
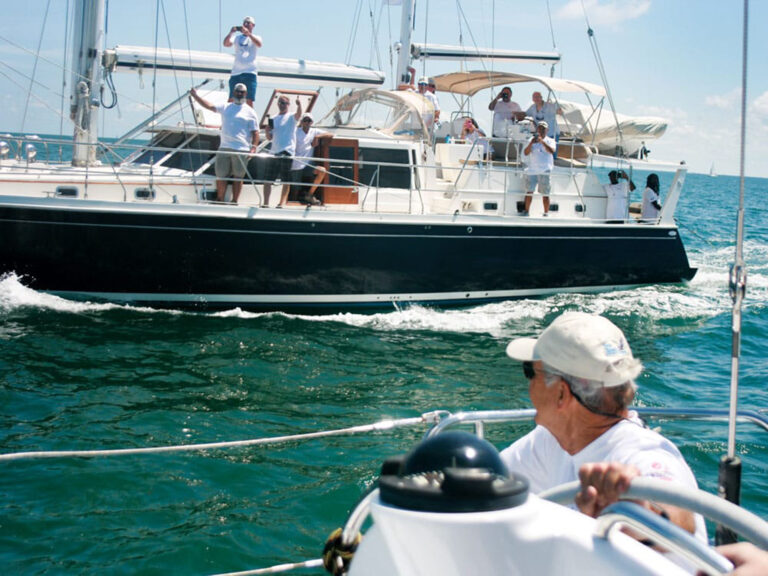
My Cruiser Life Magazine

7 Best Trailerable Sailboats for Cruising
Many sailors balk at the idea of leaving their boat in the water at a marina. Slip fees are expensive, and maintenance bills get bigger the longer you leave a boat in the water. However, if you want a boat under 30 feet long, there are trailerable sailboats that will fit the bill.
Like any boat purchase, you’ll need to analyze precisely what kind of trailer sailer you want. Will a simple weekend sailboat suffice, or do you really need the best trailerable cruising sailboat you can find?
Here’s a look at some of the pros and cons of the best trailerable sailboat. Plus, we’ll look at how to compare them for your purposes.
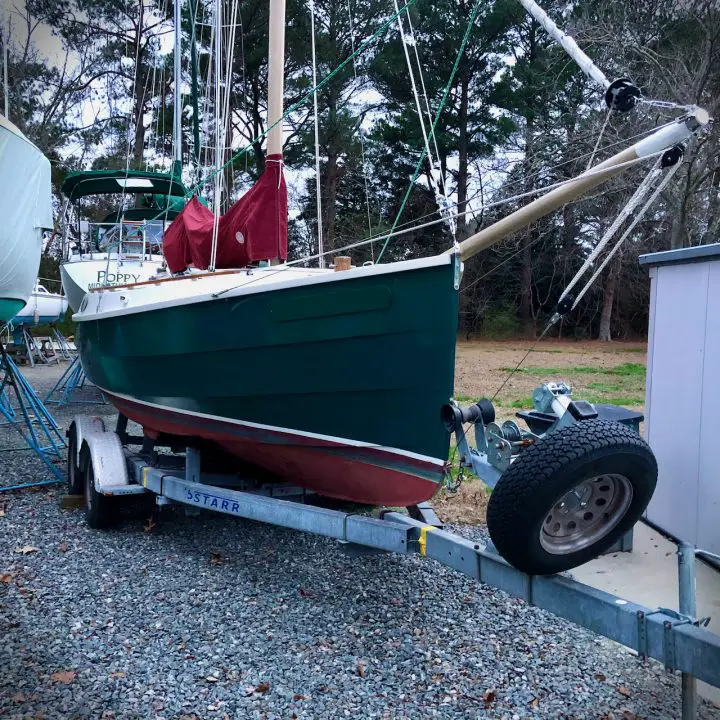

Table of Contents
Best trailerable sailboats, easy to launch trailerable sailboats, quick setup time, towing weight, catalina 22/25 “pop-top”, com-pac horizon cat for classic coastal cruising, marshall sanderling — small, portable, classy, west wight potter 19 — the tiny go-anywhere sailboat, seaward 26rk with retractable lead keel, corsair f-24 trimaran – sporty sailing, macgregor 26m — maximum speed meets maximum living space, long-range cruising boats, 7 best trailerable boats – a recap, what’s the best trailerable sailboat for a cruise, trailerable sailboats faqs.
- Catalina 22/25
- Com-Pac Horizon Cat
- Marshall Sanderling
- West Wight Potter 19
- Seaward 26RK
- Corsair F-24 Trimaran
- MacGregor 26M
We’ll get into more detail about each brand in my post today, so hang tight!
What Is a Trailerable Sailboat, Exactly?
For this article, the priorities for a trailerable sailboat are:
- Easy to launch
- Require minimum setup to launch and store
- Lightweight enough to be towed by the average vehicle
Before you can really classify a sailboat as trailerable, you need to evaluate and narrow your search criteria. Truthfully, 50-plus-foot ocean-going sailboats are regularly put on trailers. But that’s done commercially, on a big rig, with special permits for oversized loads, and even led cars.
That probably isn’t what most people mean when they think of a trailerable sailboat. But what is the priority here, the trailerable part or the sailboat part? Compromises are going to have to be made somewhere.
If you’re looking at the 20-foot-and-under sailboat crowd, finding a trailerable example should not be hard. Most sailboats this size are designed for trailers anyway since they aren’t the sort of boats people want to pay to leave in a slip year-round.
Things get more interesting when you look at the 20 to 30-foot boats. In this class, there are stout ocean-going cruisers with deep keels and lightweight centerboard trailer sailboats designed from the get-go to be trailered by the average car or SUV. The differences between these boats are night and day.
Sailboats often have a hard time at boat ramps. First, deep keels mean that the trailer must extend farther into the water than the average boat ramp allows. This means the ramp needs to go back far enough, and the trailer tongue needs to be long enough not to swamp the car.
If you have a boat like this, you’ll need to find the right boat ramps. Unfortunately, not all ramps are created equally. If your boat draws more than two or three feet on the trailer, you’re going to be limited to steep, paved, and high-quality boat ramps. Unfortunately, those aren’t standard features, so your cruising grounds are going to be limited.
Usually, ramps aren’t built steeply because they are often slippery. Your tow vehicle will need excellent traction and torque to pull your fully loaded boat out of a steep ramp. The steeper the ramp, the more trouble you’ll have.
The alternative to finding steep ramps is to use a trailer tongue extender. This lets you get the trailer into deeper water without swamping the tow vehicle. But it also means that the ramp needs to extend deep enough. Many ramps end abruptly. Allowing your trailer to sink off the edge is an excellent way to get stuck or pop a tire.
Pick a boat as easy to launch and retrieve as a similarly sized powerboat to remove all of these boat ramp problems. The soft chines of most sailboats will always require a little more water, but a swing keel and the hinged rudder raised mean that the boat can sit low on the trailer bunks. That way, you only need one or two feet of water to launch, an easy feat at nearly every boat ramp you can find.
The next consideration for a sailboat to be portable enough to call it “trailerable” is the amount of time it takes to step the mast and get it ready to cruise.
To accomplish this, you need a mast that can be stepped by a two-person team–maximum. Ideally, it will have some tabernacle hardware to enable one person to do the task for solo sailing.
There is an entire family of pocket cruisers that could ideally fit on trailers. But you won’t find the Fickas or the Falmouth cutters on my list, simply because they aren’t easy to launch or easy to rig. But, of course, they’re also too heavy for most vehicles to tow, which leads us to the final point of excluding them this trailable pocket cruiser’s list.
One of the most significant financial burdens the trailer sailer faces is their tow vehicle. You are all set if you already drive a two-ton dually diesel pickup truck. But if your daily driver is an SUV or light pickup, you need to think long and hard about the math of the towing equation.
Whatever boat you buy cannot exceed the towing rating limits of your tow vehicle. If you don’t have a tow vehicle, you’ll need to buy one. This will double or triple the cost of getting a trailer sailer in most cases. For the same money, you may want to look at a boat that stays in the water at a traditional boat slip. For the cost of a trailer sailer and a tow vehicle, you can probably step into a nice boat that is larger and more comfortable than any towable.
If you have a tow vehicle, you need a light enough vessel for it to tow. Most modern SUVs tow less than 2,500 pounds. Anything more than 5,000 will require a full-size pickup. Remember that the tow weight isn’t just the boat’s displacement—it’s the empty hull weight, plus the weight of the trailer and any extra gear you need to pack into the boat.
Finding a vessel that fits these limitations on weight isn’t easy. If the manufacturer’s goal is to make it towable, immediate limits are placed on the materials they can use. This means less seaworthiness since boats are built light and thin. As far as stability goes, lead keels are generally out, and water ballast systems or centerboards might be used instead. It doesn’t mean these boats aren’t safe and fun, but they aren’t designed for rough conditions, crossing oceans, or living on in the water full-time .

7 Best Trailerable Cruising Sailboats
There are more trailerable sailboats out there than you might imagine. Here’s a look at seven popular options of all shapes and sizes to give you a taste of what you might want to take to sea.
The boats here are selected for their storage and living space. With these boats and a little outfitting, you can spend weeks gunk-holing in the Chesapeake Bay or island hopping the Bahamas. If you broaden your scope to include daysailers with no cabin space, there are countless more options.
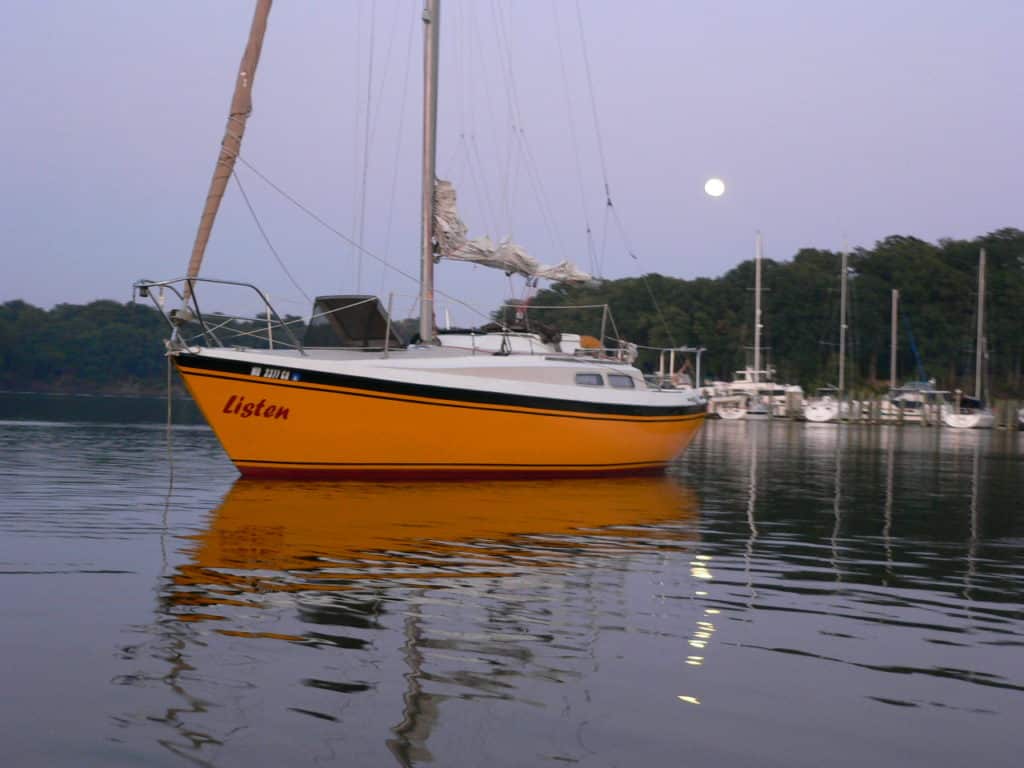
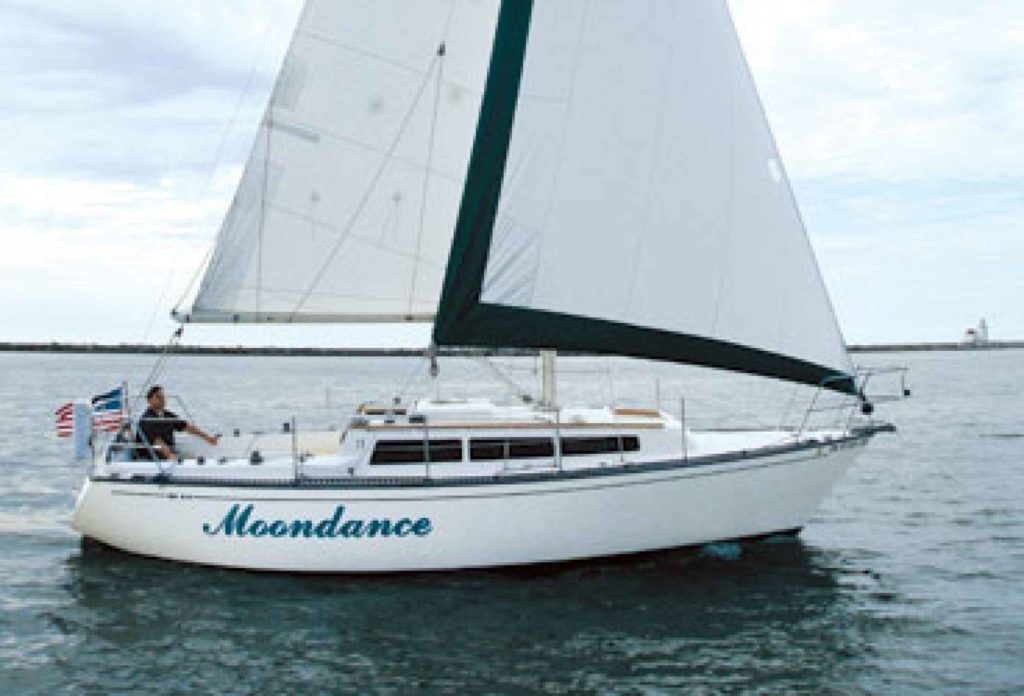
One of the worst parts of a small trailerable sailboat or pocket cruiser is the lack of stand-up headroom. One clever solution that you’ll find on some weekend sailboat types is the pop-top.
The pop-top is simply an area around the companionway hatch that extends upward on struts. So when you’re at the dock or anchor, you get standing headroom down below—at least right inside the pop-top.
You can build a canvas enclosure for your pop-top to use it in all weather. A pop-top makes your boat feel much larger than it is and allows you to move freely to cook or get changed down below or even do a nice boat bed area.
Later models of the Catalina Sport 22 and Capri 22s lacked this cool pop-top feature, so if you want it, you’ll need to seek out an older model on the used market.
Com-Pac has been building small sailboats since the early 1970s. They currently sell two lines, each with various-sized boats. All are well built, and a majority of their boats are trailerable.
Most interesting at the Com-Pac traditional catboats . The rigging is more straightforward than modern sloops, with only one large mainsail. Com-Pac boats come with a unique quick-rig system to make getting on the water fast and simple.
The Horizon Cat Coastal Cruising has a displacement of 2,500 pounds with a 2’2″ draft when the board is up. She has a separate head forward and space to lounge either topside or down below. The smaller Sun Cat has slightly few amenities but shaves off a few feet and pounds, making it easier to tow and it is one of these amazing small sailboats. Com-Pacs features stub keels, so their centerboard and hinged rudder do not take up space in the cabin.
On the sloop rig side, the Com-Pac 23 comes in a 3,000-pound traditional sailboat or a very interesting pilothouse. Both are incredibly livable for their size , with shallow two-foot-long fixed keels and high-quality construction.
Another option if you like catboats is the Marshall Sanderling. This salty 18-footer oozes traditional charm , all while being easy to sail and easier to tow. And while she has wooden boat lines, she has a modern laminated fiberglass hull.
The Sanderling has a 2,200-pound displacement, so tow weights will be around 3,000 pounds. At only 18-feet, she’s on the small side for cruising. The cuddy cabin has no galley, and the portable toilet is not enclosed. But that small size means a simple boat that’s easy to maintain and take anywhere.
An electric motor package is an exciting option on this weekend sailboat!
View this post on Instagram A post shared by @marshallmarinecat
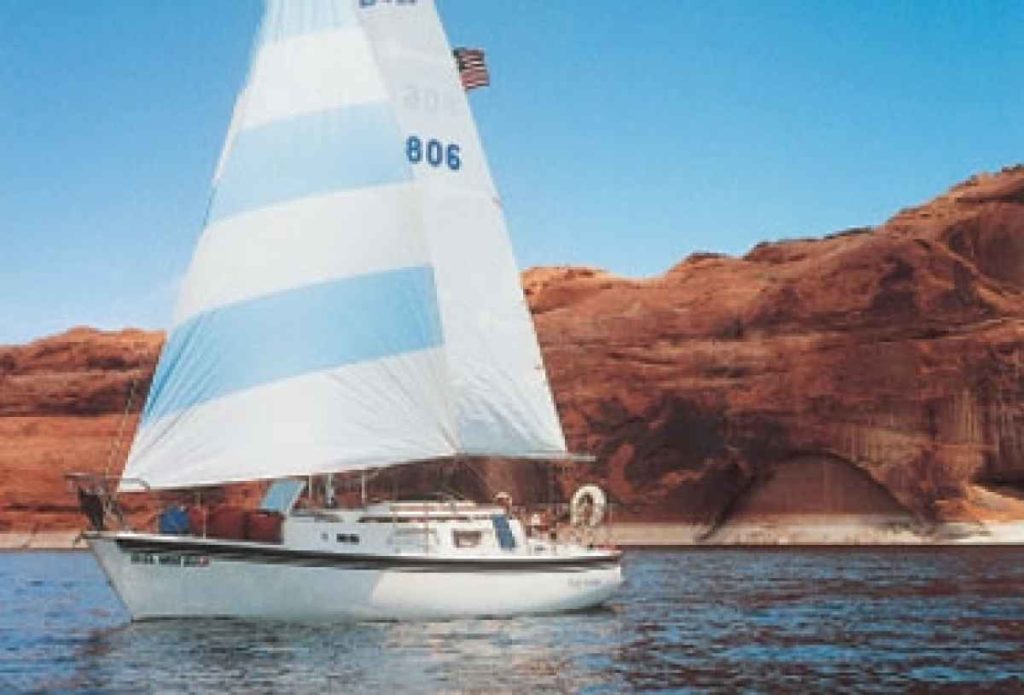
You can’t mention tiny trailer sailers without touching on the famous West Wight Potter . These 15 and 19-foot pocket cruisers have earned a worldwide reputation as the ultimate go-anywhere coastal cruiser.
The West Wight Potter 19 offers the most living space for staying aboard and cruising. So even though its dimensions are diminutive, this little boat packs a lot in. There’s a single burner hotplate and sink and a porta-potty tucked under a cushion. Yes, it’s tight—but the company claims the little boat can sleep five people. Any more than two will feel pretty crowded, however.
The boat comes standard with a mast-raising system that a single person can manage alone. It has a daggerboard for a shallow draft of a half-foot when the board is up. The total towing weight is around 1,500 pounds, which means nearly any car can tow a West Wight Potter.
This little-known trailer sailer is produced at the same Florida factory that makes Island Packet Yachts. That should give you a little bit of an idea of what sort of boat it is—trailerable, yes, but also high-quality, beautiful, and built for cruising. In other words, it’s one of the nicest all round pocket cruisers and it feels like a much larger boat.
The Seaward is easily the saltiest boat on this list . It’s beefy and seaworthy. Instead of a lightweight centerboard, Seaward fits the RK with a bulb-shaped retracting keel. Other big-boat items include a Yanmar diesel inboard motor and an enclosed head. The spacious cabin of the boat features a double berth and is ready for salt water cruising.
According to sailboatdata.com , the tow weight of the 26RK is 6,000 pounds. With the keel up, the draft is 1.25 feet.
Multihull sailors need not feel left out from the trailer sailer club and the pocket cruiser. Beyond the ubiquitous beach Hobie Cat, there are not many options for catamarans. But trimarans are uniquely suited to be towed.
Why? For one thing, performance oriented boats like trimarans are based on it being built light. There is no ballast—a trimaran’s stability comes from its two outer hulls. Additionally, the living space is entirely housed in the central hull–the outer floats are small and sometimes foldable. Finally, there are no keels on tris, so they are extremely shallow draft and perfect for trailering.
If you’re looking for adrenaline-pumping sporty and fun sailing, it’s impossible to beat what a trimaran will offer. Let’s not beat around the bush—most of the trailer sailers on this list have hull speeds around five knots. The Corsair has no such limits, routinely sailing at 15 knots or more .
The new Corsair 880 trimaran has an unloaded weight of 3,659 pounds. It is trailerable behind a big SUV or small pickup and is probably the most fun sailing option that is trailerable at all.
An even more portable option is the older Corsair F-24. It has a light displacement of under 2,000 pounds—so nearly any SUV can tow it.
MacGregor owns the market on trailerable motor sailers since they more or less created the product to fit the bill. The MacGregor 26 is not like other boats. The design combines a planing powerboat with a centerboard sailboat. Imagine scooting along at 20 knots or more when the wind is down or enjoying a sporty sail on a breezy day–in the same boat.
The entire boat is built from the ground up for towing and long-range sailing. So if you want a big sailboat that you can tow behind pretty much any SUV, the MacGregor has to be on your list.
Depending on the model, the 26-foot-long boats have incredibly light dry weights of between 1,650 and 2,350 pounds. Considering the massive volume of the roomy cabin, the ability to tow such a large vessel opens up an entire world of opportunities for owners.
It’s not all good news, of course. MacGregor owners love their boats, but they are built light and are not ideally suited for offshore cruising or rough weather. But in bays and for coastal sailing on nice days, few boats can get as much use as a MacGregor.
The motorboat capability of the 26M and 26X might not appeal to hardcore sailors, but for those looking to maximize their use of the boat depending on the weather, their mood, or location, it makes a lot of sense.
MacGregor shut down in 2015, but the daughter and son-in-law of the original owners took over production and renamed the boat the Tattoo 26 . The company will soon release a smaller version, the Tattoo 22 .
If the 26 is a bit big to make your list of best trailerable small sailboats, consider the smaller Powersailer 19. It’s nearly identical to the 26, just smaller and lighter.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Dale Roddick (@droddick33)
What Do You Want Your Trailer Sailer To Do?
After you’ve settled on how you will tow and launch your trailer sailer, now it’s time to dream about what you want it to do. Where will it take you?
The beauty of a towable boat is that you can travel anywhere. A boat in the water might take weeks or months to move a few hundred miles. But if you can attach it to your car and do 65 mph on the interstate, you could sail on the Pacific on Monday, the Gulf of Mexico on Wednesday, and the Atlantic on Friday.
We can divide our trailerable sailboats into three groups – daysailers, weekenders, and cruisers.
These are designed with open cockpits and no space to sleep. This is a majority of the sub-22-foot boats on the market. They are designed to be launched, play for the day, and return to the ramp or dock.
A weekender will have rudimentary sleeping facilities. Think of it as a floating tent—it’s not a five-star hotel, but you can sleep under the stars or get out of the rain. Conceivably you could stay aboard indefinitely, but it doesn’t have much room for gear. So most people are ready to get off after a day or two.
A cruising boat has sleeping, cooking, and toilet facilities built-in. These might be small and simple, but in any quantity, they mean you can disconnect from shore for a long time. Unfortunately, squeezing all of this into a tow-friendly package isn’t easy, and very few boats do it well.

The best trailer sailor for your adventures will depend on many factors. Like any boat, whatever you decide on will be a compromise – boats always are. But there are plenty of choices out there, no matter what size your tow vehicle is and no matter what sailing adventures you have in mind.
What size sailboat is trailerable?
Even large yachts are routinely transported by towing across land, so the question is more of how big a sailboat can you tow? Your tow vehicle will be the limiting factor. The upper limit for most large SUVs and trucks is usually a sailboat around 26 feet long.
Sailboats are generally very heavily built, with ballast and lead keels. Sailboats specifically made to be trailer sailers are lighter. They may use drainable water ballast tanks instead of fixed ballast and have fewer fixtures and amenities.
To find the best trailer sailer, you need to balance the total tow weight, the ease of rig setup at the boat ramp, and the boat’s draft. Shallow draft boats with centerboards are the easiest to launch and retrieve.
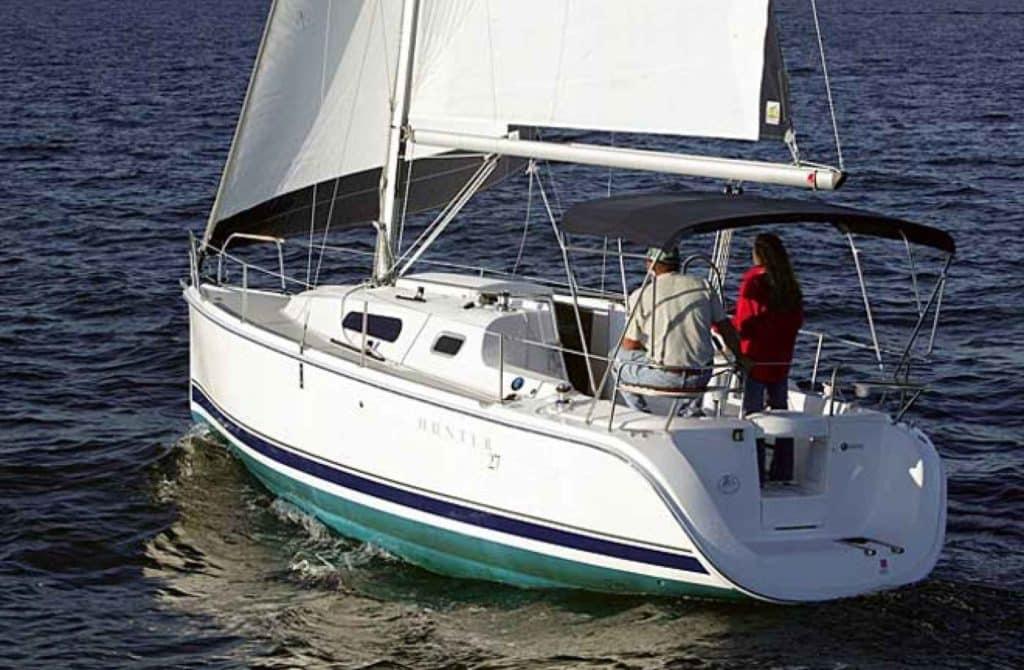
Is a Hunter 27 trailerable?
No. The Hunter 27 is a one of those fixed-keel larger boats built from 1974 to 1984. The boat’s displacement is 7,000 pounds, not including trailer and gear. That alone makes it too heavy to tow by all but the beefiest diesel trucks.
Furthermore, the fixed keels had drafts between 3.25 and 5 feet, all of which are too much for most boat ramps. In short, the standard Hunter Marine 27 is too big to tow for most people.
On the other hand, Hunter has made several good trailer sailers over the years. For example, the Hunter 240 and 260 were explicitly designed for trailering. They have drainable water ballast and shallow keel/centerboard drafts less than two feet.
Is a Catalina 22 trailerable?
Yes, the Catalina 22 is easily trailerable and makes a wonderful weekend sailboat. In fact, there were over 15,000 Catalina 22s made and sold over the years.
The boat’s displacement is 2,250 pounds, which means your total tow weight with trailer and gear will be under 3,000 pounds. This is within the capabilities of most mid to full-size SUVs and light trucks. Be sure to check your vehicle’s towing capacity, of course.
The centerboard on the Catalina 22 is another factor in its easy towing. With the board up, the boat draws only two feet. This makes it easy to float off the trailer at nearly any boat ramp. You should avoid fixed keel versions of the 22 for towing unless you have access to extra deep ramps.
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
Can someone tell me why no other manufacturer makes pop tops? Those who have them, love them. Makes sense for head space with a trailerable boat too. Catalina stopped making them decades ago, yet people still swear by them. So, why isn’t there any newer models?
MacGregor put pop tops on many of its trailerables
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
- Best Marine Electronics & Technology
11 Best Pocket Cruiser Sailboats to Fit a Budget
- By Cruising World Staff
- Updated: August 9, 2021
Looking for a trailerable pocket cruiser that offers that liveaboard feeling? This list features 11 small sailboats with cabins that have the amenities often found on larger vessels. They may not be ocean crossing vessels, but they’re certainly capable of handling big bays and open waters.
What is a pocket cruiser? It’s a small trailerable sailboat, typically under 30 feet in length, that’s ideal for cruising big lakes, bays, coastal ocean waters, and occasionally bluewater cruising. Pocket cruisers are usually more affordable, compact, and offer a level of comfort that’s comparable to bigger liveaboards.
Small cruising sailboats are appealing for many reasons, but if you’re like most of us, you want to maintain a certain level of comfort while on the water. We took a poll and these are what we found to be the best cruising sailboats under 30 feet.
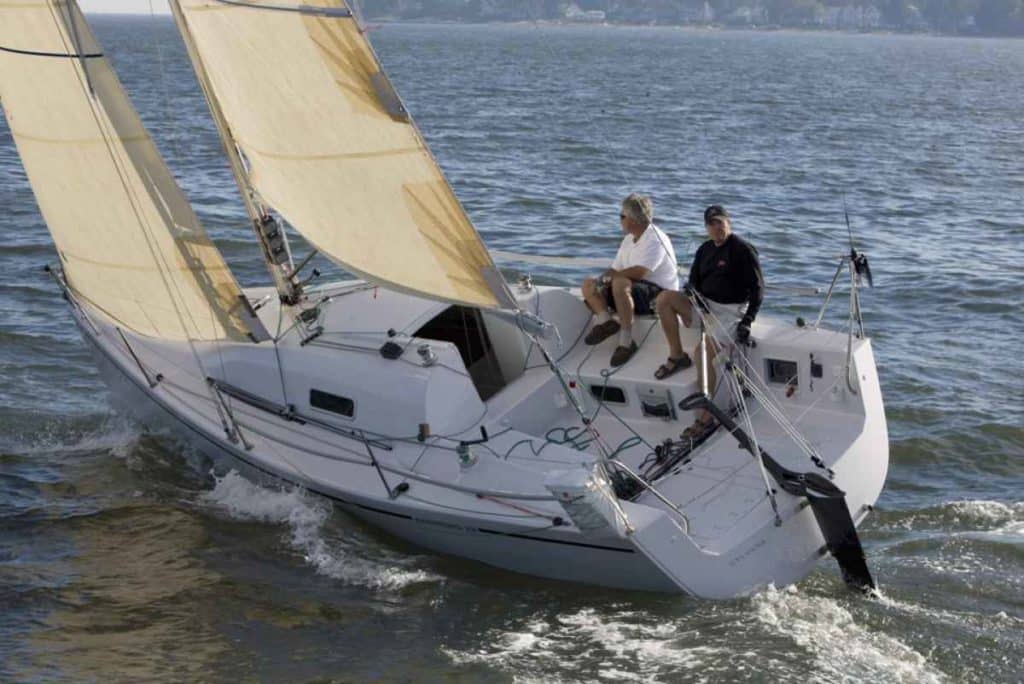

Open and airy below deck, the Andrews 28 doesn’t sacrifice comfort for speed. Designed by Alan Andrews, the Southern California naval architect renowned for his light, fast raceboats, this 28-footer will certainly appeal to the cruiser who also enjoys a little club racing. Sporting a total of 6 berths, a galley, head and nav area, you might forget you are on a boat small enough to be easily trailered. The retractable keel allows the Andrews 28 to be easily launched and hauled and ensures it’s as comfortable as a daysailer as it is a racer. Click here to read more about the Andrews28.
Beneteau First 20
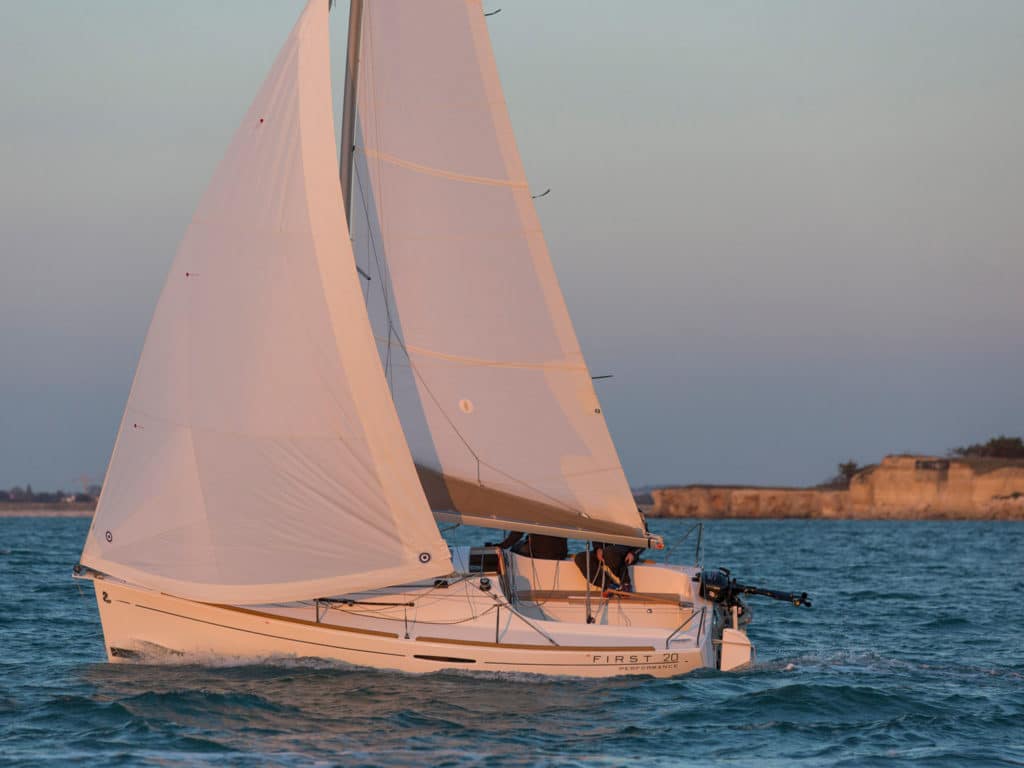

Small sailboat with a cabin? Check! Fun to sail? Modern design? Capable of flying a spinnaker? Check! Check! Check! The Finot-Conq-designed Beneteau First 20, which replaced the popular Beneteau first 211 nearly a decade ago now, is a sporty-but-stable pocket cruiser suitable for newcomers to the sport who are eager to learn their chops before moving up to a bigger boat or for old salts looking to downsize to a trailerable design. The boat features twin rudders, a lifting keel, and a surprisingly roomy interior with bunks for four. Click here to read more about the Beneteau First 20 .
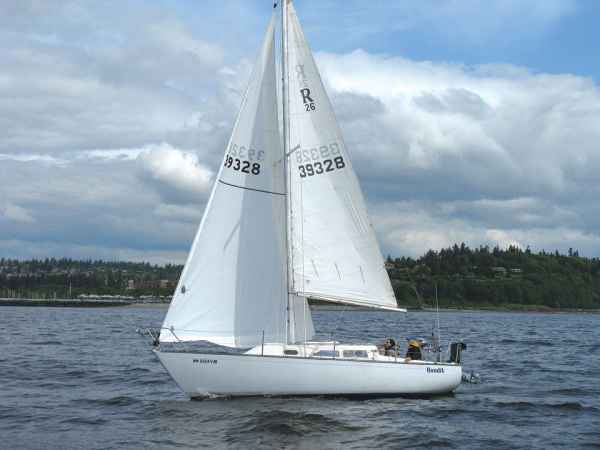

Conceived as a way to bridge the gap between a safe, comfortable, family cruiser and a competitive racer, Gary Mull’s Ranger 26 does exactly as it was designed to. Undeniably fast, (one won the 1970 IOR North American Half-Ton Cup) the boat sails as well as it looks. However speed isn’t the Ranger’s only strong-suit, with over 7 feet of cockpit there’s plenty of room for socializing after an evening of racing. The Ranger 26 sports a nice balance of freeboard and cabin height ensuring that a handsome profile wasn’t sacrificed for standing headroom. Click here to read more about the Ranger 26.
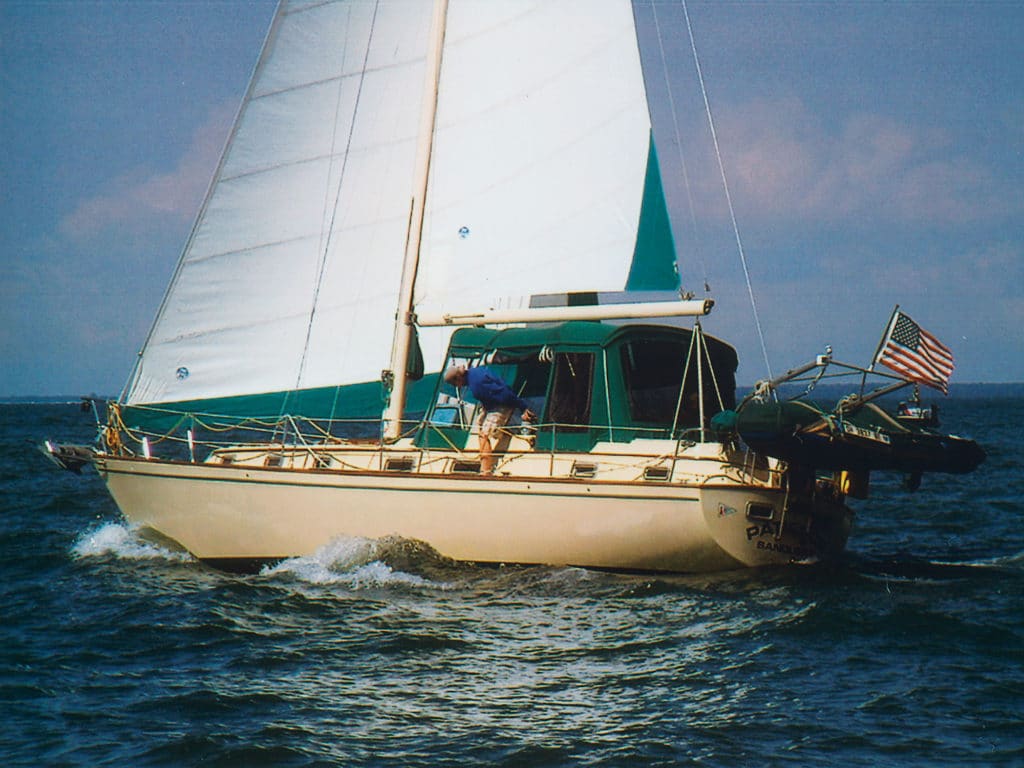

Catboats were once a common site in coastal waters, where they sailed the shallow bays as fishing or work boats. Their large single and often gaff-rigged sail provided plenty of power, and a centerboard made them well-suited for the thin waters they frequently encountered. In the late 1970s, Canadian builder Hinterhoeller introduced the Nonsuch 30, a fiberglass variation of the catboat design, with a modern Marconi sail flown on a stayless mast, and a keel instead of a centerboard. The boat’s wide beam made room below for a spacious interior, and the design caught on quickly with cruising sailors looking for a small bluewater sailboat. Click here to read more about the Nonsuch 30 .

Debuted in 1971 in California, the Newport 27 was an instant success on the local racing scene. For a modest 27-footer, the Newport 27 has an unusually spacious interrior with over 6 feet of standing headroom. With 4 berths, a table, nav station, head and galley the Newport 27 has all the amenities you might find in a much bigger boat, all in a compact package. While quick in light air, the drawback of the tiller steering becomes apparent with increasing breeze and weather helm often leading to shortening sail early. Click here to read more about the Newport 27.

First splashed in 1969, the Balboa 26 continues to enjoy a strong following among budget-minded cruisers. Built sturdy and heavy, all of the boat’s stress points are reinforced. The spacious cockpit comfortably seats 4 and is self bailing, ensuring that sailors stay dry. While only 26 feet, the Balboa still has room for a double berth, galley with stove and freshwater pump, and an optional marine head or V-berth. The Balboa has the ability to sleep five, though the most comfortable number is two or three. Under sail, the Balboa is fast and maneuverable, but may prove a handful in heavy breeze as weather helm increases. Click here to read more about the Balboa 26.
Cape Dory 28

While the sleek lines and the teak accents of the Cape Dory 28 may grab the eye, it is the performance of the boat that make it unique. The Cape Dory comes with all amenities that you might need available, including a V-berth, 2 settees, and a head. Safe, sound and comfortable as a cruiser it is still capable of speed. Quick in light wind and sturdy and capable in heavy air, it is off the wind where the Cape Dory 28 shines with a balanced helm and the ability to cut through chop and still tack perfectly. Click here to read more about the Cape Dory 28.
Islander Bahama 28

On top of being a real eye-catcher, the Islander Bahama 28, with its 5-foot-6-inch draft and 3,300 pounds of ballast, sails beautifully, tracks well, and responds quickly to the helm. Inspired by the International Offshore Rule, it is unusually wide, offering stability in breeze without sacrificing the sheer and lines that make it so attractive. Below deck, the Islander Bahama 28 comes standard with plenty of berths and storage space and a galley complete with stove, icebox and sink. Click here to read more about the Islander Bahama 28.

Much like its older sibling, the S2 8.6 still holds its contemporary style, despite its 1983 introduction. Like all other S2 Yachts, the 8.6 is recognized for the quality craftsmanship that allows the boat to hold up today.The S2 8.6 is a very comfortable and easily managed coastal cruiser and club racer. It’s relatively stiff, its helm feels balanced, and it tracks well. On most points of sail, it compares favorably with other boats of similar size and type. Click here to read more about the S2 8.6.
Contessa 26

When the Contessa 26 was released in 1965, it immediately proved itself to be a strong, seaworthy vessel. The Contessa has continued to prove itself throughout its lifetime, being the boat of choice for two solo circumnavigations under the age of 21. While upwind performance leaves some wanting, the boat is sturdy and can carry full sail in up to 20 knots of breeze. Suited more for single-handing, the Contessa lacks standing headroom and the accommodations are sparse. Nonetheless, the Contessa 26 performs well as a daysailer with guests aboard. Click here to read more about the Contessa 26.

The Hunter 27 perfectly encompasses the pocket cruiser ideal. Even if you don’t want a big boat, you can still have big boat amenities. With the generously spacious layout, wheel steering and a walkthrough transom the Hunter feels much larger than 27 feet. Step below deck and any doubts you had that the Hunter was secretly a big boat will be gone. The amenities below are endless; a full galley including stove, microwave and cooler, head with full shower, several berths and not to mention a saloon with seating for 6. The Hunter 27 has reset the benchmark for 27-footers. Click here to read more about the Hunter 27.
- More: 21 - 30 ft , Boat Gallery , monohull , Sailboat Reviews , Sailboats , used boat guide
- More Sailboats

Balance 442 “Lasai” Set to Debut
Sailboat Review: Tartan 455

Meet the Bali 5.8

Celebrating a Classic

Kirsten Neuschäfer Receives CCA Blue Water Medal

2024 Regata del Sol al Sol Registration Closing Soon

US Sailing Honors Bob Johnstone

Bitter End Expands Watersports Program
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding

What’s the deal with Centerboards?
Most of you who have followed our journey for some time are familiar with our somewhat infamous centerboard issue, where we ran aground in the Illinois river in 8′ of water when our boat should only draw 4′ . This was the most dramatic and expensive example of the issues we’ve had with the centerboard thus far, but that’s not to say it’s been the only trouble our centerboard has caused us.
In this week’s video, This Little Thing could SINK our Boat , we’re highlighting another pain point and some of the additional maintenance that comes along with having a pivoting centerboard. We’d like to take this opportunity to talk a little bit about the pros and cons of the centerboard system and shed some light on how we’ve been using it with real life examples.
Sailors love to talk shop. It seems everyone has an opinion when it comes to boats, and if you’re not too careful, it can lead lead to hours upon hours of enjoyable and sometimes educational discussion. Invariably anytime we get beyond the general pleasantries of “She’s a beaut!” or “What’s the length?” we know with more and more certainty that we’re talking with a sailor. As the questions get more specific e.g. “How much fuel do you carry?” or “How tall is the mast?” we will eventually hit this question: “What’s the draft?”
Up until this point, it’s only a Q&A session, but as soon as we divulge the boat has a centerboard — and that with the board up we draw between 4-4.5′ but when it’s down closer to 8′ — the discussion will turn one of three ways:
- The questioner wasn’t quite prepared for that answer and is dumbstruck because they didn’t know as much about boats as they thought they did, and were unaware of the centerboard concept or are unaware a boat of our size could have a centerboard.
- The questioner’s face lights up with a twinkle in their eye and responds with something like: “A perfect Bahamas boat, nice!”
- The questioner’s face scrunches up with terror in their eyes: “Why on god’s green earth would you want to maintain a system like that!”
And after three years of owning, maintaining and traveling aboard a boat with a centerboard, we’ve been in each of these 3 camps at one point or another. Let’s dive in and tackle each point of view.

What is a centerboard on a sailboat?
A centerboard is a retractable appendage that pivots in and out of a slot (centerboard trunk) in the hull/keel of a sailboat. Having the ability to raise and lower the centerboard allows the the boat to operate in shallow waters when lifted, while maintaining good upwind sailing characteristics with the centerboard down. Similarly, lifting the centerboard reduces the wetted surface area, resulting in lower drag while sailing downwind. This combination of characteristics makes it possible to build a safe, seaworthy boat, capable of easily sailing upwind off a lee shore, while still allowing the boat to tuck way up into shallow anchorages when necessary.

When first looking for our sailboat , weren’t specifically looking for a boat with a centerboard. It wasn’t on any “avoid ” list of ours either; it just wasn’t on our radar. So when we first saw the boat online and noticed it had a centerboard, we were pretty ambivalent about it.
Is that like a Swing Keel?
Many people have incorrectly referred to our boat as having a swing keel, and for good reason as they are quite similar on the surface. Before finding our boat, we were aware of other boats with swing keels (specifically Southerly Yachts popularized by “ Distant Shores “) and some of their unique benefits. While the swing keel is similar on the surface, it’s an entirely different animal from our centerboard. They both feature large underwater wing-shaped appendages that pivot from underneath the boat to provide additional wetted surface area to reduce leeway and increase lift for sailing upwind. The main difference is that in a swing keel boat the pivoting appendage is actually the keel. In cruising boats, swing keels weigh several thousand pounds, while centerboards weigh a couple hundred. Thus, a swing keel also contains a large part of the boat’s ballast, so the position of the keel can have a substantial effect on the stability and motion of the boat. Additionally, when retracted all the way up into the hull, the boat can be left to dry out while sitting upright in the sand — pretty cool.

Distant Shores II, a Southerly 480
The flip side is this: In the fully retracted position, the keel needs somewhere to go — which takes up interior volume of the boat. Additionally, moving an extremely large and heavily ballasted keel up and down requires some serious mechanical gear, and unless the swing keel is lowered to some extent, there is nothing counteracting the force of the sails to prevent leeway and the boat will not sail to windward.
Whereas with our boat, in addition to the centerboard, we have a shoal draft keel (which actually doubles as a housing for the centerboard). Even without the centerboard down the boat will still sail to windward. Dropping the centerboard only serves to increase the pointing ability and windward performance. The centerboard does not contribute meaningfully to the ballast of the boat (as it weighs about 200lbs), so its effects on stability in the up or down position are muted. It is designed primarily as a hydrofoil to prevent leeway when sailing upwind and is significantly lighter than its swing keel cousin. Lastly, by retracting into the keel instead of all the way into the hull it does not have any negative effect on the interior volume of the boat.
What are the benefits of having a centerboard on a sailboat?
Besides increased upwind sailing performance, the major benefit of a boat with a centerboard is a shallow draft. For our needs navigating the inland river system, sailing the notoriously shallow Gulf of Mexico , and cruising Bahamaian waters, these are fantastic qualities to have in a boat.
The inland river system has a controlled depth of no less than 9′ in the channel from Chicago to Mobile, Alabama, but most of the channel is significantly deeper than that. However , s earching for marinas and anchorages for the night where you have to exit the channel means the depths start changing quickly. With our shoal draft keel we were able to sneak into a number of marinas with sub 5′ depth at their entrance or at the dock that would’ve been impossible in many other sailboats of our size. Even in Mobile we ran aground twice while moving through the marina to get to our dock.

In the Bahamas we find ourselves anchoring way up towards shore with the catamarans instead of much further out near the monohulls. Yet when it comes time to sail to windward, we’re able to drop the board and point much higher than we otherwise would’ve been able to with the shoal draft keel alone. This can shave miles off long passages and minimizes the number of tacks required in a tight channel.
Additionally, dropping the centerboard just a little bit can give us much better handling in tight quarters, as it prevents the bow from falling off downwind when trying to dock in strong crosswinds.
This all sounds pretty good, right? Why would you not want a boat with a centerboard?
What are the issues with centerboards?
With all the apparent benefits, you’d think the centerboard would be a no-brainer. And if you’re purely concerned with performance, then absolutely, it is. However, the centerboard represents an added layer of complexity that just isn’t absolutely necessary for the operation of the boat. Along with this added complexity comes additional maintenance to ensure the system continues operating normally, and even then, when everything is operating correctly, the maintenance itself can create some stressful situations. Below are a few of the negatives of having a centerboard we’ve discovered so far:
General Maintenance

Our centerboard is raised and lowered via a control line, or centerboard pennant. The line is always underwater inside the centerboard trunk, and is incredibly difficult to inspect. The line exits the boat below the waterline meaning we have an unprotected thru-hull without a seacock to close, should there be a leak. The through-hull is connected to a hose and the hose connects to a conduit in the mast that rises well above the waterline.

The centerboard line runs through this conduit and then exits the mast through a sheave at the deck level. It then runs through a turning block and clutch/winch to lock it off. Each of these items require some level of maintenance and/or at least inspection on a regular basis. These are all fairly simple parts, and the system is quite well-designed. However you can probably already imagine some of the issues…
Stepping & unstepping the mast is more difficult

Because the line runs through the mast, stepping and unstepping the mast requires a few more steps to ensure everything goes smoothly. When unstepping our mast, we need to temporarily slacken the centerboard pennant to allow the mast to be raised out of the boat. To ensure we can run the line back through the mast we need to run a messenger line in the mast to be able to retrieve it again when re-stepping.
When re-stepping the mast, extra care needs to be taken to ensure the mast doesn’t get hung up on the centerboard pennant or the conduit it runs through. We’ve heard of other boats stepping their mast only to realize later that they pinched their centerboard control line.
Naturally (or accidentally) slackening the centerboard pennant allows the centerboard to drop, increasing our draft to 8′, unless it’s secured in some other way. We did this at the start of our river trip by securing a line athwartship from each of the midship cleats to act as a set of suspenders to keep the centerboard pinned up inside the trunk. Unfortunately this wasn’t tight enough and slipped off the centerboard allowing it to drop into the fully-down position. This set us back a few days as we fabricated a much stronger system to secure the centerboard line using an exit sheave at the mast partners.

The centerboard trunk is difficult to clean & paint
While our boat was hauled out, we repainted the bottom with CopperCoat . However we were unable to paint the centerboard or the trunk with the same. Had we known better, we would’ve pulled the centerboard immediately after hoisting the boat out of the water with the travel lift. But since it was our first time hauling the boat for storage, we didn’t realize that once we were moved to the hydraulic trailer which the yard used to position boats, we would not be able to get enough height to drop the board and remove it.

We did hang in the slings over the weekend prior to splashing, which gave us time to get underneath the boat with the board down to clean the centerboard trunk and repaint the board and trunk with ablative bottom paint. But we couldn’t repaint with CopperCoat because of how long it needs to dry before being splashed.
The centerboard pivot point is difficult to inspect

The centerboard pivots on a large stainless steel hinge. This plate is bolted into the keel of the boat and has a large pin that runs through the centerboard allowing it to pivot around this point. There is also a heavy duty stainless eye on the backside of the centerboard that the pennant line connects to. Both of which are always submerged in water, and while they are stainless, stainless corrodes in environments lacking oxygen. So these parts need to be inspected on a regular basis, and this means removal of the entire board, which is easier said than done.

The centerboard can get stuck in the up or down position
The centerboard is designed to pivot up and down in the trunk with fairly small tolerances on either side. Any more space than what is needed to get the board out, and it will interfere with the flow of water over the hull, increasing water resistance and drag. Any extra space will also allow sea life to make its way up into the trunk. Thankfully it’s very dark up in there, there isn’t much water flow carrying nutrients into that space, and we have been diligent about keeping it clean. While we haven’t run into this particular issue yet, we’ve heard of some boats that have had so much growth in the trunk that they can’t get the board to move.
While, we haven’t had our board stuck in the up position, but we have had the board stuck down. The centerboard is a hydrofoil, so the leading edge is a bit wider than the trailing edge, much like an airplane wing. And whereas dagger board trunks (where the board drops in vertically) can be contoured to follow the shape of the board almost exactly, our centerboard trunk is rectangular, as it needs to accomodate the width of the leading edge moving all the way through it. This means the trailing edge of the board (which is on the top when in the retracted position) leaves a lot of extra space between it and the trunk, creating a wedge shape… Maybe you can see where I’m going with this…
A perfect storm scenario can brew under just the right conditions. Imagine for a moment you are loosening the centerboard pennant line to drop the board down, but for one reason or another, the sideways pressure of the water against the board when sailing upwind, growth in the centerboard trunk, stops or slows the dropping motion of board — perhaps it even gets pushed back up slightly as the boat pitches forward and backward in a large wave. You, as the unsuspecting crewman, continue to slacken the line thinking the board is dropping, but in reality what is happening is the line comes to rest on the top of the board, and because of the wedge-shaped trailing edge, the line slips down ever so slightly between the board and the trunk, and gets trapped . Once there it wedges in between the board and the trunk making it extremely difficult to move.
This has happened to us twice. The first was an easy fix, which occurred during a daysail after purchasing the boat. We could’ve easily addressed it without getting into the water, but it was hot, the water was clear, and despite being warned about this particular scenario, I didn’t have a good visualization of what was happening and wanted to see it for myself.

There is actually a built-in mediator of this problem which saved us considerable effort: A short section of exhaust hose with a diameter that almost exactly matches the width of the centerboard trunk serves as a conduit for the last 18″ of line of the centerboard. This prevents the slacked line from getting wedged in too tightly and allowed us to break it free with a tiny bit of force.
The second time however, was much worse, and is covered in detail in Episode 24 . We were in the Illinois Sanitary & Ship Canal, in incredibly disgusting water with no visibility, and because we hadn’t secured the centerboard line properly, the board unbeknownst to us dropped all the way down, and under zero tension actually hung forward of its pivot point. In this position, the geometry for pulling it back up is all out of whack. With the protective hose completely out of the trunk, pulling the control line, only wedging it further in between the trunk and the centerboard.
So is a centerboard actually worth it?
While we’ve been both super happy we have a centerboard and a shallow draft, we have also been exasperated by the extra maintenance, sometimes wishing we had a “normal keel.” But at this point we’ve circled back around to mostly ambivalent. The maintenance while sometimes stressful is all part of owning a boat and the benefit of having a shallow draft when needed are immeasurable.
In reality, we probably only use the centerboard 15-20% of the time we’re actually sailing. If you think about the benefits discussed above, it’s really only necessary in moderate upwind scenarios, which we often avoid anyway. It’s just way more comfortable sailing downwind! We’ve also found in light wind conditions the extra drag created by the centerboard outweighs the pointing ability it generates, so we leave the board up. To top it all off, when we’re not actually sailing (which is most of the time when the boat is at the dock, at anchor, or hauled out for storage) the centerboard is always in the retracted position. For the actual lifespan of the boat, the centerboard is in the down position much less than 10% of the time.
On more than one occasion I’ve thought that I’d rather have a keel full of lead where the centerboard trunk exists now. It would give us added stability 100% of the time, we’d have no additional maintenance, and we’d only miss out on the benefits 10% of the time. However that 10% of the time could potentially make all the difference if we really needed to get off a lee shore. Whenever we are using the board — i.e. upwind especially in a narrow channel or maneuvering under power in tight quarters — we’re often saying to each other “Thank goodness for the centerboard!”
In the end, as with everything on a boat, it’s a trade-off. There’ll always be pros and cons of every design decision. There isn’t one right design for every boat or every boat owner. Overall, we’re happy with our Tartan37c and would not pretend to know more than the S&S design team who dedicated their lives to designing these spectacular boats.
Let us know what you think!
Do you have any experience with a centerboard? Did we miss anything? We’d love your feedback.
This ONE LITTLE THING could SINK our Boat
How to Run Aground in 8’ of Water When You Only Draw 4’
About the Author: Kirk

Related Posts

Building a Sailrite 3-Bow Bimini

Coppercoat as a DIY Project

Is Coppercoat the Best Antifouling for Your Boat?
21 comments.
We had a centerboard on our very first keelboat, a William Tripp designed Polaris 26. Sailing in Michigan on Lake St. Clair, it was a great feature as we could gunk-hole into all kinds of places. Our horror story was that we once forgot we had it down when sailing into a shallow bay and we touched and pivoted under a pretty brisk wind. That was enough to slightly torque and twist the centerboard foil such that it would only retract about 1/3 the way up before getting jammed in the trunk. We had to sail the rest of the season that way until we were hauled out for winter and the yard could bend it back flat. Our subsequent three boats have all been shoal draft versions, which opens up a whole ‘nother discussion of the merits of shoal keel versus deep keel on the same boat model. Fortunately, we switched our home port to Charlevoix 20 years ago, where sailing depths are almost never an issue on Lake Charlevoix/Lake Michigan/Lake Huron. As you said, everything is a compromise with sailboat design. We were glad we had the shoal draft when we delivered our current boat from Annapolis to Charlevoix last year. We draw 6′-6″ and we bottomed out three or four times in the Erie Canal (supposedly a 9′ controlling depth, but who’s counting?). The deep keel version of our boat draws 7′-6″, so we would have never made it back to the Great Lakes. We are eventually going to be bringing this boat back out to the Atlantic permanently when we retire and plan to cruise the Bahamas and the Caribbean, so even the 6’-6″ shoal draft is going to be less than ideal. But hey, if Delos can do it, hopefully we can. Best to you and Lauren.
Jeff W SV Échappé Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 54DS Charlevoix, MI

Thanks Jeff, 6’6″ is the shoal draft?! We were so thankful for our 4’6″ draft in the Abacos. We could anchor in so many great places!
Yeah as usual your videos and blogs are so helpfull to use on my tartan too, you guys are my teachers, when I bought the boat I had the problem with growth inside the trunk, I left the line loose by unexperience and in a sail trip it went down with the shocking waves, I didn’t know it happened and then on another short trip we ran aground because I didn’t know the keel was down. But after that it got cleaned and all works perfect, thanks!!!
Good to hear! Rest assured, if you’ve done it, we probably have as well!
I had many maintenance issues with the centerboard system on my T 37. I managed to drift into shoal water while anchored with the centerboard half down – a position I often used to reduce roll. This resulted in breaking the lower 3/4 of the centerboard off. I recovered it and on next haul out, epoxied it back together and reinstalled it. Next haul out, the SS pivot assembly had a problem in the flange that received the pin – had to be re-fabricated. A couple of years later (I went way too long without a haul out from this point) the bolts holding the pivot assembly became loose and I was unable to lower the centerboard as the pennant was the only thing keeping it in the boat. Sailing with it up didn’t seem problematic.
It all sounds pretty familiar. I think we have a love/hate relationship with ours. 😉
Hello and love your information, site, etc. Your trips are completely unique to me and the blogs and video are welcome adventures. Keep on cruising and writing. Please.
Centerboards: I was raised sailing all manner of boats with them. We had a 48 Alden yawl with a centerboard. I think it went down twice! We cruised Cape Cod, the US East Coast into the Keys, and Bahamas in that boat and all the reasons to have a board were apparent. I was a kid then and wondered why anyone would build a boat without a centerboard.
Then, I started racing and fell in love with deep draft. Our boat now is 32 feet long and draws 6 feet. Oh my, do we go to windward! We have raced a T37 (same handicap) and we out point him but he out foots us and usually finishes ahead. Cruising is not about hours of close hauled sailing. I get it now!
In our harbor and on the next mooring is the referenced T37 that I am coming to love. Pretty boat and shallow draft. Back to my youthful exuberance for a centerboard. If you guys find you way up to the Cape, I hope we see you. Look into Stage Harbor.
Norm Martin Averisera
Hi Norm, thank you for sharing your story. It’s interesting how some boats just reach out and speak to certain people. All the best!
I have a membership in a sailing club with a collection of Capri 22’s that are not all identical. We have weekly races with them, where you show up and draw boat names out of a hat. One of them has a shoal draft keel, it is always the least favorite draw. Typically, while you might be able to point the bow upwind, it’s moving sideways far more than they other boats (regular keel versions of the same boat). But every now and then the wind is just right, and she’ll clean up, just own every race, but this is rare, relies on just right wind (5-10 knots) and tide conditions that allow her to get speed without being pushed leeward. Downwind, she also has a slightly shorter mast (several others also have shorter masts), but still usually keeps up. Possibly an advantage, but not sure. A centerboard would clearly help her upwind in some conditions. But it’s often going to be hard to really see those conditions without head to head comparisons and if your not caring you can just start the engine.
Sounds about right. That shoal draft boat likely does well on downwind legs given there is less surface area under the water.
We’re definitely not the fastest boat to windward, but we’re not racing. There some shoal draft boats that simply can’t sail upwind at all when the wind picks up. They have too much windage and not enough leverage on the water. We will hit hull speed at 30 degrees apparent in 15 knots apparent wind, which I’m quite happy with 🙂 All the best!
A daggerboard is a centerboard, just as one is an integer and a whole number. If the daggerboard is off center it is a leeboard.
Is that so? I always heard it as a centerboard pivots and a daggerboard slides up and down. But I suppose your explanation makes sense!
You guy’s are such centerboard rookies, but then again, most sailors are. I cruise the extremely shallow waters of the Southeast coast of the US and have always sailed centerboard boats for over 40 years, In fact my present boat is a Presto 36, a 18,000 displacement, ketch rigged, true or pure centerboarder, designed in 1884 by Ralph Middleton Munroe. I have no external keel at all, except for a 9″ X 6″X 12′ long lead grounding shoe, designed for “taking the Ground upright”. My draft, board up is 2′-6″ and approx.. 5′-6″ ” board down. The board weights approx. 400 lbs. My centerboard pendant, a 3/8″ super synthetic line runs upwards from the aft end of the centerboard trunk, to the cabin top via 1-1/4″ SS tube and is attached when it exits the top of the cabin, to a simple 6 to 1 tackle to help raise and lower the board. My centerboard trunk runs almost the entire length of the main cabin and has a 2″ dia. hole in it’s aft end. That hole and a short length of broom handle are extremely helpful for for coaxing a resistant board into going down as needed. I have spent many days pleasantly aground on a convenient sand bar, for recreation or maintenance needs and many a night secure in the knowledge, that no matter how busy the surrounding water are, I’m freed from the worries of getting “run” down in the night. Incidentally, I oft use the board along with my mizzen in assisting in self-steering. Never needed any auto-pilot. Up wind, she’s a drag, but any other course, with her sheets eased, she simply can’t be caught..
My wife and I have a Bristol 35.5 with a centerboard. Our installation is much simpler than the one Tartan came up with – I was very surprised when I saw that yours comes up though your mast. Ours is on a wire winch on the cabin house that runs through sealed pipes over sheaves to the board. I’d say that the vast majority of the issues you’ve had with your board are due to that somewhat quirky design. That said, I’ve always loved the look of the Tartan, and you guys have definitely made fantastic improvements.
My wife and I thoroughly enjoy your channel and following your adventures. Keep them coming!
It is a bit of a quirky system, but running it through the mast is kind of a neat way to hide the control line, which needs to enter and exit the hull and deck. It does present some challenges, but it’s neat out of the box thinking. As you know everything on the boat is a tradeoff, and overall we’re extremely happy with the boat. Thank you for watching!
Hi, how confident are you with the centre board in heavy weather … blue water … hove-to? We are going to look at a 47′ sloop with one tomorrow. I love our current smaller steel boat with a full keel but who knows …
Hi Melissa, Tartan 37s have sailed in every ocean on the planet, there have been multiple circumnavigations. As long as we keep the boat properly maintained, I have confidence in it. I don’t know what type of boat you’re looking at or what type of sailing it was designed for, but I don’t think there is anything fundamentally wrong with a centerboard. Good luck!
We have a 79 Irwin 39 with shoal draft an centerboard, the pennant is mid deck and runs through the sole to cabin top” stripper pole” that is attached to the galley and also serves as handhold under way, the pivot is a SS pin that runs abeam and is puttied over, I need to remove this soon as there is a bit more play in this joint than I’m comfortable with, The boat is very tender and we are contemplating the best way to add ballast to the keel as it heels very quickly and carries a lot of sail. The centerboard isn’t very effective when she’s on her ear for limiting leeway losses . She draws 4’3″ up and 9’6″ down, I never thought about partially dropping to improve turning so am excited to try that when maneuvering around docks. I’m hoping adding some lead will make it less tender and will be pursuing this after haulout.

Peter, sounds like you’re at the beginning of a fun adventure learning more about your centerboard and how it can improve the handling of your boat. It was a fun learning journey for us, and we really began to respect the purpose and design of the CB.
I have a 1966 Morgan 34. The bronze centerboard has deteriatiated beyond repair. Especially in the hinge pin and pennant attachment area Draft board up 3 1/2 ft, board down about 7 ft. Bronze board is at least 250 lbs, about 5 ft long, and is a great template
1..Any guidance on where I can get a replacement , perhaps Foss Foam?
2. Is the weight important to proper deployment. Sure cranks hard..a challenge for an old fart to raise
Hi Capt Ron, sorry to hear of your CB woes. Unfortunately I don’t have any sources for replacement. Weight is important, the heavier the better, to an extent. You obviously want to be able to lift/lower it under your own power. At a minimum you need some weight at the bottom of the CB to prevent it from floating and get it to drop down and stay down while underway. But the more weight you can drop down there the better.
Leave A Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

What Is a Swing Keel?

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
August 30, 2022
Swing keels are a robust and useful alternative to centerboards, and they’re common on variable draft sailboats.
Swing keels are retractable keels that are hinged in the front and swing into a slot called a trunk. Sailors lift and lower the keel with a crank, pulley, or hydraulic system. Sailboats with swing keels can reduce their draft for shallow water sailing or to make them fit on a trailer.
In this article, we’ll show you everything you need to know about swing keels and the sailboats that use them. We’ll go over the benefits and drawbacks of swing keel designs, compare them to centerboards, and cover the different variations you’re likely to find on common sailboats.
We sourced the information used in this article from sailboat design guides, sailboat plans, and from the sailing community.
Table of contents
What are Swing Keels For?
Swing keels are commonly outfitted on trailerable sailboats that need low clearance. These vessels are usually longer than 20 feet and would normally have a fixed keel if they weren’t designed to be towed.
Swing keels are used in applications where centerboards are cumbersome or have insufficient ballast. Also, a swing keel allows additional ballast to be placed underneath the hull and around the keel trunk.
What is a Keel Trunk?
A keel trunk is a simple rectangular box located on the bottom of the hull. The box, which is open on the bottom and closed on the top, houses the swing keel and its hinge mechanism. The keel retracts into and out from the keel trunk.
The keel trunk can be located inside or outside of the hull. Some vessels have an external keel trunk that protrudes a few inches from the bottom of the hull and usually contains ballast for stability. Most swing keel sailboats have a recessed keel trunk, which is flush with the bottom of the hull.
How a Swing Keel Works
Swing keels, also known as lifting keels, are simple. They act a lot like a lever. The keel is contained in a trunk-mounted to the hull with a pin, which serves as a hinge. The keel is raised and lowered by a system of ropes and pulleys or by a hydraulic system.
Some swing keels are retracted into the trunk using a crank. This system is common on some Catalina sailboats and has proven to be very reliable. These systems usually use a ratcheting pulley which can be locked in one direction for lifting and lowering.
The weight of the keel keeps it in the lowered position, but some vessels have a simple locking device to keep the keel in the down position. When raised, the keel or the raising mechanism is locked securely into place.
Swing Keel vs. Centerboard
Swing keels and centerboards are not the same, but they share some characteristics.
Centerboards are distinguishable from fin keels because, unlike fixed fin keels, centerboards can be retracted into the hull. Swing keels may appear like fin keels from the bottom, but they also retract into the hull.
So then, how are they different from centerboards? Unlike centerboards, which must be lifted vertically out of the centerboard trunk, swing keels hang on a hinge and fold into the hull. Hence, they ‘swing’ instead of raise.
Benefits of Swing Keels
Swing keels have several distinct advantages over centerboards. Chiefly, swing keels don’t require a massive trunk in the center of the cabin or cockpit.
Most swing keels retract into a trunk located below the hull. Others retract into a trunk under the deck, and some require a small amount of cabin space.
Swing keels never need to be removed or lifted into the boat. Additionally, it’s physically easier to raise a swing keel. This is because the keel distributes some of its weight to the hinge, and lifting it is easier thanks to the physics of levers.
Additionally, swing keel trunks are usually sealed. This is good for a number of reasons—especially in rough weather. Water rarely floods a boat through the centerboard trunk.
But lifting out a centerboard can make a mess, and a pitching and rolling boat could allow water in through an open centerboard trunk. Swing keels don’t suffer from this issue, as the only hole they have is for the rope and block system used to lift and lower the keel.
Drawbacks of Swing Keels
Swing keels have a few notable drawbacks. For one, they’re not as strong or robust as fixed keels. They don’t provide the stability of a full or semi-displacement keel, and they don’t have the windward performance of bilge or fin keels.
Additionally, these keels still require a trunk, which can still take up cabin space on some models. The systems used to raise and lower a swing keel are prone to failure and add complexity where it otherwise wouldn’t exist.
Are Swing Keels Strong?
Swing keels are not as strong as fixed keels. This is because they’re usually smaller and lose rigidity at the hinge. Usually, the addition of mechanical complexity reduces the strength of a system, and that rule applies to swing keels.
A fixed keel can be mounted to a boat with numerous rigid bolts, whereas a swing keel is mounted to a pin and adds a level of complexity. That said, swing keels have an advantage in one respect, which we’ll cover next.
Advantages of Swing Keels in Shallow Water
Most swing keels swing down to the front, meaning their hinge is mounted forward. This is advantageous in shallow water, as it allows the keel to swing up into the boat instead of snapping off should the boat run aground. It’s like an automatic failsafe.
However, some swing keels lock into place in the lowered position. Sailboat owners should always proceed with caution in shallow water and lift the keel if the water isn’t deep enough.
Can You Beach a Sailboat with a Swing Keel?
One of the advantages of having a swing keel is that you can easily beach the boat. All you have to do is build up a bit of momentum, retract the keel, and head for the beach.
Sailboats with swing keels are particularly popular for island hopping due to their transformable flat bottoms. They can also utilize more seaworthy hull shapes than other shallow-draft vessels, thanks to their long retractable keels.
However, some sailboats with swing keels cannot be beached. If the keel retracts fully into the hull, and your rudder does too, you’re in luck. But if you have a fixed rudder, a prop, or any protrusion of the keel under the hull, you have to proceed with caution.
What Sailboats Have Swing Keels?
Dozens of different sailboat brands and models have utilized swing keel systems at some point. One notable and extremely popular example is the famous Catalina 22. The Catalina 22 is a trailerable coastal cruiser with a masthead sloop rig and a typical swing keel.
This small cruiser has a spacious cabin thanks to its keel, which retracts into a hidden trunk. The raising and lowering of the keel is performed by a pulley system and hides out of the way when not in use. The Catalina 22 keel is made of heavy metal.
The Catalina 22 is an example of a sailboat with a semi-hidden swing keel. The trunk only partially covers the keel, as the boat is designed for trailering—beaching abilities were not considered key in its development.
As a result, the keel swings up and still protrudes out from the bottom of the hull. But the swinging design gives the vessel a variable draft and a much deeper keel for stability. The boat otherwise wouldn’t have good handling characteristics if it weren’t for the swing keel.
Not all Catalina 22 sailboats came with a swing keel, but many of them did. It’s the most common boat of its type and a great example of the benefits of swing keels on smaller cruising sailboats.
Do Large Sailboats Have Swing Keels?
Large sailboats aren’t known for having any sort of retractable keel system. However, many ultra-modern big cruising vessels utilize some version of a retractable keel for performance and shallow water operations.
New sailboats that utilize swing keels usually do so for increasing hydrodynamic performance at high speeds and for reducing the draft of an otherwise deep keel.
For example, a vessel with a long 8-foot keel can reduce its draft to 4 feet or so when navigating a harbor and then extend the keel to increase performance offshore.
However, most large sailboats use fixed keels for strength, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. This is also because most designers simply don’t bother with complex keel systems on larger cruising boats.
What are Swing Keels Made Of?
Swing keels are usually made of strong materials like steel. They’re extremely heavy, as they function as part of the sailboat’s ballast. Swing keels are typically made of a solid steel plate between one and one and one-half inches thick.
Some swing keels on high-performance yachts are made of composite materials like carbon fiber and filled with ballast, but this is exceedingly rare. Much of the sailboat’s ballast is usually internal on swing keel vessels.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy

Sailboat Keel Types: Illustrated Guide (Bilge, Fin, Full)
The keel type is one of the most important features of your boat. But the different designs can be confusing, so I've set out to create a very clear guide that will help you understand sailboat keels once and for all.
What are the most common sailboat keel types? The most common sailboat keel types are full-length keels, fin keels, bulb keels, wing keels, bilge keels, and lifting keels. Full keels are popular among cruisers, while fin keels are generally used for racing. Bilge keels and lifting keels are typically used in tidal waters, on small fishing boats for example.
In this article, we'll explore the most common keel types together. I'll use diagrams to really hit home the differences of all these keel types, and we'll discuss what keel types are best for liveaboard, ocean cruising, and lake weekend trips. After reading this article, you'll know what to choose - and why.

Sailboat Keels Explained
On this page:, overview of sailboat keel types, keel types: fundamentals, modified full keel, centerboard.
If you just want a quick overview, here's a list with the most common keel types and a short description. More detail will follow below.
The most common keel types
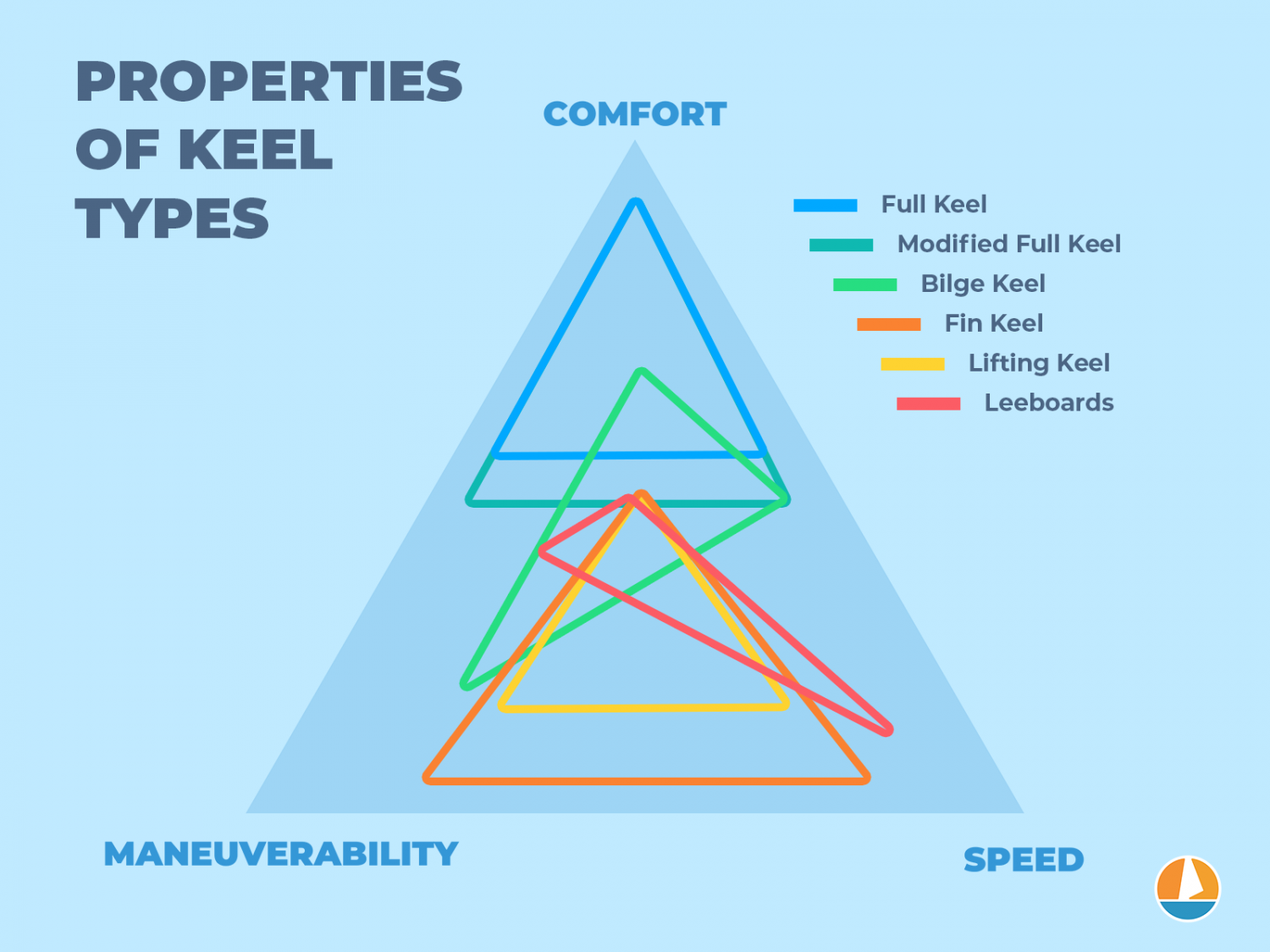
- Full keels run from front to aft and are the most stable keel type, making them the most popular cruising keel.
- Fin keels offer the best performance but are less comfortable. This makes them popular for racing. Fin keels are bolted on to the hull and generally run deep and thin.
- Bulb and wing keels are both variants on the fin keel.
- Bulb keels carry additional ballast in the tip, making them more stable.
- Wing keels have two tips at the end of the keel, which reduces crossflow, improving directional stability.
- Bilge keels are double fin or double full kees, which allows the boat to be beached, making them the most popular keel for tidal waters.
- Lifting keels are moveable keels that can be lowered and raised, allowing the boat to enter shallow waters as well.
- Centerboard keels are a pivoting lifting keel, allowing to sail both coastal and inland waters.
- Leeboards are fins on the sides of flat-bottomed hulls boats, making a keel unnecessary.
Properties of each keel type
What does a keel do?
What does the keel do? A keel is a vertical blade running down from the hull. It is weighted and acts as a ballast, countering the boat's tendency to heel and preventing it from tipping over. The wetted surface under the waterline reduces slippage to leeward by creating a track, which counters the sideway force of the wind on the sails.
The reason sailboats don't tip over is that the weight of the keel counters the buoyancy of the hull, which means it will pull the boat downward. This downward force reduces heel and prevents the boat from rolling.
A canoe doesn't have a keel. Try stepping into that: it will want to roll.
It counters the horizontal force the wind puts on the sails. Whenever the force on the sails increases, the resistance of the water on the keel increases proportionally.
The heavier the keel, the less heel you'll get.
A keel reduces slippage to leeward. Slippage is simply the amount you fall off course because of the direction of the wind and current. Leeward is the side of the boat behind the wind.
So if you don't have a keel, you will fall off course quite a lot because the wind will push you over the water surface.
You will also heel quite a lot since there is nothing beneath the water surface to counter the force of the wind high up in your sails.
A keel fixes both of these issues and makes sailboats one of the most reliable boats in heavy winds and storms.
You can read on about how keels work here.
Keels can be classified by multiple dimensions. You can look at them from the side or the front. You can also classify them based on properties.
Before I dive into each keel type in-depth and show examples, let's make sure we have the same starting point.
There are essentially two sorts of keels:
Fixed keels
Movable keels.

Fixed keels are keels that are integrated into the hull or bolted on. They can't be moved or lifted.
When looking at fixed keels, you can divide them up further based on the side view. There are three main categories:
Bilge keels
Full keels are more comfortable, provide better stability and protection, but are also slower than fin keels.
Fin keels are less comfortable, provide less stability, are more vulnerable, but they're also a lot faster than full keels.
Bilge keels are double keels: one on each side of the hull. This allows them to be beached, which comes in handy in tidal waters. They are generally a lot slower and less maneuverable compared to fin keels.
Movable keels can be lifted from the water, creating a shoal (shallow) draft, allowing the boat to enter both shallow waters and coastal waters. This makes it a very versatile keel type. There are two main designs:
Lifting keels
Lifting keels can be lowered and raised through a slit in the hull. Examples of lifting keels are the daggerboard and centerboard.
Leeboards are wooden swords attached to the side of the hull and prevent slippage to leeward, but they don't stabilize the boat, nor counter heel by adding ballast.

With fin keels, there are different tip designs available. The most common two tip designs are:
These are both variants of the fin keel. Generally, these keel designs are mentioned in one breath with full keels and fin keels, creating confusion on what kind of keel they are. But it's important to understand that they are a sub-category of fin keels.

Rudder design
As with the tip of the fin, there are different rudder designs that may apply to both fin and full keels. The two most common rudder designs are:
Skeg rudder
Spade rudder.
A skeg is a structural part of the keel in front of the rudder that protects the rudder. The keel encompasses the rudder, preventing any rogue ropes, weeds, or rocks from damaging the rudder.

A spade rudder is an unprotected rudder: it doesn't have any structural protection from the keel design. It is simply attached to the hull. This design is very common.
Alright, we understand the big picture. Let's dive into more detail for each keel type and discuss the pros and cons.
Fixed keel Good for cruising and liveaboards Comfortable
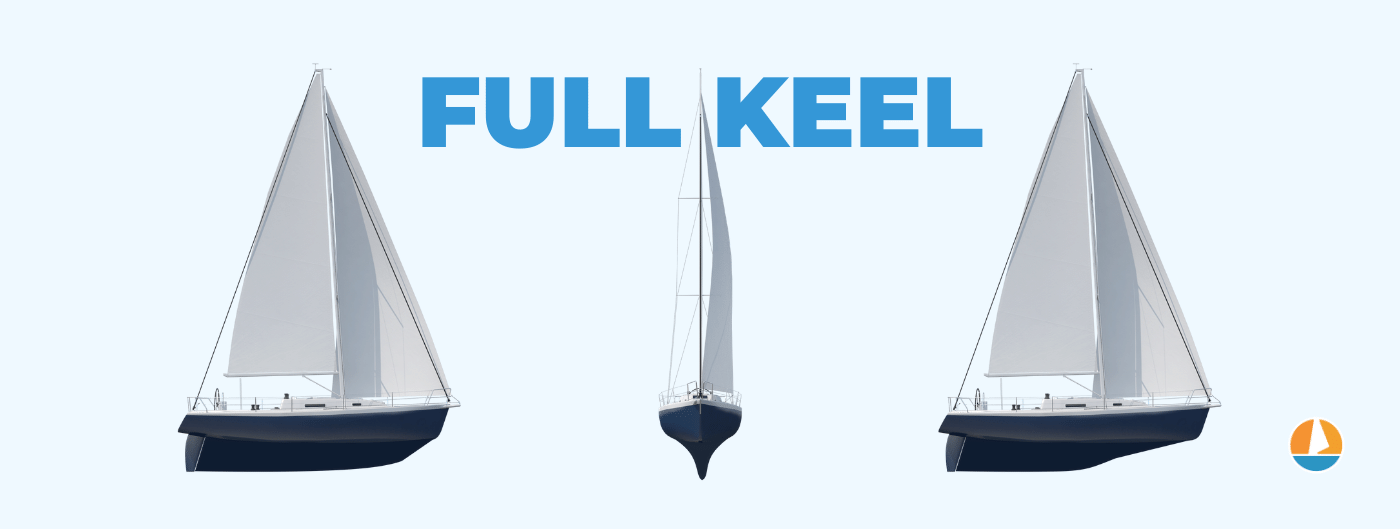
What is a full keel? A full keel runs from front to aft for at least 50% of the hull and is fully integrated into the hull. It has the largest wetted surface of any keel type, and it is also the heaviest. This results in directional stability and reduced heeling, providing the most comfortable ride, but also the slowest.
The wetted surface simply means the amount of water contact area. With such a large wetted surface, it decreases slippage to leeward the most of all keel types, while it counters heeling the most as well.
The full keel is the most comfortable and stable keel type available. However, comfort comes at a price. It delivers the worst performance due to this large wetted area. It is the slowest of the keel types, and it has the worst windward performance.
This makes full keels particularly great for longtime cruisers or liveaboards who prefer comfort over speed, but less ideal for daysailers who need to navigate in and out of slips regularly.
Since it runs for at least 50% of the hull, it doesn't need to run as deep as a fin keel, resulting in a more shoal draft.
Heavier keels result in increased displacement, so a full keel boat will need a larger sail area to compensate for its weight.
For a more detailed discussion on full keel advantages, I recommend reading William's excellent article 5 Surprising Advantages of a Full Keel Sailboat here.
Example sailboats with a full keel:
- Nicholson 22
- Island Packet 380
- Beneteau Oceanis 411 Clipper
- Beneteau First 50
- Jeanneau Sun Shine 38
- Dufour 455 Grand Large
There are a lot of great cruising boats with full keel designs , some of them considered classics.
Full Keel with skeg rudder
Full keels with a skeg rudder design have a protected rudder, thanks to putting a structural part of the keel directly in front of the rudder. This helps with fending off any hazards to the rudder, like floating pieces of rope, rocks, or garbage, and protects it in case of running aground. The skeg design ensures the rudder is nearly impossible to break off.
Fixed keel Good for cruising and liveaboards Faster than a regular full keel

What is a modified full keel? A modified full keel is a full keel with a cutout at the front, reducing the wetted surface slightly, which increases performance without sacrificing too much comfort and stability. After the full keel, it has the best directional stability and the least amount of heel.
The modified full keel is popular among (bluewater) cruisers, thanks to its increased handling and performance. Most modified full keels have a skeg rudder, ensuring it is well-protected.
The slightly reduced weight and wetted surface improve windward performance quite a lot, but it is still one of the most stable keel designs out there.
Example sailboats with a modified full keel:
- Hallberg-Rassy HR 40
- Dufour Arpege 30
- Beneteau Oceanis Clipper 281
- Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 37.2
Fixed keel Good for racing Fast
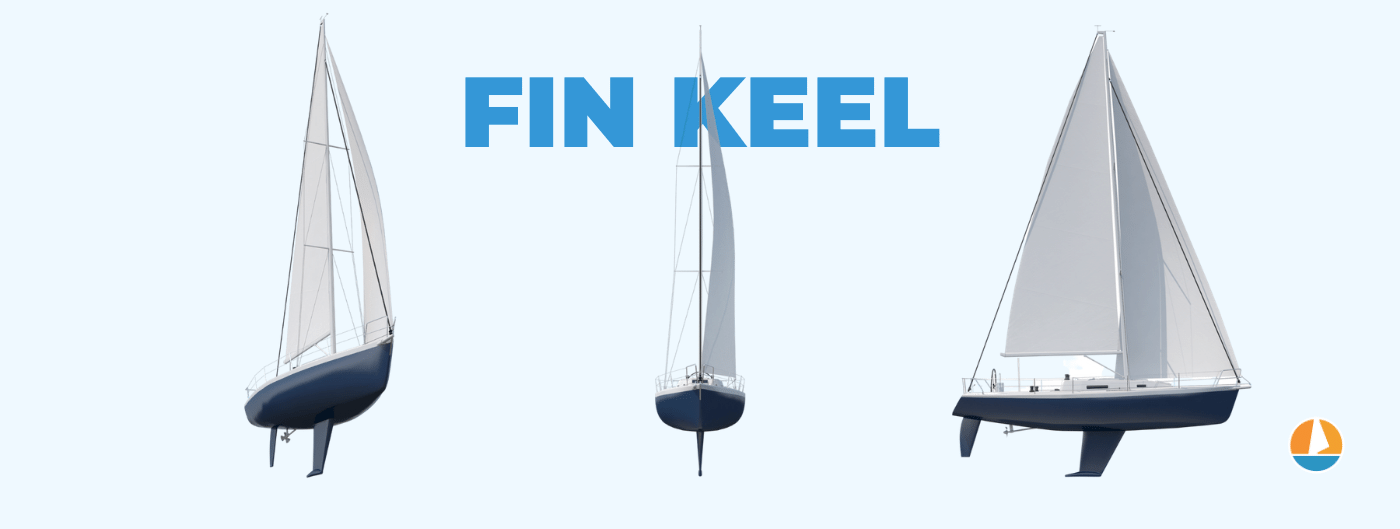
What is a fin keel? A fin keel is a long, weighted blade attached to the bottom of the hull. It is lighter, faster, and more maneuverable than a full keel, but also more vulnerable. The increased distance between ballast and sails provides a lever, reducing the need for a large wetted surface or additional ballast.
Fin keels are generally bolted onto the hull and run deeper and thinner than a full keel. They are also lighter. This helps increasing performance (a lot), making fin keels a lot faster in all situations.
There are some major disadvantages to fin keels, however. Fin keels are a lot less comfortable than full keels and allow for more heel and a less solid track, so less directional stability. Fin keels are also a lot more vulnerable than full keels. They can break off when running aground, or get damaged.
They are very popular among racers and perform better when maneuvering in tight spots, like getting in and out of slips.
Example sailboats with a fin keel:
- Catalina 30
- Jeanneau Sun Odyssey 36.2
Fin keel with skeg rudder
Fin keels with a skeg rudder use a small structural part in front of the rudder to protect it. This design is mostly integrated into the hull, making it less vulnerable, and a great compromise between speed and safety.
Fin keel with spade rudder
Fin keels with a spade rudder have a completely exposed rudder, and typically a fin that is simply bolted on. The keel isn't integrated into the hull, making it more vulnerable and less comfortable.

Fin keel variant Good for cruising Less crossflow
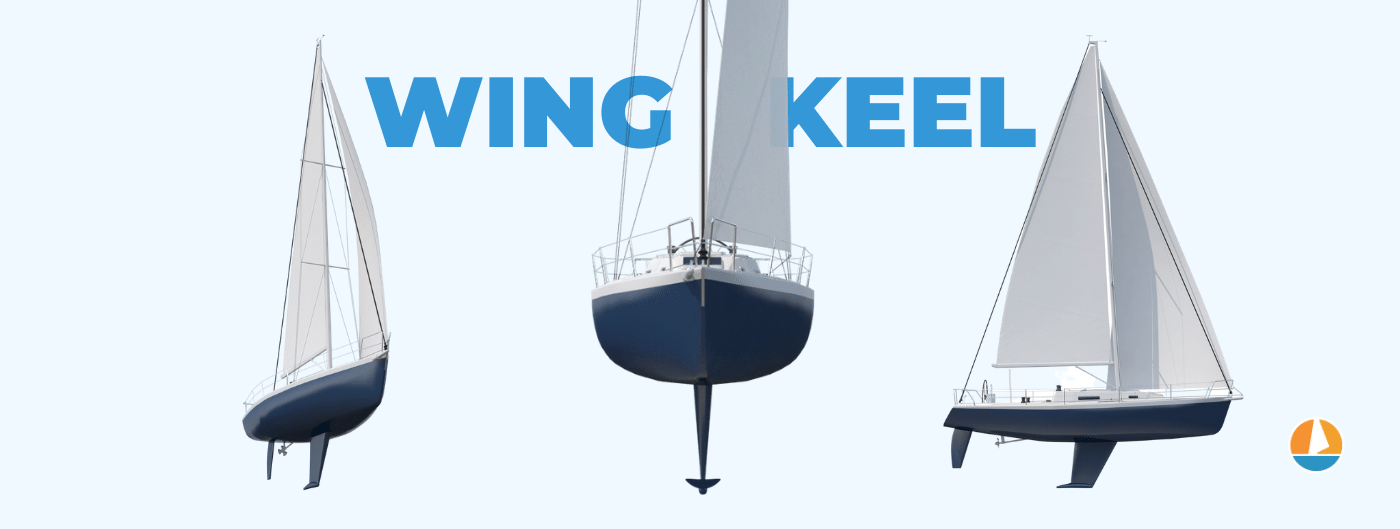
What is a wing keel? A wing keel is a fin keel with a horizontal foil at the tip, which is wing-shaped and generally weighted. Its shape reduces crossflow, improving directional stability, and its ballast decreases heel, resulting in a more comfortable ride. The addition of a wingtip allows for a shorter fin, reducing draft.
Wing keels are good for cruising since this design improves directional stability compared to a regular fin keel or a bulb keel.
We'll discuss the wing keel's advantages and disadvantages in more detail in this article.
Fin keel variant Good for cruising Stability

What is a bulb keel? A bulb keel is a high-aspect-ratio fin keel with additional ballast at the end, which generally has a bulb or teardrop shape. This ballast improves stability and utilizes the distance between force and counterforce as a lever. This design reduces the need for a deep fin, resulting in a shoal draft.
By placing the weight at the largest possible distance from the force on the sails, you need relatively little extra weight for the same reduction in heel, making bulb keels very effective for cruising.
This design reduces the wetted area while increasing the weight of the keel just slightly, which increases sailing comfort big time.
Example sailboats with a bulb keel:
- Bavaria B/One
- Beneteau First 24
Fixed keel Good for racing Can be beached
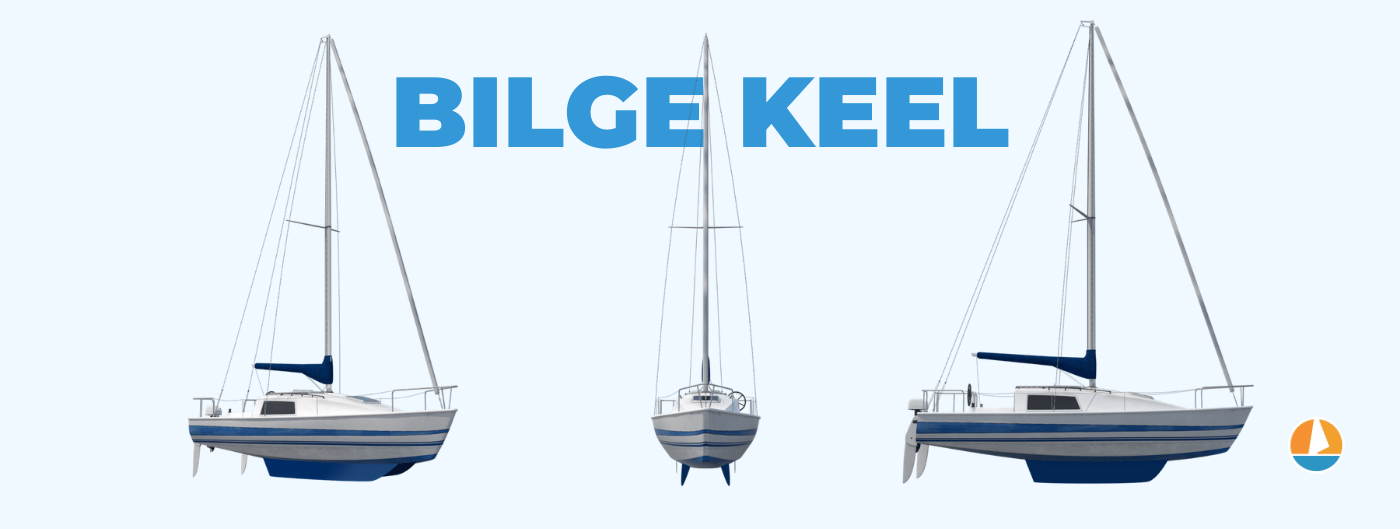
What is a bilge keel? A bilge keel is a twin keel which uses double fins, allowing the boat to be beached and rest on its keel upright. Bilge keels have double the wetted surface, which increases comfort and directional stability while decreasing heel. Modern bilge keels often provide decent windward performance, thanks to better design.
The bilge keel does sacrifice speed compared to the fin keel but doesn't necessarily offer worse performance overall. Older designs performed considerably worse than other keels and were especially slow.

Bilge keels have some major advantages over full keels and fin keels. The most important is that the boat can be beached, making it a popular design in tidal waters. Bilge keels are especially common along the British coastline, where fishermen keep their boats in tidal harbors.
Another major advantage is that the boat can be stored resting on its keels, making dry storage and maintenance a lot easier.
Of course, there are many more pros and cons to the bilge keel , which we go into here.
Example sailboats with a bilge keel:
- Dufour Dynamique 62
- Hunter Duette
- Patagonia Patago 39
- Macwester 27
Lifting keel Good for daysailers Versatile
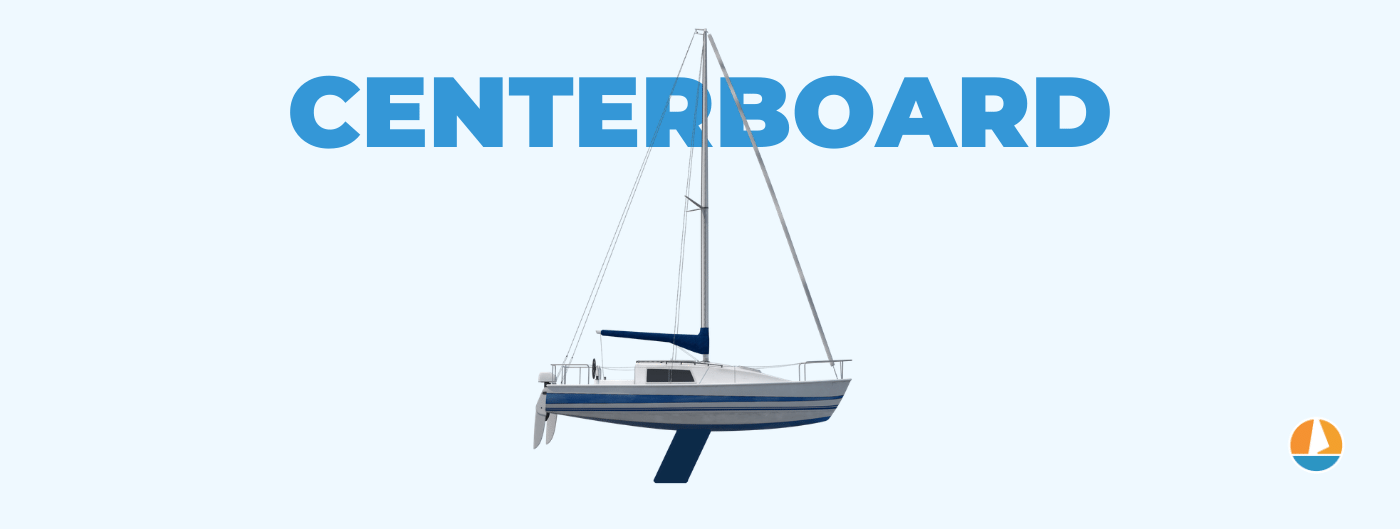

What is a centerboard? A centerboard is a type of retractable keel that rests on a hinge and can be lowered through a slot in the hull. It folds out like a pocket knife and allows you to increase or reduce the draft of the boat. Centerboards are mostly used on small fishing boats.
The centerboard is a very versatile keel type, allowing you to have both a very shoal draft for inland waters, as well as steadying the boat and reducing heel for larger bodies of water, or even oceans.
I've sailed a Cornish Crabber with a centerboard for a week, and while we stayed inland, having the option to increase the keel depth really came in handy when crossing the IJsselmeer (a former sea in The Netherlands).
There's more to the center
Olaf Roethele
https://www.theyachtmarket.com/en/new-boats/cornish-crabbers/adventure-17/218/
My name is Olaf and I am the owner of a Cornish Crabber 17 Adventure boat.
I would like to ask you if you can imagine to install on this boat a Torqeedo 2.0 Pod motor? Therefore i guess a modification of the keel/skeg is necessary ?!
Best regards from Uruguay,
You completely missed the hybrid planing/water-ballast keel of the Macgregor range
Thanks a lot for this explanation
Roger Bannon
Very well written article which provides an excellent guide for us small wooden boat builders. Thanks.
Leave a comment
Own your first boat within a year on any budget.
A sailboat doesn't have to be expensive if you know what you're doing. If you want to learn how to make your sailing dream reality within a year, leave your email and I'll send you free updates . I don't like spam - I will only send helpful content.
Ready to Own Your First Boat?
Just tell us the best email address to send your tips to:
Daggerboard vs Centerboard: Choosing the Right Option for Your Sailboat
by Emma Sullivan | Aug 7, 2023 | Sailboat Maintenance
Short answer daggerboard vs centerboard:
A daggerboard is a retractable keel that can be raised or lowered vertically, providing stability and reducing sideways drift. On the other hand, a centerboard is also a retractable keel but pivots horizontally instead of vertically. While both serve similar purposes, their designs and mechanisms differ in terms of usage and effectiveness depending on the type and size of vessels they are used for.
Comparing Daggerboard vs Centerboard: What You Need to Know
Introduction:
When it comes to sailing, understanding the different types of boards used in sailboats is essential. Two commonly used boards are the daggerboard and centerboard . While both serve a similar purpose of providing stability and preventing lateral movement, there are a few key differences between these two options. So, let’s dive deeper into comparing daggerboards versus centerboards to shed some light on what you need to know.
1. Definition:
To start with, let’s define each board type. A daggerboard is a retractable keel that can be raised or lowered vertically through a slot in the hull of a sailboat. On the other hand, a centerboard is also an adjustable keel-like appendage but pivots around a single point when lifted out of the water .
2. Functionality:
The primary function of both boards is to counteract the sideways forces generated by wind acting on the sails and maintain stability in the water. However, they achieve this goal using slightly different mechanisms.
With a daggerboard, sailors have more control over adjusting its depth as it can be raised or lowered at will. This allows them to fine-tune their boat’s performance according to wind conditions and desired speed.
On the contrary, centerboards offer less adjustability and usually have set positions determined by design. Nevertheless, they still provide adequate lift and resistance against sideways drift while sailing close-hauled or upwind.
3. Performance:
When it comes to performance comparison between these two options, both have their pros and cons depending on factors such as boat size, sail plan, and intended use.
Daggerboards generally provide superior upwind performance due to their ability to be adjusted for various wind angles precisely. They allow sailors to optimize for maximum lift while minimizing drag in challenging conditions like gusty winds.
Centerboards excel in downwind sailing situations where maintaining optimal balance becomes critical. Their fixed position contributes additional stability during fast runs or when navigating waves, making them a favorable choice for racing scenarios or larger sailboats .
4. Construction and Maintenance:
Another aspect to consider is the construction and maintenance of these boards. Daggerboards are often made from materials such as fiberglass, carbon fiber, or wood laminates, requiring periodic inspection for wear and tear. However, they can be easily removed during maintenance or storage.
Centerboards are commonly built using similar materials but differ in their pivot point mechanism. The pivot offers simplicity and fewer moving parts that could potentially fail over time. Nonetheless, periodic inspections are still recommended to ensure the board remains secure within its casing.
5. Adaptability:
For sailors who enjoy exploring various water conditions, adaptability becomes a significant factor when comparing daggerboards and centerboards.
Daggerboards prove to be more versatile in this regard as their adjustability allows for experimentation with different sailing techniques on changing water types. This attribute makes them particularly suitable for sailors looking to venture into both shallow waters and deeper offshore locations while keeping their vessel stable.
Centerboards, although limited in terms of adjustability, offer reliability and ease of use across a wide range of sailing environments. They work exceptionally well for recreational sailors who primarily navigate deepwater areas without the need for frequent adjustments.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the differences between daggerboards and centerboards is crucial when considering which option best suits your sailing needs. While daggerboards provide greater performance optimization capabilities across wind angles and various conditions, centerboards offer stability and reliability in both recreational cruising and racing scenarios.
Ultimately, it’s essential to carefully evaluate your requirements based on boat type, desired performance characteristics under specific weather conditions, as well as personal preferences before making a decision between these two distinct but equally valuable options: the versatile daggerboard or steadfast centerboard.
Understanding the Difference: A Step-by-Step Guide to Daggerboards and Centerboards
If you’re passionate about sailing or have recently taken up the sport, you might have come across the terms “daggerboard” and “centerboard.” While these two components are integral to a sailboat ‘s performance, their roles and characteristics can sometimes be confusing. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you step-by-step through everything you need to know about daggerboards and centerboards – shedding light on their differences and helping you make informed decisions for your own sailing adventures.
First things first, let’s define both daggerboards and centerboards. Both of these structures are essentially appendages that extend from the hull beneath a sailboat. They serve a shared purpose: providing lateral resistance against the force of the wind, preventing the boat from being blown sideways while allowing it to move forward effectively. However, there are distinct variations in design, functionality, and usage between them.
Let’s start with daggerboards. As their name suggests, these boards resemble daggers due to their shape – long and narrow blades that slide vertically into slots in a boat’s hull. Typically located amidships or towards the stern of a vessel, daggerboards are commonly used in high-performance racing yachts or catamarans . Their primary function is to counteract the sideways force generated by wind acting on sails positioned away from where they attach to the mast – an effect known as “lee helm.” By adjusting or deploying multiple daggerboards asymmetrically, sailors can optimize their boats’ performance by minimizing drag while maximizing lift.
On the other hand, centerboards serve a similar purpose but differ significantly in design and usage compared to daggerboards. Unlike fixed daggerboads that slide vertically into slots within a hull structure permanently mounted on a boat’s keel or inside its hull at centreline position (often hollow), centerboard systems rely on pivoting mechanics and vertical movement.
To put it simply, centerboards pivot around a fulcrum or a pin attached to the hull, allowing them to be raised or lowered as needed. They are often found in sailboats designed for recreational purposes – such as small dinghies, daysailers, or even some keelboats. Centerboards can be retracted fully into the hull for shallow-water sailing and ease of launching or landing – an especially useful feature when dealing with beach landings. When lowered into position, they provide similar lateral resistance as daggerboards but typically offer less efficiency due to their simplified shape and lesser surface area.
Now that you understand the basic concepts behind daggerboards and centerboards, let’s explore their advantages and considerations. Daggerboards excel in providing substantial lateral resistance and increased lift capability due to their more refined shape and positioning options. The ability to adjust multiple daggerboards asymmetrically can lead to improved performance under varying wind conditions, making these boards indispensable for competitive sailors seeking optimal speed.
In contrast, centerboards are known for their versatility and convenience. Their pivoting mechanism enables them to be easily raised or lowered while on the water – a valuable asset when navigating shallow waters without risking damage or grounding the boat. Moreover, many small sailboats with centerboard designs also benefit from enhanced stability since the board’s weight aids in counteracting heeling forces acting on the sails.
When choosing between a daggerboard setup or a boat equipped with a centerboard system, several factors come into play. Firstly, consider your sailing intentions: are you primarily interested in casual cruising, racing competitively with precise maneuvering requirements or something in-between? Secondly, assess your local sailing conditions: do you frequently encounter challenging wind patterns or navigate areas with shallow waters ? These aspects will help steer you towards the most suitable option for your needs.
Ultimately, whether you opt for a sailboat equipped with a daggerboard system or one featuring a centerboard mechanism depends on various factors, including performance goals, sailing preferences, and intended use. Don’t hesitate to consult with experienced sailors, boat designers, or reputable manufacturers to ensure you make the right choice.
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between daggerboards and centerboards empowers sailors to select the appropriate configuration for their specific needs while navigating diverse sailing environments. Both appendages play crucial roles in enhancing sailboat stability and maneuverability, but their designs and functionalities vary significantly. Take into account your sailing aspirations and local conditions when making a decision – ensuring an enjoyable and successful experience on the water !
FAQ: Decoding the Pros and Cons of Daggerboards vs Centerboards
Title: FAQ: Decoding the Pros and Cons of Daggerboards vs Centerboards for Smooth Sailing
Introduction: Ahoy, fellow boating enthusiasts ! As you venture into the exciting world of sailing, one critical decision awaits you on your quest to harness the wind’s power. Today, we dive deep into deciphering the age-old conundrum—daggerboards or centerboards? Strap on your life vests as we embark on a journey to unravel the pros and cons of these two remarkable appendages that determine our vessel’s stability and maneuverability.
1. Understanding Daggerboards: Daggerboards, like stealthy underwater swords, elegantly slice through waters beneath our hulls. These vertically retractable boards are typically found in high-performance sailboats, optimized for speed and agility. But what makes daggerboards such an enticing choice?
Advantages of Daggerboards: a) Enhanced Speed: When engaged correctly, daggerboards create less drag compared to fixed keels or centerboards while maintaining lateral resistance. This enables your vessel to cut through water with minimal resistance, giving you a serious edge in speed races. b) Improved Upwind Performance: Daggerboards lend invaluable assistance in maximizing upwind sailing angles by resisting leeway—a fantastic asset when navigating against adverse currents or winds . c) Advanced Maneuverability: The ability to raise and lower these boards allows for easy adaptation to different sailing conditions without limiting boat movement possibilities.
Disadvantages of Daggerboards: a) Costly Investment: Opting for daggerboard-equipped vessels may lead to a higher upfront investment due to their intricate design and construction. b) Maintenance Complexities: Attending to daggerboard mechanisms demands regular inspection and occasional repairs; proper care is essential for long-term performance . c) Limited Draft Range: Some sailors argue that daggerboards hinder access to shallow waters due to their deeper draft range compared to centerboards.
2. Unveiling Centerboards’ Secrets: Now, let’s dive into the undeniable allure of centerboards—a versatile alternative that has carved its place in the sailing community. Positioned within a sailboat’s hull, these retractable appendages offer unique advantages worth considering.
Advantages of Centerboards: a) Versatility: The retractable nature of centerboards allows for easy maneuvering in shallow waters or when navigating close to shore. No more worrying about running aground! b) Cost-efficiency: Boats with centerboards tend to be more affordable compared to their daggerboard-equipped counterparts, making them an attractive choice for budget-conscious sailors . c) Simplicity in Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and mechanisms, the maintenance requirements for centerboards are often less complex and demanding.
Disadvantages of Centerboards: a) Compromised Performance: Sailing aficionados argue that centerboards might sacrifice performance compared to daggerboards due to increased drag and reduced lateral resistance. b) Limited Upwind Performance: When faced with strong winds or currents pushing against your vessel, centerboards may struggle to maintain course stability effectively.
Conclusion: Now that we’ve embarked on this quest through the pros and cons of daggerboards versus centerboards, it’s time for you to weigh your options carefully. Consider factors like your desired sailing style, local water conditions, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance commitments. Remember, whether you opt for the sleek agility of daggerboards or the versatile adaptability of centerboards—safe voyages and thrilling adventures await as you navigate through uncharted waters!
Exploring the Advantages of Daggerboards and Centerboards in Sailing
Are you an avid sailor or someone looking to dip their toes into the exhilarating world of sailing ? If so, understanding the advantages that daggerboards and centerboards provide can significantly enhance your sailing experience. These essential components are not only cleverly designed but also play a paramount role in improving a sailboat’s performance on the water . In this blog post, we will delve into the details of these devices, uncovering their remarkable benefits.
Firstly, let’s start by demystifying what daggerboards and centerboards actually are. Both of these apparatuses serve the same purpose – they stabilize a sailboat by providing lateral resistance, preventing it from drifting sideways due to wind pressure. However, they accomplish this task through different mechanisms.
Daggerboards are retractable foils that typically slide vertically from within the hull. These appendages are often found on high-performance racing boats as they offer numerous advantages. One notable advantage is their ability to maximize speed by minimizing hydrodynamic drag. When deployed correctly, daggerboards reduce sideways drift and lift the boat out of the water slightly, reducing wetted surface area and frictional resistance – resulting in enhanced speed through the water .
Additionally, daggerboards have another trick up their sleeve – adjustable angle-of-attack. Sailors can fine-tune these boards to suit different wind conditions, allowing for optimal performance based on variable factors such as wind strength or direction. This adaptability ensures that you are always at an advantage when facing changing weather conditions during races or leisurely sails.
On the other side of things, centerboards – unlike daggerboards – pivot horizontally from within the hull towards the boat’s midline. Although they lack some of the advantages provided by daggerboards regarding drag reduction and adjustment capabilities, centerboards excel in versatility and accessibility.
One significant advantage that centerboards offer is their ability to navigate shallow waters easily. You’ll find these boats cruising close to shorelines and in areas where draft limitations exist, such as lakes, rivers, or even windy coastal havens with numerous sandbanks. The retractable nature of centerboards allows sailors to raise them fully when entering shallow waters, minimizing the risk of grounding the boat while still maintaining excellent balance and control .
Furthermore, the positioning of a centerboard closer to the boat’s center of mass assists in preventing excessive heeling (tilting) during sailing . For those new to sailing or those who prefer a more stable ride, this can provide a greater sense of safety and security on the water.
In conclusion, both daggerboards and centerboards bring distinct advantages to sailboat enthusiasts. Daggerboards offer improved hydrodynamics for speed enthusiasts while providing adjustability for varying wind conditions – perfect for competitive racing or achieving top-notch performance. On the other hand, centerboards excel in versatility by allowing sailors access to shallow waters without sacrificing stability.
Whether you’re aiming for podium finishes in a regatta or simply seeking an invigorating recreational experience on the water, having a good understanding of these vital components will undoubtedly elevate your sailing adventures . So next time you hoist those sails and feel the saltwater spray on your face, appreciate how these cleverly designed daggerboards and centerboards optimize your vessel’s performance, granting you unparalleled control and enjoyment throughout every voyage.
How to Choose Between a Daggerboard and a Centerboard for Your Sailboat
Choosing the right type of board for your sailboat is a crucial decision that can greatly impact your sailing experience. Two popular options are the daggerboard and the centerboard , each with its own unique advantages and considerations. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of these two board types to help you make an informed choice for your vessel.
Let’s start by understanding what a daggerboard and a centerboard actually are. Both are vertical boards positioned in the keel to provide stability and prevent sideways drift. The primary difference lies in their configuration and functionality.
1. Daggerboards: Imagine a dagger slicing through water with precision – that’s precisely how daggerboards operate! These long, narrow boards are fully retractable, typically made from high-strength materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber. They offer excellent hydrodynamic efficiency, leading to enhanced upwind performance and minimizing leeway (sideways drift) during sailing .
Why opt for a daggerboard? Well, if you’re passionate about racing or want to explore faster sailing speeds, daggerboards should top your list. With their ability to be raised or lowered at will, they allow countless adjustment possibilities while on the water – from optimizing your boat ‘s balance based on wind conditions to maneuvering through shallow waters without worrying about grounding.
However, there are some drawbacks worth considering before committing to a daggerboard. Due to their intricate design and construction, they tend to be more expensive than centerboards. Additionally, retracting them may require physical effort or even hydraulic assistance on larger vessels.
2. Centerboards: Centerboards share similar functionality as daggerboards but differ in construction and operation. Unlike daggerboards that slide vertically within casing built into the hull of the sailboat, centerboards pivot horizontally from its midpoint inside the hull itself.
So why go for a centerboard instead? Primarily known for their versatility and adaptability across various boat types – dinghies, daysailers, or cruisers – centerboards provide easy access to shallow waters. As they pivot up into the hull, the sailboat’s draft decreases, allowing you to explore areas that would otherwise remain inaccessible.
If budget constraints are a concern, opting for a centerboard might be more economical compared to a daggerboard . They are generally simpler in design and easier to maintain due to their horizontal movement mechanism.
Nevertheless, keep in mind that centerboards may compromise your sailing performance slightly. Although they perform reasonably well upwind and allow sailing closer to the wind than boats without any keel at all (known as leeboards), they are not as efficient as daggerboards when it comes to performance-oriented sailing.
In conclusion, choosing between a daggerboard and a centerboard ultimately depends on your specific requirements and intended use of the sailboat. If you crave exhilarating speeds, impeccable upwind capabilities, and have room in your budget for a high-performance board, go for a daggerboard without hesitation. On the other hand, if versatility, cost-effectiveness, and shallow-water exploration take precedence over pure speed obsession, opt for a centerboard.
Remember that regardless of which board you choose; practice and experience will play crucial roles in mastering its deployment and optimizing its effect on your sailing adventures . Happy cruising!
Going Beyond Basics: Mastering the Use of Daggerboards vs Centerboards
Title: Going Beyond Basics: Mastering the Art of Daggerboards vs Centerboards
Introduction: When it comes to sailing, achieving optimum performance requires more than just a basic understanding of the equipment. To truly excel in this beautiful sport, sailors need to delve deeper into the intricacies of their vessel’s components. One such critical component is the choice between daggerboards and centerboards. In this blog post, we will explore these options in detail, shedding light on their characteristics, benefits, and how mastering their use can take your sailing skills to new heights.
The Difference Between Daggerboards and Centerboards: Before we dive into their nuances, let’s begin by understanding the fundamental difference between daggerboards and centerboards. Both are retractable fins intended to prevent leeway (sideways drift) when sailing against the wind . The primary variation lies in their location on the hull. Daggerboards are inserted vertically through slots located towards the middle of each hull side on catamarans or near the keel area on monohulls. Conversely, centerboards are mounted on pivots below the hull at its central point.
Daggerboard Dominance: 1. Performance Advantages: Daggerboards provide sailors with remarkable advantages when it comes to sailboat performance. Their vertical positioning allows for reduced drag and enhanced lift characteristics compared to centerboards. 2. Upwind Sailing Power: Due to their dynamic design, daggerboards enable better upwind sailing as they can be further extended downwards into deeper water when necessary – increasing resistance against being pushed sideways by wind pressure. 3. Higher Speed Potential: By reducing leeway during upwind maneuvers, daggerboard-equipped boats experience less resistance and consequently achieve higher speeds. 4. Enhanced Steering Control: Another noteworthy benefit of daggerboard usage is improved steering control under demanding conditions like strong winds or rough seas.
Centerboard Superiority: 1. Versatility across Depths: Compared to daggerboards that require specific water depths, centerboards allow sailors to venture into shallower waters. The ability to raise the centerboard partially or completely reduces grounding risks and grants access to areas otherwise inaccessible. 2. Simplified Maneuverability: With a fixed pivot point across all wind conditions, centerboards are more straightforward and hassle-free to operate. Their stability provides consistent performance, making sailing a breeze for beginners and less experienced crews. 3. Safety in Grounding Situations: In the unfortunate event of running aground, a centerboard is designed to kick up easily upon contact with solid objects, minimizing potential damage to both the board and the hull.
Mastering Daggerboards vs Centerboards: 1. Understanding Conditions: To make an informed choice between daggerboards and centerboards, it’s crucial to assess the predominant sailing conditions you encounter. For open-water excursions where speed reigns supreme, daggerboards are often favored. Conversely, if your voyages take you through varied depths or potentially shallow areas, a centerboard may be more advantageous. 2. Gradual Familiarization & Practice: Like any skill in sailing, mastering the use of daggerboards or centerboards necessitates practice and experimentation. Sailors who wish to truly harness these components should gradually familiarize themselves with how they influence the boat’s performance by adjusting their depth according to wind strength and direction. 3. Seek Expert Guidance: Advanced sailors seeking technical expertise can benefit from reaching out to experienced professionals or participating in sailing clinics focused on advanced techniques involving daggerboard or centerboard utilization.
Conclusion: In summary, going beyond the basics of sailing involves mastering intricate aspects such as choosing between daggerboards and centerboards. Each has unique advantages catering to different sailing scenarios and personal preferences. By honing your understanding of these components’ functionality along with practice at utilizing them optimally under varying conditions enable sailors to unlock remarkable improvements in speed, maneuverability, and control – elevating their overall proficiency in the art of sailing.
Recent Posts

- Sailboat Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Lifestyle
- Sailboat Maintenance
- Sailboat Racing
- Sailboat Tips and Tricks
- Sailboat Types
- Sailing Adventures
- Sailing Destinations
- Sailing Safety
- Sailing Techniques
- Sailboat Maintenance Tips
- Eco-Friendly Sailing Practices
- Sailboat Buying Guide
- Sailboat Insurance and Finance
- Sailboat Safety and Regulations
- Sailboat Technology Advances
- Sailing Gear and Equipment
- Sailboat Navigation Essentials
- Sailboat Restoration Projects
- Sailboat Interior Design
- Sailing Destinations Worldwide
- Sailboat Types and Designs

Essential Components for the Force 5 Sailboat: A Comprehensive Guide
force 5 sailboat parts specs
Force 5 sailboat parts specifications.
The Force 5 sailboat is an exceptional vessel that requires reliable and high-quality parts to perform at its best on the water. Here, we provide you with a comprehensive guide to the essential components you need to know about when it comes to your Force 5 sailboat.
- Main Sail: The main sail is the largest sail on the Force 5 sailboat, responsible for capturing the wind and propelling the boat forward.
- Jib: The jib sail is smaller and is used to control the direction and balance of the boat, enhancing its maneuverability.
- Spinnaker: The spinnaker sail is used to harness the wind from behind the boat, providing an extra boost of speed when sailing downwind.
- Mast: The mast is a crucial component that supports the sails and helps maintain their shape while sailing.
- Boom: The boom connects to the mast and holds the bottom edge of the main sail, controlling its position and shape.
- Standing Rigging: This refers to the wires and cables that provide stability and support to the mast and rigging system.

force 5 sailboat parts review
When it comes to the Force 5 sailboat, having the right parts can make all the difference in enhancing your sailing experience. In this review, we will take a closer look at some of the essential components that every Force 5 sailboat owner should consider. From mast and rigging to sails and hardware, these parts play a crucial role in maximizing performance and ensuring a smooth sailing journey.
1. Mast and Rigging: The mast and rigging are the backbone of any sailboat, and the Force 5 is no exception. High-quality masts are made from lightweight yet durable materials, providing optimal strength and flexibility. Similarly, top-notch rigging that includes shrouds, spreaders, and halyards ensures proper sail control and stability.
2. Sails: The sails are the driving force behind any sailboat, and the Force 5 excels in this aspect. Crafted from premium materials such as Dacron or Mylar, these sails offer exceptional durability and performance. The main sail and jib work in perfect harmony, providing power and maneuverability. Additionally, adjustable battens enhance sail shape, optimizing aerodynamics for varying wind conditions.
These essential components are crucial in unlocking the true potential of the Force 5 sailboat. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a beginner looking to explore the world of sailing, investing in reliable sailboat parts will undoubtedly enhance your sailing experiences. So, set sail with confidence and embrace the freedom that the Force 5 sailboat has to offer!

force 5 sailboat parts pros and cons
Force 5 sailboat parts: pros and cons.
When it comes to the Force 5 sailboat, understanding the pros and cons of its various parts is essential for any sailing enthusiast. Here, we present an overview of the key components of a Force 5 sailboat, discussing their advantages and drawbacks to help you make informed decisions:
The hull is the main body of the sailboat, and its design affects the boat’s stability and performance on the water.
- Durable and lightweight fiberglass construction.
- A streamlined shape for optimal speed and maneuverability.
- Susceptible to damage from impacts with rocks or other boats.
- May require maintenance, such as hull repairs or repainting, over time.
The sails capture the wind’s energy, propelling the sailboat forward.
- Efficient in various wind conditions, allowing for versatile sailing experiences.
- Option to choose sails of different sizes for customized performance.
- Learning to properly trim and adjust sails can require skill and practice.
- In strong winds, the sailboat can become more challenging to control.

force 5 sailboat parts interior photos
Step inside the world of Force 5 sailboats and uncover the hidden treasures found within their interiors. From the sleek design to the carefully crafted components, every detail in a Force 5 sailboat’s interior serves a purpose. Explore the following features that make these sailboats a sailor’s dream:
1. Spacious Cabin
The interior of a Force 5 sailboat offers ample space, ensuring comfort during those long days at sea. The cabin is thoughtfully designed, allowing for easy movement and providing a relaxing environment for occupants.
2. Ergonomic Seating
Sitting for extended periods is a breeze with the ergonomic seating found in Force 5 sailboats. The seats are contoured to provide maximum support and prevent fatigue, allowing sailors to focus on the journey ahead.
3. Storage Solutions
Efficient storage is a key feature of the sailboat’s interior. Well-designed cabinets, lockers, and compartments provide ample room for stowing gear and personal belongings. Stay organized and make the most of every inch of space.
Discovering the essential components of a Force 5 sailboat is the first step towards an exceptional sailing experience. The comprehensive guide above sheds light on key features that contribute to the sailboat’s functionality and performance. Whether you’re a novice sailor or a seasoned seafarer, these components ensure a safe and enjoyable journey on the open waters.

force 5 sailboat parts specifications
The Force 5 sailboat is a remarkable vessel known for its speed, maneuverability, and durability. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice looking to explore the world of sailing, understanding the specifications of the parts that make up this incredible sailboat is vital. We’ve compiled a comprehensive guide below that outlines the essential components of the Force 5 Sailboat.
- Mast : Constructed from weather-resistant aluminum, this vital part provides the necessary support for the sail.
- Boom : Made from lightweight materials, the boom attaches to the mast and holds the foot of the sail in position.
- Centerboard : A retractable fin, typically made of fiberglass, that provides stability and prevents lateral drift.
- Main Sail : The primary sail that captures the wind’s power and drives the sailboat forward.
- Jib : A smaller sail located at the front of the sailboat that aids in steering and balance.
- Spinnaker : A specialized sail used for downwind sailing, providing an extra burst of speed.

force 5 sailboat parts layout
The Force 5 sailboat is a versatile and exciting vessel that requires a solid understanding of its essential components. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the parts layout of the Force 5 sailboat, ensuring you have a clear understanding of its various elements and how they work together to enhance your sailing experience.
Below is a detailed overview of the key components that make up the Force 5 sailboat:

force 5 sailboat parts data
When it comes to your Force 5 sailboat, having access to accurate and reliable parts data is crucial for ensuring smooth sailing and optimal performance. At [Company Name], we understand the importance of having the right components for your vessel, which is why we have compiled a comprehensive collection of parts data specifically tailored for the Force 5 sailboat.
Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a beginner, our extensive database provides detailed information on various Force 5 sailboat parts, enabling you to make informed decisions about repairs, upgrades, and maintenance. From masts and sails to rigging and rudders, our parts data covers a wide range of essential components that are integral to the functionality of your Force 5 sailboat. With our user-friendly search interface, you can quickly find the exact part you need, ensuring a hassle-free sailing experience .
These are just a few examples of the essential components you will find in our comprehensive guide. Our detailed descriptions, accurate measurements, and recommended materials ensure that you have all the necessary information to maintain and upgrade your Force 5 sailboat. Explore our parts data today and sail with confidence!

force 5 sailboat parts diagram
The Force 5 Sailboat is a classic, single-handed sailing vessel loved by sailors worldwide. To help you navigate the intricate workings of this fantastic sailboat, we have prepared a comprehensive parts diagram. Whether you are a seasoned sailor or new to the sport, this diagram will be essential in understanding the various components that make up the Force 5 Sailboat.
Below, we have highlighted some of the key parts of the Force 5 Sailboat:
- Hull: The main body of the sailboat that provides buoyancy and stability.
- Mast: A tall vertical spar that holds up the sail and provides support.
- Boom: A horizontal spar that extends from the mast and holds the foot of the sail, controlling its angle.
- Sail: The main driving force of the sailboat, catching the wind and propelling the vessel forward.
- Daggerboard: A retractable centerboard that helps prevent sideways drift while maintaining stability.
- Tiller: A long handle connected to the rudder used for steering the sailboat.
- Rigging: The system of ropes and wires that controls the position and shape of the sail.
- Blocks and Cleats: Various pulleys and mechanisms that help control the tension and movement of the rigging.

force 5 sailboat parts for sale
Looking for top-quality parts to enhance your Force 5 sailboat performance? Look no further! We offer a wide range of premium-grade sailboat components that will take your sailing experience to new heights. From essential gear to specialized accessories, we have everything you need to keep your Force 5 sailboat in tip-top shape.
Our inventory includes an extensive selection of parts specifically designed for the Force 5 sailboat. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a beginner, our high-quality components are sure to meet your needs. With our affordable prices and durable products, you can trust that our sailboat parts will stand the test of time and withstand even the most demanding sailing conditions.
These are just a few examples of the essential components you’ll find in our comprehensive guide. Each component is crafted with utmost care and precision, guaranteeing optimal performance and longevity. So why wait? Upgrade your Force 5 sailboat with our top-of-the-line parts today!
Q: What are the essential components required for a Force 5 sailboat? A: The essential components for a Force 5 sailboat include the hull, sails, mast, boom, rudder, centerboard, lines, hiking straps, and various fittings.
Q: Can you explain the significance of each component? A: Certainly! The hull forms the main body and provides buoyancy. It is usually made of fiberglass, ensuring durability and lightness. Sails are crucial for harnessing wind power, and they comprise a main sail and a jib. The mast holds the sails up, while the boom keeps the bottom of the main sail in place. The rudder controls direction, and the centerboard serves to prevent sideways drift while sailing. Lines such as halyards, sheets, and control lines enable sailors to control sail trim. Hiking straps allow the crew to maintain balance in high winds, and fittings ensure all components are securely attached.
Q: What materials are commonly used for the sailboat components? A: The hull is typically made of fiberglass due to its strength-to-weight ratio, affordability, and maintenance ease. Sails are often made of Dacron or Mylar, both durable yet flexible materials. The mast and boom are commonly made using aluminum or carbon fiber, providing strength and lightness. The rudder, centerboard, and fittings are usually crafted from materials like fiberglass, aluminum alloy, or stainless steel to ensure durability and resistance to corrosion.
Q: Are there any specific maintenance requirements for these components? A: Yes, proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and performance of the components. It is important to regularly inspect the hull for cracks or damage, as well as ensuring the integrity of the sails, mast, boom, rudder, and centerboard. Regular cleaning and lubrication of the fittings will prevent corrosion. Proper storage, covering, and protection from harsh weather conditions are also vital for maintaining the components in good condition.
Q: Can the components be replaced or upgraded? A: Yes, sailboat components can be replaced or upgraded to improve performance or keep up with advancing technologies. For instance, sails can be replaced to improve speed and maneuverability. Upgrading the mast or boom to different materials may reduce weight and increase durability. Centerboards and rudders can be upgraded for enhanced control. However, it is important to ensure any changes comply with class rules and regulations, especially for competitive sailing.
Q: Where can one purchase these essential components? A: Essential components for the Force 5 sailboat can be purchased from various marine retailers, both online and in physical stores. Some well-known manufacturers and suppliers specialize in sailboat components and offer a wide range of options to handle different needs and budgets.
Q: Are there any specific safety considerations related to these components? A: Yes, safety is paramount while sailing. It is important to ensure all components are in good condition before heading out on the water. Regularly check the lines for wear and tear, ensure fittings are securely fastened, and verify the integrity of the hull. Additionally, wearing appropriate safety gear like life jackets and harnesses is crucial. Properly maintaining and inspecting all components will help avoid mishaps on the water.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, the Force 5 sailboat boasts a range of essential components that ensure optimal performance and a remarkable sailing experience. From its robust mast and rigging system to its efficient sail and ergonomic cockpit, every element of the Force 5 is carefully designed and crafted to enhance speed, stability, and maneuverability on the water. By understanding and investing in these vital components, sailors can unlock the full potential of their Force 5 sailboat and embark on countless thrilling adventures. Whether you are a novice sailor or an experienced racer, the comprehensive guide provided here offers a valuable resource to help you navigate the essential components of this exceptional sailboat, empowering you to meet your sailing goals with confidence. So set sail with the Force 5, and let its outstanding components propel you towards unforgettable sailing experiences.
- Recent Posts
- Ocean Catamarans Ocean Cat 48.8 1998 Boats for Sale & Yachts Updated to 2023 - March 21, 2024
- Explore the Everglades Boats 260CC 2006 for Sale & Yachts in 2023 - March 21, 2024
- 2023 Pacific Seacraft Yachts and Boats for Sale - March 21, 2024
Related posts:

LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Ocean Catamarans Ocean Cat 48.8 1998 Boats for Sale & Yachts Updated to 2023
Explore the everglades boats 260cc 2006 for sale & yachts in 2023, 2023 pacific seacraft yachts and boats for sale, sunseeker 46 1992 boats for sale & yachts updated for 2023, sunseeker 46 portofino 2004 boats for sale & yachts updated for 2023, more from author.

Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Popular Articles

- Forums New posts Unanswered threads Register Top Posts Email
- What's new New posts New Posts (legacy) Latest activity New media
- Media New media New comments
- Boat Info Downloads Weekly Quiz Topic FAQ 10000boatnames.com
- Classifieds Sell Your Boat Used Gear for Sale
- Parts General Marine Parts Hunter Beneteau Catalina MacGregor Oday
- Help Terms of Use Monday Mail Subscribe Monday Mail Unsubscribe
Retractable centerboard issues...
- Thread starter Fred
- Start date Jan 4, 2005
- Forums for All Owners
- Ask All Sailors
I have an older daysailor from the mid-60s (Sailstar Defender) that has a lever-retractable centerboard/keel. However, when I first received the boat, I disassembled the lever portion in the cockpit to polish the brass. When I replaced the lever, I must have done something wrong because the centerboard drops freely when the trailer sinks at the boat ramp. This causes a problem because the centerboard, which is ~3 feet long, gets caught inside the trailer frame and the boat cannot float free. My make-shift remedy is to put a large strap around underneath the boat and hook it together in the cockpit so I can release it once the boat floats free from the trailor. I have no idea even where to start with this issue, where to look or what might be wrong. I am hoping that it isn't something that requires cutting into the trunk or something that drastic. Anyone have a suggestion? Thanks in advance! Fred
Mel Elliott
Center board Unless you're fortunate enough to find someone familiar with this system, you're going to need to post some pictures so us old mechanic guys can tell you what you did wrong.
Fred Ficarra
And when you take the pictures,,,, you'll know what you did wrong.
Unfortunately, I doubt it... I will take some pictures tonight and post them in reply to this thread. Unfortunately, I doubt I will know what I am looking at. The boat is on a trailer in my driveway and it is difficult to see into the trunk at all. I have no means of lifting the boat off of the trailer, so the centerboard is currently retracted and being held in by the center roller on the trailer. My fear is that to fix it I will need to somehow get the boat off of the trailer and let the centerboard fall out of the trunk so I can see and possibly work inside the trunk. Anywho, thanks huys for the quick responses, I'll post tomorrow. Thanks! Fred A.
robert taylor
off the trailor i have lifted, flipped and rotated my 18 foot vanguard volant at least 5 times. i have had it for almost 30 years (absolute mint condition). i flip it every four or five years to re-epoxy and paint the bottom. i use a couple of 'come-alongs' and 3/8 yacht braid to harness the boat. one come along front, one in back. be sure to lash the two harnesses together so they can not slip apart. i use a parking garage truss to attach the come alongs to. you can also use a couple of big trees. i did that with an o'day 23. jacked it up 6 feet between 4 pine trees, drove the trailor out from under it and spent the whole winter doing a barrier coat.
Here are the pictures I promised: Here is a link to the pictures....
questions I have seen other daysailers with a similar setup, some with only one pawl to hold the cb up. Question 1 When you engage the thumb 'knob' by sliding it down the lever, does it make contact with the pawls? Q 2 If it makes contact with and engages the pawls, does rolling if off the boat, lift the 'knob/lever' and disengage the mechanism? Q 3 If it does not make contact with or engage the pawls, you may have slid the knob on 180 from its original orientation. I would highly suspect the description in Q 2 as being the culprit. Let us know.
To add to Rogers questions, does the lever move when the CB contacts the roller when launching the boat? Or is the lever free of any load, all the time? Your original post makes no mention of the pawls and the lever tab. At launch, the slide tab on the lever has to engage the highest pawl. Fred, you knew that, right?
Fred, another question Morning: Do you know if it was working properly when you first got the boat before taking the mechanism apart? I have a 12 foot O'Day Widgeon with a similar keel mechanism, only without the pawls. If that lever works freely, no matter where the board is, it's possible that the key in the shaft that goes through the board could be stripped or missing. Not trying to scare you, just another guess!
Answers to questions... Thank you guys for all o fyour great feedback and assistance. Here are my answers: Q1 When you engage the thumb 'knob' by sliding it down the lever, does it make contact with the pawls? If the pawls are the brass teeth, then yes, it actually moves pretty freely up and down the lever shaft. Q2 If it makes contact with and engages the pawls, does rolling if off the boat, lift the 'knob/lever' and disengage the mechanism? It sounds as if you are thinking that the 'brass teeth' move, and therefore lower the CB. The 'brass teeth' only serve to lock the lever in place, either up or down, essentially creating a multi-position CB for different depths. Q3 If it does not make contact with or engage the pawls, you may have slid the knob on 180 from its original orientation. There are actually 'knobs' on either side of the handle, but as I learned the first time I removed it, it only fits on one way. does the lever move when the CB contacts the roller when launching the boat? It used to, now I'm not sure. I think it wiggles back-and-forth sideways a bit. Or is the lever free of any load, all the time? I can now move the lever, while sitting in the trailer, all the way up and down with no effect on the CB. At launch, the slide tab on the lever has to engage the highest pawl. Fred, you knew that, right? I always keep it there, however, even with it furthest 'forward', the CB still drops freely once there isn't a roller holding it up inside the trunk. Do you know if it was working properly when you first got the boat before taking the mechanism apart? Yes, the first time I launched the boat, it worked properly. Somewhere along the way my meddling and tinkering for educational purposes caused it to no longer function. JB I think you might have hit the nail on the head. It sounds like whatever mechanism causes the forward and aft motion of the lever to make the centerboard go up and down is not working. I will disassemble it this evening (east coast) and see if (hopefully) there is some sort of pin or key that I can access without tearing open the trunk. If I have to get inside the trunk to fix the problem, it'll just have to stay that way ;-) Thanks again guys! I'll post pics of the disassembly tonight if you are interested. Fred A.
Fred I'd like to see them to compare yours with the way mine works. Luck with it!
Thanks! Not able to get to taking it apart tonight. Thanks again for all of your feedback! I'll post a link to the pics tomorrow night! Fred A.
square peg... round hole So, from you answers, I think you have stripped the hole that the 'axel' from the lever peg goes through in the cb. This is not uncommon in an older boat. The peg or axel is square or in some cases triangular and fits into a similar shaped hole in the fiberglass centreboard. Eventually the hole rounds out, and the triangular or square peg just turns freely within it. Pull the mechanism out, drop the board, add fg into the hole shape it with a file or dremmel tool to get it to accept the peg again without spinning. On some boards, there is a brass insert that is the same shape as the axel from the lever, and is held in place by flanges on one or both sides of the centreboard, by a few (3 or 4) screws. If this is the case with your situation, refilling the screwholes and replacing with new screws is all that is required after pulling the board out. (Should you be so lucky.)
Final Saga..... Ok for those of you who were patient enough to stick around... I decided to take it apart! (See link for pics of the event) As it turns out, although Roger tells a wild tale (See the 'out of control' thread), I think he gets the gold medal. I pulled out the mechanism and it was a 'bolt' that went through the CB in the trunk, and was squared off. Obviously, the hole in the CB is rounded and needs to be fixed. (Probably as prescribed) Now for some interesting tid-bits.... The gent that I bought her from must have had this problem in the past, because when I pulled out the 'bolt', there were many shredded chunks of duct tape in there that tells me that it was a quick-fix because it worked the first couple of times I took it out. Also, tomorrow morning, the buyer of my boat is coming to pick it up. I have too much integrity to jsut slap some more duct tape in there, so I'll see if he wants to take it as-is or wants me to fix it and will come back to pick it up. Thanks again everyone for all of your great feedback! Fred A.
thanks for the gold star fred I had earlier indicated a fix by adding fg into the hole and shaping it with a file or dremmel tool to get it to accept the peg again without spinning. I am rethinking that after seeing your pictures. Another method which may work is now that you have the board out, lay it down with the hole facing up, and rig some supports to hold the handle in place so that the squared bolt sits inside the hole in its proper orientation. You may have to back the hole with some duct tape to create a cup so that when you add the liguid fg, it does not run out. Apply some fg release agent to the bolt, (dip it in melted paraffin wax), then using two part epoxy, the syringe type you buy at a hardware store, fill in the hole. When cured, remove the bolt, and replace the cb. The hole should match the peg exactly. I noted in your pictures that it tapered somewhat. This method may decrease the amount of fiddling you would have to do with a dremmel tool or file in order to get the peg to fit again. Hope this helps.
- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn more…
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Slovenščina
- Science & Tech
- Russian Kitchen
Check out Moscow’s NEW electric river trams (PHOTOS)

Water transportation has become another sector for the eco-friendly improvements the Moscow government is implementing. And it means business. On July 15, 2021, on the dock of Moscow’s ‘Zaryadye’ park, mayor Sergey Sobyanin was shown the first model of the upcoming river cruise boat.

The model of the electrical boat with panoramic windows measures 22 meters in length. The river tram - as Muscovites call them - has a passenger capacity of 42, including two disabled seats. The trams will also get cutting edge info panels, USB docking stations, Wi-Fi, spaces for scooters and bicycles, as well as chairs and desks for working on the go. The boats will be available all year round, according to ‘Mosgortrans’, the regional transport agency.
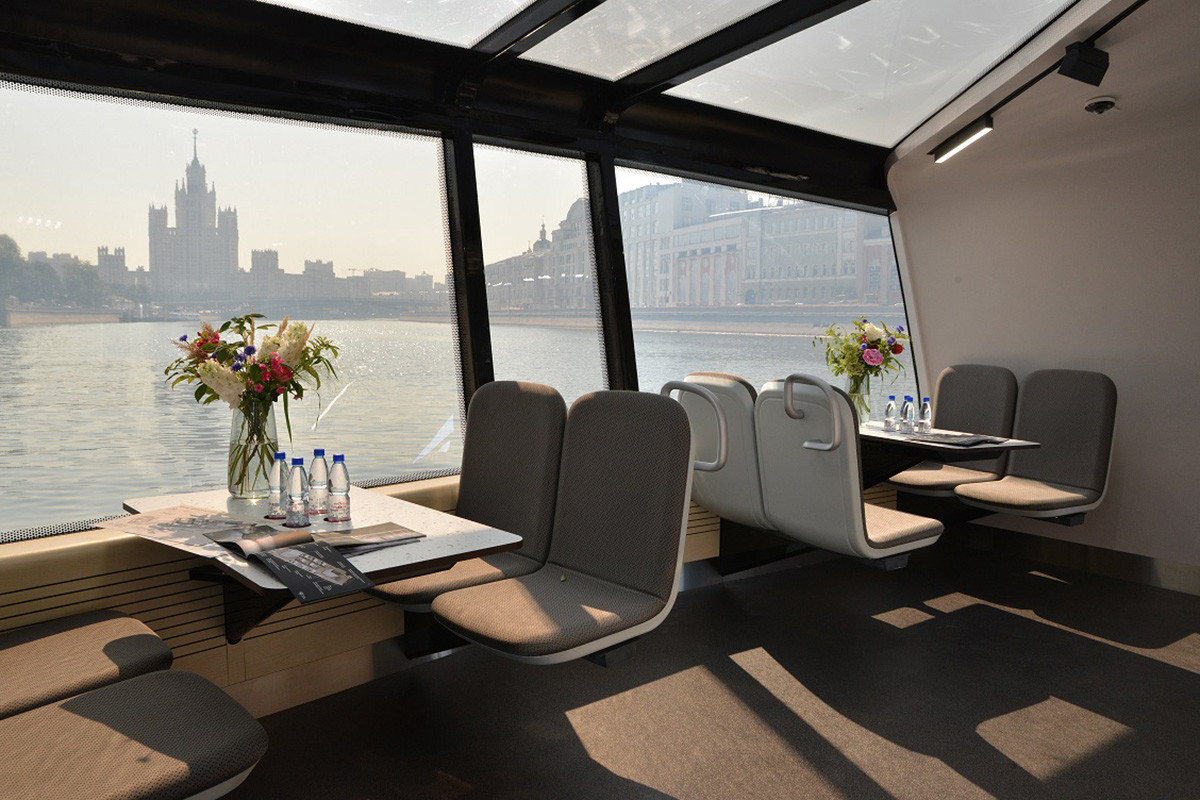

Passengers will be able to pay with their ‘Troika’ public transport card, credit cards or bank cards.
The main clientele targeted are people living in Moscow’s river districts - the upcoming trams will shorten their travel time in comparison to buses and other transportation by five times, Mosgortrans stated.

As the river trams are being rolled out, Moscow docks will also see mini-stations, some of which will also be outfitted with charging docks for speed-charging the boats.

Moscow is set to announce the start of the tender for construction and supply in September 2021. The first trams are scheduled to launch in June 2022 on two routes - from Kievskaya Station, through Moscow City, into Fili; and from ZIL to Pechatniki.

“Two full-scale routes will be created in 2022-2023, serviced by 20 river trams and a number of river stations. We’ll continue to develop them further if they prove to be popular with the citizens,” the Moscow mayor said .
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, always provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
to our newsletter!
Get the week's best stories straight to your inbox
- Face it: Moscow Metro to introduce FACIAL payment technology
- What does Moscow smell like?
- Riding Moscow’s train of tomorrow (PHOTOS)
This website uses cookies. Click here to find out more.
Moscow Boat Tour
- Page active

Description
See all the gems of historical and cultural center of the capital in short time and without traffic jams or tiresome walking.
Depending on the itinerary and duration of the Moscow River boat trip, the tour can be 3 or 5 hours.
Highlights of the tour
- St Basil’s Cathedral;
- Stalin skyscraper on Kotelnicheskaya (Tinkers) embankment;
- The Kremlin;
- “House on the Embankment” Stalin skyscraper;
- Monument to Peter I;
- The Central House of Artists;
- Christ the Savior Cathedral;
- Gorky Park;
- Moscow State University;
- Russian Academy of Sciences;
- Luzhniki stadium;
- Novodevichy Monastery;
- Kiev railway station;
- Europe Square;
- Moscow City Hall;
- Government House;
- Expocentre Exhibition Complex;
- and other famous sights.
You will learn about the different epochs of the city from the foundation in 1147 till Soviet times of 20 th century.
Moscow River
Moskva river has the form of a snake and is the main waterway of Moscow, consisting of a cascade of reservoirs. Within the city, Moskva river is 80 km long, 120 m - 200 m wide and up to 14 m deep. The narrowest part of the river is the Kremlin area in the city center, and the most extensive is around the Luzhniki Stadium in the south.
Bridges in Moscow
Undoubtedly, bridges and embankments are among the most scenic spots and main attractions of Moscow. Plus, they are so romantic.
- Bolshoy Kamenny Bridge – Great Stone Bridge – is the main bridge of Moscow . The first stone bridge was constructed here in the 17th century.
- Patriarshy Bridge is one of the youngest pedestrian bridges, built in 2004. The bridge connects the iconic Christ the Saviour Cathedral with funky Bersenevskaya embankment, extremely popular place among locals for its trendy art galleries, cafes and panoramic views. Patriarshy Bridge used to be a shooting location for ex-Russian President Dmitry Medvedev's New Year speech to the nation.
- Borodinsky Bridge, erected in honor of the 100th anniversary of the glorious victory in the Battle of Borodino (which every Russian kid knows about), a fierce legendary battle during the Russo-French war of 1812.
- Bagration Bridge one of the pedestrian bridges with most picturesque views of the Moskva River with its numerous upper-level observation platforms. The bridge was erected to celebrate the 850th anniversary of Moscow city in 1997.
- Krymsky Bridge used to be in Top 5 Europe’s longest bridges some 100 years ago. The bridge got its name after the ancient Krymsky ford which Crimean Tartars used to invade Moscow in the 16 th century.
Embankments of Moscow
Moscow river boats 37 embankments, the most popular being Kremlevskaya, Sofiyskaya, Pushkinskaya, Vorobyovskaya and Kolomenskaya.
You can get the most spectacular views of the Kremlin from Kremlevskaya and Sofiyskaya embankments.
- Pushkinkaya embankment is the most romantic in Moscow. It meanders along Gorky Park and Neskuchnyi garden and is rich for all kinds of entertainment as well as cozy nooks, including Olivkovy beach, the famous Zeleny theater as well as a pier for river cruisers.
- Vorobyevskaya embankment is part of Sparrow Hills nature reserve. This place opens a beautiful panorama of the river and city from the observation deck and is considered to be the place for taking serious decisions in life.
- Embankment in Kolomenskoye Museum-Reserve has a special charm due to its peculiar geographical relief. The boat trip around Kolomenskoye would be the most peaceful in your life.
- Taras Shevchenko embankment is popular among photographers for its modern Moscow City skyscrapers. Highly recommended for your night boat trip.
- Embankments of Moscow are the pride of the capital. A distinctive feature of each of the promenades is its architecture and beautiful views. In addition, almost all the embankments of Moscow have a rich history and a lot of notable buildings.
Different epochs
Taking a walk along the Moskva River by boat, you will witness the architecture of Moscow from different eras and styles. Archaeological studies indicate that already in the XI century there stood a fortified settlement on Borovitsky hill, which is now called the Kremlin. Little fortress could not accommodate all the residents of the rapidly growing city, and the Grand Duke ordered the construction of a new Kremlin, larger than the former.
Boat trip around Kolomenskoe Park
Moscow river boat trip starts from the pier Klenovy (Maple) Boulevard and provides reat views of Nicholas Perervinsky monastery.
Nicholas Perervinsky monastery was founded at the time of the Battle of Kulikov (1380). The monastery, got its name from the surrounding area – “Pererva”, which can be translated like “tear off” and because of the location – here it abruptly changed its course, turning to Kolomna, standing on the opposite bank.
Nowadays Kolomenskoye is State Art, Historical, Architectural and Natural Landscape Museum-Reserve, which doors are open to everyone who wants to get in touch with the ancient history of Russia.
Take a break from the big city hustle in the shady parks and gardens of the Kolomenskoe Museum-Reserve. Don’t miss a wonderful Church of the Ascension and Tsar Alexey’s Palace in Kolomenskoye!
Monasteries and temples
- Novospassky Monastery
- Founded in the 13th century on the site where now is located the Danilovsky monastery. After a few decades, in 1330, Ivan Kalita moved the monastery onto the Borovitskii hill of the Kremlin. However, in the 15th century, Spassky Monastery again moved, this time to a more spacious place on Krasnoholmskaya waterfront.
- Church of St. Nicholas in Zayaitskom
- Erected in the middle of the XVIII century in baroque style. The building survived after the 1812 fire, but the utensils were destoyed. Parishioners collected donations and restored the temple on their own. In Soviet times, it was closed and re-opened only in 1992.
- Cathedral of Christ the Savior
- The church was originally erected in honor of the victory over Napoleon and was being under construction for long 44 years. Notoriously demolished in 1937 to be a giant swimming pool under open sky. The current building was constructed in 1990s. It is the tallest and one of the largest Orthodox churches in the world.
- The temple was built in 1679-82, during the reign of Tsar Fedor Alekseevich, in late Muscovite Baroque style and can be characterized as bonfire temple. Each gable is a symbol of a heavenly fire.
- Novodevichy Convent
- The most famous concent and monastery in Moscow, presumably founded in 1524. Novodevichy’s status has always been high among other monasteries, it was in this monastery where the women of the royal blood, the wives of Tsars and local rulers of Moscow were kept in prison as nuns.
- St. Andrew’s church (male acts as Compound Patriarch of Moscow)
- St. Andrew’s church stands right on the slopes of the Sparrow Hills, on the way down to the Moskva River, on the territory of the Nature Reserve “Sparrow Hills”. The monastery is small in size but is very cozy. It’s situated in a quiet courtyard surrounded by temples, fruit trees and flowers.
What you get:
- + A friend in Moscow.
- + Private & customized Moscow river cruise.
- + An exciting pastime, not just boring history lessons.
- + An authentic experience of local life.
- + Flexibility: changes can be made at any time to suit individual preferences.
- + Amazing deals for breakfast, lunch, and dinner in the very best cafes & restaurants. Discounts on weekdays (Mon-Fri).
- + A photo session amongst spectacular Moscow scenery that can be treasured for a lifetime.
- + Good value for souvenirs, taxis, and hotels.
- + Expert advice on what to do, where to go, and how to make the most of your time in Moscow.
Write your review
- Guided tour
River Cruise on Luxurious Radisson Boat
- Description
- Choose date

Equipped with ice-breaking technology, these huge fancy yachts are the only river cruisers running all year around. The round trip journey takes two and a half hours and floats past all the big sights like the White House, Novodevichy monastery and the Kremlin. There’s a large open air observation deck up top, while the main body of the ship houses a restaurant with a dance floor for a romantic post dinner dance. For a particularly romantic experience take one of the evening boats and admire the bright lights of the city skyline at night.
The most relaxing and picturesque tour that Moscow can offer: a great way to see the city center and its main attractions. This is a perfect alternative to exploring the city by car, if you only have time to do sightseeing during weekday rush hours.
Your English-speaking guide is eager to share every bit of their knowledge about the surrounding landscape, the architecture and historical details.
We conduct Moscow river tour on Radisson Flotilla boats all year around! It’s warm inside during winter months, while there’s air conditioning during hot summer days. You may also treat yourself to drinks, lunch or dinner on board (drinks and food are not included in tour price).
The cost of an excursion with a personal guide for 1 person
Quay at Radisson Collection Hotel
Government Headquarters ("the White House")
Kievsky Railway Central
Novodevichy Convent
Luzhniki Stadium
Academy of Sciences
Monument to Peter I
Cathedral of Christ the Saviour
Moscow Kremlin
St.Basil's Cathedral
Novospassky Monastery
U-turn and back to Quay at Radisson Royal Hotel
Choose your dates
Who's going.
- Excursion River Cruise on Luxurious Radisson Boat
- Date and time:
- Who's going:
See photo of the meeting point

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
One of the larger boats on this list, the Seaward 26 RK, is still easy to move over land with a trailered weight under 6,000 pounds. The boat alone displaces 3,800 pounds, with 1,200 lbs. of that in retractable ballast with a bulb on the bottom. The keel lifts with an electric motor and is simple to operate.
Daniel Wade. June 15, 2022. A sailboat centerboard is a retractable fin that protrudes from the bottom of the hull. The centerboard keeps the boat stable and on course. Centerboards are an important and often overlooked part of a sailboat, but they're essential to stability and effective navigation. Centerboards perform the function of a keel ...
A sailboat centerboard is a retractable keel or fin located in the center of the boat's hull. It provides stability by counteracting lateral forces from wind, allowing the vessel to sail closer to the wind. The centerboard can be raised or lowered based on water depth and sailing conditions, optimizing performance and preventing damage.
A centerboard is a form of retractable keel that's common on the smallest types of trailerable sailboats. A centerboard is essentially a long, thin blade that descends through a hole in the bottom of the boat. Half of the centerboard remains inside the boat in a box called the 'centerboard trunk.'
A centreboard or centerboard (US) is a retractable hull appendage which pivots out of a slot in the hull of a sailboat, known as a centreboard trunk (UK) or centerboard case (US). The retractability allows the centreboard to be raised to operate in shallow waters, to move the centre of lateral resistance (offsetting changes to the sailplan that move the centre of effort aft), to reduce drag ...
7 Best Trailerable Cruising Sailboats. Catalina 22/25 "Pop-Top". Com-Pac Horizon Cat for Classic Coastal Cruising. Marshall Sanderling — Small, Portable, Classy. West Wight Potter 19 — The Tiny Go-Anywhere Sailboat. Seaward 26RK with Retractable Lead Keel. Corsair F-24 Trimaran - Sporty Sailing.
== Short answer centerboard sailboats == Centerboard sailboats are vessels equipped with a retractable keel, called the centerboard, which improves stability and prevents drifting. These boats are highly versatile, allowing navigation in shallow waters by raising the centerboard or deeper waters when lowered. This design is commonly found in small to mid-sized sailing craft.
Their large single and often gaff-rigged sail provided plenty of power, and a centerboard made them well-suited for the thin waters they frequently encountered. In the late 1970s, Canadian builder Hinterhoeller introduced the Nonsuch 30, a fiberglass variation of the catboat design, with a modern Marconi sail flown on a stayless mast, and a ...
Short answer centerboard sailboat: A centerboard sailboat is a type of sailing vessel that includes a retractable fin-like appendage called a centerboard. Centerboards provide stability and help prevent lateral drift when sailing upwind. They can be raised in shallow waters or when the boat is not under sail, and lowered for enhanced stability while underway.
New RHODES 19 SAILBOATS - Keel & Centerboard Models. ... The Classically styled Rhodes 19, available in fixed keel and full retractable centerboard models, is the ideal family daysailer and spirited one-design racer. She's an accomplished heavy-weather performer built upon a fast and forgiving hull. Fifty years and 3500 hulls have proven her ...
In the case of the Seward 46RK, the daggerboard, or lifting keel, is comprised of a solid polyester composite, with a fiberglass skin and a series of stainless rods running the length of the foil to both increase stiffness and carry a 7,500lb cast-lead ballast bulb. An electric motor, operated by a set of buttons at the mast, raises and lowers ...
A centerboard is a retractable appendage that pivots in and out of a slot (centerboard trunk) in the hull/keel of a sailboat. Having the ability to raise and lower the centerboard allows the the boat to operate in shallow waters when lifted, while maintaining good upwind sailing characteristics with the centerboard down.
Swing keels are the most versatile keels available, but it comes at a cost. Let's discuss those costs. I'll also show you two technical diagrams to explain t...
August 30, 2022. Swing keels are a robust and useful alternative to centerboards, and they're common on variable draft sailboats. Swing keels are retractable keels that are hinged in the front and swing into a slot called a trunk. Sailors lift and lower the keel with a crank, pulley, or hydraulic system. Sailboats with swing keels can reduce ...
It s no secret that J/Boats is an industry leader when it comes to fast, innovative sailboats; the retractable sprit pole introduced with the J/105 gave new life to the asymmetric spinnaker, and the company practically invented the sport-boat genre. Now the Rhode Island-based company has done it again, this time with the sporty J/95, a 31-footer with twin rudders, a
A centerboard is a type of retractable keel that rests on a hinge and can be lowered through a slot in the hull. It folds out like a pocket knife and allows you to increase or reduce the draft of the boat. Centerboards are mostly used on small fishing boats.
Short answer daggerboard vs centerboard: A daggerboard is a retractable keel that can be raised or lowered vertically, providing stability and reducing sideways drift. On the other hand, a centerboard is also a retractable keel but pivots horizontally instead of vertically. While both serve similar purposes, their designs and mechanisms differ in terms of usage
The centerboard is a retractable fin that helps to balance and stabilize the Force 5 sailboat, allowing it to sail upwind more efficiently. Tiller The tiller is a long handle connected to the rudder, enabling the sailor to steer the sailboat by applying pressure or releasing tension.
I have an older daysailor from the mid-60s (Sailstar Defender) that has a lever-retractable centerboard/keel. However, when I first received the boat, I disassembled the lever portion in the cockpit to polish the brass. When I replaced the lever, I must have done something wrong because the...
Prices start at $13 (800 rubles) for one ride, and for an additional $6.5 (400 rubles) you can purchase an unlimited number of tours on the same boat on any given day.
On July 15, 2021, on the dock of Moscow's 'Zaryadye' park, mayor Sergey Sobyanin was shown the first model of the upcoming river cruise boat. The model of the electrical boat with panoramic ...
Moscow river boat trip starts from the pier Klenovy (Maple) Boulevard and provides reat views of Nicholas Perervinsky monastery. Nicholas Perervinsky monastery was founded at the time of the Battle of Kulikov (1380). The monastery, got its name from the surrounding area - "Pererva", which can be translated like "tear off" and because ...
Moscow City: View Moscow Beneath Your Feet. $96. Details. River Cruise on Luxurios Radisson Ship with a guided excursion: time to relax and soak in the gorgeous Moscow landscape. Our guide will accompany you and reveal the details behind the structures on the river banks around you.