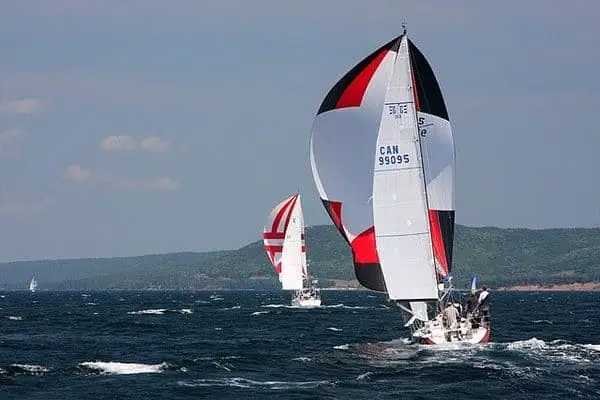

A spinnaker sail is a fun sail to use since it’s quite large, colorful, and can pick up a lot of wind.
Unlike a genoa sail, they’re often symmetrical making them more sensitive to the reaching points of sail and thus more appropriate for the running point of sail. They’re also lighter and have a “kite” kind of feel to them.
The reason they resemble a “kite” is not only that they’re generally lighter and more colorful than other types of jibs, but also they don’t cover the mast like a genoa sail.
Instead, they don’t attach to the forestay and stretch out toward and past the bow of a sailboat. Since they’re bigger than genoa sails, you want to be even more careful to only use them in relatively low and non-volatile wind environments.

A gennaker sail is a more recent type of sail on sailboats since they were developed around 1990.
Gennakers are a cross between genoa and spinnaker sails (as the name might suggest), which are big like a spinnaker, aren’t as symmetric as a spinnaker, and aren’t attached to the forestay like a genoa sail or headsail.
The reason for the invention of the gennaker is that sailors wanted to take advantage of lighter winds without having to resort to using a spinnaker if the winds change from a pure dead run to more of a reaching point of sail.
All in all, the gennaker sail is able to bridge the performance gap between a genoa and spinnaker sail in terms of being able to take on a more flexible point of sail while taking advantage of relatively softer winds.
Popular Sail and Mast Configurations
Now that you’re familiar with the most popular types of sails on a sailboat, it’s good to get an idea of how these sail types relate to the configuration of a sailboat’s mast.
There are a huge number of combinations when it comes to sails and mast configurations, so I thought I’d lay out the most popular ones you’ll likely run into out on the water.

A sloop is the most common type of sail and mast configuration for sailboats. The sloop is the classic single mast, double sail setup.
The sails on a sloop consist of a mainsail and a headsail. The headsail can be different types of jibs, including the genoa, spinnaker, or gennaker sails. The headsail is connected to the forestay on the mast and runs all the way to the top of the mast.
Fractional Rig Sloop
Similar to a sloop, a fractional rig sloop has a single mast, double sail setup. The only difference, however, is that the forestay doesn’t reach the top of the mast, resulting in the headsail being restricted to a fractional amount of space a normal sloop would allow for.
This reduction of surface area for the headsail means that less wind can be captured and, thus, reduced sailboat speed.

A cutter is an interesting setup since it’s just like the sloop and fractional rig sloop setup, but instead of one forestay it has two. With two forestays on the mast, cutters are able to house two headsails.
This can be a preferred setup because it allows for easy cruising due to it offering a diverse combination of points of sail for different strengths of wind.
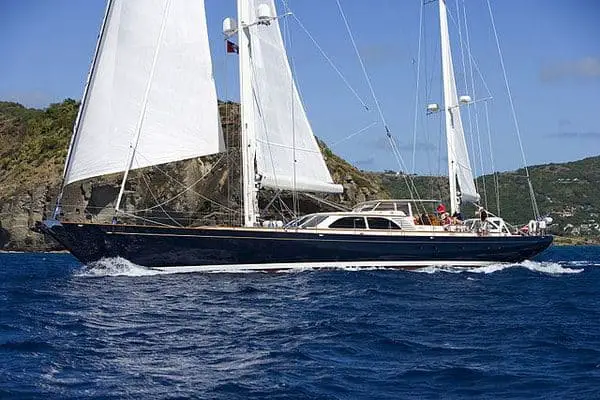

A ketch is a less common setup when compared to the previous setups since it has two masts.
Just like a sloop, it has a mast that allows for a mainsail and headsail with a full range forestay, but it also has a smaller sized mast between the mainmast and the stern of the sailboat.
This mast configuration was commonly used in Northern European freighter and fishing boats and is called the mizzen mast.
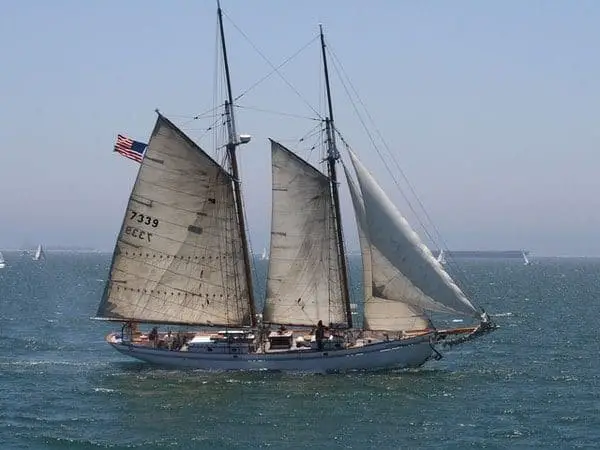

If you’ve ever seen Pirates of the Carribean, you’ll have seen almost nothing but schooners. A schooner is when a sailboat has two or more masts, similar to a ketch, while having a number of sails to manage.
The main differences between a ketch and a schooner are that a schooner’s aft mast (the rear mast) is taller than the forward mast and a schooner can have up to six masts some including a square sail or two. This makes names of sails on a schooner the fore and aft sail (or fore and aft rig).
A yawl is almost identical to a ketch with the only difference being that the mizzen mast is located directly behind the sailboat’s rudder post. In terms of a ketch vs yawl, the mizzen sail is also much smaller than the mizzen sail on a ketch due to its position on the sailboat.

A cat has one mast and one sail with the mast being positioned at the bow of the sailboat. This mast configuration is most commonly found on smaller sailboats, especially dingy sailboats. These types of sailboats are colloquially called “catboats”.
Get the very best sailing stuff straight to your inbox
Nomadic sailing.
At Nomadic Sailing, we're all about helping the community learn all there is to know about sailing. From learning how to sail to popular and lesser-known destinations to essential sailing gear and more.
Quick Links
Business address.
1200 Fourth Street #1141 Key West, FL 33040 United States
Copyright © 2024 Nomadic Sailing. All rights reserved. Nomadic Sailing is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.

No products in the cart.
Sailing Ellidah is supported by our readers. Buying through our links may earn us an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
The Most Popular Types Of Sails On A Sailboat
A sloop-rigged sailboat typically features a mainsail, a headsail, and an additional light-wind sail, such as a spinnaker or Gennaker. The mainsail is rigged aft of the mast, while the headsail is attached to the forestay. The two most commonly used headsails are the Genoa and Jib.
The sails are vital parts of a sailboat since you obviously couldn’t sail without them! There are many different sails depending on the type of sailboat and its rig configuration, and we’ll walk through them together in this article.
The different types of sails on a sailboat
We can divide the selection of sails on a sailboat into three categories:
- Standard sails
Light-wind sails
- Storm sails
Each category serves different purposes depending on the vessel’s rig configuration and the sail’s functionality.
The standard sails
The standard sails usually form a sailboat’s basic sail plan and include :
- The Mainsail
- The Staysail
- The Mizzen sail
These sails are the ones that are used most frequently on sloop, ketch, and cutter-rigged sailboats and are usually set up to be ready to use quickly.
Headsails are often rolled up on a furler, while the main and mizzen sail are stored on the boom or furled into the mast.
The halyards and sheets are kept within easy reach, making these sails the primary choice in most situations. Let’s dive further into each of them.
The mainsail is a triangular sail that flies behind the mast on top of the boom . Although it may not always be the largest sail on the vessel, we commonly refer to it as “the main.”
It is a vital sail, and keeping the sail shape trimmed properly on every point of sail is crucial for the stability and performance of the boat.
A Jib sail is a headsail that does not overlap the mainsail. It is typically between 100% and 115% of the foretriangle but can also be smaller. The foretriangle is the triangular area formed by the mast, deck, and forestay. The Jib is often used with a self-tacking system involving a sheet traveler in front of the mast.
This sail is often seen on newer boats with fractional rigs, which typically have a larger mainsail area than the headsail area. However, the Jib is versatile and also used in other configurations.
People often mix the terms Genoa and Jib. Many refer to any headsail as a Jib, which is incorrect. I personally prefer to use the correct terms to avoid confusion .
A Genoa sail resembles a large Jib but extends past the mast and overlaps the mainsail. Genoas are usually larger than 115% of the foretriangle , with sizes ranging from 120% to 150%. They are often used on vessels with masthead rigs and smaller mainsails but are also common on fractional rigs.
The Staysail is typically found on cutter rigs and is set on the inner forestay or cutter stay. It can be combined with other sails, such as a Jib, Genoa, or Yankee, or on its own in stronger winds.
The Staysail is also useful when sailing downwind, as it can be paired with a headsail and extended to opposite sides of the boat using a pole.
The Yankee sail resembles a Genoa and Jib but has a high-cut clew. This shape allows for improved airflow when used with another headsail. The Yankee is often used on cutter-rigged boats in combination with a staysail and is known for its versatility in different wind conditions.
Mizzen Sail
A mizzen sail is similar to the mainsail, only smaller . It is set on the aft mast of a boat with multiple masts, such as a ketch rig. The mizzen sail is usually used to provide balance and stability to the vessel and provides additional power when sailing downwind.
Another handy usage is to fly the mizzen at anchor to keep the bow up against waves and swell.
The light-wind sails are large, made of thin nylon, and typically shaped like a half-balloon. They are a type of headsails that are great when the winds are too light to fill the standard headsail and are often used when sailing downwind.
The four most commonly used light-wind sails are:
- The Spinnaker
- The Gennaker
- The Code Zero
- The Parasailor
They all provide excellent forward propulsion on a sailboat but usually require some extra rigging to be set.
Experienced cruisers love to use light-wind sails in nice weather, but they have a critical weakness to be aware of. These sails easily get overpowered when the wind increases, and I strongly advise being careful and observant of the wind conditions when flying them.
(Yes, I have managed to rip mine on one occasion due to getting overpowered, but that’s a different story…)
Let’s continue and take a closer look at each of the light wind sails.
A Spinnaker sail is a large, lightweight downwind sail used at deep angles between 120 and 180 degrees. It is symmetrical in shape with two clews and is often brightly colored.
The Spinnaker is set by using a pole to extend the sail’s clew to the vessel’s side. Then, a sheet is attached to the other clew and led back to the stern of the boat.
A Gennaker sail combines the characteristics of the Genoa and Spinnaker. It is made of nylon like the Spinnaker but is asymmetrical like a Genoa and rigged slightly differently. The tack is attached to the bow, and the clew has a sheet led aft to the cockpit. The Gennaker can be equipped with a snuffer to make it even easier to set up and take down.
It is popular among cruisers because it is simpler to use than a spinnaker and it doesn’t require a pole. The sail is effective at angles between 90 degrees and almost all the way down to 180 degrees, making it versatile for various light-wind conditions.
A Parasailor is similar to the Spinnaker in many aspects but has some distinct differences. It has a double-layer wing that inflates as the sail is filled with air, creating a batten-like effect pushing the leech out while providing lift to the bow.
The wing also helps to prevent the rolling movements you get with a Spinnaker and the collapsing of the leech that can occur with a Gennaker at deep angles.
This makes the parasailor effective at sailing angles between 70 and 180 degrees dead downwind. Parasailors can be set like a Gennaker when reaching or with a pole like the Spinnaker for running downwind.
A Code Zero sail combines some elements of the Genoa and Gennaker. Unlike the Gennaker, the Code Zero has a different shape, allowing it to be used while sailing upwind.
Another benefit is that it can be used with a furler which makes it easy to roll in and out. However, it can’t replace the Gennaker or Spinnaker entirely, as it is not effective at sailing angles deeper than 120 degrees.
If you see a big yacht with three forestay’s, the forward one probably holds a code zero sail. A bow spirit allows the ability to fly additional light wind sails as well!
Storm Sails
The storm sails consist of a small Mainsail and Jib in heavy-duty materials designed for rough conditions. These sails enable us to maintain speed and stability in the boat in severe weather too strong for the standard sails.
Storm sails are often brightly colored , such as red, orange, or yellow, to make them more visible at sea.
Storm Mainsail
A storm mainsail is used when the reefing setup doesn’t allow the standard mainsail area to be reduced enough to prevent overpowering. The sail can handle rough conditions and is excellent for maintaining stability.
A storm Jib is used when the headsail has been furled to the point where it is no longer effective. It is especially useful for sailboats rigged with a Genoa, as the Genoa gets inefficient when heavily reefed. As the storm Jib is smaller than the standard headsail, it also lowers the center of gravity, making the vessel heel less and become more stable.
Explaining the terms for the parts of a sail
Let us talk some more about sails. The goal is to go sailing, right?
Identifying the different parts of the sails is crucial to understanding which lines go where.
Let’s zoom in on a sail and break down the terms :
The head is the top corner of the sail . Most mainsails have a headboard or plate where the halyard is connected, while headsails use a metal ring. A halyard is a line we use to raise and lower sails with.
The leech is the aft part of a sail , located between the clew and head. We use a combination of the outhaul, main sheet, and traveler to trim and adjust the leech on the mainsail.
The headsail’s leech is trimmed by adjusting sheet tension and angle according to the wind speed and direction. A traveler is a track with a movable car or pulley system for adjusting the position and angle of a sheet, and most sailboats have one main traveler for the mainsail and car tracks along the side decks for the headsail.
The luff of a sail is the front part of the sail between the tack and head. On a mainsail, the luff runs vertically along the mast and along or close to the forestay on a headsail. Headsails are often equipped with luff foam to help maintain their shape when partially reefed on a furler.
Battens are slats or tubes inserted into pockets on the mainsail to help the sail maintain its shape and increase its lifespan . A traditional sail hoisted and lowered on the boom typically has horizontal battens. Vessels with in-mast furling can use vertical battens instead of horizontal ones.
- A fully battened Mainsail has the battens run through the entire sail length from the luff to the leech.
- A standard battened main sail has the battens along the sail’s leech.
Telltales are small ropes, bands, or flags attached to a sail to give an indication of the airflow around the sail. They help us understand how the wind affects the sail and allow us to fine-tune the trim for optimal performance. Telltales are usually found on the mainsail’s leech and in the front of the headsail’s leech.
The clew of a sail is the lower aft corner and where the outhaul is connected on a mainsail. Headsails have sheets attached to their clew for controlling and trimming the shape and tension.
The tack is the lower, forward corner of a sail. On a traditional Mainsail, the tack is attached to the Gooseneck, a hinge in front of the boom attached to the mast.
With in-mast furling, the tack is connected to the furling mechanism. This mechanism is used to roll the sail into the mast.
The headsails tack is connected to a furler drum on the forestay on most sailboats. Vessels using traditional hank-on headsails connect the tack to a fixed point on the bow.
The foot of the mainsail is the bottom portion of the sail between the clew and the tack. It is trimmed using the outhaul, a line attached to the clew, and used to adjust the tension on the foot of the sail. Some mainsail are configured loose-footed, and others are attach-footed.
The foot of the headsail is trimmed by adjusting the tension and angle of the sheets, which are the lines used to control the headsail’s clew. We use cars, or pulleys, to adjust the angle of the sheets and thus the trim of the headsail.
Traditional and less commonly seen sails
We’ve now looked at the most commonly used sails and walked through the different parts of them. But what about the less common ones? The art of sailing has a rich history, with some unique sail designs that we rarely see today.
Read on if you want to peek into some traditional sails, or skip straight to popular sail and mast configurations here.
Square sails
Square sails are rectangular and usually set across a ship’s mast, mostly seen on traditional square-rigged sailing ships and Viking ships. These sails are efficient for downwind sailing and are hung from horizontal spars called yards. Though not as agile as modern fore-and-aft sails when sailing upwind, they were central to naval exploration for centuries. Today, they’re mainly seen on traditional vessels and tall ships, symbolizing maritime heritage.
If you’ve been to Martinique in the summer, you may also have noticed the round skiff sailboats the local fishermen traditionally used for fishing in the Atlantic Ocean with their distinctive big squared sails. Tour de Martinique des Yoles Rondes is a popular yearly event where the locals race and show off these beautiful old boats with colorful sails!
A gaff sail is a traditional four-sided sail held up by a horizontal spar called the “gaff.” They are used on classic gaff-rigged sailboats and allow for a larger sail area with a shorter mast. Gaff-rigged boats were traditionally popular and usually carried 25% more sail area than the equivalent Bermudan rig, making them fast on a downwind run. The Gaff rig could also carry a topsail between the gaff and the mast.
However, they don’t sail well to windward, and modern designs have shifted towards triangular sails for better upwind performance.
Jib-headed topsail
The Jib-headed topsail is a small triangular sail used on gaff rigs and is set between the gaff and the top of the mast.
A lug sail is an angled, four-sided sail that attaches at a point on its top side, making it hang tilted. The sail is simple to use and often found on smaller or older boats. There are different types, like standing, dipping, and balance lugs, each hanging differently around the mast.
The lug sail evolved from the square sail to improve how close the vessels could sail into the wind. Because of their upwind performance, fishermen used them widely in Europe from the seventeenth through the nineteenth centuries.
Sprit sails
The spritsail, with its unique four-sided design, stands out thanks to a diagonal support called the “sprit.” It was traditionally popular in Thames sailing barges due to its ability to accommodate high-deck cargo. These days, it’s primarily found in smaller boats like the Optimist dinghy in a variant called “leg of mutton spritsail.”
The spritsail was also used in traditional wooden boats like the fearing version of the Oselvar wooden boat traditionally used in western Norway.
It is also commonly used by the indigenous Guna Yala tribes in Panama in their dugout Ulu’s up to this day. We saw plenty of them when we cruised along the coast, and some of them approached us to sell us their delicious catch of the day!
Lateen sails
A lateen sail is a triangular sail set on a long spar angled on the mast. It was originally popular in the Mediterranean and on Arab shows, and its design enhanced maneuverability and played a crucial role in historic sea exploration.
The lateen sail was used on lateen rigs, the predecessor to the Bermuda rig – one of today’s most commonly used rigs!
Which brings us to the following topic:
Popular sail and mast configurations
There are many different rigs and sail configurations between sailing vessels. From the old-school square rigs to schooners, gaff rigs, and more. However, this article will focus on the three most popular rigs seen on modern sailboats:
- The Bermuda Sloop Rig
- The Cutter Rig
- The Ketch Rig
The three rigs have similarities and differences between their sail and mast configurations. We’ll walk through each of them to understand how they utilize their different types of sail.
If you want to learn more about other rigs, take a look here .
Bermuda Sloop Rig
The Bermuda sloop rig is the most common rig on modern vessels. It is characterized by a single mast, a triangular mainsail, and a headsail. This rig is named after the Bermuda Islands, where it was developed in the 17th century.
Some of the key features of the Bermuda sloop rig:
- The mast is typically tall and raked, which allows for a large sail area and excellent stabilit y.
- The mainsail is attached to the mast and boom. It is usually combined with a single headsail at the front of the boat, making it powerful and easy to sail.
- The Sloop is usually equipped with a masthead or fractional rig and flies a Jib or Genoa as its primary headsail.
The Bermuda Sloop rig is known for its simplicity, is often used for racing and cruising, and is popular among sailors worldwide.
The cutter rig is very similar to the sloop rig. The significant difference is that it has a single mast and two headsails – a Staysail and a Yankee. The cutter rig is known for its versatility due to the multiple options in sail plans and the double headsail setup.
Some key aspects that separate the Cutter from the Sloop:
- The rig is often more robust than its Sloop sister because of the additional cutter stay and running backstays.
- The mast is located closer to the center of the boat.
- The Cutter has a staysail on the inner forestay and a Yankee sail on the outer. The sails can be used in combination with each other or independently.
- Tacking the headsail between the forestay and cutter stay is more involved than on a sloop.
- The Cutter rig has two similar variations: the Slutter rig and the Solent rig.
Like the Sloop, the Cutter rig is relatively easy to operate. Still, the additional headsail and rigging make it costlier to maintain. It is also less suitable for racing than the Sloop, but the added versatility helps in different weather conditions and makes it an excellent choice for cruisers.
The ketch rig is also similar to the Sloop but has an additional mizzen mast placed further aft of the main mast. Another mast gives it the advantage of even higher versatility in sail plans. The ketch typically uses three sails. The mizzen sail, a mainsail, and a headsail. The mizzen mast also allows it to fly a second light-wind sail.
Here are a few more distinctions of the ketch rig:
- The ketch typically carries a smaller mainsail than a similarly sized sloop and a smaller mizzen sail.
- A small mizzen and a medium mainsail are easier to handle than one large mainsail.
- The additional mizzen sail makes the vessel easy to balance and gives extra stability downwind.
- The ketch usually doesn’t point as close to the wind as the Sloop and Cutter.
The headsail setup on a ketch is generally the same as for the Sloop. But the ketch can also be rigged as a cutter ketch, which gives it the benefits of the cutter rig! The tradeoff with a cutter-rigged ketch is the higher complexity and additional rigging, hardware, and sails required.
Final words
Well done, you now have a good grasp of the most common sails and their strengths. We have discussed a few rigs and how they utilize different kinds of sails in various sail plans. Remember that more sail types, other rigs, and even more variations are available. It is a complex topic, but this guide covers the basics and gives you a great starting point.
If you still have questions, look below at the FAQ, or leave me a comment. I’m more than happy to help you out!
A sailboat is only as good as its sails, and sails need wind to work. The next logical step is learning how the wind works when we sail and practicing some wind awareness! Head to the following guide to continue your research: Learn The Difference Between True And Apparent Wind Speed.
FAQ: The Different Types of Sails On A Sailboat
What is the foretriangle on a sailboat.
The foretriangle on a sailboat refers to the triangular area formed between the mast, forestay, and deck. If you want to order a new headsail, for example, you’ll have to measure and supply the sailmaker with these details.
What is the difference between a loose-footed and attached-footed mainsail?
A loose-footed mainsail is attached to the boom only at its corners, leaving the rest of the sail’s bottom edge free. An attached-footed mainsail, on the other hand, is secured to the boom along its entire length. The main difference lies in how the bottom of the sail connects to the boom, with the loose-footed design offering more adjustability in the sail shape.
What is a high-cut clew on a sail?
A high-cut clew refers to the design of a foresail, such as a jib or genoa, where the back lower corner (the clew) is raised or “cut” higher above the deck compared to standard designs. This design allows for better visibility beneath the sail and makes it easier to sail over waves without the sail touching the water, which is especially beneficial for offshore or blue-water cruising. Very high-cut clews are commonly seen on yankee sails on cutter-rigged sailboats.
What is luff foam on a sail?
Luff foam is a padded strip sewn into the forward edge of roller furling sails. It ensures the sail is appropriately shaped when partially rolled up, especially in strong winds. This foam not only helps with sail performance but also protects the sail when it’s furled.
What are the most common sails?
The sloop rig sailboat is the most common and usually features a mainsail, a headsail, and an additional light-wind sail, such as a spinnaker or Gennaker.
What are the different types of sails?
There are several different types of sails, and we can divide the most common into three categories:
The standard sails:
- Mizzen sail
The light-wind sails
The storm sails:
- Storm mainsail
- Storm jib
What is a spinnaker sail?
A Spinnaker sail is a large, lightweight downwind sail used at deep angles between 120 and 180 degrees.
What is a Jib sail?
A Jib sail is a headsail that does not overlap the mainsail and is set on the forestay. The Jib can also be set up with a self-tacking system, making it very effective when sailing into the wind.
Is Genoa sail the same as a jib?
People often mix the terms Genoa and Jib. The Genoa is different from a Jib sail as it is larger and overlaps the mainsail, whereas the Jib is smaller and does not overlap the mainsail.
What is a Genoa sail?
A Genoa is a headsail larger than the Jib extending past the mast and overlapping the mainsail. The advantage over the Jib is the larger sail area, making it more effective when sailing off the wind.
How many types of sail plans are there?
Sail plans refer to the configuration and arrangement of sails on a boat or ship. While there are countless customizations and variations, the three most common sail plans are:
Sloop: Characterized by a single mast, a triangular mainsail, and a headsail.
Cutter: Similar to a sloop but has a single mast and carries two or more headsails.
Ketch: Features two masts, with the aft mast (called the mizzen) shorter than the main mast.
What is a Mainsail?
The mainsail is a triangular sail that flies behind the mast on top of the boom.
What is a Gennaker?
A gennaker is basically an asymmetrical spinnaker. A hybrid sail that combines the characteristics of a Genoa and a Spinnaker, designed for sailing off the wind and often used in light to moderate wind conditions.
What is a Storm Jib?
A storm jib is a small, heavy-duty sail used in strong winds or stormy conditions. It is commonly used when the headsail has been furled to the point where it is no longer effective.
What factors determine the type of sail to be used?
The type of sail to be used depends on various factors such as wind conditions, points of sail, sailboat size , and sailing experience. It’s smart to choose the appropriate sail for optimal performance. A Jib, for example, will be more effective than a Genoa while sailing to windward, and vice versa.
How do sails affect the performance of a sailboat?
Sails are the engine of a sailboat. Their design, size, and trim influence the boat’s speed, direction, and stability. Properly adjusted sails capture wind efficiently, allowing the boat to move faster and in the desired direction.
The balance and condition of the sails also impact comfort and safety, with well-maintained sails ensuring optimal performance. The sails are essential in determining how a sailboat performs in various wind conditions.
Sharing is caring!
Skipper, Electrician and ROV Pilot
Robin is the founder and owner of Sailing Ellidah and has been living on his sailboat since 2019. He is currently on a journey to sail around the world and is passionate about writing his story and helpful content to inspire others who share his interest in sailing.
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you.
What specifically do you want my point of view on?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Types of Sails for Sailboats: A Comprehensive Guide
by Emma Sullivan | Jul 28, 2023 | Sailboat Racing

Short answer types of sails for sailboats:
Sailboats typically use four primary types of sails: mainsails, genoas/jibs, spinnakers, and staysails. Mainsails are the largest and provide forward propulsion. Genoas/jibs enable efficient sailing upwind. Spinnakers are used for downwind sailing and maximizing speed. Stay-sails provide stability in heavy wind conditions.
Understanding the Basics: Different Types of Sails for Sailboats
Sailing is not just a passion but a way of life for many people. Whether you are an experienced sailor or just starting out, understanding the different types of sails for sailboats is essential to navigate the vast seas. In this blog post, we will delve into the basics of sail types, their functionalities, and how they can enhance your sailing experience.
1. The Mainsail: Starting with the star of the show, the mainsail is the largest and most important sail on a sailboat. It is typically positioned behind the mast and provides primary propulsion when sailing upwind or reaching across different wind angles. With its triangular shape, it catches wind efficiently and drives the boat forward like a well-oiled engine.
2. The Genoa or Jib: Next in line is the genoa or jib sail (pronounced ‘jīb’) that complements the mainsail perfectly. Positioned at the bow, it adds extra horsepower to help propel the boat forward even faster. The genoa sail offers versatility by allowing adjustment to different wind conditions without compromising speed and agility.
3. The Spinnaker: Often called “the wild card” among sails, spinnakers come in vibrant colors and are usually used for downwind sailing situations. When deployed, this balloon-shaped beauty fills with air like a parachute, harnessing every ounce of wind power available – perfect for exhilarating rides in light breeze conditions. However, handling a spinnaker requires skill as it can become untamable when winds pick up speed!
4. The Storm Sail: Just like its name suggests, storm sails are designed specifically for rough weather conditions – think rainstorms and gale-force winds! Smaller in size compared to other sails on board, these heavy-duty wonders provide stability during adverse weather situations by ensuring that sailors stay safe while navigating through treacherous waters.
5. The Gennaker: A combination of genoa and spinnaker, the gennaker is a true hybrid sail. Perfect for reaching and running downwind, it comes in handy when you want to sail at higher speeds without dealing with the complexity of managing a traditional spinnaker. Its lightweight nature and ease of control make it an excellent choice for both racing enthusiasts and leisurely cruisers alike.
Now that we’ve covered some key types of sails, it’s important to note that each sail type has various designs within its category. These designs cater to specific sailing conditions, such as heavy winds or light breezes, ensuring optimal performance during your time on the water.
Before wrapping up, let’s briefly touch on the importance of choosing the right sails for your sailboat. The type of sail you select can significantly impact your sailing experience – from optimizing speed and maneuverability to ensuring safety while exploring new horizons. Therefore, consulting with experienced sailors, researching different options, and considering factors such as boat size and intended use are crucial steps in making an informed decision.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of different types of sails for sailboats is vital for anyone stepping into this exciting world. From the powerful mainsail to the versatile genoa or jib, each sail plays a unique role in enhancing your sailing experience. So whether you’re looking to set out on lengthy ocean crossings or simply enjoy peaceful coastal cruises, knowing your sails will help you navigate every nautical mile with confidence and style!
Choosing the Right Sail: A Step-by-Step Guide to Types of Sails for Sailboats
Welcome to our blog where we will embark on a sailing adventure and explore the intricate world of sail selection. Choosing the perfect sail for your sailboat can seem like a daunting task, but fear not! We are here to break it down step-by-step and help you navigate through the vast sea of options. So grab your compass and let’s set sail!
Step 1: Assess your Sailing Style Before diving into the ocean of sail choices, it’s important to identify your sailing style. Are you a casual cruiser who enjoys leisurely trips across calm waters? Or do you yearn for thrilling high-speed races under challenging conditions? Determining this will play a vital role in selecting the most suitable sails for your needs.
Step 2: Consider Sail Material The material used in constructing sails significantly impacts their performance and longevity. Traditional woven Dacron sails are cost-effective, durable, and ideal for recreational sailors. However, if you’re an avid racer or prefer enhanced performance in varying wind conditions, composite laminated sails might be worth exploring.
These advanced sails utilize lightweight materials like carbon fiber or Kevlar, providing exceptional strength-to-weight ratios that optimize speed and maneuverability. Just keep in mind that these high-performance sails often come with a higher price tag.
Step 3: Understanding Sail Shapes Sail shape directly affects how efficiently your boat harnesses wind power. Depending on your sailing intentions, different shapes offer distinct advantages:
a) Bermuda Rig: This popular triangular mainsail design is commonly found on cruising boats due to its versatility. It offers easy handling and adaptability to various wind angles.
b) Gaff Rig: If you appreciate traditional aesthetics combined with robust downwind performance, gaff rig may satisfy your desires. Its distinctive four-sided configuration enables larger sail area while maintaining control during gusty conditions.
c) Cat Rig: Designed for simplicity and ease of use, cat rigs feature a single mast and sail, usually located at the front of the boat. This setup is excellent for beginners or those seeking a straightforward sailing experience.
Step 4: Size Does Matter Now that we’ve covered shapes let’s discuss the importance of sail size. Sailboat sizes can vary significantly, ranging from small dinghies to massive ocean-crossing yachts. Matching your sail size to your boat’s specifications ensures optimal performance and safety on the water.
Factors such as wind conditions in your local area, desired speed, and crew abilities must also be considered when determining the ideal sail size.
Step 5: Seek Expert Advice When in doubt, enlist the knowledge and assistance of professionals in the sailing community. Local sailmakers or experienced sailors can provide valuable insights catered specifically to your needs. They possess a wealth of firsthand information regarding local conditions, popular sails within your sailing community, and potential upgrades that could elevate your sailing experience.
So there you have it! A step-by-step guide to choosing the right sails for your sailboat. By assessing your sailing style, considering materials and shapes, properly sizing your sails, and seeking expert advice, you’ll be well on your way to embarking on unforgettable voyages atop glistening waves.
Remember that selecting the perfect sails for any sailor is ultimately an art as much as a science – enjoy exploring this exciting world while keeping safety and performance at heart!
Frequently Asked Questions About Types of Sails for Sailboats
Welcome to our blog where we aim to provide you with detailed, professional, witty, and clever explanations on frequently asked questions about types of sails for sailboats. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or just starting your sailing journey, understanding the different types of sails available is crucial for maximizing your boating experience. So, let’s dive in!
1. What are the different types of sails commonly used in sailboats?
Ahoy! When it comes to sailboat sails, you’ll often encounter three main types: mainsails, headsails (also known as jibs), and spinnakers. Each serves a specific purpose and contributes differently to the overall sailing performance.
– Mainsails: The largest and most important sail on a boat, mainsails are primarily responsible for propelling the vessel forward. Positioned behind the mast, they generate power through their large surface area and can be adjusted using various controls like boom vangs and cunninghams.
– Headsails/Jibs: Located at the bow of the boat, headsails come in various sizes such as genoas or jibs. Jibs are generally smaller than genoas but offer better maneuverability in heavier winds. These sails help balance the forces acting on the boat by providing lift from the front.
– Spinnakers: For those seeking exhilaration on reaching or downwind courses, spinnakers are a must-have! These big billowy sails catch wind from behind and enable higher speeds. Used in lighter winds when sailing off course or downwind, they can turn an ordinary sail into an extraordinary adventure.
2. Which type of sail should I use during upwind sailing?
When battling against the wind while navigating upwind (or close-hauled), it’s essential to hoist your headsail/jib rather than relying solely on your mainsail. This combination allows for efficient airflow diversion around both sides of your boat – creating that sought-after lift required to sail efficiently and beat upwind.
3. Are there any sail types specifically designed for downwind sailing?
Absolutely! For a fantastic downwind experience, you’ll want to unleash the power of a spinnaker. These beautifully large sails are uniquely shaped to capture every gust of wind from behind, propelling your boat at exhilarating speeds. But beware, handling a spinnaker can be quite challenging, so practice and caution are vital.
4. Can I use more than one headsail on my sailboat?
Ahoy mates, this is where it gets exciting! Sailors often employ multiple headsails simultaneously for enhanced maneuverability and increased propulsion. Known as “sail combinations,” common setups include using both a jib and genoa together or even deploying two genoas with different sizes at once – affording great control options in varying wind conditions.
5. How do sails differ in shape and material construction?
Sails come in various shapes and constructions tailored for specific purposes. The materials used range from traditional woven fabrics like Dacron (popular for its durability) to high-performance laminated fabrics such as Kevlar or carbon fiber composites (offering increased strength but potentially at higher costs). Each material has its advantages, so it’s crucial to choose the right sail based on your sailing goals, preferences, and budget.
So there you have it, sailors – an informative yet entertaining rundown of frequently asked questions about types of sails for sailboats. Remember that selecting the appropriate sails depends on numerous factors like wind conditions, desired speed, boat size/type, and personal preference. Now go out there, catch the wind in your sails, and embark on unforgettable nautical adventures!
Exploring the World of Main Sails: An In-Depth Look at Types and Features
Title: Exploring the World of Main Sails: An In-Depth Look at Types and Features
Introduction: Welcome aboard, fellow adventure-seekers! Today, we embark on an exhilarating journey into the enchanting realm of main sails. As sailors, we understand the pivotal role that these magnificent pieces of cloth play in driving our vessels forward. So, let us unfurl our curiosity as we delve into the vast expanse of main sail types and features. From traditional designs to cutting-edge innovations, fasten your seatbelts or rather hoist your clew lines; for it’s time to set sail on this epic exploration!
Main Sail Types: 1. Bermuda Rig: This timeless and widely used design originates from Bermuda (hence the name) and showcases a triangular shape with a pronounced mast incline. Known for its versatility and effectiveness across various wind conditions, the Bermuda rig offers superb control while maintaining desirable speed.
2. Gaff Rig: Picture a charming vintage schooner gracefully sailing across crystal-clear waters under an expansive gaff-rigged main sail – pure nautical bliss! Here, a wooden spar called a gaff supports the top edge of the sail, allowing for easier manipulation during maneuvers without sacrificing performance.
3. Lateen Sail: Embark on an exotic journey to distant shores with the lateen sail adorning your vessel. Hailing from ancient maritime civilizations such as Egypt and Phoenicia, this triangular sail is rigged with its base along one side of the boat—a sight that effortlessly evokes captivating tales from seafaring lore.
4. Junk Rig: Pay homage to centuries-old Chinese traditions by embracing a junk rig main sail configuration – perfect for those who crave a taste of both beauty and functionality in their sailing escapades. With multiple battens enhancing structural stability while reducing stress on individual components, this unconventional yet ingenious setup unlocks exciting possibilities in terms of ease-of-use and adaptability.
Main Sail Features: 1. Battens: These slender, lightweight rods serve as key components within a sail, improving its shape retention by preventing unwanted fluttering and enhancing overall efficiency. Modern main sails often boast battens made from sturdy materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass for optimal durability.
2. Luff Systems: Achieving precise control of the leading edge of the main sail is crucial to maximizing performance. Here, the choice between traditional hanks or convenient luff slides and cars comes into play – seamlessly balancing heritage with modernity while enabling ease of reefing and tweaking for swift adjustments.
3. Headboards: Crown jewels atop our main sails! These structures reinforce the upper portion, ensuring longevity by distributing stress during rough weather conditions. Ingenious evolution has given rise to lightweight alternatives such as carbon-fiber headboards that offer exceptional strength while minimizing weight aloft.
4. Reefing Mechanisms: Navigating formidable seas sometimes calls for reducing sail area to maintain stability and safety onboard. With various reefing systems at our disposal, like slab reefing or in-mast furling, we can swiftly decrease the main sail’s size while retaining ultimate control over your vessel’s destiny!
Conclusion: Ahoy fellow adventurers! We have traversed uncharted territories on this voyage through the enchanting world of main sails—unveiling their mesmerizing types and navigating their irresistible features along the way! Whether you favor tradition or embrace innovation with open arms, it’s clear that every sailor possesses unique preferences when it comes to these majestic fabrics that propel us forward into breathtaking oceanscapes. So, hoist your favorite mainsail high and let winds carry you toward endless horizons as you embark on extraordinary maritime exploits!
Jib or Genoa? Unraveling the Differences in Types of Headsails for Sailboats
When it comes to headsails for sailboats, there are two popular options that often leave sailors scratching their heads: jibs and genoas. Understanding the differences between these two types of headsails is crucial for making informed decisions on the water. So, let’s weigh anchor and set sail into unraveling the mysteries behind jibs and genoas.
Starting with the basics, a headsail is any sail set forward of the mast, aiding in propulsion by capturing wind energy. Now, onto our contenders – the jib and genoa!
A jib is traditionally defined as a headsail that is smaller than 100% of a boat’s foretriangle – that triangular area between bow, mast, and forestay. This compact size allows for enhanced maneuverability and responsiveness in challenging wind conditions. Jibs come in various sizes, including the storm jib (ideal for heavy weather) and the working jib (perfect for moderate breezes). If you’re aiming to finesse your way through tight spots or swiftly navigate crowded marinas, a jib might be your trusted mate.
On the other hand, we have our vivacious challenger – the genoa! Unlike its smaller cousin, a genoa spans beyond 100% or even up to 150% of a vessel’s foretriangle. Picture an oversized butterfly wing gracefully caressing through the air. Genoas provide tremendous power when sailing upwind or reaching under lighter wind conditions due to their substantial surface area.
Now you may ask yourself: “Why would I need all that extra canvas flapping about?” Well, dear sailor, here’s where physics enters our nautical narrative! A larger sail area means more lift generated by airflow over its surface. This added lift helps counteract heeling forces caused by wind pressure on other sails (mainly your mainsail), thereby improving stability and reducing strain on both crew and rigging.
But beware! With great power comes some caveats. Handling a genoa can be quite daunting when winds pick up or narrow channels beckon for precise maneuvering. Its increased size may hinder boat agility and make tacking (turning into the wind) a delicate dance with unpredictable results.
Ultimately, your choice between a jib and genoa depends on several factors: sailing style, prevailing weather conditions, crew size, and boat design. For spirited sailors seeking fast-paced thrills or seasoned racers trying to outpace competitors, the performance of a genoas’s extra sail area unquestionably tickles their fancy.
Meanwhile, those leisurely cruising along calm waters might favor the nimbleness of a jib that effortlessly responds to steering inputs.
Remember, dear sailor – understanding these trade-offs allows you to harness the wind more effectively. So weigh your options wisely before hoisting your favorite headsail type atop its lofty perch!
In conclusion, whether you opt for a diminutive jib or embrace the allure of an expansive genoa, each headsail brings its own unique sailing experience. Just like choosing between a swift steed or a graceful partner in dance, finding the perfect match requires careful consideration – for it is this match that will carry you across vast oceans or whisk you away to secluded coves. Ahoy!
All About Specialty Sails: Discovering Unique Types for Specific Wind Conditions
Sailing is not just a sport or hobby; it’s an art that requires skill, precision, and a deep understanding of the elements. One crucial factor that can make or break your sailing experience is the type of sail you choose. Just as different brushes serve various painting techniques, specialty sails are designed to address specific wind conditions. In this blog post, we will dive into the depths of specialty sails, exploring their unique types and unveiling the secrets behind matching them to specific wind conditions.
1. Battened Mainsail: Let’s start with one of the most common specialty sails used in sailing – the battened mainsail. This sail is equipped with long, lightweight battens that run parallel to its leech edge, enhancing its ability to maintain shape and stability. Suitable for light winds and cruising situations, the battened mainsail ensures optimal control even when gusts try to play tricks on you.
2. Genoa: When it comes to flying through moderate winds with grace and speed, every sailor worth their salt knows about the mighty genoa. This specially designed foresail boasts a larger overlapping area compared to a jib and can adapt seamlessly to various wind angles without compromising maneuverability. Whether you’re racing or embarking on an adventurous voyage, having a genoa onboard will give you that extra oomph!
3. Spinnaker: Are you craving adrenaline-pumping downwind rides? Then look no further than the spinnaker – often referred to as a “kite” due to its distinctive shape and vibrant colors! This asymmetric sail is made for strong winds blowing from behind your vessel’s beam or even dead astern. Its massive size catches every gust available, propelling you forward in exhilarating bursts over endless blue waters.
4. Storm Sail: Mother Nature holds many surprises up her sleeve, including unexpected storms that can leave even the most experienced sailors feeling like novices. This is when a storm sail comes to the rescue. Made from heavy-duty material and featuring a smaller hoist, this compact sail keeps you safe, stable, and in control when strong winds threaten to overpower your vessel.
5. Code Zero: Meet the ultimate weapon for light wind sailing – the code zero. Ideal for symmetrical or asymmetrical layouts, this specialty sail offers exceptional performance in extremely light wind conditions. Its distinctive design allows it to harness even the slightest breeze with minimal drag, effortlessly propelling your boat forward when other sails would hang limp.
6. Gennaker: Imagine combining the best of both worlds – the speed and power of a spinnaker with the ease of use of a genoa. Enter gennakers! Perfect for those cruising days where optimal performance is paired with user-friendly handling, these specialized sails bring joy to sailors looking for an all-around solution in moderate wind situations.
The world of specialty sails goes far beyond what we’ve explored here today, but this overview should give you a taste of their fascinating variety and purposefulness. These unique sails are meticulously crafted by experts who understand not only their complex aerodynamics but also how they interact with different wind conditions to unlock your vessel’s true potential.
So next time you embark on a sailing adventure, take into consideration the specific wind conditions you may encounter and make sure to equip yourself with the right specialty sail that will turn your voyage into an extraordinary experience worth cherishing. Happy sailing!
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
Types of Sails: Explained
While all sailboats rely on wind, the types of sails used can vary greatly based on weather and craft type!
The reason for all the different types of sails is important to understand. Depending on the time of day and location of the water body, you might experience varying weather conditions. The sail acts like a motor, propelling your sailboat forward. The performance depends heavily on wind conditions. Different sails work to navigate weather conditions to maximize your performance.
In this article, we’re going to look at the most common types of sails found on sailboats.
- A mainsail is the most commonly-used sail.
- The gennaker is a cross between the genoas and spinnakers.
- A popular sail used in sailboats is the headsail/jib.
It’s important to know that various sails pose different dangers when it comes to strong winds, which is why knowing which to avoid or use is extremely helpful. Here we discuss the different types of sails and when to use them.
Types of Sails
Let’s look at the most common types of sails here.
1. Mainsail
Most sailboats have a mainsail . It’s the most commonly seen sail on boats and the first thing you think of when you think of sails. The mainsail is attached to the mast behind the boom, so it’s easy to keep an eye on since it occupies a lot of space.
Regarding incoming winds, mainsails have a large surface area, mainly due to how they are mounted on the boom.
Due to their large surface area, they do not require powerful winds to propel a sailboat forward. As the mainsail position is easily adjustable using the boom, you can reach all points of sail.
2. Spinnaker
Due to the large dimensions and vivid colors of spinnakers, they are considered one of the most whimsical sails you can use. The sails are also often balanced, making them more suitable for reaching various points, including the sail’s running point.
Sails of this type are lighter, unlike genoa sails attached to the mast (see below). The spinnaker is not attached to the forestay , but stretches past the boat’s bow.
A spinnaker’s broad surface makes choosing the right conditions for use even more critical. When the wind is too strong, you and your passengers can be seriously injured by deploying this sail. This is why you should only deploy a spinnaker in calm conditions such as low winds.
A genoa is a sailboat with a genoa sail attached. The genoa sail is similar to a headsail, with large jibs mounted on the forestay. Compared to a normal headsail, a larger genoa sail partly or completely covers the main sail behind the mast.
A genoa sail is used when there is light to moderate wind or when your sailboat is mostly in dead run sailing (with the wind blowing directly behind).
A genoa sail with such a large surface area is best in low-wind conditions. If you don’t, you’ll be moving very fast, which can lead to a potentially dangerous situation if you’re not careful.
4. Gennaker
Since 1990, gennaker sails have been a more recent sail type on sailboats. Gennakers are sails that resemble both genoas and spinnakers. They are larger than genoas but have a different shape from a spinnaker, unlike genoas and headsails, which are attached to the forestay.
To take advantage of lighter winds, sailors invented the gennaker without resorting to a spinnaker if the wind was strong. Overall, regarding a sail’s performance, a gennaker sail bridges the gap between genoas and spinnakers by taking advantage of relatively softer winds while allowing a greater range of motion.
5. Headsail/Jib
Headsails, or the jib, are second in popularity among sailboat sails. In most cases, it goes with the mainsail, the most common type.
Generally, the headsail hangs over the boat’s bow on a sailboat. The sizing is often smaller than the mainsail.
You can especially benefit from a smaller headsail when a strong wind blows. As a result, you won’t want to use the main sail (or trim it heavily) to move more slowly and avoid being thrown around. The smaller the sail, the less wind it catches, so it doesn’t propel your boat as effectively as a larger one.
It is extremely important to have a good headsail, regardless of how wild or unpredictable the seas are.
6. Drifter Reacher
A drifter is a sail designed for light wind conditions, and they are larger genoas that can only be used in light weather conditions. Compared to a genoa, it has a larger sail area that increases performance downwind. It is primarily made up of nylon, which is a synthetic fiber.
7. Code Zero
Racing fans love these sails. Code zero sails have large genoas that overlap the mast heavily. The gennaker is roughly 200% larger than a regular jib and resembles a spinnaker and a gennaker combined. This sail is flatter than most. The design does not resemble a balloon, so it allows for better close-reaching, which makes it faster and easier to maneuver.
Common Types of Sailboats
A sloop is a classic sailing vessel with a single mast and two sails. A headsail may be a variety of jibs attached to the mast forestay and extends to the mast cap.
A sailing boat with multiple masts with several sails. Schooners have tall aft masts and can have as many as six masts.
The boat is easy to cruise with due to the cutters and two forestays capable of storing two headsails and varied sail points for varying wind conditions.
Fractional Rig Sloop
Fractional riggers sail sloops differently because their forestays don’t reach the mast top. The sailboat’s headsail occupies a fraction of the sail area, so less wind is captured, so the sailboat moves slower.
A ketch has a mast similar to a sloop, so its mainsail and headsail can reach up to the forestay. There is also a smaller mast positioned right between the stern of the boat and the mainmast.
Cats have one mast and one sail, similar to dinghies. You can find the sailboat mast at the bow.
Sails are essential to the performance of your sailboat. Using the correct one for the water and weather conditions is important for success out on the water! You can become a more competent and knowledgeable sailor by understanding the common types of sails and mast configurations.
After reading this article, we hope you will feel more comfortable in your sea skills. The danger levels associated with different sails also vary according to the strength of the wind, making it essential that you know what to look out for.
Related Posts
Clean marine: how to clean boat seats, how long to sail 100 miles average sailing speed calculations, types of anchors. find the right anchor for your boat, best boat wax reviews. it’s time to shine.

- Aug 14, 2023
A Breakdown of the Different Types of Sailboats and Their Uses
Updated: Jan 8
To the untrained eye, all sailboats are pretty much the same (some are just bigger than others). They’re essentially floating vessels with a mast, a set of sails, and the ability to navigate the waters by harnessing wind power. But if you dive a bit deeper, you’ll see there are drastic differences in the designs, capabilities, and uses of each type of sailboat.
Whether you’re new to sailboats or already an American Sailing Association (ASA) certified skipper, knowing the difference between the different types of vessels is essential. We’ll provide you with a basic understanding of the different types of sailboats, the advantages of each, and which type of voyage they’re best used for.
Sailboat Rigging Types
When you start sailing, one of the first things you’ll notice is how complicated the rigging seems. The rigging system includes ropes, furling jibs, booms, winches, cables, chains, masts, and much more. It takes time to identify and understand each one, but each type of sailboat has a distinct rigging system. A few of the main types of rigging you can expect to see on the water include:
Sloop: The sloop is arguably the most common rigging system. With one mast and two sails (mainsail & headsail), this type of rigging is simple, but efficient and prepared for all types of situations.
Cutter: If you squint, you could easily mistake a cutter for a slope, but there are slight differences. A cutter has a smaller headsail and an additional staysail between the mast and forestay of the vessel. The extra sail allows for more stability and control in heavy winds.
Ketch and Yawl: Both the ketch and yawl rigging types have two masts. However, what makes them different is in a ketch rigging, the aft mast (mizzen) is taller than the one on a yawl. Also, it’s positioned in front of the rudder post. These riggings are known for their excellent balance and flexibility in most conditions.
Schooner: If you have ever toured older wooden ships built to sail around the world and explore the ocean, then you have probably been aboard a Schooner. This configuration can have two or more masts and the aft mast is taller than the forward one(s). These vessels are powerful and equipped for the long haul.
Types of Sailboats and Their Uses
There are many types of sailboats (not to be confused with rigging types), each with its own pros, cons, and uses. Here’s a look at five of the most popular sailboats and why sailors use them.

When most people think of sailboats, they think of sailing dinghies. These small sailboats are less than 15-feet long and can be sailed by one person or a small crew. In most cases, they have small sloop rigs, are monohulls, and are excellent as a first sailboat. Dinghies are also great for racing or using as a lifeboat for bigger vessels.
Pros of a dinghy: Easily managed, relatively inexpensive, and great for beginners.
Cons of a dinghy: Not much space, only designed for short trips, and not recommended for rough waters or harsh weather conditions.

A daysailer is like the dinghy’s older brother. It’s usually about 14-20 feet in length and sloop-rigged. As the name suggests, they’re best for day trips on the ocean. In most cases, daysailers have a small cabin or open cockpit. They’re designed more for fun rather than long distances.
Pros of daysailers: Easy handling, stable, and great for outings with family or friends.
Cons of daysailers: Assmaller boats, they aren’t designed for overnight trips or long voyages.

The catamaran is where luxury on the sea begins. Its two parallel and equal-sized hulls make the vessel much more stable and comfortable than its single-hull counterparts. It’s a highly customizable boat that can be small and sporty or large and luxurious, depending on your needs.
More experienced sailors use these types of sailboats for longer trips and smaller charter trips .
Pros of the catamaran: A lot of space, fast, and perfect for cruising at sea.
Cons of the catamaran: Since they have such a wide beam, it can be a challenge to find places to dock or maneuver in tight marinas.

If you’re drawn to the size and stability of the catamaran, but yearn for more speed and power then you’ll love the trimaran. Instead of two hulls, this bigger boat has three: a main hull in the middle, and two smaller outrigger hulls on its sides. It’s an excellent sailboat for racing and cruising due to its stability and speed.
Pros of trimarans: Ability to be very fast, stable, and less likely to capsize in rough waters than smaller sailboats.
Cons of trimarans: They’re larger boats, so it can be difficult and more expensive to dock or store them in certain places.
Cruising Keelboat

Suppose you want to take an overnight cruise or even a trip across the Atlantic Ocean. In that case, a cruiser is your best bet. These large-sized sailboats (usually more than 30 feet long) are designed to be comfortable and self-sufficient, which makes them ideal for long voyages.
Pros of Cruising Keelboats: Well-suited to go on long-distance cruises for weeks or months with the ability to support multiple passengers.
Cons of Cruising Keelboats: You’ll not only have to invest in the sailboat (including storage and upkeep), but it also requires a large crew and an experienced captain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Sailboat Types
What is the most common type of sailboat.
Sloop-rigged sailboats (particularly daysailers and dinghies) are among the most popular types of sailboats. However, generally, the most commonly used sailboat depends on who’s using it. For example, a racer will have much different needs than someone who just wants the right boat for cruising.
What’s the difference between a sailboat and a yacht?
In the U.S., the determination between a sailboat and a yacht is that a sailboat only uses wind power, while a yacht can use wind, a motor, or a combination of both. However, internationally, sailboats and all other boats are usually considered “yachts.” Size can also be a determining factor. For example, some people consider any boat longer than 40 feet to be a yacht.
What’s the best beginner sailboat?
If you don’t have any sailing experience , the best sailboats are usually smaller, easy to maneuver, and less complicated than multihulls. Some of the best small sailboats for beginners have tiller steering and no winches.
This can include vessels like small dinghies, catamarans (though these are multihull boats), rotomolded boats, and those that can be easily trailered to different locations.
What is the safest type of sailboat?
In most cases, larger cruising keelboats are usually considered much safer than smaller dinghies and catamarans. That’s because they’re less likely to capsize and can handle adverse weather more safely, which is especially useful for new sailors. However, sailboat safety depends on the sailor, type of boat, and conditions.
What are the most popular sailboat brands?
There are countless high-quality sailboats on the market. Some of the most popular brands include Beneteau, Jeanneau, Hunter, Catalina, Dufour, Sunfish, Hobie, and many others. These brands have built a reputation of trust and reliability over the years, making them prime choices for new and seasoned sailors alike.
Which type of boat is best for offshore cruising?
If you want to take your sailboat for an offshore cruise, you’ll need something sturdy, reliable, and able to handle harsh sea conditions. In most cases, a cruising keelboat is your best bet for casual offshore cruising as they’re comfortable and self-sufficient vessels. In regards to rigging, ketch, cutter, and schooner rigs are best for sailing offshore because they are adaptable to varying wind speeds.
Learn How to Sail From The Experts
Are you interested in learning more about sailing or getting certified ? First Reef Sailing is one of the top ASA sailing schools in the Boston area.
We can help you learn the basics of sailing so you can get out on the water with confidence. Our certification courses, such as the beginner ASA 101 and ASA 103 courses, will teach you how to sail everything from 20-foot keelboats to 50-foot catamarans.
Take a look at this timeline of how many of our students learn, gain sailing experience, and go on to buy their own sailboats.
Recent Posts
(Article) Tenant Spotlight: First Reef Sailing
Take a look at a quick spotlight about the origins of First Reef Sailing, written by our friends at the Boston Harbor Shipyard and Marina. Read the article here
ASA 101 Overview: What to Expect From Basic Keelboat Sailing
The 9 Best Marine Navigation Apps of 2023
Comentários
- Types of Sailboats
- Parts of a Sailboat
- Cruising Boats
- Small Sailboats
- Design Basics
- Sailboats under 30'
- Sailboats 30'-35
- Sailboats 35'-40'
- Sailboats 40'-45'
- Sailboats 45'-50'
- Sailboats 50'-55'
- Sailboats over 55'
- Masts & Spars
- Knots, Bends & Hitches
- The 12v Energy Equation
- Electronics & Instrumentation
- Build Your Own Boat
- Buying a Used Boat
- Choosing Accessories
- Living on a Boat
- Cruising Offshore
- Sailing in the Caribbean
- Anchoring Skills
- Sailing Authors & Their Writings
- Mary's Journal
- Nautical Terms
- Cruising Sailboats for Sale
- List your Boat for Sale Here!
- Used Sailing Equipment for Sale
- Sell Your Unwanted Gear
- Sailing eBooks: Download them here!
- Your Sailboats
- Your Sailing Stories
- Your Fishing Stories
- Advertising
- What's New?
- Chartering a Sailboat
The Different Types of Sailboats
If you’re a sailboat fanatic like me, all types of sailboats will attract your attention. Some more so than others admittedly, but all will have something about them that catches your eye.
If you’re not a fanatic (not yet, that is) but just an interested observer, then the first thing you’ll notice about a sailboat will be how many masts it has and the configuration of its sails - in other words, its 'rig'.
This observation alone will enable you to identify the five main types of sailboats — sloops, cutters, ketches, yawls and schooners - all of which are described here.
But apart from the various rig types, you can describe types of sailboats from a different viewpoint - sailing dinghies, dayboats, motorsailors, monohulls, catamarans and trimarans.
Let's make a start with the various rig types...
A single-masted sailboat with just two sails — a foresail (aka headsail or jib) and a mainsail — is a sloop, the purest type of sailboat.
The sloop rig can also be described as a Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig or Marconi rig.
Read more about sloops...
Examples of Sloops

If a sloop has an additional sail between the headsail and the mainsail, then it's no longer a sloop - it's a cutter.
Some cutters - like the one shown here - have the foresail set forward on a bowsprit, with the inner forestay permanently rigged to the stemhead where the foresail otherwise would be, or to a central chainplate further aft on the foredeck.
Read more about cutters...
Examples of Cutters

The following boats may look like cutters with their double headsails, but they're not cutters at all...

To find out why, click here...
A ketch is a two-masted sailboat, a main mast forward and a shorter mizzen mast aft.
But not all two-masted sailboats are ketches — they might be yawls (see below).
A ketch may also sport a staysail, with or without a bowsprit, in which case it would be known as a cutter-rigged or staysail ketch.
Read more about ketches...
Examples of Ketches

Note that the Ocean 71 and the Irwin 52 are cutter-rigged, and are traditionally referred to as Staysail Ketches .
Cat Ketches
Cat-ketches are recognised by the lack of any standing rigging to support their pair of unstayed masts.
And yes, if the after mast is taller than the foremast then it's called a cat- schooner sailboat.
Read more about cat-ketches...

Yawls have their origins as old-time sail fishing boats, where the small mizzen sail was trimmed to keep the vessel steady when hauling the nets.
Much like a ketch, the difference being that the yawl has the mizzen mast positioned aft of the rudder post whereas the ketch has its mizzen mast ahead of the rudder post.
You’ll not be surprised to learn that a yawl with a staysail is known as cutter-rigged yawl.

A schooner is a two-or-more masted sailboat, in which the aft-most mast - the mainmast - is the same height or taller than the foremast.
The one shown here is gaff cutter rigged, with a topsail set on the mainmast.
Many sailors agree that of all the different types of sailboats, a schooner under full sail is one of the most beautiful sights afloat.

Gaffed-rigged sailboats, or 'gaffers', have their mainsail supported by a spar - the 'gaff' - which is hauled up mast by a separate halyard.
Often these types of sailboats are rigged with a topsail, as shown here and in the gaff schooner above, which really adds some grunt in light airs.
All this comes at a price of course, both in terms of material cost and weight aloft, which is why very few modern yachts are fitted with gaff rigs these days.
All artwork on this page is by Andrew Simpson

Examples of the Various Types of Sailboats...

Other Types of Sailboats
The seven sailboat rig variations shown here are the most popular types of modern cruising boat rigs, but there are other rig versions which were once found on commercial, fishing, and naval sailing vessels.
They include:
- Full square-rigged sailing vessels
- Barkentines
- Brigantines
And you can see examples of them here ...
In this article I've said that ketches, yawls and schooners with two headsails can be called cutter rigged. This is a commonly used description but strictly speaking, there's only one rig that can accurately be called a cutter - and that's a single-masted sailboat with two headsails. My thanks to 'Old Salt' for drawing my attention to this!
Recent Articles
A Hunter Passage 42 for Sale
Jul 16, 24 01:41 PM
The Wauquiez Centurion 40 Sailboat
Jul 15, 24 04:50 AM
The Elan 431 Sailboat
Jul 13, 24 03:03 AM
Here's where to:
- Find Used Sailboats for Sale...
- Find Used Sailing Gear for Sale...
- List your Sailboat for Sale...
- List your Used Sailing Gear...
Our eBooks...

A few of our Most Popular Pages...

Copyright © 2024 Dick McClary Sailboat-Cruising.com

Choosing the Right Boat for Your Sailing Adventure
T he pleasure derived from sailing is largely contingent on the kind of boat employed and, crucially, the sailor's ability to navigate it. A sailor will find it greatly more enjoyable to sail a boat that they are proficient and at ease with compared to one where they don't fully understand its operations.
Ideally, the latter circumstance should be avoided as it elevates the risks of sailing. The open sea can pose significant threats. Hence, navigating a boat under challenging conditions should only be undertaken by individuals who are thoroughly knowledgeable about their actions.
In this article, we'll introduce you to the most common small vessels so you can keep them in mind when choosing the right boat for your time on the water.
Types of Boats
Ski and wakeboard boats.
Ski and wakeboard boats are primarily designed for water sports activities and are not typically used for cruising. Depending on the model, they may come equipped with various features tailored to water sports.
These features might include ballasts for cruise control, wave enhancement, a heating system to prolong the boating season, and a tower for skis, attaching ropes, and wakeboards.
Uniquely, a wake boat utilizes an internal engine and a shaft propulsion system instead of a conventional sterndrive, enhancing the safety of skiers and wakeboarders. However, these boats have their drawbacks.
They are not well-suited for cruising or navigating choppy waters due to their flatter hull design and configuration, making sailing through waves uncomfortable or even downright unpleasant.
Additionally, these boats are generally more expensive and consume significant fuel when used for water sports.
Pontoon Boats
Whether you're sailing on an Arizona lake or an Atlantic seaboard bay, pontoon boats are a common sight. These boats don't rely on a fiberglass hull but instead float on two or three aluminum “logs.”
These boats were often slow, unattractive, and not particularly seaworthy in the past, but those days are long gone. Modern pontoon boats are quick, aesthetically pleasing, and incredibly comfortable.
While it's true that they may not be the best choice for waters that frequently see large waves, their stability is unparalleled, they offer plentiful deck space, and their flexibility allows for a myriad of seating configurations. You can even enhance them with features like wet bars, towing arches, and more.
High-performance Boats
Similar to sports cars, high-performance boats offer an unrivaled cruising experience. Their striking colors and sporty designs ensure you won't blend into the crowd when out on the water.
Thanks to their higher cruising speeds , these boats can traverse longer distances and quickly transport you to far-off places. Their speed and pronounced V-shape hull make them capable of handling choppy waters with ease.
While their fuel consumption at lower speeds matches smaller vessels, it increases significantly at higher speeds. However, their ability to reach destinations quicker reduces the time spent consuming fuel, thus narrowing the gap with other boat types regarding fuel efficiency.
One intriguing aspect of these sporty high-performance boats is that, due to their narrower beam and lower height, even larger models over 30 feet can be towed, a feat impossible with cruisers of the same size.
This feature allows exploring new, remote bodies of water or ones off-limits to other vessels.
On the downside, these boats come with high-performance mechanical parts, which means they carry a higher purchase price and maintenance cost.
High-quality boats are less comfortable and accommodating than cruisers of the same length. This is especially true as recent years have seen more balanced models replaced by extreme boats. Additionally, the insurance costs for these boats are also on the higher side.
Some people relish the sensation of wind blowing through the sails, even though sailing necessitates a unique skill set that isn't required for motorboating. If you're drawn to sailing , mastering the art is essential, and the ideal way to start is by taking a beginner's sailing course.
The absence of a motor means your journey is entirely at the mercy of the wind, which could be thrilling if you have an adventurous spirit. A detailed online directory of various boat types can also assist you in making informed decisions.
Console Boats
?Typically, console boats feature an open hull with ample deck space or seating at the front and central controls for steering and ignition. They are specifically engineered to endure offshore waters, making them perfect for ocean fishing.
The boat cover design ensures it doesn't hinder a fisherman's casting. These boats are spacious and have facilities to store fish in icy conditions.
Despite rough seas, they provide both safety and comfort. There's plenty of room for gunwale rod holders, outriggers, and bait wells. Outboard engines power all console boats. Their size can vary from 18 to 65 feet and reach speeds of 30 knots or more.
Personal Watercraft
Personal watercraft (PWCs) are widely recognized for their superior maneuverability and ease of operation. They are relatively inexpensive, easy to tow even with a car, and allow for exploration of various bodies of water.
Their distinctive turbine propulsion system requires less water depth than traditional vessels, making them suitable for areas larger boats can't reach.
Some models boast impressive engine power, allowing for higher speeds that enhance the thrill of the ride. Compared to other crafts, the upkeep expenses of these watercraft are comparatively minimal.
On the downside, their operation costs can be relatively high due to increased fuel consumption caused by their high-speed capability. This also impacts insurance costs.
The limited onboard space, accommodating one to three passengers depending on the model, also restricts the possibility of group trips unless you're in company with other boaters. This often results in a solitary experience, which may not appeal to everyone.
Dinghy Boats
Rubber-made, inflatable small boats, also known as dinghies, come in three distinct types: those with air floors, rigid bottoms, and a hybrid featuring jointed or slatted bottoms. These dinghies are typically stowed on larger vessels and utilized in shallow areas inaccessible to their larger counterparts.
Often referred to as inflatables or rowboats, these dinghies are equipped with oars and a compact outboard engine. Their ability to navigate shallow waters makes them ideal for fishing activities in such locations. They are also commonly brought along on camping trips.
RIBS (Rigid Inflatable Bottoms), which are inflatables with rigid bottoms, are favored due to their lightweight nature and stability. They can be deflated for easy storage, and their soft-sided design prevents any potential damage to the motherships they are carried on.
One can confidently assert that the majority of these vessels are multi-functional. A compact fishing boat could easily double as a recreational boat and the other way round.
The ideal type of boat for you hinges on several factors, such as your preferred type of water body, the duration of your sea journey, and your storage needs. A thorough investigation can guide you towards the perfect boat tailored to your requirements.
This story is brought to you in partnership with Supra Boats.
The post Choosing the Right Boat for Your Sailing Adventure appeared first on Go Backpacking .


Tall Ships Are a Slow Travel Adventure—Here’s Where to Find Them in the U.S.
A historic experience yes, and lots of fun..
- Copy Link copied

Travel with a sense of adventure on tall ships like the Matthew Turner .
Photo by John Skoriak
White sails dot San Francisco Bay all year—thanks to its moderate climate. For those lucky enough to own or have access to a boat, it’s one of the most inviting and scenic urban playgrounds in the nation. I’m not a sailor and don’t know any sailors, but this past spring I went sailing one Saturday afternoon on the Matthew Turner , a tall ship that sails out of Sausalito. In addition to a history lesson, I gained a fresh perspective of the bay, after decades of living and working near it. The primary mission of the Matthew Turner is teaching sailing to young people, but it also offers passage to the general public.
Before I stepped on the ship’s deck, the closest I’d gotten to this form of slow travel was in books about seafaring explorations centuries earlier. And aside from short ferry rides to Angel and Alcatraz islands, my only previous sailing on SF Bay did not augur well. That was on the Oceanic Society’s 60-foot motorboat heading 25 nautical miles west to the Farallon Islands; half of the eight hours aboard were choppy. Although I didn’t get seasick, I also didn’t eat the apple I’d brought along. And several passengers looked as though death could not come soon enough.
In contrast, sailing via Call of the Sea on the larger MT was smooth—and among assorted small sailboats and gigantic cargo ships, it’s the classiest boat on the bay. With wind power, traveling at about five knots per hour, it’s genuine slow travel. That speed lets you take in the scenery, which includes dolphins, seals, birds, and wind surfers among the other vessels. It also lets you appreciate the vast size of the bay: Rocky Alcatraz, green Angel Island, and the Golden Gate Bridge were backdrops, not closeups. The winds determine the route. And the fresh air vanquished the theme from Gilligan’s Island (“a three-hour tour”) that had been stuck in my head for days.
Built in the 21st century, over seven years, the Matthew Turner is named for the designer and builder of the brigantine Galilee, which had an advanced design for its time, in the late 19th century. (The Galilee long held the passage record of 19 days from San Francisco to Tahiti.) The fir and oak 132-foot MT brigantine has 11 sails (including several that are square); the main mast rises 100 feet. Its few modern features include an electric hybrid motor used for leaving the harbor. Otherwise, it’s strictly wind powered. That means no smell and no noise—aside from the crew leader calling out instructions about modifying sails—on an eco-friendly trip.
The brigantine sails on select Fridays, Saturdays, and Sundays throughout the year, ranging from 90 minutes to several hours . When I booked in May, I skipped the Mother’s Day special, figuring it would be crowded (it sold out) and got lucky: The amiable, enthusiastic young crew outnumbered the passengers. I chatted with nearly everyone aboard, including Alan Olson, the force behind the original project to build the ship. Highlights included watching the crew, which included a few volunteers and several women, set the sails. At the end of the too-short, two-hour trip, they scampered up the rigging to the top of the masts to roll up and tie the sails closed. So many ropes and sails: It’s not easy to travel this old-school way.
Among the passengers was a couple who had sailed on the ship before. I didn’t need to ask why.

Oftentimes, tall ships offer sailing classes.
Photos by Pat Tompkins
How to find your own tall ship adventure
Opportunities to participate in a day sail in the USA are more widely available than you might think. That’s partly because “tall ship” includes topsail and two- and three-masted schooners, barques, and other sailboats smaller and less grand than the Matthew Turner . Many tall ships with trips open to the public also operate as hands-on “classrooms” with programs to teach young people how to sail. For example, the Los Angeles Maritime Institute has tall ships for families or groups to charter; these private charters help support the educational programs.
You’ll find more possibilities through Tall Ships America, an organization based in Newport, Rhode Island, that promotes learning to sail and learning from sailing.
Where to sail on a tall ship in the United States
- Book now: Seattle’s Tall Ship ; Tall Ship Lady Washington
See the city from a tall ship on the gaff-rigged schooner Bay Lady , an 85-footer. A two-hour sail from Seattle’s Tall Ship starts at $45 for adults; $35 for kids 2–12; there are several sailings daily on Puget Sound from late April through the end of October.
Another nearby option: the Lady Washington brig, the official tall ship of the state of Washington, has day sails of two hours or more during July from Anacortes, Port Ludlow, Everett, and other cities. It’s a replica of the original Lady Washington , the first U.S. ship to sail the West Coast. For a two-hour sail: $70 for adults, $50 kids 4–12; four-hour voyages are also available.
- Book now: Pride of Baltimore II
Besides public two-hour sails, the Pride of Baltimore II , a topsail schooner, provides several guest crew opportunities for hands-on experience during the summer. While it visits New York in July, evening two-hour trips are available from Greenpoint on Long Island on the 19th and 20th (adults $55, $35 kids).
- Book now: Tall Ship Adventure
Enjoy a tall ship trip on the Californian through the Maritime Museum of San Diego. In addition to four-hour sails on Sundays (through October) at $119 for adults, $69 for children 3–12, this summer, for the first time since 2020, the Maritime Museum offers two chances for families to spend the night aboard the 1863 Star of India. (The boat stays docked but staff will teach the night’s “crew” about life for sailors long ago.) Overnights are Friday July 26 and August 9, 2 p.m. to 9 a.m., with two meals, $125 per person.
- Book now: Tall Ship Windy
Aboard the 148-foot schooner Windy , offerings include a daily Chicago Skyline tour from Lake Michigan (75 minutes; $49 adults, $39 kids) and an educational 90-minutes hands-on sail (Saturday–Monday, $35 adults, $25 kids). Summer features two-hour blues concert trips on Monday nights, $59 adults, $49 kids.
Gloucester, Massachusetts
- Book now: Schooner Adventure
During a 2.5-hour jaunt from the nation’s oldest fishing port, Gloucester Harbor, passengers can participate—helping raise the sails—or not, as they wish. You’ll be on the restored 1926 Adventure , a dory-fishing schooner and a National Historic Landmark. Those age 18 and under can enjoy the experience for free; tickets for adults are a modest $52. The Adventure offers public trips June through September on Sunday afternoons and Friday evenings.


The best time to cruise Alaska

Alaska is a cruise destination with a limited season. Cruise ships arrive in southeast Alaska in spring, stay the summer and linger only into early fall. The 49th state's snowy, cold and dark winters are not conducive to cruising.
Most cruise passengers will head to Alaska between Memorial Day in late May and Labor Day in early September when temperatures range from slightly chilly to warm during the long daylight hours. Tourist attractions are in full swing, salmon swim upriver, and bears (and humans) have access to fishing.
Some adventurous cruisers will board ships when they arrive in Alaska in April to see the remnants of winter. A few big ships cruise into mid-October for those who want a peek at what life is like in Alaska towns when all other tourists have returned home.
For cruise news, reviews and tips, sign up for TPG's cruise newsletter .
Each month has its advantages, not the least of which is discounted pricing in the spring and fall shoulder seasons. Here is a guide to help you decide when to cruise in Alaska.
After a long winter, Alaska begins to wake up in April — that includes the wildlife. Small-ship cruise lines such as Lindblad Expeditions and UnCruise Adventures have sailings into the wilderness, where you might spot bears emerging from their slumber and admire huge waterfalls fueled by the snowmelt. A few big ships, such as Norwegian Cruise Line 's 4,000-passenger Norwegian Bliss out of Seattle , begin their season this month with discounted early-season pricing.

You may encounter freezing rain or even snow on your April cruise and should expect to tread through the mud. Some tourist facilities — including those at national parks — may still be shuttered for the winter.
On the other hand, you will have the opportunity to observe the change of seasons. Expect crisp mornings with temperatures in the 30s, though by the end of the month, you may find dry weather and temperatures in the 60s. As an added bonus, the skies will be dark at night; if clear, you might spot the northern lights.
Related: The best Alaska cruise for every type of traveler
As someone who has cruised Alaska many times, I love cruising in May when the weather is dry. Locals start emerging from their winter cocoons, embracing the sunshine, and the wildlife does the same. You might spot bears with their cubs, moose with their calves and humpback whales returning from their winter home in Hawaii.
Big-ship cruise lines such as Holland America Line , Princess Cruises and Royal Caribbean ramp up their operations in May, as do Disney Cruise Line and small-ship and luxury lines. Early season deals might be available.

Attractions and shops will switch to peak-season hours at the end of the month; Denali National Park and Preserve will switch into summer mode in May. You'll find those who work in tourism excited to be back in business, considering many people in southeast Alaska earn their income from out-of-state visitors. Cruise lines will offer the opportunity to extend cruises with land tours, which include accommodations, transportation and some meals.
While early May often carries a chill in the air, you might encounter temperatures in the 60s by the end of the month. The warmer weather means glaciers begin shedding ice more frequently, so you have a better chance of experiencing the sight and sound of a house-size chunk of ice calving into the sea. Another bonus is that Alaska's large mosquito population has yet to emerge.
Related: Alaska cruise guide: Best itineraries, planning tips and things to do
The cruise season beefs up in June, with the number of ships growing; the season is in full swing by the end of the month. The midnight sun means many hours of daylight — especially on June 20, the longest day of the year. You'll have to stay up late to see any darkness at all.
Early in June, the ships still mostly carry adults, with the family crowd — including multigenerational groups — arriving later in the month.
Shore excursion experiences abound. Temperatures are pleasant — in the 60s and sometimes higher, with wildflowers in bloom and glaciers calving. Anglers will find opportunities to reel in halibut along with king and sockeye salmon and rainbow trout. In addition to humpbacks, you might also spot belugas and seals with their pups as you sail.
At the beginning of the month, you might still be able to find some early-season pricing; the peak season for Alaska cruising begins in late June.
Related: Alaska cruise packing list: What to pack for a sailing up north
July and August

Summer is the height of the Alaska cruise season, which means crowds in port towns, especially when several ships are in port at the same time. You might have to wait hours for a table at the popular Tracy's King Crab Shack in Juneau.
It might surprise many, but July and especially August are rainy, so don't expect endless sunshine. That said, you are in Alaska at a time for festivals and other special events, and frontier towns really come alive.
Temperatures will be in the 60s, sometimes higher — you might even see 80s in Juneau in July. During long days of light, you'll find hearty Alaskans swimming in the sea and enjoying water sports. Shore excursion options will be in full swing.
During both months, you will encounter peak-season pricing. Unless you booked early, cabin choice could be limited — especially if you are looking for a fancy suite or cheap inside cabin; those tend to be the first categories to sell out. Balcony cabins are particularly popular in Alaska.
Mosquitos enjoy the summer, too, so pack bug spray. July and August are also spawning season for salmon, so you might spot grizzlies and brown bears near rivers and streams.
Keep an eye out for seabirds and songbirds, seals, Steller sea lions and humpback whales. Marine life is so prolific that some small-boat shore excursions guarantee you will see animals. Bears will be fishing; in late August, they will be looking for blueberries, which also become a featured item on restaurant menus. Toward the end of August, you'll see leaves changing to fall colors.
Related: Best Alaska cruise shore excursions — from heli-hiking to whale watching
The beginning of September is much like August, but after the kids go back to school and the family crowd departs, it's shoulder season for cruising and pricing drops. Most cruise ships will have repositioned out of the state by the end of the month. You will experience a change of season, with cooler temperatures (in the 50s or lower) and some rain.
Mid-to-late September is one of the best times to spot wildlife in Alaska. I have had extraordinary experiences. Once, I watched a pod of humpback whales gather together in bubble-net feeding (corralling fish in a "net" of bubbles) to fill their bellies in preparation for their annual journey to warmer waters. Bears will be hunting for the last of the berries and salmon, and caribou, deer and moose will be mating.
You'll see colorful fall foliage but not mosquitos. National park facilities and some tourist businesses will switch to winter hours. September is also a great time to get deals on souvenirs, as merchants sell off this year's goods at the end of Alaska's tourist season.
On clear nights, you have a chance of spotting the northern lights — though they won't shine as brightly as they do in winter. Rather than stay up all night, see if your ship or pre- or post-cruise hotel has a sign-up sheet for people who want a wake-up call should the lights appear.
Related: From Alaska to the Panama Canal: Here are 9 of TPG's favorite fall cruise itineraries
A limited number of cruises in October (predominantly on Norwegian Cruise Line ) make it possible for cruisers to experience a taste of Alaska in winter without sub-zero temperatures. You will want to bundle up; the average temperature in Juneau in October is 39 degrees. Days will be short — there are only about 10 hours of daylight. You are likely to experience rain and maybe snow.

Some attractions and shops will be closed for winter, though your cruise line will still operate a full roster of shore excursions. On the plus side, you will experience southeast Alaska towns as they are most of the year, sans tourist crowds. Sit in a bar and talk to the locals as they prepare for the long winter ahead. Cruise fares will be discounted.
Related: Caribbean vs. Alaska cruises: Which itinerary will I like more?
When is the best time to see the northern lights in Alaska?
If one of your primary objectives during your Alaska sailing is to get a glimpse of the northern lights , consider a sailing in late August, September or October. The lights are typically strong in Alaska from late August to mid-April.
Your best bet for a sighting will be in Fairbanks — it's situated under the "aurora oval," an area known for a high frequency of northern lights displays. Fairbanks is a popular stop on cruisetours, itineraries that combine time sailing with overnight stays on land. For example, Holland America's nine-night Denali itinerary begins with an overnight stay in Fairbanks in early September.
Denali National Park and Anchorage can offer a glimpse of the northern lights — though not as frequently as Fairbanks since they are farther south. Both destinations are popular cruisetour stops. If you're cruising into or out of Seward or Whittier, you'll fly through Anchorage on one end of your trip. Consider an extra night or two there if you want to try and catch the aurora.
It's incredibly rare to see the northern lights from aboard your ship in the Inside Passage.
Related: Northern lights cruises: A guide to chasing the aurora borealis at sea
What is the cheapest month for an Alaska cruise?
As previously mentioned, April, May, September and October are good months for an Alaska cruise if you're hoping to score a deal . In addition to cheaper fares, early and late sailings of the season see fewer crowds.
Bottom line
What is the best month for an Alaska cruise? Alaska is a thrilling cruise destination no matter which month you sail. However, some months might be better for you, depending on your interests. Look to the early and late sailings of the season if you are a bargain seeker. Choose a May or June sailing for drier weather and fewer mosquitos. Summer is the best time to cruise to see abundant marine life and birds. September can be a great month to see wildlife.
Planning an Alaska cruise? Start with these stories:
- Everything you need to know about booking a trip to Alaska on points
- 8 of the best Alaskan lodges for getting close to glaciers, Denali and more
- Best Alaska cruise tips to help you make the most of your time aboard and ashore
- 6 best Alaska cruises for families
- The best Alaska cruises for couples
- I took a $900 dog sledding and helicopter excursion on my Alaska cruise. Was it worth it?
- What to pack for a cruise
- 20 must-have cruise items — including a roll of duct tape
- The 5 most desirable cabin locations on any cruise ship
- The 8 worst cabin locations on any cruise ship

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What are the different types of sails? Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. Typically, the mainsail is a fore-and-aft bermuda rig (triangular shaped). A jib or genoa is used for the headsail. Most sailors use additional sails for different conditions: the spinnaker (a common downwind sail), gennaker, code zero (for upwind use ...
Headsail/Jib. The headsail, or the jib, is likely the second most popular kind of sail found on sailboats. This is because it often accompanies the mainsail, the most popular kind. On all sailboats, the headsail is put at the front of the mast over the sailboat's bow. It is always a smaller sail than the mainsail.
8 Types of Sails for Sailboats. As mentioned, you should carry multiple sails when sailing to prepare for various weather conditions. Here's a brief overview of the types of sails for sailboats: 1. Mainsails. The mainsail is the largest and most important sail. Therefore, it's probably the first sail to come to mind when you think of camping.
Spinnaker sails are a type of downwind sail that can be used to increase boat speed when sailing in light winds. They are typically used in wind conditions below 10 knots, which are considered light air sails. Spinnakers come in two types: symmetrical and asymmetrical. Author: Ken Heaton CC BY-SA-4..
one mast. triangular mainsail (called a Bermuda sail) a foresail (also called the jib) fore-and-aft rigged. medium-sized (12 - 50 ft) Fore-and-aft rigged just means "from front to back". This type of rigging helps to sail upwind. Any sailboat with one mast and two sails could still be a sloop.
As a general setup, sailboats will use three common sails, including headsail, mainsail, and specialty sail. Due to the varying wind conditions and the model of the sailboat, there are many types of sails including jib, genoa, trysail, storm jib, code zero, gennaker, and spinnaker. While that sounds like too many models of sails, you can easily ...
The shape of the sail plays a crucial role in how it works. Sails are designed to be curved, much like an airplane wing. This curvature creates differences in air pressure: the wind flowing over the curved side of the sail travels faster and creates lower pressure, while the wind on the flat side (facing the wind or windward) remains relatively slower with higher pressure.
Mainsails are essential for providing the boat with forward propulsion and play a significant role in steering and balancing the vessel. There are two primary types of mainsails: full-batten and partial-batten. Full-batten mainsails have horizontal battens that run the entire width of the sail, providing additional support and shape.
A daggerboard drops into a slot through the boat. They are common on sailing dinghies, as well as on high-performance catamarans and trimarans. Mast Configuration and Sails Mast configurations and sail combinations are another way of categorizing sailboats. These are just a few of the most common types. Sloop The most common type of sailboat is ...
The most common kind of sailboat is the sloop, as it's simple to operate and versatile. Other common sailboat types include the schooner, cutter, cat, ketch, schooner, catamaran, and trimaran. Other sailboat variations include pocket cruisers, motorsailers, displacement, and shoal-draft vessels. The information found in this article is sourced ...
There are different types of sails and rigs. Most sailboats have one mainsail and one headsail. The mainsail is generally fore-and-aft rigged and is triangular shaped. Various conditions and courses require adjustments to the sails on the boats, and, other than the mainsail, most boats can switch out their secondary sail depending on various ...
Gaff ketch - two-masted (mizzen), two mainsails, staysails, fore-and-aft rigged. Full-rigged ship or tall ship - three or more masts, mainsail on each mast, staysails, square-rigged. The first word is the shape and rigging of the mainsail. So this is the way the sail is attached to the mast.
Type of Sails Names: Decoding the Terminology. Mainsail and Foresail. The mainsail, as mentioned earlier, is the principal sail that catches the wind to move the boat forward. Foresail is a general term that includes various sails positioned near the bow of the sailboat, such as the jib and genoa. Genoa and Jib.
Basic Types of Sails. Sails are an essential part of any sailboat. They are used to harness the wind to propel the boat forward. There are several types of sails available for sailboats, and each serves a different purpose. Here are the three basic types of sails: Mainsail. The mainsail is the most critical sail on a sailboat.
The mainsail, headsail (or jib), genoa, spinnaker, and gennaker are the most popular types of sails on sailboats. There are also a number of different configurations when considering the type of sail and mast in use including a sloop, fractional rig sloop, cutter, ketch, schooner, yawl, and cat. Simply put, different sailboat sails serve ...
Short answer different types of sails: There are several different types of sails used in sailing, including mainsails, headsails (jibs and genoas), spinnakers, gennakers, and storm sails. Each type is designed for specific wind conditions and sailing techniques, contributing to the overall performance and maneuverability of a sailboat.
A sloop-rigged sailboat typically features a mainsail, a headsail, and an additional light-wind sail, such as a spinnaker or Gennaker. The mainsail is rigged aft of the mast, while the headsail is attached to the forestay. The two most commonly used headsails are the Genoa and Jib. The sails are vital parts of a sailboat since you obviously ...
Sailboats typically use four primary types of sails: mainsails, genoas/jibs, spinnakers, and staysails. Mainsails are the largest and provide forward propulsion. Genoas/jibs enable efficient sailing upwind. Spinnakers are used for downwind sailing and maximizing speed. Stay-sails provide stability in heavy wind conditions.
Common Types of Sailboats Sloop. A sloop is a classic sailing vessel with a single mast and two sails. A headsail may be a variety of jibs attached to the mast forestay and extends to the mast cap. Schooner. A sailing boat with multiple masts with several sails. Schooners have tall aft masts and can have as many as six masts. Cutter
To the untrained eye, all sailboats are pretty much the same (some are just bigger than others). They're essentially floating vessels with a mast, a set of sails, and the ability to navigate the waters by harnessing wind power. But if you dive a bit deeper, you'll see there are drastic differences in the designs, capabilities, and uses of each type of sailboat.Whether you're new to ...
Sailboat Shapes And Hull Types. Sailboat hulls differ in their total number and shape. They can be monohulls (one hull), catamarns (two hulls) and trimarans (three hulls). The shape of a sailboat not only changes the way it is commanded, but also how it performs on different points of sail and in different conditions.
The following is a partial list of sailboat types and sailing classes, including keelboats, dinghies and multihull (catamarans and trimarans). Olympic classes Laser. Name Year of first construction Designer Builder Notes 470: 1963: André Cornu: Several: 49er: 1999: Julian Bethwaite: Several: 49er FX: 2010: Julian Bethwaite: Several:
This observation alone will enable you to identify the five main types of sailboats — sloops, cutters, ketches, yawls and schooners - all of which are described here. But apart from the various rig types, you can describe types of sailboats from a different viewpoint - sailing dinghies, dayboats, motorsailors, monohulls, catamarans and ...
The pleasure derived from sailing is largely contingent on the kind of boat employed and, crucially, the sailor's ability to navigate it. A sailor will find it greatly more enjoyable to sail a ...
Book now: Seattle's Tall Ship; Tall Ship Lady Washington See the city from a tall ship on the gaff-rigged schooner Bay Lady, an 85-footer.A two-hour sail from Seattle's Tall Ship starts at $45 for adults; $35 for kids 2-12; there are several sailings daily on Puget Sound from late April through the end of October.
In addition to humpbacks, you might also spot belugas and seals with their pups as you sail. At the beginning of the month, you might still be able to find some early-season pricing; the peak season for Alaska cruising begins in late June. Related: Alaska cruise packing list: What to pack for a sailing up north. July and August